Myoclonic Epilepsy With Ragged Red Fibers
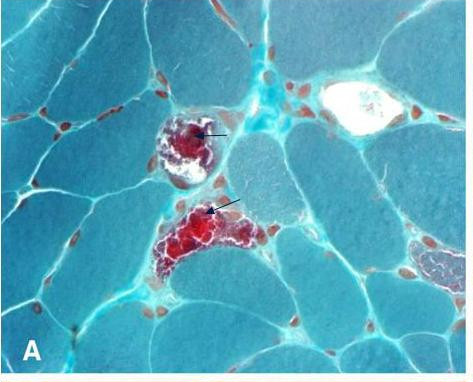
Myoclonic epilepsy with ragged red fibers (MERRF) is a multisystem disorder characterized by myoclonus, which is often the first symptom, followed by generalized epilepsy, ataxia, weakness, and dementia. Symptoms usually first appear in childhood or adolescence after normal early development. The features of MERRF vary widely from individual to individual, even within families. Other common findings include hearing loss, short stature, optic atrophy, and cardiomyopathy with Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome. The diagnosis is based on clinical features and a muscle biopsy finding of ragged red fibers (RRF). In over 80% of cases, MERRF is caused by mutations in the mitochondrial gene called MT-TK. Several other mitochondrial genes have also been reported to cause MERRF, but many of the individuals with mutations in these other genes have additional signs and symptoms. Seizures associated with MERRF are generally treated with conventional anticonvulsant therapy. Coenzyme Q10 and L-carnitine are often used with the hope of improving mitochondrial function.