Upper Respiratory Tract Infection
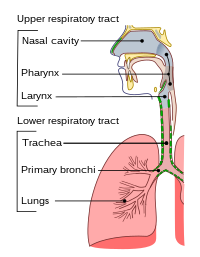
An upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) is an illness caused by an acute infection, which involves the upper respiratory tract, including the nose, sinuses, pharynx, or larynx. This commonly includes nasal obstruction, sore throat, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, sinusitis, otitis media, and the common cold. Most infections are viral in nature, and in other instances, the cause is bacterial. URTIs can also be fungal or helminthic in origin, but these are less common.
In 2015, 17.2 billion cases of URTIs are estimated to have occurred. As of 2014, they caused about 3,000 deaths, down from 4,000 in 1990.
Signs and symptoms

In uncomplicated colds, coughing and nasal discharge may persist for 14 days or more even after other symptoms have resolved. Acute URTIs include rhinitis, pharyngitis/tonsillitis, and laryngitis often referred to as a common cold, and their complications: sinusitis, ear infection, and sometimes bronchitis (though bronchi are generally classified as part of the lower respiratory tract.) Symptoms of URTIs commonly include cough, sore throat, runny nose, nasal congestion, headache, low-grade fever, facial pressure, and sneezing.
Symptoms of rhinovirus in children usually begin 1–3 days after exposure. The illness usually lasts 7–10 more days.
Color or consistency changes in mucous discharge to yellow, thick, or green are the natural course of viral URTI and not an indication for antibiotics.
Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis/tonsillitis (strep throat) typically presents with a sudden onset of sore throat, pain with swallowing, and fever. Strep throat does not usually cause runny nose, voice changes, or cough.
Pain and pressure of the ear caused by a middle-ear infection (otitis media) and the reddening of the eye caused by viral conjunctivitis are often associated with URTIs.
Mouth
Small round red lesions may occur on the soft palate. Decongestants may also cause decreased saliva.
Cause
In terms of pathophysiology, rhinovirus infection resembles the immune response. The viruses do not cause damage to the cells of the upper respiratory tract, but rather cause changes in the tight junctions of epithelial cells. This allows the virus to gain access to tissues under the epithelial cells and initiate the innate and adaptive immune responses.
Up to 15% of acute pharyngitis cases may be caused by bacteria, most commonly Streptococcus pyogenes, a group A streptococcus in streptococcal pharyngitis ("strep throat"). Other bacterial causes are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Bordetella pertussis, and Bacillus anthracis.
Sexually transmitted infections have emerged as causes of oral and pharyngeal infections.
Diagnosis
| Symptoms | Allergy | URI | Influenza |
|---|---|---|---|
| Itchy, watery eyes | Common | Rare (conjunctivitis may occur with adenovirus) | Soreness behind eyes, sometimes conjunctivitis |
| Nasal discharge | Common | Common | Common |
| Nasal congestion | Common | Common | Sometimes |
| Sneezing | Very common | Very common | Sometimes |
| Sore throat | Sometimes (post-nasal drip) | Very common | Sometimes |
| Cough | Sometimes | Common (mild to moderate, hacking) | Common (dry cough, can be severe) |
| Headache | Uncommon | Rare | Common |
| Fever | Never | Rare in adults, possible in children | Very common 100–102 °F (or higher in young children), lasting 3–4 days; may have chills |
| Malaise | Sometimes | Sometimes | Very common |
| Fatigue, weakness | Sometimes | Sometimes | Very common (can last for weeks, extreme exhaustion early in course) |
| Muscle pain | Never | Slight | Very common (often severe) |
Classification
A URTI may be classified by the area inflamed. Rhinitis affects the nasal mucosa, while rhinosinusitis or sinusitis affects the nose and paranasal sinuses, including frontal, ethmoid, maxillary, and sphenoid sinuses. Nasopharyngitis (rhinopharyngitis or the common cold) affects the nares, pharynx, hypopharynx, uvula, and tonsils generally. Without involving the nose, pharyngitis inflames the pharynx, hypopharynx, uvula, and tonsils. Similarly, epiglottitis (supraglottitis) inflames the superior portion of the larynx and supraglottic area; laryngitis is in the larynx; laryngotracheitis is in the larynx, trachea, and subglottic area; and tracheitis is in the trachea and subglottic area.
Prevention
Low- or very-low quality evidence indicates probiotics may be better than placebo in preventing acute URTIs. Vaccination against influenza viruses, adenoviruses, measles, rubella, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, diphtheria, Bacillus anthracis, and Bordetella pertussis may prevent them from infecting the URT or reduce the severity of the infection.
Treatment

Treatment comprises symptomatic support usually via analgesics for headache, sore throat, and muscle aches. Moderate exercise in sedentary subjects with a naturally acquired URTI probably does not alter the overall severity and duration of the illness. No randomized trials have been conducted to ascertain benefits of increasing fluid intake.
Antibiotics
Prescribing antibiotics for laryngitis is not a suggested practice. The antibiotics penicillin V and erythromycin are not effective for treating acute laryngitis. Erythromycin may improve voice disturbances after a week and cough after 2 weeks, but any modest subjective benefit is not greater than the adverse effects, cost, and the risk of bacteria developing resistance to the antibiotics. Health authorities have been strongly encouraging physicians to decrease the prescribing of antibiotics to treat common URTIs because antibiotic usage does not significantly reduce recovery time for these viral illnesses. A 2017 systematic review found three interventions which were probably effective in reducing antibiotic use for acute respiratory infections: C-reactive protein testing, procalcitonin-guided management, and shared decision-making between physicians and patients. The use of narrow-spectrum antibiotics has been shown to be just as effective as broad-spectrum alternatives for children with acute bacterial URTIs, and has a lower risk of side effects in children. Decreased antibiotic usage could also have prevented drug-resistant bacteria. Some have advocated a delayed antibiotic approach to treating URTIs, which seeks to reduce the consumption of antibiotics while attempting to maintain patient satisfaction. A Cochrane review (updated 2017) of 11 studies and 3,555 participants explored antibiotics for respiratory tract infections. It compared delaying antibiotic treatment to either starting them immediately or to no antibiotics. Outcomes were mixed depending on the respiratory tract infection; symptoms of acute otitis media and sore throat were modestly improved with immediate antibiotics with minimal difference in complication rate. Antibiotic usage was reduced when antibiotics were only used for ongoing symptoms and maintained patient satisfaction at 86%.
For sinusitis while at the same time discouraging overuse of antibiotics the CDC recommends:
- Target likely organisms with first-line medications: amoxicillin, amoxicillin/clavulanate
- Use the shortest effective course; should see improvement in 2–3 days. Continue treatment for 7 days after symptoms improve or resolve (usually a 10–14 day course).
- Consider imaging studies in recurrent or unclear cases; some sinus involvement is frequent early in the course of uncomplicated viral URI
Cough medicine
No good evidence exists for or against the effectiveness of over-the-counter cough medications for reducing coughing in adults or children. Children under 2 years old should not be given any type of cough or cold medicine due to the potential for life-threatening side effects. In addition, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics, the use of cough medicine to relieve cough symptoms should be avoided in children under 4 years old, and the safety is questioned for children under 6 years old.
Decongestants

According to a Cochrane review, a single oral dose of nasal decongestant in the common cold is modestly effective for the short-term relief of congestion in adults; however, data on the use of decongestants in children are insufficient. Therefore, decongestants are not recommended for use in children under 12 years of age with the common cold. Oral decongestants are also contraindicated in patients with hypertension, coronary artery disease, and history of bleeding strokes.
Mucolytics
Mucolytics such as acetylcysteine and carbocystine are widely prescriped for upper and lower respiratory tract infection without chronic broncho-pulmonary disease. However, in 2013 a Cochrane review reported their efficacy to be limited. Acetylcystine is considered to be safe for the children older than 2 years.
Alternative medicine
Routine supplementation with vitamin C is not justified, as it does not appear to be effective in reducing the incidence of common colds in the general population. The use of vitamin C in the inhibition and treatment of upper respiratory infections has been suggested since the initial isolation of vitamin C in the 1930s. Some evidence exists to indicate that it could be justified in persons exposed to brief periods of severe physical exercise and/or cold environments. Given that vitamin C supplements are inexpensive and safe, people with common colds may consider trying vitamin C supplements to assess whether they are therapeutically beneficial in their case.
Some low-quality evidence indicates the use of nasal irrigation with saline solution may alleviate symptoms in some people. Also, saline nasal sprays can be of benefit.
Epidemiology
Children typically have two to nine viral respiratory illnesses per year. In 2013, 18.8 billion cases of URTIs were reported. As of 2014, they caused about 3,000 deaths, down from 4,000 in 1990. In the United States, URTIs are the most common infectious illness in the general population, and are the leading reasons for people missing work and school.
See also
- Lower respiratory tract infection