Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis
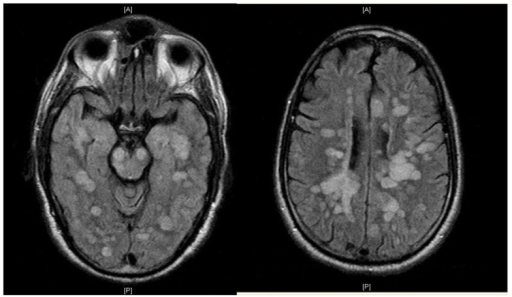
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM) is a neurological condition characterized by a brief but intense attack of inflammation in the brain and spinal cord. This may lead to damage of the layer of insulation around the nerves (myelin) within affected areas. ADEM often follows viral infection, or less often, vaccinations for measles, mumps, or rubella (MMR). Symptoms usually appear rapidly, beginning with fever, fatigue, headache, nausea and vomiting. Treatment for ADEM is targeted at suppressing inflammation in the brain using anti-inflammatory drugs. Most people begin to recover within days, with total or near-total recovery within a few months. Some people may have lifelong neurological impairments, and very rarely, severe cases can be fatal.