Diabetes

Diabetes mellitus (DM), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased appetite. If left untreated, diabetes can cause many complications. Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or death. Serious long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, damage to the nerves, damage to the eyes and cognitive impairment.
Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced. There are three main types of diabetes mellitus:
- Type 1 diabetes results from the pancreas's failure to produce enough insulin due to loss of beta cells. This form was previously referred to as "insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus" (IDDM) or "juvenile diabetes". The loss of beta cells is caused by an autoimmune response. The cause of this autoimmune response is unknown.
- Type 2 diabetes begins with insulin resistance, a condition in which cells fail to respond to insulin properly. As the disease progresses, a lack of insulin may also develop. This form was previously referred to as "non insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus" (NIDDM) or "adult-onset diabetes". The most common cause is a combination of excessive body weight and insufficient exercise.
- Gestational diabetes is the third main form, and occurs when pregnant women without a previous history of diabetes develop high blood sugar levels.
Type 1 diabetes must be managed with insulin injections. Prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes involves maintaining a healthy diet, regular physical exercise, a normal body weight, and avoiding use of tobacco. Type 2 diabetes may be treated with medications such as insulin sensitizers with or without insulin. Control of blood pressure and maintaining proper foot and eye care are important for people with the disease. Insulin and some oral medications can cause low blood sugar. Weight loss surgery in those with obesity is sometimes an effective measure in those with type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes usually resolves after the birth of the baby.
As of 2019[update], an estimated 463 million people had diabetes worldwide (8.8% of the adult population), with type 2 diabetes making up about 90% of the cases. Rates are similar in women and men. Trends suggest that rates will continue to rise. Diabetes at least doubles a person's risk of early death. In 2019, diabetes resulted in approximately 4.2 million deaths. It is the 7th leading cause of death globally. The global economic cost of diabetes related health expenditure in 2017 was estimated at US$727 billion. In the United States, diabetes cost nearly US$327 billion in 2017. Average medical expenditures among people with diabetes are about 2.3 times higher.
Signs and symptoms
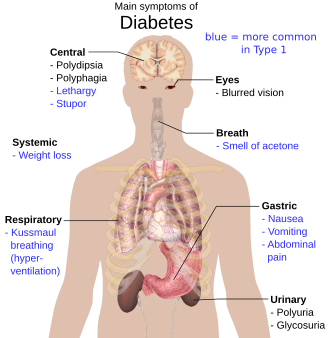
The classic symptoms of untreated diabetes are unintended weight loss, polyuria (increased urination), polydipsia (increased thirst), and polyphagia (increased hunger). Symptoms may develop rapidly (weeks or months) in type 1 diabetes, while they usually develop much more slowly and may be subtle or absent in type 2 diabetes.
Several other signs and symptoms can mark the onset of diabetes although they are not specific to the disease. In addition to the known ones above, they include blurred vision, headache, fatigue, slow healing of cuts, and itchy skin. Prolonged high blood glucose can cause glucose absorption in the lens of the eye, which leads to changes in its shape, resulting in vision changes. Long-term vision loss can also be caused by diabetic retinopathy. A number of skin rashes that can occur in diabetes are collectively known as diabetic dermadromes.
Diabetic emergencies
People (usually with type 1 diabetes) may also experience episodes of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a metabolic disturbance characterized by nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain, the smell of acetone on the breath, deep breathing known as Kussmaul breathing, and in severe cases a decreased level of consciousness. A rare but equally severe possibility is hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS), which is more common in type 2 diabetes and is mainly the result of dehydration.
Treatment-related low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) is common in people with type 1 and also type 2 diabetes depending on the medication being used. Most cases are mild and are not considered medical emergencies. Effects can range from feelings of unease, sweating, trembling, and increased appetite in mild cases to more serious effects such as confusion, changes in behavior such as aggressiveness, seizures, unconsciousness, and (rarely) permanent brain damage or death in severe cases. Rapid breathing, sweating, and cold, pale skin are characteristic of low blood sugar but not definitive. Mild to moderate cases are self-treated by eating or drinking something high in sugar. Severe cases can lead to unconsciousness and must be treated with intravenous glucose or injections with glucagon.
Complications

All forms of diabetes increase the risk of long-term complications. These typically develop after many years (10–20) but may be the first symptom in those who have otherwise not received a diagnosis before that time.
The major long-term complications relate to damage to blood vessels. Diabetes doubles the risk of cardiovascular disease and about 75% of deaths in people with diabetes are due to coronary artery disease. Other macrovascular diseases include stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
The primary complications of diabetes due to damage in small blood vessels include damage to the eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Damage to the eyes, known as diabetic retinopathy, is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina of the eye, and can result in gradual vision loss and eventual blindness. Diabetes also increases the risk of having glaucoma, cataracts, and other eye problems. It is recommended that people with diabetes visit an eye doctor once a year. Damage to the kidneys, known as diabetic nephropathy, can lead to tissue scarring, urine protein loss, and eventually chronic kidney disease, sometimes requiring dialysis or kidney transplantation. Damage to the nerves of the body, known as diabetic neuropathy, is the most common complication of diabetes. The symptoms can include numbness, tingling, pain, and altered pain sensation, which can lead to damage to the skin. Diabetes-related foot problems (such as diabetic foot ulcers) may occur, and can be difficult to treat, occasionally requiring amputation. Additionally, proximal diabetic neuropathy causes painful muscle atrophy and weakness.
There is a link between cognitive deficit and diabetes. Compared to those without diabetes, those with the disease have a 1.2 to 1.5-fold greater rate of decline in cognitive function. Having diabetes, especially when on insulin, increases the risk of falls in older people.
Causes
| Feature | Type 1 diabetes | Type 2 diabetes |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Sudden | Gradual |
| Age at onset | Mostly in children | Mostly in adults |
| Body size | Thin or normal | Often obese |
| Ketoacidosis | Common | Rare |
| Autoantibodies | Usually present | Absent |
| Endogenous insulin | Low or absent | Normal, decreased or increased |
| Concordance in identical twins |
50% | 90% |
| Prevalence | ~10% | ~90% |
Diabetes mellitus is classified into six categories: type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, hybrid forms of diabetes, hyperglycemia first detected during pregnancy, "unclassified diabetes", and "other specific types". The "hybrid forms of diabetes" contains slowly evolving, immunemediated diabetes of adults and ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes. The "hyperglycemia first detected during pregnancy" contains gestational diabetes mellitus and diabetes mellitus in pregnancy (type 1 or type 2 diabetes first diagnosed during pregnancy). The "other specific types" are a collection of a few dozen individual causes. Diabetes is a more variable disease than once thought and people may have combinations of forms. The term "diabetes", without qualification, refers to diabetes mellitus.
Type 1
Type 1 diabetes is characterized by loss of the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreatic islets, leading to insulin deficiency. This type can be further classified as immune-mediated or idiopathic. The majority of type 1 diabetes is of the immune-mediated nature, in which a T cell-mediated autoimmune attack leads to the loss of beta cells and thus insulin. It causes approximately 10% of diabetes mellitus cases in North America and Europe. Most affected people are otherwise healthy and of a healthy weight when onset occurs. Sensitivity and responsiveness to insulin are usually normal, especially in the early stages. Although it has been called "juvenile diabetes" due to the frequent onset in children, the majority of individuals living with type 1 diabetes are now adults.
"Brittle" diabetes, also known as unstable diabetes or labile diabetes, is a term that was traditionally used to describe the dramatic and recurrent swings in glucose levels, often occurring for no apparent reason in insulin-dependent diabetes. This term, however, has no biologic basis and should not be used. Still, type 1 diabetes can be accompanied by irregular and unpredictable high blood sugar levels, and the potential for diabetic ketoacidosis or serious low blood sugar levels. Other complications include an impaired counterregulatory response to low blood sugar, infection, gastroparesis (which leads to erratic absorption of dietary carbohydrates), and endocrinopathies (e.g., Addison's disease). These phenomena are believed to occur no more frequently than in 1% to 2% of persons with type 1 diabetes.

Type 1 diabetes is partly inherited, with multiple genes, including certain HLA genotypes, known to influence the risk of diabetes. In genetically susceptible people, the onset of diabetes can be triggered by one or more environmental factors, such as a viral infection or diet. Several viruses have been implicated, but to date there is no stringent evidence to support this hypothesis in humans. Among dietary factors, data suggest that gliadin (a protein present in gluten) may play a role in the development of type 1 diabetes, but the mechanism is not fully understood.
Type 1 diabetes can occur at any age, and a significant proportion is diagnosed during adulthood. Latent autoimmune diabetes of adults (LADA) is the diagnostic term applied when type 1 diabetes develops in adults; it has a slower onset than the same condition in children. Given this difference, some use the unofficial term "type 1.5 diabetes" for this condition. Adults with LADA are frequently initially misdiagnosed as having type 2 diabetes, based on age rather than cause.
Type 2

Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, which may be combined with relatively reduced insulin secretion. The defective responsiveness of body tissues to insulin is believed to involve the insulin receptor. However, the specific defects are not known. Diabetes mellitus cases due to a known defect are classified separately. Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes mellitus. Many people with type 2 diabetes have evidence of prediabetes (impaired fasting glucose and/or impaired glucose tolerance) before meeting the criteria for type 2 diabetes. The progression of prediabetes to overt type 2 diabetes can be slowed or reversed by lifestyle changes or medications that improve insulin sensitivity or reduce the liver's glucose production.
Type 2 diabetes is primarily due to lifestyle factors and genetics. A number of lifestyle factors are known to be important to the development of type 2 diabetes, including obesity (defined by a body mass index of greater than 30), lack of physical activity, poor diet, stress, and urbanization. Excess body fat is associated with 30% of cases in people of Chinese and Japanese descent, 60–80% of cases in those of European and African descent, and 100% of Pima Indians and Pacific Islanders. Even those who are not obese may have a high waist–hip ratio.
Dietary factors such as sugar-sweetened drinks are associated with an increased risk. The type of fats in the diet is also important, with saturated fat and trans fats increasing the risk and polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fat decreasing the risk. Eating white rice excessively may increase the risk of diabetes, especially in Chinese and Japanese people. Lack of physical activity may increase the risk of diabetes in some people.
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs), including abuse, neglect, and household difficulties, increase the likelihood of type 2 diabetes later in life by 32%, with neglect having the strongest effect.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes resembles type 2 diabetes in several respects, involving a combination of relatively inadequate insulin secretion and responsiveness. It occurs in about 2–10% of all pregnancies and may improve or disappear after delivery. It is recommended that all pregnant women get tested starting around 24–28 weeks gestation. It is most often diagnosed in the second or third trimester because of the increase in insulin-antagonist hormone levels that occurs at this time. However, after pregnancy approximately 5–10% of women with gestational diabetes are found to have another form of diabetes, most commonly type 2. Gestational diabetes is fully treatable, but requires careful medical supervision throughout the pregnancy. Management may include dietary changes, blood glucose monitoring, and in some cases, insulin may be required.
Though it may be transient, untreated gestational diabetes can damage the health of the fetus or mother. Risks to the baby include macrosomia (high birth weight), congenital heart and central nervous system abnormalities, and skeletal muscle malformations. Increased levels of insulin in a fetus's blood may inhibit fetal surfactant production and cause infant respiratory distress syndrome. A high blood bilirubin level may result from red blood cell destruction. In severe cases, perinatal death may occur, most commonly as a result of poor placental perfusion due to vascular impairment. Labor induction may be indicated with decreased placental function. A caesarean section may be performed if there is marked fetal distress or an increased risk of injury associated with macrosomia, such as shoulder dystocia.
Other types
Maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY) is a rare autosomal dominant inherited form of diabetes, due to one of several single-gene mutations causing defects in insulin production. It is significantly less common than the three main types, constituting 1–2% of all cases. The name of this disease refers to early hypotheses as to its nature. Being due to a defective gene, this disease varies in age at presentation and in severity according to the specific gene defect; thus there are at least 13 subtypes of MODY. People with MODY often can control it without using insulin.
Some cases of diabetes are caused by the body's tissue receptors not responding to insulin (even when insulin levels are normal, which is what separates it from type 2 diabetes); this form is very uncommon. Genetic mutations (autosomal or mitochondrial) can lead to defects in beta cell function. Abnormal insulin action may also have been genetically determined in some cases. Any disease that causes extensive damage to the pancreas may lead to diabetes (for example, chronic pancreatitis and cystic fibrosis). Diseases associated with excessive secretion of insulin-antagonistic hormones can cause diabetes (which is typically resolved once the hormone excess is removed). Many drugs impair insulin secretion and some toxins damage pancreatic beta cells, whereas others increase insulin resistance (especially glucocorticoids which can provoke "steroid diabetes"). The ICD-10 (1992) diagnostic entity, malnutrition-related diabetes mellitus (MRDM or MMDM, ICD-10 code E12), was deprecated by the World Health Organization (WHO) when the current taxonomy was introduced in 1999. Yet another form of diabetes that people may develop is double diabetes. This is when a type 1 diabetic becomes insulin resistant, the hallmark for type 2 diabetes or has a family history for type 2 diabetes. It was first discovered in 1990 or 1991.
The following is a list of disorders that may increase the risk of diabetes:
|
|
New-onset diabetes has been observed in patients with Covid-19.
Pathophysiology


Insulin is the principal hormone that regulates the uptake of glucose from the blood into most cells of the body, especially liver, adipose tissue and muscle, except smooth muscle, in which insulin acts via the IGF-1. Therefore, deficiency of insulin or the insensitivity of its receptors play a central role in all forms of diabetes mellitus.
The body obtains glucose from three main sources: the intestinal absorption of food; the breakdown of glycogen (glycogenolysis), the storage form of glucose found in the liver; and gluconeogenesis, the generation of glucose from non-carbohydrate substrates in the body. Insulin plays a critical role in regulating glucose levels in the body. Insulin can inhibit the breakdown of glycogen or the process of gluconeogenesis, it can stimulate the transport of glucose into fat and muscle cells, and it can stimulate the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen.
Insulin is released into the blood by beta cells (β-cells), found in the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas, in response to rising levels of blood glucose, typically after eating. Insulin is used by about two-thirds of the body's cells to absorb glucose from the blood for use as fuel, for conversion to other needed molecules, or for storage. Lower glucose levels result in decreased insulin release from the beta cells and in the breakdown of glycogen to glucose. This process is mainly controlled by the hormone glucagon, which acts in the opposite manner to insulin.
If the amount of insulin available is insufficient, or if cells respond poorly to the effects of insulin (insulin resistance), or if the insulin itself is defective, then glucose is not absorbed properly by the body cells that require it, and is not stored appropriately in the liver and muscles. The net effect is persistently high levels of blood glucose, poor protein synthesis, and other metabolic derangements, such as metabolic acidosis in cases of complete insulin deficiency.
When glucose concentration in the blood remains high over time, the kidneys reach a threshold of reabsorption, and the body excretes glucose in the urine (glycosuria). This increases the osmotic pressure of the urine and inhibits reabsorption of water by the kidney, resulting in increased urine production (polyuria) and increased fluid loss. Lost blood volume is replaced osmotically from water in body cells and other body compartments, causing dehydration and increased thirst (polydipsia). In addition, intracellular glucose deficiency stimulates appetite leading to excessive food intake (polyphagia).
Diagnosis
| Condition | 2-hour glucose | Fasting glucose | HbA1c | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | mmol/L | mg/dL | mmol/L | mg/dL | mmol/mol | DCCT % |
| Normal | < 7.8 | < 140 | < 6.1 | < 110 | < 42 | < 6.0 |
| Impaired fasting glycaemia | < 7.8 | < 140 | 6.1–7.0 | 110–125 | 42–46 | 6.0–6.4 |
| Impaired glucose tolerance | ≥ 7.8 | ≥ 140 | < 7.0 | < 126 | 42–46 | 6.0–6.4 |
| Diabetes mellitus | ≥ 11.1 | ≥ 200 | ≥ 7.0 | ≥ 126 | ≥ 48 | ≥ 6.5 |
Diabetes mellitus is characterized by recurrent or persistent high blood sugar, and is diagnosed by demonstrating any one of the following:
- Fasting plasma glucose level ≥ 7.0 mmol/L (126 mg/dL)
- Plasma glucose ≥ 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL) two hours after a 75 gram oral glucose load as in a glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
- Symptoms of high blood sugar and casual plasma glucose ≥ 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL)
- Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C) ≥ 48 mmol/mol (≥ 6.5 DCCT %).
A positive result, in the absence of unequivocal high blood sugar, should be confirmed by a repeat of any of the above methods on a different day. It is preferable to measure a fasting glucose level because of the ease of measurement and the considerable time commitment of formal glucose tolerance testing, which takes two hours to complete and offers no prognostic advantage over the fasting test. According to the current definition, two fasting glucose measurements above 7.0 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) is considered diagnostic for diabetes mellitus.
Per the WHO, people with fasting glucose levels from 6.1 to 6.9 mmol/L (110 to 125 mg/dL) are considered to have impaired fasting glucose. People with plasma glucose at or above 7.8 mmol/L (140 mg/dL), but not over 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), two hours after a 75 gram oral glucose load are considered to have impaired glucose tolerance. Of these two prediabetic states, the latter in particular is a major risk factor for progression to full-blown diabetes mellitus, as well as cardiovascular disease. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) since 2003 uses a slightly different range for impaired fasting glucose of 5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L (100 to 125 mg/dL).
Glycated hemoglobin is better than fasting glucose for determining risks of cardiovascular disease and death from any cause.
Prevention
There is no known preventive measure for type 1 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes—which accounts for 85–90% of all cases worldwide—can often be prevented or delayed by maintaining a normal body weight, engaging in physical activity, and eating a healthy diet. Higher levels of physical activity (more than 90 minutes per day) reduce the risk of diabetes by 28%. Dietary changes known to be effective in helping to prevent diabetes include maintaining a diet rich in whole grains and fiber, and choosing good fats, such as the polyunsaturated fats found in nuts, vegetable oils, and fish. Limiting sugary beverages and eating less red meat and other sources of saturated fat can also help prevent diabetes. Tobacco smoking is also associated with an increased risk of diabetes and its complications, so smoking cessation can be an important preventive measure as well.
The relationship between type 2 diabetes and the main modifiable risk factors (excess weight, unhealthy diet, physical inactivity and tobacco use) is similar in all regions of the world. There is growing evidence that the underlying determinants of diabetes are a reflection of the major forces driving social, economic and cultural change: globalization, urbanization, population aging, and the general health policy environment.
Management
 Play media
Play mediaDiabetes management concentrates on keeping blood sugar levels as close to normal, without causing low blood sugar. This can usually be accomplished with dietary changes, exercise, weight loss, and use of appropriate medications (insulin, oral medications).
Learning about the disease and actively participating in the treatment is important, since complications are far less common and less severe in people who have well-managed blood sugar levels. Per the American College of Physicians, the goal of treatment is an HbA1C level of 7-8%. Attention is also paid to other health problems that may accelerate the negative effects of diabetes. These include smoking, high blood pressure, metabolic syndrome obesity, and lack of regular exercise. Specialized footwear is widely used to reduce the risk of ulcers in at-risk diabetic feet although evidence for the efficacy of this remains equivocal.
Lifestyle
People with diabetes can benefit from education about the disease and treatment, dietary changes, and exercise, with the goal of keeping both short-term and long-term blood glucose levels within acceptable bounds. In addition, given the associated higher risks of cardiovascular disease, lifestyle modifications are recommended to control blood pressure.
Weight loss can prevent progression from prediabetes to diabetes type 2, decrease the risk of cardiovascular disease, or result in a partial remission in people with diabetes. No single dietary pattern is best for all people with diabetes. Healthy dietary patterns, such as the Mediterranean diet, low-carbohydrate diet, or DASH diet, are often recommended, although evidence does not support one over the others. According to the ADA, "reducing overall carbohydrate intake for individuals with diabetes has demonstrated the most evidence for improving glycemia", and for individuals with type 2 diabetes who cannot meet the glycemic targets or where reducing anti-glycemic medications is a priority, low or very-low carbohydrate diets are a viable approach. For overweight people with type 2 diabetes, any diet that achieves weight loss is effective. Implementing a plant-based diet may help manage or prevent type-2 diabetes by lowering glycated hemoglobin levels. In addition, improvement in health may reduce the need for or number of medications needed by people who adopt a plant-based diet.
Medications
Glucose control
Most medications used to treat diabetes act by lowering blood sugar levels through different mechanisms. There is broad consensus that when people with diabetes maintain tight glucose control – keeping the glucose levels in their blood within normal ranges – they experience fewer complications, such as kidney problems or eye problems. There is however debate as to whether this is appropriate and cost effective for people later in life in whom the risk of hypoglycemia may be more significant.
There are a number of different classes of anti-diabetic medications. Type 1 diabetes requires treatment with insulin, ideally using a "basal bolus" regimen that most closely matches normal insulin release: long-acting insulin for the basal rate and short-acting insulin with meals. Type 2 diabetes is generally taken with medication that is taken by mouth (e.g. metformin) although some eventually require injectable treatment with insulin or GLP-1 agonists.
Metformin is generally recommended as a first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes, as there is good evidence that it decreases mortality. It works by decreasing the liver's production of glucose. Several other groups of drugs, mostly given by mouth, may also decrease blood sugar in type 2 diabetes. These include agents that increase insulin release (sulfonylureas), agents that decrease absorption of sugar from the intestines (acarbose), agents that inhibit the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) that inactivates incretins such as GLP-1 and GIP (sitagliptin), agents that make the body more sensitive to insulin (thiazolidinedione) and agents that increase the excretion of glucose in the urine (SGLT2 inhibitors). When insulin is used in type 2 diabetes, a long-acting formulation is usually added initially, while continuing oral medications. Doses of insulin are then increased until glucose targets are reached.
Blood pressure lowering
Cardiovascular disease is a serious complication associated with diabetes, and many international guidelines recommend blood pressure treatment targets that are lower than 140/90 mmHg for people with diabetes. However, there is only limited evidence regarding what the lower targets should be. A 2016 systematic review found potential harm to treating to targets lower than 140 mmHg, and a subsequent systematic review in 2019 found no evidence of additional benefit from blood pressure lowering to between 130 - 140mmHg, although there was an increased risk of adverse events.
2015 American Diabetes Association recommendations are that people with diabetes and albuminuria should receive an inhibitor of the renin-angiotensin system to reduce the risks of progression to end-stage renal disease, cardiovascular events, and death. There is some evidence that angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) are superior to other inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system such as angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), or aliskiren in preventing cardiovascular disease. Although a more recent review found similar effects of ACEIs and ARBs on major cardiovascular and renal outcomes. There is no evidence that combining ACEIs and ARBs provides additional benefits.
Aspirin
The use of aspirin to prevent cardiovascular disease in diabetes is controversial. Aspirin is recommended by some in people at high risk of cardiovascular disease, however routine use of aspirin has not been found to improve outcomes in uncomplicated diabetes. 2015 American Diabetes Association recommendations for aspirin use (based on expert consensus or clinical experience) are that low-dose aspirin use is reasonable in adults with diabetes who are at intermediate risk of cardiovascular disease (10-year cardiovascular disease risk, 5–10%). National guidelines for England and Wales by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommend against the use of aspirin in people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes who do not have confirmed cardiovascular disease.
Surgery
Weight loss surgery in those with obesity and type 2 diabetes is often an effective measure. Many are able to maintain normal blood sugar levels with little or no medications following surgery and long-term mortality is decreased. There is, however, a short-term mortality risk of less than 1% from the surgery. The body mass index cutoffs for when surgery is appropriate are not yet clear. It is recommended that this option be considered in those who are unable to get both their weight and blood sugar under control.
A pancreas transplant is occasionally considered for people with type 1 diabetes who have severe complications of their disease, including end stage kidney disease requiring kidney transplantation.
Support
In countries using a general practitioner system, such as the United Kingdom, care may take place mainly outside hospitals, with hospital-based specialist care used only in case of complications, difficult blood sugar control, or research projects. In other circumstances, general practitioners and specialists share care in a team approach. Home telehealth support can be an effective management technique.
Epidemiology
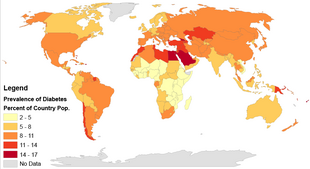

In 2017, 425 million people had diabetes worldwide, up from an estimated 382 million people in 2013 and from 108 million in 1980. Accounting for the shifting age structure of the global population, the prevalence of diabetes is 8.8% among adults, nearly double the rate of 4.7% in 1980. Type 2 makes up about 90% of the cases. Some data indicate rates are roughly equal in women and men, but male excess in diabetes has been found in many populations with higher type 2 incidence, possibly due to sex-related differences in insulin sensitivity, consequences of obesity and regional body fat deposition, and other contributing factors such as high blood pressure, tobacco smoking, and alcohol intake.
The WHO estimates that diabetes resulted in 1.5 million deaths in 2012, making it the 8th leading cause of death. However another 2.2 million deaths worldwide were attributable to high blood glucose and the increased risks of cardiovascular disease and other associated complications (e.g. kidney failure), which often lead to premature death and are often listed as the underlying cause on death certificates rather than diabetes. For example, in 2017, the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) estimated