Stroke

A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly. Signs and symptoms of a stroke may include an inability to move or feel on one side of the body, problems understanding or speaking, dizziness, or loss of vision to one side. Signs and symptoms often appear soon after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than one or two hours, the stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke. A hemorrhagic stroke may also be associated with a severe headache. The symptoms of a stroke can be permanent. Long-term complications may include pneumonia and loss of bladder control.
The main risk factor for stroke is high blood pressure. Other risk factors include tobacco smoking, obesity, high blood cholesterol, diabetes mellitus, a previous TIA, end-stage kidney disease, and atrial fibrillation. An ischemic stroke is typically caused by blockage of a blood vessel, though there are also less common causes. A hemorrhagic stroke is caused by either bleeding directly into the brain or into the space between the brain's membranes. Bleeding may occur due to a ruptured brain aneurysm. Diagnosis is typically based on a physical exam and supported by medical imaging such as a CT scan or MRI scan. A CT scan can rule out bleeding, but may not necessarily rule out ischemia, which early on typically does not show up on a CT scan. Other tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) and blood tests are done to determine risk factors and rule out other possible causes. Low blood sugar may cause similar symptoms.
Prevention includes decreasing risk factors, surgery to open up the arteries to the brain in those with problematic carotid narrowing, and warfarin in people with atrial fibrillation. Aspirin or statins may be recommended by physicians for prevention. A stroke or TIA often requires emergency care. An ischemic stroke, if detected within three to four and half hours, may be treatable with a medication that can break down the clot. Some hemorrhagic strokes benefit from surgery. Treatment to attempt recovery of lost function is called stroke rehabilitation, and ideally takes place in a stroke unit; however, these are not available in much of the world.
In 2013, approximately 6.9 million people had an ischemic stroke and 3.4 million people had a hemorrhagic stroke. In 2015, there were about 42.4 million people who had previously had a stroke and were still alive. Between 1990 and 2010 the number of strokes which occurred each year decreased by approximately 10% in the developed world and increased by 10% in the developing world. In 2015, stroke was the second most frequent cause of death after coronary artery disease, accounting for 6.3 million deaths (11% of the total). About 3.0 million deaths resulted from ischemic stroke while 3.3 million deaths resulted from hemorrhagic stroke. About half of people who have had a stroke live less than one year. Overall, two thirds of strokes occurred in those over 65 years old.
Classification
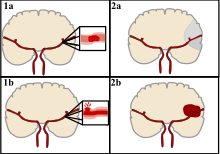
Strokes can be classified into two major categories: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes are caused by interruption of the blood supply to the brain, while hemorrhagic strokes result from the rupture of a blood vessel or an abnormal vascular structure. About 87% of strokes are ischemic, the rest being hemorrhagic. Bleeding can develop inside areas of ischemia, a condition known as "hemorrhagic transformation." It is unknown how many hemorrhagic strokes actually start as ischemic strokes.
Definition
In the 1970s the World Health Organization defined stroke as a "neurological deficit of cerebrovascular cause that persists beyond 24 hours or is interrupted by death within 24 hours", although the word "stroke" is centuries old. This definition was supposed to reflect the reversibility of tissue damage and was devised for the purpose, with the time frame of 24 hours being chosen arbitrarily. The 24-hour limit divides stroke from transient ischemic attack, which is a related syndrome of stroke symptoms that resolve completely within 24 hours. With the availability of treatments that can reduce stroke severity when given early, many now prefer alternative terminology, such as brain attack and acute ischemic cerebrovascular syndrome (modeled after heart attack and acute coronary syndrome, respectively), to reflect the urgency of stroke symptoms and the need to act swiftly.
Ischemic
In an ischemic stroke, blood supply to part of the brain is decreased, leading to dysfunction of the brain tissue in that area. There are four reasons why this might happen:
- Thrombosis (obstruction of a blood vessel by a blood clot forming locally)
- Embolism (obstruction due to an embolus from elsewhere in the body),
- Systemic hypoperfusion (general decrease in blood supply, e.g., in shock)
- Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis.
A stroke without an obvious explanation is termed cryptogenic (of unknown origin); this constitutes 30–40% of all ischemic strokes.
There are various classification systems for acute ischemic stroke. The Oxford Community Stroke Project classification (OCSP, also known as the Bamford or Oxford classification) relies primarily on the initial symptoms; based on the extent of the symptoms, the stroke episode is classified as total anterior circulation infarct (TACI), partial anterior circulation infarct (PACI), lacunar infarct (LACI) or posterior circulation infarct (POCI). These four entities predict the extent of the stroke, the area of the brain that is affected, the underlying cause, and the prognosis. The TOAST (Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment) classification is based on clinical symptoms as well as results of further investigations; on this basis, a stroke is classified as being due to (1) thrombosis or embolism due to atherosclerosis of a large artery, (2) an embolism originating in the heart, (3) complete blockage of a small blood vessel, (4) other determined cause, (5) undetermined cause (two possible causes, no cause identified, or incomplete investigation). Users of stimulants such as cocaine and methamphetamine are at a high risk for ischemic strokes.
Hemorrhagic
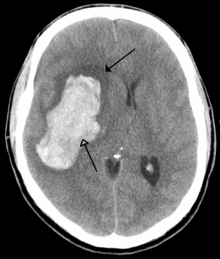
There are two main types of hemorrhagic stroke:
- Intracerebral hemorrhage, which is basically bleeding within the brain itself (when an artery in the brain bursts, flooding the surrounding tissue with blood), due to either intraparenchymal hemorrhage (bleeding within the brain tissue) or intraventricular hemorrhage (bleeding within the brain's ventricular system).
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage, which is basically bleeding that occurs outside of the brain tissue but still within the skull, and precisely between the arachnoid mater and pia mater (the delicate innermost layer of the three layers of the meninges that surround the brain).
The above two main types of hemorrhagic stroke are also two different forms of intracranial hemorrhage, which is the accumulation of blood anywhere within the cranial vault; but the other forms of intracranial hemorrhage, such as epidural hematoma (bleeding between the skull and the dura mater, which is the thick outermost layer of the meninges that surround the brain) and subdural hematoma (bleeding in the subdural space), are not considered "hemorrhagic strokes".
Hemorrhagic strokes may occur on the background of alterations to the blood vessels in the brain, such as cerebral amyloid angiopathy, cerebral arteriovenous malformation and an intracranial aneurysm, which can cause intraparenchymal or subarachnoid hemorrhage.
In addition to neurological impairment, hemorrhagic strokes usually cause specific symptoms (for instance, subarachnoid hemorrhage classically causes a severe headache known as a thunderclap headache) or reveal evidence of a previous head injury.
Signs and symptoms
Stroke symptoms typically start suddenly, over seconds to minutes, and in most cases do not progress further. The symptoms depend on the area of the brain affected. The more extensive the area of the brain affected, the more functions that are likely to be lost. Some forms of stroke can cause additional symptoms. For example, in intracranial hemorrhage, the affected area may compress other structures. Most forms of stroke are not associated with a headache, apart from subarachnoid hemorrhage and cerebral venous thrombosis and occasionally intracerebral hemorrhage.
Early recognition
Various systems have been proposed to increase recognition of stroke. Different findings are able to predict the presence or absence of stroke to different degrees. Sudden-onset face weakness, arm drift (i.e., if a person, when asked to raise both arms, involuntarily lets one arm drift downward) and abnormal speech are the findings most likely to lead to the correct identification of a case of stroke, increasing the likelihood by 5.5 when at least one of these is present. Similarly, when all three of these are absent, the likelihood of stroke is decreased (– likelihood ratio of 0.39). While these findings are not perfect for diagnosing stroke, the fact that they can be evaluated relatively rapidly and easily make them very valuable in the acute setting.
A mnemonic to remember the warning signs of stroke is FAST (facial droop, arm weakness, speech difficulty, and time to call emergency services), as advocated by the Department of Health (United Kingdom) and the Stroke Association, the American Stroke Association, the National Stroke Association (US), the Los Angeles Prehospital Stroke Screen (LAPSS) and the Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale (CPSS). Use of these scales is recommended by professional guidelines. FAST is less reliable in the recognition of posterior circulation strokes.
For people referred to the emergency room, early recognition of stroke is deemed important as this can expedite diagnostic tests and treatments. A scoring system called ROSIER (recognition of stroke in the emergency room) is recommended for this purpose; it is based on features from the medical history and physical examination.
Subtypes
If the area of the brain affected includes one of the three prominent central nervous system pathways—the spinothalamic tract, corticospinal tract, and the dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway, symptoms may include:
- hemiplegia and muscle weakness of the face
- numbness
- reduction in sensory or vibratory sensation
- initial flaccidity (reduced muscle tone), replaced by spasticity (increased muscle tone), excessive reflexes, and obligatory synergies.
In most cases, the symptoms affect only one side of the body (unilateral). Depending on the part of the brain affected, the defect in the brain is usually on the opposite side of the body. However, since these pathways also travel in the spinal cord and any lesion there can also produce these symptoms, the presence of any one of these symptoms does not necessarily indicate a stroke. In addition to the above CNS pathways, the brainstem gives rise to most of the twelve cranial nerves. A brainstem stroke affecting the brainstem and brain, therefore, can produce symptoms relating to deficits in these cranial nerves:
- altered smell, taste, hearing, or vision (total or partial)
- drooping of eyelid (ptosis) and weakness of ocular muscles
- decreased reflexes: gag, swallow, pupil reactivity to light
- decreased sensation and muscle weakness of the face
- balance problems and nystagmus
- altered breathing and heart rate
- weakness in sternocleidomastoid muscle with inability to turn head to one side
- weakness in tongue (inability to stick out the tongue or move it from side to side)
If the cerebral cortex is involved, the CNS pathways can again be affected, but also can produce the following symptoms:
- aphasia (difficulty with verbal expression, auditory comprehension, reading and writing; Broca's or Wernicke's area typically involved)
- dysarthria (motor speech disorder resulting from neurological injury)
- apraxia (altered voluntary movements)
- visual field defect
- memory deficits (involvement of temporal lobe)
- hemineglect (involvement of parietal lobe)
- disorganized thinking, confusion, hypersexual gestures (with involvement of frontal lobe)
- lack of insight of his or her, usually stroke-related, disability
If the cerebellum is involved, ataxia might be present and this includes:
- altered walking gait
- altered movement coordination
- vertigo and or disequilibrium
Associated symptoms
Loss of consciousness, headache, and vomiting usually occur more often in hemorrhagic stroke than in thrombosis because of the increased intracranial pressure from the leaking blood compressing the brain.
If symptoms are maximal at onset, the cause is more likely to be a subarachnoid hemorrhage or an embolic stroke.
Causes
Thrombotic stroke

In thrombotic stroke, a thrombus (blood clot) usually forms around atherosclerotic plaques. Since blockage of the artery is gradual, onset of symptomatic thrombotic strokes is slower than that of a hemorrhagic stroke. A thrombus itself (even if it does not completely block the blood vessel) can lead to an embolic stroke (see below) if the thrombus breaks off and travels in the bloodstream, at which point it is called an embolus. Two types of thrombosis can cause stroke:
- Large vessel disease involves the common and internal carotid arteries, the vertebral artery, and the Circle of Willis. Diseases that may form thrombi in the large vessels include (in descending incidence): atherosclerosis, vasoconstriction (tightening of the artery), aortic, carotid or vertebral artery dissection, various inflammatory diseases of the blood vessel wall (Takayasu arteritis, giant cell arteritis, vasculitis), noninflammatory vasculopathy, Moyamoya disease and fibromuscular dysplasia.
- Small vessel disease involves the smaller arteries inside the brain: branches of the circle of Willis, middle cerebral artery, stem, and arteries arising from the distal vertebral and basilar artery. Diseases that may form thrombi in the small vessels include (in descending incidence): lipohyalinosis (build-up of fatty hyaline matter in the blood vessel as a result of high blood pressure and aging) and fibrinoid degeneration (a stroke involving these vessels is known as a lacunar stroke) and microatheroma (small atherosclerotic plaques).
Sickle-cell anemia, which can cause blood cells to clump up and block blood vessels, can also lead to stroke. A stroke is the second leading cause of death in people under 20 with sickle-cell anemia. Air pollution may also increase stroke risk.
Embolic stroke
An embolic stroke refers to an arterial embolism (a blockage of an artery) by an embolus, a traveling particle or debris in the arterial bloodstream originating from elsewhere. An embolus is most frequently a thrombus, but it can also be a number of other substances including fat (e.g., from bone marrow in a broken bone), air, cancer cells or clumps of bacteria (usually from infectious endocarditis).
Because an embolus arises from elsewhere, local therapy solves the problem only temporarily. Thus, the source of the embolus must be identified. Because the embolic blockage is sudden in onset, symptoms usually are maximal at the start. Also, symptoms may be transient as the embolus is partially resorbed and moves to a different location or dissipates altogether.
Emboli most commonly arise from the heart (especially in atrial fibrillation) but may originate from elsewhere in the arterial tree. In paradoxical embolism, a deep vein thrombosis embolizes through an atrial or ventricular septal defect in the heart into the brain.
Causes of stroke related to the heart can be distinguished between high and low-risk:
- High risk: atrial fibrillation and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, rheumatic disease of the mitral or aortic valve disease, artificial heart valves, known cardiac thrombus of the atrium or ventricle, sick sinus syndrome, sustained atrial flutter, recent myocardial infarction, chronic myocardial infarction together with ejection fraction <28 percent, symptomatic congestive heart failure with ejection fraction <30 percent, dilated cardiomyopathy, Libman-Sacks endocarditis, Marantic endocarditis, infective endocarditis, papillary fibroelastoma, left atrial myxoma and coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery.
- Low risk/potential: calcification of the annulus (ring) of the mitral valve, patent foramen ovale (PFO), atrial septal aneurysm, atrial septal aneurysm with patent foramen ovale, left ventricular aneurysm without thrombus, isolated left atrial "smoke" on echocardiography (no mitral stenosis or atrial fibrillation), complex atheroma in the ascending aorta or proximal arch.
Among those who have a complete blockage of one of the carotid arteries, the risk of stroke on that side is about one percent per year.
A special form of embolic stroke is the embolic stroke of undetermined source (ESUS). This subset of cryptogenic stroke is defined as a non-lacunar brain infarct without proximal arterial stenosis or cardioembolic sources. About one out of six ischemic strokes could be classified as ESUS.
Cerebral hypoperfusion
Cerebral hypoperfusion is the reduction of blood flow to all parts of the brain. The reduction could be to a particular part of the brain depending on the cause. It is most commonly due to heart failure from cardiac arrest or arrhythmias, or from reduced cardiac output as a result of myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, pericardial effusion, or bleeding. Hypoxemia (low blood oxygen content) may precipitate the hypoperfusion. Because the reduction in blood flow is global, all parts of the brain may be affected, especially vulnerable "watershed" areas—border zone regions supplied by the major cerebral arteries. A watershed stroke refers to the condition when the blood supply to these areas is compromised. Blood flow to these areas does not necessarily stop, but instead it may lessen to the point where brain damage can occur.
Venous thrombosis
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis leads to stroke due to locally increased venous pressure, which exceeds the pressure generated by the arteries. Infarcts are more likely to undergo hemorrhagic transformation (leaking of blood into the damaged area) than other types of ischemic stroke.
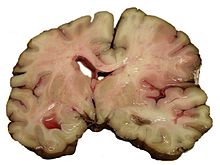
Intracerebral hemorrhage
It generally occurs in small arteries or arterioles and is commonly due to hypertension, intracranial vascular malformations (including cavernous angiomas or arteriovenous malformations), cerebral amyloid angiopathy, or infarcts into which secondary hemorrhage has occurred. Other potential causes are trauma, bleeding disorders, amyloid angiopathy, illicit drug use (e.g., amphetamines or cocaine). The hematoma enlarges until pressure from surrounding tissue limits its growth, or until it decompresses by emptying into the ventricular system, CSF or the pial surface. A third of intracerebral bleed is into the brain's ventricles. ICH has a mortality rate of 44 percent after 30 days, higher than ischemic stroke or subarachnoid hemorrhage (which technically may also be classified as a type of stroke).
Other
Other causes may include spasm of an artery. This may occur due to cocaine.
Silent stroke
A silent stroke is a stroke that does not have any outward symptoms, and people are typically unaware they have had a stroke. Despite not causing identifiable symptoms, a silent stroke still damages the brain and places the person at increased risk for both transient ischemic attack and major stroke in the future. Conversely, those who have had a major stroke are also at risk of having silent strokes. In a broad study in 1998, more than 11 million people were estimated to have experienced a stroke in the United States. Approximately 770,000 of these strokes were symptomatic and 11 million were first-ever silent MRI infarcts or hemorrhages. Silent strokes typically cause lesions which are detected via the use of neuroimaging such as MRI. Silent strokes are estimated to occur at five times the rate of symptomatic strokes. The risk of silent stroke increases with age, but may also affect younger adults and children, especially those with acute anemia.
Pathophysiology
Ischemic
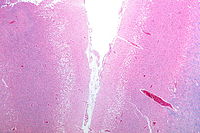

Ischemic stroke occurs because of a loss of blood supply to part of the brain, initiating the ischemic cascade. Brain tissue ceases to function if deprived of oxygen for more than 60 to 90 seconds, and after approximately three hours will suffer irreversible injury possibly leading to the death of the tissue, i.e., infarction. (This is why fibrinolytics such as alteplase are given only until three hours since the onset of the stroke.) Atherosclerosis may disrupt the blood supply by narrowing the lumen of blood vessels leading to a reduction of blood flow, by causing the formation of blood clots within the vessel, or by releasing showers of small emboli through the disintegration of atherosclerotic plaques. Embolic infarction occurs when emboli formed elsewhere in the circulatory system, typically in the heart as a consequence of atrial fibrillation, or in the carotid arteries, break off, enter the cerebral circulation, then lodge in and block brain blood vessels. Since blood vessels in the brain are now blocked, the brain becomes low in energy, and thus it resorts to using anaerobic metabolism within the region of brain tissue affected by ischemia. Anaerobic metabolism produces less adenosine triphosphate (ATP) but releases a by-product called lactic acid. Lactic acid is an irritant which could potentially destroy cells since it is an acid and disrupts the normal acid-base balance in the brain. The ischemia area is referred to as the "ischemic penumbra".
As oxygen or glucose becomes depleted in ischemic brain tissue, the production of high energy phosphate compounds such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP) fails, leading to failure of energy-dependent processes (such as ion pumping) necessary for tissue cell survival. This sets off a series of interrelated events that result in cellular injury and death. A major cause of neuronal injury is the release of the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate. The concentration of glutamate outside the cells of the nervous system is normally kept low by so-called uptake carriers, which are powered by the concentration gradients of ions (mainly Na+) across the cell membrane. However, stroke cuts off the supply of oxygen and glucose which powers the ion pumps maintaining these gradients. As a result, the transmembrane ion gradients run down, and glutamate transporters reverse their direction, releasing glutamate into the extracellular space. Glutamate acts on receptors in nerve cells (especially NMDA receptors), producing an influx of calcium which activates enzymes that digest the cells' proteins, lipids, and nuclear material. Calcium influx can also lead to the failure of mitochondria, which can lead further toward energy depletion and may trigger cell death due to programmed cell death.
Ischemia also induces production of oxygen free radicals and other reactive oxygen species. These react with and damage a number of cellular and extracellular elements. Damage to the blood vessel lining or endothelium is particularly important. In fact, many antioxidant neuroprotectants such as uric acid and NXY-059 work at the level of the endothelium and not in the brain per se. Free radicals also directly initiate elements of the programmed cell death cascade by means of redox signaling.
These processes are the same for any type of ischemic tissue and are referred to collectively as the ischemic cascade. However, brain tissue is especially vulnerable to ischemia since it has little respiratory reserve and is completely dependent on aerobic metabolism, unlike most other organs.
In addition to damaging effects on brain cells, ischemia and infarction can result in loss of structural integrity of brain tissue and blood vessels, partly through the release of matrix metalloproteases, which are zinc- and calcium-dependent enzymes that break down collagen, hyaluronic acid, and other elements of connective tissue. Other proteases also contribute to this process. The loss of vascular structural integrity results in a breakdown of the protective blood brain barrier that contributes to cerebral edema, which can cause secondary progression of the brain injury.
Hemorrhagic
Hemorrhagic strokes are classified based on their underlying pathology. Some causes of hemorrhagic stroke are hypertensive hemorrhage, ruptured aneurysm, ruptured AV fistula, transformation of prior ischemic infarction, and drug-induced bleeding. They result in tissue injury by causing compression of tissue from an expanding hematoma or hematomas. In addition, the pressure may lead to a loss of blood supply to affected tissue with resulting infarction, and the blood released by brain hemorrhage appears to have direct toxic effects on brain tissue and vasculature. Inflammation contributes to the secondary brain injury after hemorrhage.
Diagnosis

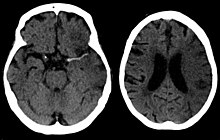
Stroke is diagnosed through several techniques: a neurological examination (such as the NIHSS), CT scans (most often without contrast enhancements) or MRI scans, Doppler ultrasound, and arteriography. The diagnosis of stroke itself is clinical, with assistance from the imaging techniques. Imaging techniques also assist in determining the subtypes and cause of stroke. There is yet no commonly used blood test for the stroke diagnosis itself, though blood tests may be of help in finding out the likely cause of stroke.
Physical examination
A physical examination, including taking a medical history of the symptoms and a neurological status, helps giving an evaluation of the location and severity of a stroke. It can give a standard score on e.g., the NIH stroke scale.
Imaging
For diagnosing ischemic (blockage) stroke in the emergency setting:
- CT scans (without contrast enhancements)
- sensitivity= 16% (less than 10% within first 3 hours of symptom onset)
- specificity= 96%
- MRI scan
- sensitivity= 83%
- specificity= 98%
For diagnosing hemorrhagic stroke in the emergency setting:
- CT scans (without contrast enhancements)
- sensitivity= 89%
- specificity= 100%
- MRI scan
- sensitivity= 81%
- specificity= 100%
For detecting chronic hemorrhages, MRI scan is more sensitive.
For the assessment of stable stroke, nuclear medicine scans SPECT and PET/CT may be helpful. SPECT documents cerebral blood flow and PET with FDG isotope the metabolic activity of the neurons.
CT scans may not detect an ischemic stroke, especially if it is small, of recent onset, or in the brainstem or cerebellum areas. A CT scan is more to rule out certain stroke mimics and detect bleeding.
Underlying cause
When a stroke has been diagnosed, various other studies may be performed to determine the underlying cause. With the current treatment and diagnosis options available, it is of particular importance to determine whether there is a peripheral source of emboli. Test selection may vary since the cause of stroke varies with age, comorbidity and the clinical presentation. The following are commonly used techniques:
- an ultrasound/doppler study of the carotid arteries (to detect carotid stenosis) or dissection of the precerebral arteries;
- an electrocardiogram (ECG) and echocardiogram (to identify arrhythmias and resultant clots in the heart which may spread to the brain vessels through the bloodstream);
- a Holter monitor study to identify intermittent abnormal heart rhythms;
- an angiogram of the cerebral vasculature (if a bleed is thought to have originated from an aneurysm or arteriovenous malformation);
- blood tests to determine if blood cholesterol is high, if there is an abnormal tendency to bleed, and if some rarer processes such as homocystinuria might be involved.
For hemorrhagic strokes, a CT or MRI scan with intravascular contrast may be able to identify abnormalities in the brain arteries (such as aneurysms) or other sources of bleeding, and structural MRI if this shows no cause. If this too does not identify an underlying reason for the bleeding, invasive cerebral angiography could be performed but this requires access to the bloodstream with an intravascular catheter and can cause further strokes as well as complications at the insertion site and this investigation is therefore reserved for specific situations. If there are symptoms suggesting that the hemorrhage might have occurred as a result of venous thrombosis, CT or MRI venography can be used to examine the cerebral veins.
Misdiagnosis
Among people with ischemic strokes, misdiagnosis occurs 2 to 26% of the time. A "stroke chameleon" (SC) is stroke which is diagnosed as something else.
People not having a stroke may also be misdiagnosed as a stroke. Giving thrombolytics (clot-busting) in such cases causes intracerebral bleeding 1 to 2% of the time, which is less than that of people with strokes. This unnecessary treatment adds to health care costs. Even so, the AHA/ASA guidelines state that starting intravenous tPA in possible mimics is preferred to delaying treatment for additional testing.
Women, African-Americans, Hispanic-Americans, Asian and Pacific Islanders are more often misdiagnosed for a condition other than stroke when in fact having a stroke. In addition, adults under 44 years-of-age are seven times more likely to have a stroke missed than are adults over 75 years-of-age. This is especially the case for younger people with posterior circulation infarcts. Some medical centers have used hyperacute MRI in experimental studies for persons initially thought to have a low likelihood of stroke. And in some of these persons, strokes have been found which were then treated with thrombolytic medication.
Prevention
Given the disease burden of strokes, prevention is an important public health concern. Primary prevention is less effective than secondary prevention (as judged by the number needed to treat to prevent one stroke per year). Recent guidelines detail the evidence for primary prevention in stroke. In those who are otherwise healthy, aspirin does not appear beneficial and thus is not recommended. In people who have had a myocardial infarction or those with a high cardiovascular risk, it provides some protection against a first stroke. In those who have previously had a stroke, treatment with medications such as aspirin, clopidogrel, and dipyridamole may be beneficial. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends against screening for carotid artery stenosis in those without symptoms.
Risk factors
The most important modifiable risk factors for stroke are high blood pressure and atrial fibrillation although the size of the effect is small with 833 people have to be treated for 1 year to prevent one stroke. Other modifiable risk factors include high blood cholesterol levels, diabetes mellitus, end-stage kidney disease, cigarette smoking (active and passive), heavy alcohol use, drug use, lack of physical activity, obesity, processed red meat consumption, and unhealthy diet. Smoking just one cigarette per day increases the risk more than 30%. Alcohol use could predispose to ischemic stroke, as well as intracerebral and subarachnoid hemorrhage via multiple mechanisms (for example, via hypertension, atrial fibrillation, rebound thrombocytosis and platelet aggregation and clotting disturbances). Drugs, most commonly amphetamines and cocaine, can induce stroke through damage to the blood vessels in the brain and acute hypertension. Migraine with aura doubles a person's risk for ischemic stroke. Untreated, celiac disease regardless of the presence of symptoms can be an underlying cause of stroke, both in children and adults.
High levels of physical activity reduce the risk of stroke by about 26%. There is a lack of high quality studies looking at promotional efforts to improve lifestyle factors. Nonetheless, given the large body of circumstantial evidence, best medical management for stroke includes advice on diet, exercise, smoking and alcohol use. Medication is the most common method of stroke prevention; carotid endarterectomy can be a useful surgical method of preventing stroke.
Blood pressure
High blood pressure accounts for 35–50% of stroke risk. Blood pressure reduction of 10 mmHg systolic or 5 mmHg diastolic reduces the risk of stroke by ~40%. Lowering blood pressure has been conclusively shown to prevent both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes. It is equally important in secondary prevention. Even people older than 80 years and those with isolated systolic hypertension benefit from antihypertensive therapy. The available evidence does not show large differences in stroke prevention between antihypertensive drugs—therefore, other factors such as protection against other forms of cardiovascular disease and cost should be considered. The routine use of beta-blockers following a stroke or TIA has not been shown to result in benefits.
Blood lipids
High cholesterol levels have been inconsistently associated with (ischemic) stroke. Statins have been shown to reduce the risk of stroke by about 15%. Since earlier meta-analyses of other lipid-lowering drugs did not show a decreased risk, statins might exert their effect through mechanisms other than their lipid-lowering effects.
Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus increases the risk of stroke by 2 to 3 times. While intensive blood sugar control has been shown to reduce small blood vessel complications such as kidney damage and damage to the retina of the eye it has not been shown to reduce large blood vessel complications such as stroke.
Anticoagulation drugs
Oral anticoagulants such as warfarin have been the mainstay of stroke prevention for over 50 years. However, several studies have shown that aspirin and other antiplatelets are highly effective in secondary prevention after a stroke or transient ischemic attack. Low doses of aspirin (for example 75–150 mg) are as effective as high doses but have fewer side effects; the lowest effective dose remains unknown. Thienopyridines (clopidogrel, ticlopidine) might be slightly more effective than aspirin and have a decreased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, but are more expensive. Both aspirin and clopidogrel may be useful in the first few weeks after a minor stroke or high risk TIA. Clopidogrel has less side effects than ticlopidine. Dipyridamole can be added to aspirin therapy to provide a small additional benefit, even though headache is a common side effect. Low-dose aspirin is also effective for stroke prevention after having a myocardial infarction.
Those with atrial fibrillation have a 5% a year risk of stroke, and this risk is higher in those with valvular atrial fibrillation. Depending on the stroke risk, anticoagulation with medications such as warfarin or aspirin is useful for prevention. Except in people with atrial fibrillation, oral anticoagulants are not advised for stroke prevention—any benefit is offset by bleeding risk.
In primary prevention, however, antiplatelet drugs did not reduce the risk of ischemic stroke but increased the risk of major bleeding. Further studies are needed to investigate a possible protective effect of aspirin against ischemic stroke in women.
Surgery
Carotid endarterectomy or carotid angioplasty can be used to remove atherosclerotic narrowing of the carotid artery. There is evidence supporting this procedure in selected cases. Endarterectomy for a significant stenosis has been shown to be useful in preventing further strokes in those who have already had one. Carotid artery stenting has not been shown to be equally useful. People are selected for surgery based on age, gender, degree of stenosis, time since symptoms and the person's preferences. Surgery is most efficient when not delayed too long—the risk of recurrent stroke in a person who has a 50% or greater stenosis is up to 20% after 5 years, but endarterectomy reduces this risk to around 5%. The number of procedures needed to cure one person was 5 for early surgery (within two weeks after the initial stroke), but 125 if delayed longer than 12 weeks.
Screening for carotid artery narrowing has not been shown to be a useful test in the general population. Studies of surgical intervention for carotid artery stenosis without symptoms have shown only a small decrease in the risk of stroke. To be beneficial, the complication rate of the surgery should be kept below 4%. Even then, for 100 surgeries, 5 people will benefit by avoiding stroke, 3 will develop stroke despite surgery, 3 will develop stroke or die due to the surgery itself, and 89 will remain stroke-free but would also have done so without intervention.
Diet
Nutrition, specifically the Mediterranean-style diet, has the potential for decreasing the risk of having a stroke by more than half. It does not appear that lowering levels of homocysteine with folic acid affects the risk of stroke.
Women
A number of specific recommendations have been made for women including taking aspirin after the 11th week of pregnancy if there is a history of previous chronic high blood pressure and taking blood pressure medications during pregnancy if the blood pressure is greater than 150 mmHg systolic or greater than 100 mmHg diastolic. In those who have previously had preeclampsia other risk factors should be treated more aggressively.
Previous stroke or TIA
Keeping blood pressure below 140/90 mmHg is recommended. Anticoagulation can prevent recurrent ischemic strokes. Among people with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation, anticoagulation can reduce stroke by 60% while antiplatelet agents can reduce stroke by 20%. However, a recent meta-analysis suggests harm from anticoagulation started early after an embolic stroke. Stroke prevention treatment for atrial fibrillation is determined according to the CHA2DS2–VASc score. The most widely used anticoagulant to prevent thromboembolic stroke in people with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation is the oral agent warfarin while a number of newer agents including dabigatran are alternatives which do not require prothrombin time monitoring.
Anticoagulants, when used following stroke, should not be stopped for dental procedures.
If studies show carotid artery stenosis, and the person has a degree of residual function on the affected side, carotid endarterectomy (surgical removal of the stenosis) may decrease the risk of recurrence if performed rapidly after stroke.
Management
Ischemic stroke
Aspirin reduces the overall risk of recurrence by 13% with greater benefit early on. Definitive therapy within the first few hours is aimed at removing the blockage by breaking the clot down (thrombolysis), or by removing it mechanically (thrombectomy