Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease

Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), also known as metabolic (dysfunction) associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), is excessive fat build-up in the liver without another clear cause such as alcohol use. There are two types; non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), with the latter also including liver inflammation. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is less dangerous than NASH and usually does not progress to NASH or liver cirrhosis. When NAFLD does progress to NASH, it may eventually lead to complications such as cirrhosis, liver cancer, liver failure, cardiovascular disease.
Obesity and type 2 diabetes are strong risk factors for NAFLD. Other risks include being overweight, metabolic syndrome (defined as at least three of the five following medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum HDL cholesterol), a diet high in fructose, and older age. NAFLD and alcoholic liver disease are types of fatty liver disease. Obtaining a sample of the liver after excluding other potential causes of fatty liver can confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for NAFLD is weight loss by dietary changes and exercise. There is tentative evidence for pioglitazone and vitamin E; bariatric surgery can improve or resolve severe cases. Those with NASH have a 2.6% increased risk of dying per year.
NAFLD is the most common liver disorder worldwide and is present in approximately 25% of the world's population. It is also very common in developed nations, such as the United States, and affected about 75 to 100 million Americans in 2017. Over 90% of obese, 60% of diabetic, and up to 20% normal-weight people develop it. NAFLD is the leading cause of chronic liver disease and the second most common reason for liver transplantation in the US and Europe as of 2017. NAFLD affects about 20 to 25% of people in Europe. In the United States, estimates suggest between 30 and 40% of adults have NAFLD, and about 3 to 12% of adults have NASH. The annual economic burden was approximately US$103 billion in the US in 2016.
Definition
An abnormal accumulation of fat in the liver in the absence of secondary causes of fatty liver, such as significant alcohol use, viral hepatitis, or medications that can induce fatty liver characterizes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The term NAFLD encompasses a continuum of liver abnormalities, from non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL, simple steatosis) to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). These diseases begin with fatty accumulation in the liver (hepatic steatosis). A liver can remain fatty without disturbing liver function (NAFL), but by various mechanisms and possible insults to the liver, it may also progress into non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a state in which steatosis is combined with inflammation and sometimes fibrosis (steatohepatitis). NASH can then lead to complications such as cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
A new name, metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease, was proposed after 70% of a panel of experts expressed support for this name.
Signs and symptoms
 Play media
Play mediaPeople with NAFLD often have no noticeable symptoms, and NAFLD is often only detected during routine blood tests or unrelated abdominal imaging or liver biopsy. In some cases, NAFLD can cause symptoms related to liver dysfunction such as fatigue, malaise, and dull right-upper-quadrant abdominal discomfort. Mild yellow discoloration of the skin may occur, although this is rare. NASH can severely impair liver function, leading to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer.
Comorbidities
NAFLD is strongly associated with or caused by type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome (defined as at least three of the five following medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein). It is also associated with hormonal disorders (panhypopituitarism, hypothyroidism, hypogonadism, polycystic ovary syndrome), persistently elevated transaminases, increasing age and hypoxia caused by obstructive sleep apnea, with some of these conditions predicting disease progression.
The majority of normal-weight people affected by NAFLD ("lean NAFLD") have impaired insulin sensitivity, are sedentary, and have increased cardiovascular disease risk and increased liver lipid levels. These are the consequences of a decreased capacity for storing fat and reduced mitochondrial function in adipose tissue and increased hepatic de novo lipogenesis.
Risk factors
Genetics
Two-thirds of families with a history of diabetes type 2 report more than one family member having NAFLD. There is a higher risk of fibrosis for family members where someone was diagnosed with NASH. Asian populations are more susceptible to metabolic syndrome and NAFLD than their western counterparts. Hispanic persons have a higher prevalence of NAFLD than white individuals, whereas the lowest prevalence is observed in black individuals. NAFLD is twice as prevalent in men compared to women, which might be explained by lower levels of estrogen in men.
Genetic variations in two genes are associated with NAFLD: non-synonymous single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in PNPLA3 and TM6SF2. Both correlate with NAFLD presence and severity, but their roles for diagnosis remain unclear. Although NAFLD has a genetic component, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) does not recommend screening family members as there is not enough confirmation of heritability, although there is some evidence from familial aggregation and twin studies.
Diet
According to the Asia-Pacific Working Group (APWG) on NAFLD, overnutrition is a major factor of NAFLD and NASH, particularly for lean NAFLD. Diet composition and quantity, in particular omega-6 fatty acid and fructose, have important roles in disease progression from NAFL to NASH and fibrosis. Choline deficiency can lead to the development of NAFLD.
Pathophysiology
The primary characteristic of NAFLD is the accumulation of lipids in the liver, largely in the form of triglycerides. However, the mechanisms by which triglycerides accumulate and the reasons that accumulation can lead to liver dysfunction are complex and incompletely understood. NAFLD can include steatosis along with varied signs of liver injury: either lobular or portal inflammation (a form of liver injury) or ballooning degeneration. Similarly, NASH can include histological features such as portal inflammation, polymorphonuclear cell infiltrates, Mallory bodies, apoptotic bodies, clear vacuolated nuclei, microvesicular steatosis, megamitochondria, and perisinusoidal fibrosis. NASH increases hepatocyte death via apoptosis or necroptosis is increased in NASH compared with simple steatosis, and inflammation is a hallmark of NASH.
One debated mechanism proposes that hepatic steatosis progresses to steatosis with inflammation following some further injury, or second hit. Oxidative stress, hormonal imbalances, and mitochondrial abnormalities are potential causes of this "second hit" phenomenon. A further nutrigenomics model named multiple hit extends the second hit model, suggesting that multiple disease biomarkers and factors such as genes and nutrition influence NAFLD and NASH progression. This model attempts to use these factors to predict the impact of lifestyle changes and genetics for the evolution of the NAFLD pathology. Many researchers describe NAFLD as a multisystem disease, as it impacts and is influenced by organs and regulatory pathways other than the liver.
The accumulation of senescent cells in the liver is seen in persons with NAFLD. In mice, liver senescent hepatocytes result in increased liver fat deposition. Treatment of NAFLD mice with senolytic agents has been shown to reduce hepatic steatosis.
Fructose consumption
Non-alcoholic and alcoholic fatty liver disease share similar histological features, which suggests that they might share common pathogenic pathways. Fructose can cause liver inflammation and addiction similarly to ethanol by using similar metabolic pathways, unlike glucose. Therefore, some researchers argue that non-alcoholic and alcoholic fatty liver diseases are more alike than previously thought. Furthermore, high fructose consumption promotes fat accumulation in the liver by stimulating de novo lipogenesis in the liver and reducing the beta-oxidation of fat. Unlike the sugar glucose, the enzyme fructokinase rapidly metabolizes fructose. This leads to a decreased level of intracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The decrease in ATP increases oxidative stress and impairments in proper protein synthesis and mitochondrial function in the liver.
Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance contributes to the accumulation of toxic fat in the liver in several ways. First, it promotes the release of free fatty acids (FFAs) from adipose tissue into the blood. Typically, adipose tissue stores lipids in the form of triglycerides, slowly releasing them into the bloodstream when insulin is low. In insulin-resistant adipose tissue, such as in people with obesity and type 2 diabetes, more triglycerides are broken down into FFAs and released into the bloodstream, promoting uptake by the liver. Second, insulin promotes the production of new FFAs in the liver via de novo lipogenesis; this production of liver fats continues to be stimulated by insulin, even when other tissues are insulin-resistant. These FFAs are combined back into triglycerides in the liver, forming the major constituent of the accumulated fat in the liver. The three sources of free fatty acids that contribute to liver triglyceride accumulation include FFAs circulating in the bloodstream (59%), FFAs derived from carbohydrates such as fructose and glucose (26%), and diet (14%). Despite the accumulation of triglycerides in the liver, they are not directly toxic to liver tissue. Instead, alteration of the profile of the other lipid subtypes present in the liver, such as diacylglycerols, phospholipids, ceramides, and free cholesterol, have a more significant role in the pathogenesis of NAFLD.
Once NAFLD progresses in severity to the point of NASH, this promotes further insulin resistance in the adipose tissue and liver, which results in a harmful cycle of insulin resistance, liver fat accumulation, and inflammation. Adipose tissue dysfunction also decreases secretion of the insulin-sensitizing adipokine adiponectin in people with NAFLD. Adiponectin has several properties that protect the liver. These properties include improved liver fat metabolism, decreased de novo lipogenesis, decreased glucose production in the liver, anti-inflammatory properties, and anti-fibrotic properties. Skeletal muscle insulin resistance may also play a role in NAFLD. Insulin-resistant skeletal muscle is not as efficient at taking up glucose from the bloodstream after a meal. This inefficient glucose uptake promotes the redistribution of consumed carbohydrates from glucose destined for use in glycogen stores in the skeletal muscles to being used as a substrate for de novo lipogenesis in the liver.
Dysbiosis
Disruptions in the intestinal microbiota seem to influence NAFLD risk in several ways. People with NASH can have elevated levels of blood ethanol and proteobacteria (which produce alcohol), with dysbiosis proposed as a mechanism for this elevation. Alterations in the composition of the intestinal microbiota may influence NAFLD risk in several ways. These changes appear to increase the permeability of intestinal tissue, thereby facilitating increased liver exposure to harmful substances (e.g., translocated bacteria, bacterial toxins, and inflammatory chemical signals). The increased transport of these harmful substances to the liver promotes liver inflammation, enhances nutrient and calorie absorption, and alters choline metabolism. Higher levels of intestinal bacteria that produce butyrate may be protective.
Excessive macronutrient intake contributes to gut inflammation and perturbation of homeostasis, and micronutrients may also be involved. In addition to reducing weight and risk factors, lifestyle changes may prompt positive changes in the gut microbiota. In particular, diet diversity may play a role that was overlooked in animal studies, since they often compare a Western high-fat, low-diversity diet against a low-fat but higher-diversity chow. The health benefits after bariatric surgery may also involve changes in the gut microbiota by increasing gut permeability.

Mallory-Denk body

Ballooning degeneration

NASH (inflammation) and fibrosis stage 1
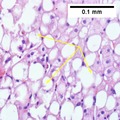
NASH (inflammation) and fibrosis stage 2

Lobular inflammation
Diagnosis

NAFLD is defined by evidence of fatty liver without another factor that could explain the liver fat accumulation, such as excessive alcohol use (>21 standard drinks/week for men and >14 for women in the USA; >30 g daily for men and >20 g for women in UK and EU, >140 g/week for men and >70 g/week for women in Asia-Pacific and most NIH clinical studies), drug-induced steatosis, chronic hepatitis C, heredity or by deficiencies in parenteral nutrition such as choline and endocrine conditions. If any of these factors are observed, an investigation into alternative causes of fatty liver unrelated to NAFLD is recommended. A history of chronic alcohol usage is an important consideration.
NAFLD comprises two histological categories: NAFL, and the more aggressive form NASH. The presence of at least 5% fatty liver is common to both NAFL and NASH, but the features of substantial lobular inflammation and hepatocyte injuries such as ballooning or Mallory hyaline only occur in NASH. The majority of NAFL cases show minimal or no inflammation. Pericentral and perisinusoidal fibrosis occur more often in adult-onset NASH, whereas portal fibrosis is more common in children with the disorder. NASH represents a more advanced stage of NAFL and is associated with poor outcomes such as cardiovascular events, cirrhosis, or hepatocellular carcinoma. ICD-11 does not use the term NAFL as it was deemed confusing with the family of disorders NAFLD. The preferred descriptions are instead: NAFLD without NASH or simple steatosis and "NASH". Also, the modifier with or without fibrosis or cirrhosis completes the diagnostic description.
Blood tests
Elevated liver enzymes are common. According to National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidelines, it is disadvised to test enzymes levels to rule out NAFLD, as they are often within the normal range even in advanced disease.
Blood tests that are useful to confirm diagnosis or rule out others include erythrocyte sedimentation rate, glucose, albumin, and kidney function. Because the liver is important for making proteins used in blood clotting, coagulation-related studies are often carried out, especially the INR (international normalized ratio). In people with fatty liver with associated inflammatory injury (steatohepatitis) blood tests are usually used to rule out viral hepatitis (hepatitis A, B, C and herpesviruses such as Epstein-Barr virus or cytomegalovirus), rubella, and autoimmune diseases. Low thyroid activity is more prevalent in people with NASH, which would be detected by determining the thyroid-stimulating hormone. Some biomarker-based blood tests have been developed and may be useful for diagnosis.
Although blood tests cannot diagnose NAFLD, circulating serum biomarkers of liver fibrosis can give moderate estimates in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. The ratio of the transaminase liver enzyme aspartate aminotransferase (AST) to platelets in the blood, known as the AST/platelet ratio index (APRI score), and Fibrotest are recommended as the preferred noninvasive tests for cirrhosis by the Asian-Pacific Association for Study of the Liver (APASL). Several other scores such as FIB-4 score and NAFLD fibrosis score can also reflect the burden of the fibrosis in the liver, and previous studies have confirmed that these score can predict future development of mortality and liver cancer.
Imaging

A liver ultrasound scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can diagnose steatosis, but not fibrosis and confirmation of early cirrhosis detection by ultrasound by other diagnostic methods is recommended. The European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) recommends screening for steatosis whenever NAFLD is suspected as this is a strong predictor of the disease evolution and predicts future type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular events, and hypertension. These non-invasive methods can be used for NAFLD screening but are not accepted as a substitute for liver biopsy in NAFLD nor NASH clinical trials, as only a liver biopsy can define liver pathology.
CT scans and MRIs are more accurate in detecting cirrhosis than conventional ultrasound. Transient elastography is recommended for the initial assessment of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis and helps to predict complications and prognosis, but the interpretation of results is carefully weighed in the presence of limiting factors, such as steatosis, high BMI, lower degrees of hepatic fibrosis and narrow spaces between the ribs (intercostal spaces). However, transient elastography can fail for people with pre-hepatic portal hypertension. Transient elastography is not considered to be a replacement for liver biopsy.
Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) is an emerging method that can accurately assess hepatic fibrosis and is recommended by the APASL. MRE possesses a good sensitivity to quantify hepatic fat and excellent accuracy to detect fibrosis in NAFLD regardless of BMI and inflammation and is suggested as a more reliable alternative to diagnose NAFLD and its progression to NASH compared to ultrasound and blood tests.
Liver biopsy


A liver biopsy (tissue examination) is the only test widely accepted (gold standard) as definitively diagnosing and distinguishing NAFLD (including NAFL and NASH) from other forms of liver disease and can be used to assess the severity of the inflammation and resultant fibrosis. However, since most people affected by NAFLD are likely to be asymptomatic, liver biopsy presents too high a risk for routine diagnosis, so other methods are preferred, such as liver ultrasonography or liver MRI. For young people, guidelines recommend liver ultrasonography, but biopsy remains the best evidence. Liver biopsy is also the gold standard to detect hepatic fibrosis and assess its progression. Routine liver function blood tests are not sensitive enough to detect NAFLD, and biopsy is the only procedure that can reliably differentiate NAFL from NASH.
There are several liver biopsy techniques available to obtain liver tissue. Percutaneous liver biopsy remains the most common practice. Biopsies can also be performed via the transvenous route, either during surgery or by laparoscopy, especially for people with contraindications to a percutaneous approach. The liver biopsy can also be image-guided, in real-time or not, which is recommended for some clinical situations such as people with known intra-hepatic lesions, previous intra-abdominal surgery who may have adhesions, a small liver that is difficult to percuss, obese people and people with evident ascites. Vital signs must be monitored frequently afterward (at least every 15 minutes in the hour following the biopsy).
According to AASLD guidelines, a liver biopsy may be considered in people with NAFLD who are at increased risk of having steatohepatitis with or without advanced fibrosis, but only when all other competing chronic liver diseases are excluded (such as alcoholic liver disease). The presence of metabolic syndrome, NAFLD Fibrosis Score (FIB-4), or liver stiffness (as measured by Vibration-controlled transient elastography or MRE) can identify the individuals who are at higher risk of steatohepatitis or advanced fibrosis.
The AASLD and ICD-11 consider that clinically useful pathology reporting distinguishes "between NAFL (steatosis), NAFL with inflammation and NASH (steatosis with lobular and portal inflammation and hepatocellular ballooning)" with the presence or absence of fibrosis being described and optionally comment on severity. The EASL recommends the Fatty Liver Inhibition of Progression (FLIP) algorithm to grade the ballooning and classify NAFLD-associated liver injury, and the use of the NAFLD Activity Score (NAS) to grade the severity of NASH rather than for its diagnosis. They also consider the steatosis, activity, and fibrosis (SAF) score to be an accurate and reproducible scoring system. The AASLD recommends the use of the NAS scoring system with or without the SAF score if deemed appropriate. The Asia-Pacific Working Group on NAFLD disadvises the use of NAS, as it is considered uninformative for NAFLD and inappropriate to diagnose NASH.
For liver fibrosis assessment, percutaneous liver biopsy, with or without image guidance, is contraindicated in uncooperative people. Transjugular liver biopsy is indicated for any person with diffuse liver disease who needs a biopsy but has a contraindication to percutaneous biopsy or needs a hemodynamic evaluation for diagnostic purposes. A transvenous liver biopsy is recommended instead of a percutaneous approach in people with clinically evident ascites, although percutaneous biopsy is an acceptable alternative approach after the removal of ascites.
Management
NAFLD warrants treatment regardless of whether the affected person is overweight or not. NAFLD is a preventable cause of death. Guidelines are available from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE) National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), and the Asia-Pacific Working Party on NAFLD.
Lifestyle
Weight loss is the most effective treatment for NAFLD. A loss of 4% to 10% body weight is recommended, with 10% to 40% weight loss completely reversing NASH without cirrhosis. A structured weight loss program helps people with NAFLD lose more weight compared with advice alone. This type of program also leads to improvements in NAFLD measured using blood tests, ultrasound, imaging, or liver biopsies. Although fibrosis improves with lifestyle interventions and weight loss, there is limited evidence for cirrhosis improvement.
A combination of improved diet and exercise, rather than either alone, appears to best help manage NAFLD and reduce insulin resistance. Motivational support, such as with cognitive behavioral therapy, is helpful, as most people with NAFLD do not perceive their condition as a disease, and thus have a low motivation to change.
Higher-intensity behavioral weight loss therapies (diet and exercise combined) may produce more weight loss than lower-intensity ones. Weight loss is associated with improvements in biomarkers, NAFLD grade, and reduced chances of NASH, but their impact on long-term health is yet unknown. A 2019 systematic review thus suggests a change of guidelines to recommend these therapies for NAFLD management.
Diet
Treatment of NAFLD typically involves counseling to improve nutrition and calorie restriction. People with NAFLD can benefit from a moderate to low-carbohydrate diet and a low-fat diet. The Mediterranean diet also showed promising results in a 6-week study with a reduction of NASH induced inflammation and fibrosis, independently from weight loss. Tentative evidence supports dietary interventions in individuals with fatty liver who are not overweight.
The EASL recommends energy restriction of 500–1000 kcal per week less than the normal daily diet (a very-low-calorie diet), a target of 7–10% weight loss for obese/overweight NAFLD, a low- to moderate-fat, and moderate- to high-carbohydrate diet, or a low-carbohydrate ketogenic or high-protein diet such as the Mediterranean diet, and avoiding all beverages and food containing fructose.
Alcohol is an aggravating factor, and the AASLD recommends that people with NAFLD or NASH avoid alcohol consumption. The EASL allows alcohol consumption below 30g/day for men and 20g/day for women. The role of coffee consumption for NAFLD treatment is unclear though some studies indicate that regular coffee consumption may have protective effects.
Vitamin E does not improve established liver fibrosis in those with NAFLD but seems to improve certain markers of liver function and reduces inflammation and fattiness of the liver in some people with NAFLD. The Asia-Pacific Work Group advises that Vitamin E may improve liver condition and aminotransferase levels, but only in adults without diabetes or cirrhosis who have NASH. The NICE guidelines recommend Vitamin E as an option for children and adults with NAFLD with advanced liver fibrosis, regardless of whether the person has diabetes mellitus.
Herbal compounds such as silymarin (a milk thistle seed extract), curcumin, a turmeric extract, and green tea appear to improve NAFLD biomarkers and reduce the grade of NAFLD. Studies suggest an association between microscopic organisms that inhabit the gut (microbiota) and NAFLD. Reviews reported the use of probiotics and synbiotics (combinations of probiotics and prebiotics) were associated with improvement in liver-specific markers of hepatic inflammation, measurements of liver stiffness, and steatosis in persons with NAFLD.
Physical activity
Weight loss may improve NAFLD and is recommended particularly for obese or overweight people; similar physical activities and diets are advisable for overweight people with NAFLD as for other obese and overweight people. Although physical activity is less important for weight loss than dietary adaptations (to reduce caloric intake), the NICE advises physical activity to reduce liver fat even if there is no overall bodyweight reduction. Weight loss, through exercise or diet, is the most effective way to reduce liver fat and help NASH and fibrosis remission. Exercise alone can prevent or reduce hepatic steatosis, but it remains unknown whether it can improve all other aspects of the liver; hence a combined approach with diet and exercise is advised. Aerobic exercise may be more effective than resistance training, although there are contradictory results. Vigorous training is preferable to moderate training, as only the high-intensity exercise reduced the chances of NASH developing into steatohepatitis or advanced fibrosis. The EASL recommends between 150 and 200 min/week in 3 to 5 sessions of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity or resistance training. Since both effectively reduce liver fat, a pragmatic approach to the choice of physical activity that accounts for the individual's preferences for what they can maintain in the long-term is preferred. Any engagement in physical activity or increase over previous levels is better than remaining sedentary.
Medication
Treatment with medications is primarily aimed at improving liver disease and is generally limited to those with biopsy-proven NASH and fibrosis.
No medicines specifically for NAFLD or NASH had received approval, as of 2018[update], although anti-diabetic medications may help in liver fat loss. While many treatments appear to improve biochemical markers such as alanine transaminase levels, most do not reverse histological abnormalities or improve outcomes.
Insulin sensitizers (metformin and thiazolidinediones, such as pioglitazone) and liraglutide are not specifically recommended for NAFLD as they do not directly improve the liver condition. They can be indicated for diabetic individuals, after a careful assessment of risks, to reduce insulin resistance and risks of complications. Indeed, the side effects associated with thiazolidinedione medications, which include osteopenia, increased fracture risk, fluid retention, congestive heart failure, bladder cancer, and long-term weight gain, have limited their adoption. Due to these side effects, the AASLD recommends the use of pioglitazone only for individuals with biopsy-proven NASH, and the Asia-Pacific Work Group recommends them only for individuals with NAFLD with known diabetic issues. However, the AASLD advises against the use of metformin as studies were inconclusive about the improvement of the liver's histological condition. Although there was an improvement in insulin resistance and serum aminotransferases, this did not translate into NASH improvements. The NICE provides similar guidelines to the AASLD regarding pioglitazone and recommends it be administered in secondary care to adults with advanced liver fibrosis irrespective of whether or not they have diabetes.
Statin medications appear to improve liver histology and markers of liver biochemistry in people with NAFLD. Since people with NAFLD are at a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, statin treatment is indicated. People with NAFLD are not at higher risk for serious liver injury from statins, according to AASLD and EASL. However, even if statins are safe to use in people with NASH cirrhosis, the AASLD suggests avoiding them in people with decompensated cirrhosis. Guidelines recommend statins to treat dyslipidemia for people with NAFLD. According to NICE guidelines, statins can continue unless liver enzyme levels double within three months of starting statins. Treatment with pentoxifylline is not recommended.
As of 2018, neither the AASLD nor the Asia-Pacific Working Group recommends obeticholic acid or elafibranor due to inconsistent results for NASH treatment and concerns about safety.
Omega-3 fatty acids may reduce liver fat and improve blood lipid profile but do not seem to improve liver histology (fibrosis, cirrhosis, cancer). The NICE does not recommend omega-3 fatty acid supplementation since randomized trials were inconclusive. Previous systematic reviews found that omega-3 fatty acid supplementation in those with NAFLD/NASH using doses of one gram daily or more (median dose four grams/day with median treatment duration six months) has been associated with improvements in liver fat. According to AASLD guidelines, "omega-3 fatty acids should not be used as a specific treatment of NAFLD or NASH, but they may be considered to treat hypertriglyceridemia for patients with NAFLD".
Surgery

Bariatric surgery is an effective method for obese and diabetic individuals with NAFLD to induce weight loss and reduce or resolve NASH inflammation, including fibrosis, and improve longevity. For the AASLD, bariatric surgery can be considered only for NASH on a case-by-case basis by an experienced bariatric surgery program. Indeed, some individuals might develop new or worsened features of NAFLD.
About 92% of people with NAFLD saw an improvement in steatosis and 70% a complete resolution after bariatric surgery.
A preoperative diet such as a low-calorie diet or a very-low-calorie diet is usually recommended to reduce liver volume by 16–20%. Preoperative weight loss is the only factor associated with postoperative weight loss. Preoperative weight loss can reduce operative time and hospital stay, although there is insufficient evidence whether preoperative weight loss reduces long-term morbidity or complications. Weight loss and decreases in liver size may be independent of the amount of calorie restriction.
The APWG on NAFLD recommends bariatric surgery as a treatment option for those with class II obesity (BMI >32.5 kg/m² for Asians, 35 kg/m² for Caucasians). They consider its effects on improving liver-related complications as unproven yet, but it effectively increases longevity by improving cardiovascular factors.
Surgery carries more risks for individuals with NASH cirrhosis, with a review estimating overall morbidity to be 21%. For people with NAFLD who have undifferentiated cirrhosis, the APWG recommends an investigation to determine the cause of the cirrhosis as well as the person's liver function and whether they have portal hypertension.
Screening
Cardiovascular system screening is considered mandatory by the EASL, as NAFLD outcomes often result in cardiovascular complications, which can manifest as subclinical atherosclerosis, the cause of the majority of NAFLD-related deaths. People with NAFLD are at high risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and "aggressive modification of cardiovascular disease risk factors is warranted in all patients with NAFLD," according to AASLD.
The AASLD further recommends for people with a cirrhotic NASH to be systematically screened for gastric and esophageal varices and liver cancer. They do not recommend routine liver biopsies and screening for liver cancer for non-cirrhotic people with NASH, but such screening sometimes occurs on a case-by-case basis.
Also, people with NAFLD may be considered for screening for hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer) and gastroesophageal varices. The NICE advises regular screening of NAFLD for advanced liver fibrosis every three years to adults and every two years for children using the enhanced liver fibrosis (ELF) blood test. Follow-up is recommended for people with obesity and insulin resistance using the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). People with NASH with fibrosis and hypertension merit closer monitoring as there is a higher risk of disease progression.
Transplantation
NAFLD is the second most common indication for liver transplantation in the US and Europe as of 2017. NAFLD/NASH is expected to become the leading cause of liver transplantation by 2020.
For people with NASH and end-stage liver disease, liver failure, or liver cancer, liver transplantation is an accepted procedure according to the EASL. People with NASH cirrhosis NASH who are being considered for a liver transplant warrant systematic evaluation for cardiovascular diseases (whether the symptoms are apparent or not).
The overall survival is comparable to transplantation following other diseases. People with NASH cirrhosis who undergo liver transplantation are more likely to die post-transplant because of cardiovascular disease or chronic kidney disease. These people




