Multiple Epiphyseal Dysplasia
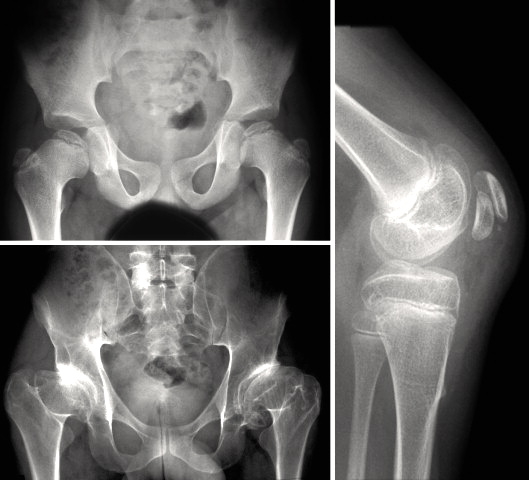
Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (MED) is a group of disorders of cartilage and bone development, primarily affecting the ends of the long bones in the arms and legs (epiphyses). There are two types of MED, which are distinguished by their patterns of inheritance - autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive. Signs and symptoms may include joint pain in the hips and knees; early-onset arthritis; a waddling walk; and mild short stature as adults. Recessive MED may also cause malformations of the hands, feet, and knees; scoliosis; or other abnormalities. Most people are diagnosed during childhood, but mild cases may not be diagnosed until adulthood. Dominant MED is caused by mutations in the COMP, COL9A1, COL9A2, COL9A3, or MATN3 genes (or can be of unknown cause), and recessive MED is caused by mutations in the SLC26A2 gene.