Marcus Gunn Phenomenon
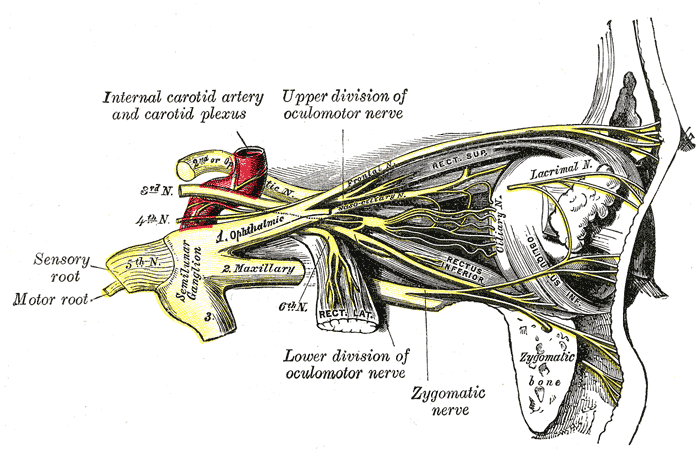
Description
The Marcus Gunn phenomenon consists of unilateral congenital ptosis and rapid exaggerated elevation of the ptotic lid on moving of the lower jaw. Although it usually persists into adult life, the phenomenon is seen in its most marked forms in infancy when the rapid spasmodic movements of the lid are apparent during sucking and thus are noted soon after birth (Doco-Fenzy et al., 2006).
InheritanceFalls et al. (1949) reported 3 cases of Marcus Gunn phenomenon in 2 generations, suggesting autosomal dominant inheritance.
Kirkham (1969) described brother and sister with unilateral Marcus Gunn phenomenon.
CytogeneticsDoco-Fenzy et al. (2006) reported a girl with Marcus Gunn phenomenon and multiple other congenital anomalies associated with a pure de novo direct duplication of chromosome 12q: dup(12)(q24.1-q24.2). Other features included facial dysmorphism, short neck, hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, and cardiac malformations.