Chromosome Abnormality
A chromosomal disorder, chromosomal anomaly, chromosomal aberration, or chromosomal mutation is a missing, extra, or irregular portion of chromosomal DNA. These can occur in the form of numerical abnormalities, where there is an atypical number of chromosomes, or as structural abnormalities, where one or more individual chromosomes are altered. Chromosome mutation was formerly used in a strict sense to mean a change in a chromosomal segment, involving more than one gene. Chromosome anomalies usually occur when there is an error in cell division following meiosis or mitosis. Chromosome abnormalities may be detected or confirmed by comparing an individual's karyotype, or full set of chromosomes, to a typical karyotype for the species via genetic testing.
Numerical abnormality
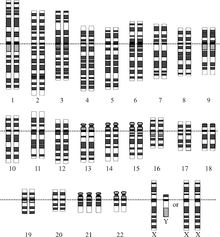
An abnormal number of chromosomes is called aneuploidy, and occurs when an individual is either missing a chromosome from a pair (resulting in monosomy) or has more than two chromosomes of a pair (trisomy, tetrasomy, etc.). Aneuploidy can be full, involving a whole chromosome missing or added, or partial, where only part of a chromosome is missing or added. Aneuploidy can occur with sex chromosomes or autosomes.
An example of trisomy in humans is Down syndrome, which is a developmental disorder caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21; the disorder is therefore also called trisomy 21.
An example of monosomy in humans is Turner syndrome, where the individual is born with only one sex chromosome, an X.
Sperm aneuploidy
Exposure of males to certain lifestyle, environmental and/or occupational hazards may increase the risk of aneuploid spermatozoa. In particular, risk of aneuploidy is increased by tobacco smoking, and occupational exposure to benzene, insecticides, and perfluorinated compounds. Increased aneuploidy is often associated with increased DNA damage in spermatozoa.
Structural abnormalities

 28/Two_Chromosome_Mutations.png/220px-Two_Chromosome_Mutations.png" decoding="async" width="220" height="306" class="thumbimage" srcset="//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/28/Two_Chromosome_Mutations.png/330px-Two_Chromosome_Mutations.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/28/Two_Chromosome_Mutations.png/440px-Two_Chromosome_Mutations.png 2x" data-file-width="616" data-file-height="856">
28/Two_Chromosome_Mutations.png/220px-Two_Chromosome_Mutations.png" decoding="async" width="220" height="306" class="thumbimage" srcset="//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/28/Two_Chromosome_Mutations.png/330px-Two_Chromosome_Mutations.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/28/Two_Chromosome_Mutations.png/440px-Two_Chromosome_Mutations.png 2x" data-file-width="616" data-file-height="856"> When the chromosome's structure is altered, this can take several forms:
- Deletions: A portion of the chromosome is missing or has been deleted. Known disorders in humans include Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome, which is caused by partial deletion of the short arm of chromosome 4; and Jacobsen syndrome, also called the terminal 11q deletion disorder.
- Duplications: A portion of the chromosome has been duplicated, resulting in extra genetic material. Known human disorders include Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A, which may be caused by duplication of the gene encoding peripheral myelin protein 22 (PMP22) on chromosome 17.
- Inversions: A portion of the chromosome has broken off, turned upside down, and reattached, therefore the genetic material is inverted.
- Insertions: A portion of one chromosome has been deleted from its normal place and inserted into another chromosome.
- Translocations: A portion of one chromosome has been transferred to another chromosome. There are two main types of translocations:
- Reciprocal translocation: Segments from two different chromosomes have been exchanged.
- Robertsonian translocation: An entire chromosome has attached to another at the centromere - in humans these only occur with chromosomes 13, 14, 15, 21, and 22.
- Rings: A portion of a chromosome has broken off and formed a circle or ring. This can happen with or without loss of genetic material.
- Isochromosome: Formed by the mirror image copy of a chromosome segment including the centromere.
Chromosome instability syndromes are a group of disorders characterized by chromosomal instability and breakage. They often lead to an increased tendency to develop certain types of malignancies.
Inheritance
Most chromosome abnormalities occur as an accident in the egg cell or sperm, and therefore the anomaly is present in every cell of the body. Some anomalies, however, can happen after conception, resulting in Mosaicism (where some cells have the anomaly and some do not). Chromosome anomalies can be inherited from a parent or be "de novo". This is why chromosome studies are often performed on parents when a child is found to have an anomaly. If the parents do not possess the abnormality it was not initially inherited; however it may be transmitted to subsequent generations.
Acquired chromosome abnormalities
Most cancers, if not all, could cause chromosome abnormalities, with either the formation of hybrid genes and fusion proteins, deregulation of genes and overexpression of proteins, or loss of tumor suppressor genes (see the "Mitelman Database" and the Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology,). Furthermore, certain consistent chromosomal abnormalities can turn normal cells into a leukemic cell such as the translocation of a gene, resulting in its inappropriate expression.
DNA damage during spermatogenesis
During the mitotic and meiotic cell divisions of mammalian gametogenesis, DNA repair is effective at removing DNA damages. However, in spermatogenesis the ability to repair DNA damages decreases substantially in the latter part of the process as haploid spermatids undergo major nuclear chromatin remodeling into highly compacted sperm nuclei. As reviewed by Marchetti et al., the last few weeks of sperm development before fertilization are highly susceptible to the accumulation of sperm DNA damage. Such sperm DNA damage can be transmitted unrepaired into the egg where it is subject to removal by the maternal repair machinery. However, errors in maternal DNA repair of sperm DNA damage can result in zygotes with chromosomal structural aberrations.
Melphalan is a bifunctional alkylating agent frequently used in chemotherapy. Meiotic inter-strand DNA damages caused by melphalan can escape paternal repair and cause chromosomal aberrations in the zygote by maternal misrepair. Thus both pre- and post-fertilization DNA repair appear to be important in avoiding chromosome abnormalities and assuring the genome integrity of the conceptus.
Detection
Depending on the information one wants to obtain, different techniques and samples are needed.
- For the prenatal diagnosis of a foetus, amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling or circulating foetal cells would be collected and analysed in order to detect possible chromosomal abnormalities.
- For the preimplantational diagnosis of an embryo, a blastocyst biopsy would be performed.
- For a lymphoma or leukemia screening the technique used would be a bone marrow biopsy.
See also
- Aneuploidy
- Chromosome segregation
- Genetic disorder
- List of genetic disorders
- Gene therapy
- Nondisjunction
- Obstetrical complications