Telangiectasia, Hereditary Hemorrhagic, Type 4
For a general phenotypic description and a discussion of genetic heterogeneity of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), see HHT1 (187300).
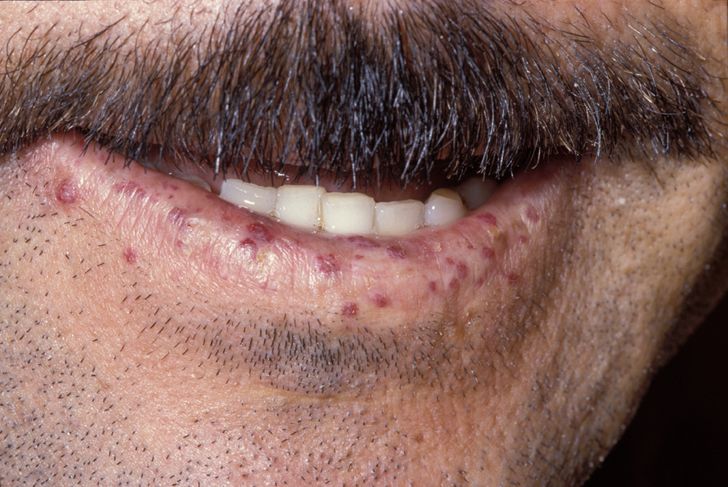
Clinical FeaturesBayrak-Toydemir et al. (2006) reported a family in which 8 members were definitely affected with HHT, and 4 were considered 'suspicious' for HHT. Inheritance was autosomal dominant. The proband was a 27-year-old woman with symptomatic hypoxia with clubbing of the fingers and multiple pulmonary arteriovenous malformations (PAVMs) treated with transcatheter embolization. She had a history of nosebleeds. Other affected family members had variable features of recurrent nosebleeds, mucocutaneous telangiectases, PAVMs, and cerebral AVMs (CAVMs). Bayrak-Toydemir et al. (2006) noted that the frequency and severity of nosebleeds and the number and size of telangiectases seen in this family were less than that typically observed in other forms of HHT.
MappingBy genomewide linkage analysis of a family with HHT, Bayrak-Toydemir et al. (2006) identified a candidate disease locus, termed HHT4, within a 7-Mb region on chromosome 7p14 between markers D7S2252 and D7S510 (maximum 2-point lod score of 3.60 at D7S817). Candidate gene analysis excluded pathogenic mutations in the BMPER (608699), CCM2 (607929), RALA (179550), and INHBA (147290) genes.