Retinitis Pigmentosa 47
A number sign (#) is used with this entry because of evidence that retinitis pigmentosa-47 (RP47) is caused by homozygous mutation in the S-antigen gene (SAG; 181031) on chromosome 2q37.
For a phenotypic description and a discussion of genetic heterogeneity of retinitis pigmentosa, see 268000.
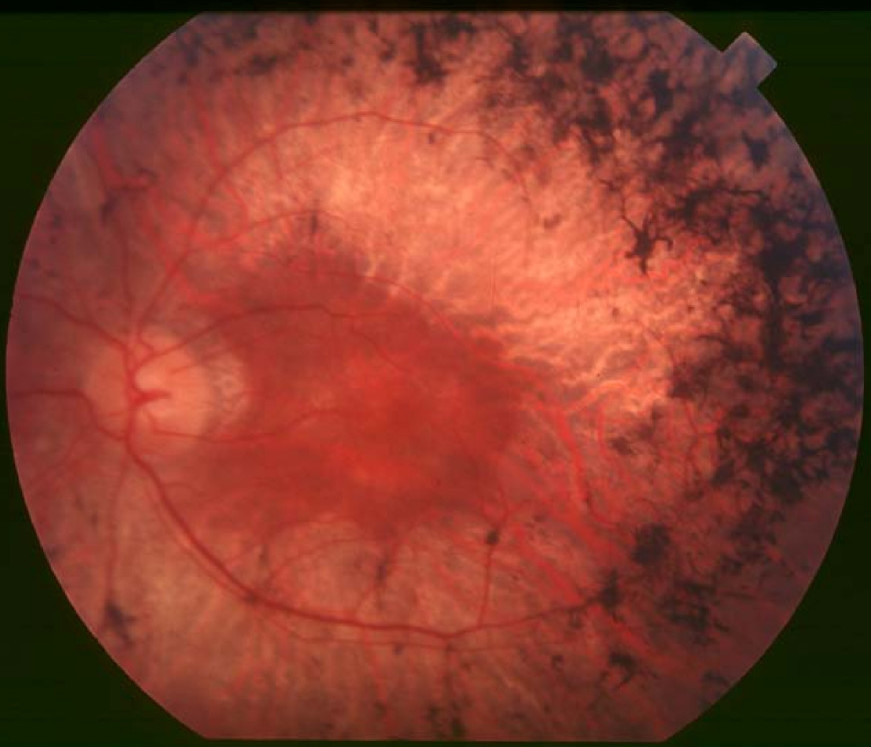
Clinical FeaturesNakazawa et al. (1998) identified 3 unrelated patients with retinitis pigmentosa (RP47) who carried the same homozygous mutation in the SAG gene (181031.0001; see MOLECULAR GENETICS). Patient 1 had a sib with Oguchi disease (258100) associated with the same mutation. Patient 2 demonstrated pigmentary retinal degeneration associated with golden-yellow reflex in the peripheral fundus. Patients 1 and 3 showed features of RP without the golden-yellow fundus reflex. Fluorescein angiography demonstrated partial chorioretinal atrophy particularly along the vascular arcade, with or without macular involvement, in all 3 patients. This region is the location in which partial chorioretinal atrophy preferentially occurs in patients with Oguchi disease.
Molecular GeneticsIn a molecular genetic screening of exon 11 of the SAG gene in 120 unrelated patients with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa, Nakazawa et al. (1998) identified a homozygous 1-bp deletion in 3 unrelated patients (1147delA; 181031.0001).