Plummer-Vinson Syndrome
Plummer-Vinson or Paterson-Kelly syndrome presents as a classical triad of dysphagia, iron-deficiency anemia and esophageal webs.
Epidemiology
Exact data about the epidemiology of the syndrome are not available; the syndrome is extremely rare.
Clinical description
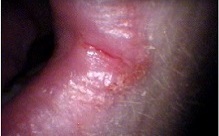
Most of the patients are white middle-aged women, in the fourth to seventh decade of life, but the syndrome has also been described in children and adolescents. The dysphagia is usually painless and intermittent or progressive over years, limited to solids and sometimes associated with weight loss. Symptoms resulting from anemia (weakness, pallor, fatigue, tachycardia) may dominate the clinical picture. Additional features are glossitis, angular cheilitis and koilonychia. Enlargement of the spleen and thyroid may also be observed. One of the most important clinical aspects of Plummer-Vinson syndrome is the association with upper alimentary tract cancers.
Etiology
The etiopathogenesis of Plummer-Vinson syndrome is unknown. The most important possible etiological factor is iron deficiency. Other possible factors include malnutrition, genetic predisposition or autoimmune processes.
Management and treatment
Plummer-Vinson syndrome can be treated effectively with iron supplementation and mechanical dilation. In case of significant obstruction of the esophageal lumen by esophageal web and persistent dysphagia despite iron supplementation, rupture and dilation of the web are necessary. Since Plummer-Vinson syndrome is associated with an increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the pharynx and the esophagus, the patients should be followed closely.