Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome
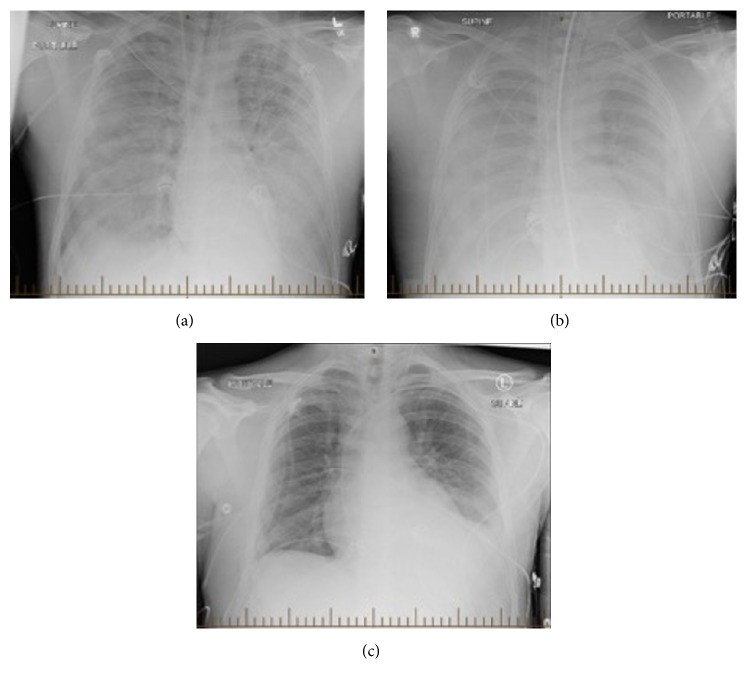
Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) is a severe, respiratory disease caused by infection with a hantavirus. People can become infected with a hantavirus through contact with hantavirus-infected rodents or their saliva, urine and/or droppings. Early symptoms universally include fatigue, fever and muscle aches (especially in the thighs, hips, and/or back), and sometimes include headaches, dizziness, chills, and abdominal problems such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and pain. Later symptoms of the syndrome occur 4 to 10 days after initial onset and include coughing and shortness of breath. HPS can be fatal; approximately 38% of individuals with HPS do not survive. There is no cure or specific treatment for HPS, but early diagnosis and treatment in intensive care may increase the chance of recovery.