Choroid Plexus Papilloma
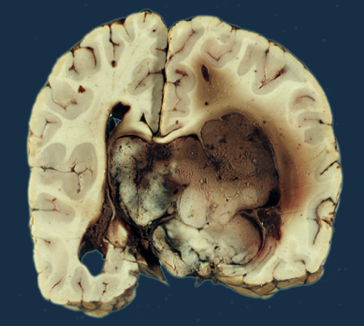
Choroid plexus papilloma (CPP) ia a non-cancerous (benign) tumor of the choroid plexus, a network of blood vessels in the brain which surrounds the ventricles and produces the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord (cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF). CPPs most commonly occur in children but may occur in adults. Symptoms are generally due to increased secretion of CSF by tumor cells, causing hydrocephalus and subsequent intracranial pressure. Affected individuals may experience headaches, nausea and vomiting, drowsiness, ocular or gaze palsies, optic nerve swelling (papilledema), visual disturbances, and possible blindness. Infants, especially those with a tumor in the third ventricle, can present with hydrocephalus or macrocephaly. Some cases of CPP may result from a mutation in the TP53 gene. Complete tumor removal often cures the condition and may also relieve the hydrocephalus.