Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
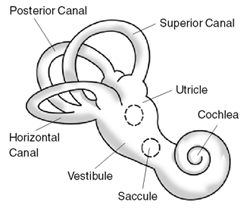
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is a disorder arising from a problem in the inner ear. Symptoms are repeated, brief periods of vertigo with movement, characterized by a spinning sensation upon changes in the position of the head. This can occur with turning in bed or changing position. Each episode of vertigo typically lasts less than one minute. Nausea is commonly associated. BPPV is one of the most common causes of vertigo.
BPPV is a type of balance disorder along with labyrinthitis and Ménière's disease. It can result from a head injury or simply occur among those who are older. Often, a specific cause is not identified. When found, the underlying mechanism typically involves a small calcified otolith moving around loose in the inner ear. Diagnosis is typically made when the Dix–Hallpike test results in nystagmus (a specific movement pattern of the eyes) and other possible causes have been ruled out. In typical cases, medical imaging is not needed.
BPPV is often treated with a number of simple movements such as the Epley maneuver or Brandt–Daroff exercises. Medications, including antihistamines such as meclizine, may be used to help with nausea. There is tentative evidence that betahistine may help with vertigo, but its use is not generally needed. BPPV is not a serious medical condition, but may present serious risks of injury through falling or other spatial disorientation-induced accidents.
Typically, it resolves in days to months. It, however, may recur in some people.
The first medical description of the condition occurred in 1921 by Róbert Bárány. Approximately 2.4% of people are affected at some point in time. Among those who live until their 80s, 10% have been affected. BPPV affects females twice as often as males. Onset is typically in people between the ages of 50 and 70.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms:
- Paroxysmal—appears suddenly, and in episodes of short duration: lasts only seconds to minutes
- Positional—is induced by a change in position, even slight
- Vertigo—a spinning dizziness, which must have a rotational component
- Torsional nystagmus—a diagnostic symptom where the top of the eye rotates toward the affected ear in a beating or twitching fashion, which has a latency and can be fatigued (vertigo should lessen with deliberate repetition of the provoking maneuver): nystagmus should only last for 30 seconds to one minute
- Pre-syncope—(feeling faint) or syncope (fainting) is unusual, but possible
- Visual disturbance—due to associated nystagmus, making it difficult to read or see during an attack
- Nausea—is often associated
- Vomiting—is common, depending on the strength of vertigo itself and the causes for this illness
Many people will report a history of vertigo as a result of fast head movements. Many are also capable of describing the exact head movements that provoke their vertigo. Purely horizontal nystagmus and symptoms of vertigo lasting more than one minute can also indicate BPPV occurring in the horizontal semicircular canal.
The spinning sensation experienced from BPPV is usually triggered by movement of the head, will have a sudden onset, and can last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes. The most common movements people report triggering a spinning sensation are tilting their heads upward in order to look at something and when rolling over in bed.
People with BPPV do not experience other neurological deficits such as numbness or weakness. If those symptoms are present, a more serious etiology, such as posterior circulation stroke or ischemia, must be considered.
Cause
Within the labyrinth of the inner ear lie collections of calcium crystals known as otoconia or otoliths. In people with BPPV, the otoconia are dislodged from their usual position within the utricle, and over time, migrate into one of the semicircular canals (the posterior canal is most commonly affected due to its anatomical position). When the head is reoriented relative to gravity, the gravity-dependent movement of the heavier otoconial debris (colloquially "ear rocks") within the affected semicircular canal causes abnormal (pathological) endolymph fluid displacement and a resultant sensation of vertigo. This more common condition is known as canalithiasis.
In rare cases, the crystals themselves can adhere to a semicircular canal cupula, rendering it heavier than the surrounding endolymph. Upon reorientation of the head relative to gravity, the cupula is weighted down by the dense particles, thereby inducing an immediate and sustained excitation of semicircular canal afferent nerves. This condition is termed cupulolithiasis.
There is evidence in the dental literature that malleting of an osteotome during closed sinus floor elevation, otherwise known as osteotome sinus elevation or lift, transmits percussive and vibratory forces capable of detaching otoliths from their normal location and thereby leading to the symptoms of BPPV.
BPPV can be triggered by any action that stimulates the posterior semi-circular canal including:
- Looking up or down
- Following head injury
- Sudden head movement
- Rolling over in bed
- Tilting the head
BPPV may be made worse by any number of modifiers which may vary among individuals:
- Changes in barometric pressure – people may feel increased symptoms up to two days before rain or snow
- Lack of sleep (required amounts of sleep may vary widely)
- Stress
An episode of BPPV may be triggered by dehydration, such as that caused by diarrhea. For this reason, it commonly occurs in people with post-operative diarrhea induced by post-operative antibiotics.
BPPV is one of the most common vestibular disorders in people presenting with dizziness; a migraine is implicated in idiopathic cases. Proposed mechanisms linking the two are genetic factors and vascular damage to the labyrinth.
Although BPPV can occur at any age, it is most often seen in people older than the age of 60. Besides aging, there are no major risk factors known for BPPV, although previous episodes of head trauma, or the inner ear infection labyrinthitis, may predispose to the future development of BPPV.
Mechanism
The inside of the ear is composed of an organ called the vestibular labyrinth. The vestibular labyrinth includes semicircular canals, which contain fluids and fine hairlike sensors that act as a monitor to the rotations of the head. An important structure in the inner ear includes the otolith organs that contain crystals that are sensitive to gravity. These crystals are responsible for sensitivity to head positions, and can also be dislocated, causing them to lodge inside one of the semicircular canals, which causes dizziness.
Diagnosis
The condition is diagnosed by the person's history, and by performing the Dix–Hallpike test or the roll test, or both.
The Dix–Hallpike test is a common test performed by examiners to determine whether the posterior semicircular canal is involved. It involves a reorientation of the head to align the posterior semicircular canal (at its entrance to the ampulla) with the direction of gravity. This test will reproduce vertigo and nystagmus characteristic of posterior canal BPPV.
When performing the Dix–Hallpike test, people are lowered quickly to a supine position, with the neck extended by the person performing the maneuver. For some people, this maneuver may not be indicated, and a modification may be needed that also targets the posterior semicircular canal. Such people include those who are too anxious about eliciting the uncomfortable symptoms of vertigo, and those who may not have the range of motion necessary to comfortably be in a supine position. The modification involves the person moving from a seated position to side-lying without their head extending off the examination table, such as with Dix–Hallpike. The head is rotated 45 degrees away from the side being tested, and the eyes are examined for nystagmus. A positive test is indicated by the patient report of a reproduction of vertigo and clinician observation of nystagmus. Both the Dix–Hallpike and the side-lying testing position have yielded similar results, and as such the side-lying position can be used if the Dix–Hallpike cannot be performed easily.
The roll test can determine whether the horizontal semicircular canal is involved. The roll test requires the person to be in a supine position with their head in 30° of cervical flexion. Then the examiner quickly rotates the head 90° to the left side, and checks for vertigo and nystagmus. This is followed by gently bringing the head back to the starting position. The examiner then quickly rotates the head 90° to the right side and checks again for vertigo and nystagmus. In this roll test, the person may experience vertigo and nystagmus on both sides, but rotating toward the affected side will trigger a more intense vertigo. Similarly, when the head is rotated toward the affected side, the nystagmus will beat toward the ground and be more intense.
As mentioned above, both the Dix–Hallpike and roll test provoke the signs and symptoms in subjects suffering from archetypal BPPV. The signs and symptoms people with BPPV experience are typically a short-lived vertigo and observed nystagmus. In some people, although rarely, vertigo can persist for years. Assessment of BPPV is best done by a medical health professional skilled in the management of dizziness disorders, commonly a physiotherapist, audiologist, or other physician.
The nystagmus associated with BPPV has several important characteristics that differentiate it from other types of nystagmus.
- Latency of onset: there is a 5–10 second delay prior to onset of nystagmus
- Nystagmus lasts for 5–60 seconds
- Positional: the nystagmus occurs only in certain positions
- Repeated stimulation, including via Dix–Hallpike maneuvers, cause the nystagmus to fatigue or disappear temporarily
- Rotatory/Torsional component is present, or (in the case of lateral canal involvement) the nystagmus beats in either a geotropic (toward the ground) or ageotropic (away from the ground) fashion
- Visual fixation suppresses nystagmus due to BPPV
Although rare, CNS disorders can sometimes present as BPPV. A practitioner should be aware that if a person whose symptoms are consistent with BPPV, but does not show improvement or resolution after undergoing different particle repositioning maneuvers — detailed in the Treatment section below — need to have a detailed neurological assessment and imaging performed to help identify the pathological condition.
Differential diagnosis
Vertigo, a distinct process sometimes confused with the broader term, dizziness, accounts for about six million clinic visits in the United States every year; between 17 and 42% of these people are eventually diagnosed with BPPV. Other causes of vertigo include:
- Motion sickness/motion intolerance: a disjunction between visual stimulation, vestibular stimulation, and/or proprioception
- Visual exposure to nearby moving objects (examples of optokinetic stimuli include passing cars and falling snow)
- Other diseases: (labyrinthitis, Ménière's disease, and migraine, etc.)
Treatment
Repositioning maneuvers
A number of maneuvers have been found to be effective including: the Epley maneuver, the Semont maneuver, and to a lesser degree Brandt–Daroff exercises. Both the Epley and the Semont maneuvers are equally effective.
Epley maneuver
The Epley maneuver employs gravity to move the calcium crystal build-up that causes the condition. This maneuver can be performed during a clinic visit by health professionals, or taught to people to perform at home, or both. Postural restriction after the Epley maneuver increases its effect somewhat.
When practiced at home, the Epley maneuver is more effective than the Semont maneuver. The most effective repositioning treatment for posterior canal BPPV is the therapist-performed Epley combined with home-practiced Epley maneuvers. Devices such as the DizzyFIX can help users conduct the Epley maneuver at home, and are available for the treatment of BPPV.
The Epley maneuver does not address the presence of the particles (otoconia); rather it changes their location. The maneuver aims to move these particles from some locations in the inner ear that cause symptoms such as vertigo, and reposition them to where they do not cause these problems.
Semont maneuver
The Semont maneuver has a cure rate of 90.3%. It is performed as follows:
- The person is seated on a treatment table with their legs hanging off the side of the table. The therapist then turns the person's head 45 degrees toward the unaffected side.
- The therapist then quickly tilts the person so they are lying on the affected side. The head position is maintained, so their head is turned up 45 degrees. This position is maintained for 3 minutes. The purpose is to allow the debris to move to the apex of the ear canal.
- The person is then quickly moved so they are lying on the unaffected side with their head in the same position (now facing downward 45 degrees). This position is also held for 3 minutes. The purpose of this position is to allow the debris to move toward the exit of the ear canal.
- Finally, the person is slowly brought back to an upright seated position. The debris should then fall into the utricle of the canal and the symptoms of vertigo should decrease or end completely.
Some people will only need one treatment, but others may need multiple treatments, depending on the severity of their BPPV. In the Semont maneuver, as with the Epley maneuver, people are able to achieve canalith repositioning by themselves.
Brandt–Daroff exercises
The Brandt–Daroff exercises may be prescribed by the clinician as a home treatment method, usually in conjunction with particle-repositioning maneuvers or in lieu of the particle-repositioning maneuver. The exercise is a form of habituation exercise, designed to allow the person to become accustomed to the position that causes the vertigo symptoms. The Brandt–Daroff exercises are performed in a similar fashion to the Semont maneuver; however, as the person rolls onto the unaffected side, the head is rotated toward the affected side. The exercise is typically performed 3 times a day with 5–10 repetitions each time, until symptoms of vertigo have resolved for at least 2 days.
Roll maneuver
For the lateral (horizontal) canal, a separate maneuver has been used for productive results. It is unusual for the lateral canal to respond to the canalith repositioning procedure used for the posterior canal BPPV. Treatment is therefore geared toward moving the canalith from the lateral canal into the vestibule.
The roll maneuver or its variations are used, and involve rolling the person 360 degrees in a series of steps to reposition the particles. This maneuver is generally performed by a trained clinician who begins seated at the head of the examination table with the person supine There are four stages, each a minute apart, and at the third position the horizontal canal is oriented in a vertical position with the person's neck flexed and on forearm and elbows. When all four stages are completed, the head roll test is repeated, and if negative, treatment ceases.
Medications
Medical treatment with anti-vertigo medications may be considered in acute, severe exacerbation of BPPV, but in most cases are not indicated. These primarily include drugs of the antihistamine and anticholinergic class, such as meclizine and hyoscine butylbromide (scopolamine), respectively. The medical management of vestibular syndromes has become increasingly popular over the last decade, and numerous novel drug therapies (including existing drugs with new indications) have emerged for the treatment of vertigo/dizziness syndromes. These drugs vary considerably in their mechanisms of action, with many of them being receptor- or ion channel-specific. Among them are betahistine or dexamethasone/gentamicin for the treatment of Ménière's disease, carbamazepine/oxcarbazepine for the treatment of paroxysmal dysarthria and ataxia in multiple sclerosis, metoprolol/topiramate or valproic acid/tricyclic antidepressant for the treatment of vestibular migraine, and 4-aminopyridine for the treatment of episodic ataxia type 2 and both downbeat and upbeat nystagmus. These drug therapies offer symptomatic treatment, and do not affect the disease process or resolution rate. Medications may be used to suppress symptoms during the positioning maneuvers if the person's symptoms are severe and intolerable. More dose-specific studies are required, however, in order to determine the most effective drug(s) for both acute symptom relief and long-term remission of the condition.
Surgery
Surgical treatments, such as a semi-circular canal occlusion, exist for severe and persistent cases that fail vestibular rehabilitation (including particle repositioning and habituation therapy). As they carry the same risks as any neurosurgical procedure, they are reserved as last resorts.