Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APML, APL) is a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a cancer of the white blood cells. In APL, there is an abnormal accumulation of immature granulocytes called promyelocytes. The disease is characterized by a chromosomal translocation involving the retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARα or RARA) gene and is distinguished from other forms of AML by its responsiveness to all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA; also known as tretinoin) therapy. Acute promyelocytic leukemia was first characterized in 1957 by French and Norwegian physicians as a hyperacute fatal illness, with a median survival time of less than a week. Today, prognoses have drastically improved; 10-year survival rates are estimated to be approximately 80-90% according to one study.
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms tend to be similar to AML in general with the following being possible symptoms:
- Anemia
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Chills
- Depression
- Difficulty breathing (dyspnea)
- Low platelets (thrombocytopenia) leading to easy bleeding
- Fever
- Infection as a result of low neutrophils (neutropenia)
- Elevated white blood cells (leukocytosis)
- Coagulopathy (including DIC)
- Bicytopenia
Easy bleeding from low platelets may include:
- Bruising (ecchymosis)
- Gingival bleeding
- Nose bleeds (epistaxis)
- Increased menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia)
Pathogenesis
Acute promyelocytic leukemia is characterized by a chromosomal translocation involving the retinoic acid receptor-alpha gene on chromosome 17 (RARA). In 95% of cases of APL, retinoic acid receptor-alpha (RARA) gene on chromosome 17 is involved in a reciprocal translocation with the promyelocytic leukemia gene (PML) on chromosome 15, a translocation denoted as t(15;17)(q24;q21). The RAR receptor is dependent on retinoic acid for regulation of transcription.
Eight other rare gene rearrangements have been described in APL fusing RARA to promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger (PLZF also known as ZBTB16), nucleophosmin (NPM1), nuclear matrix associated (NUMA1), signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b (STAT5B), protein kinase A regulatory subunit 1α (PRKAR1A), factor interacting with PAPOLA and CPSF1 (FIP1L1), BCL6 corepressor (BCOR) or oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide-binding fold containing 2A (OBFC2A also known as NABP1) genes. Some of these rearrangements are ATRA-sensitive or have unknown sensitivity to ATRA because they are so rare; STAT5B/RARA and PLZF/RARA are known to be resistant to ATRA.
The fusion of PML and RARA results in expression of a hybrid protein with altered functions. This fusion protein binds with enhanced affinity to sites on the cell's DNA, blocking transcription and differentiation of granulocytes. It does so by enhancing interaction of nuclear co-repressor (NCOR) molecule and histone deacetylase (HDAC). Although the chromosomal translocation involving RARA is believed to be the initiating event, additional mutations are required for the development of leukemia.
RAR-α/PLZF gene fusion produces a subtype of APL that is unresponsive to tretinoin therapy and less responsive to standard anthracycline chemotherapy hence leading to poorer long-term outcomes in this subset of patients.
Diagnosis
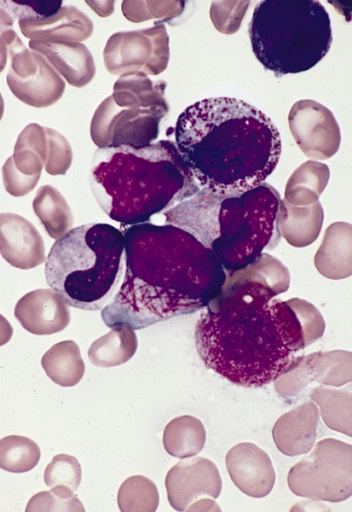
Acute promyelocytic leukemia can be distinguished from other types of AML based on microscopic examination of the blood film or a bone marrow aspirate or biopsy as well as finding the characteristic rearrangement. The presence of promyelocytes containing multiple Auer rods (termed faggot cells) on the peripheral blood smear is highly suggestive of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Definitive diagnosis requires testing for the PML/RARA fusion gene. This may be done by polymerase chain reaction (PCR), fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), or conventional cytogenetics of peripheral blood or bone marrow. This mutation involves a translocation of the long arm of chromosomes 15 and 17. On rare occasions, a cryptic translocation may occur which cannot be detected by cytogenetic testing; on these occasions PCR testing is essential to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
Initial treatment



APL is unique among leukemias due to its sensitivity to all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA; tretinoin), the acid form of vitamin A. Treatment with ATRA dissociates the NCOR-HDACL complex from RAR and allows DNA transcription and differentiation of the immature leukemic promyelocytes into mature granulocytes by targeting the oncogenic transcription factor and its aberrant action. Unlike other chemotherapies, ATRA does not directly kill the malignant cells. ATRA induces the terminal differentiation of the leukemic promyelocytes, after which these differentiated malignant cells undergo spontaneous apoptosis on their own. ATRA alone is capable of inducing remission but it is short-lived in the absence of concurrent "traditional" chemotherapy. As of 2013 the standard of treatment for concurrent chemotherapy has become arsenic trioxide, which combined with ATRA is referred to ATRA-ATO; before 2013 the standard of treatment was anthracycline (e.g. daunorubicin, doxorubicin, idarubicin or mitoxantrone)-based chemotherapy. Both chemotherapies result in a clinical remission in approximately 90% of patients with arsenic trioxide having a more favorable side effect profile.
ATRA therapy is associated with the unique side effect of differentiation syndrome. This is associated with the development of dyspnea, fever, weight gain, peripheral edema and is treated with dexamethasone. The etiology of retinoic acid syndrome has been attributed to capillary leak syndrome from cytokine release from the differentiating promyelocytes.
The monoclonal antibody, gemtuzumab ozogamicin, has been used successfully as a treatment for APL, although it has been withdrawn from the US market due to concerns regarding potential toxicity of the drug and it is not currently marketed in Australia, Canada or the UK. Given in conjunction with ATRA, it produces a response in around 84% of patients with APL, which is comparable to the rate seen in patients treated with ATRA and anthracycline-based therapy. It produces less cardiotoxicity than anthracycline-based treatments and hence may be preferable in these patients.
Maintenance therapy
After stable remission was induced, the standard of care previously was to undergo 2 years of maintenance chemotherapy with methotrexate, mercaptopurine and ATRA. A significant portion of patients relapsed without consolidation therapy. In the 2000 European APL study, the 2-year relapse rate for those that did not receive consolidation chemotherapy (ATRA not included) therapy was 27% compared to 11% in those that did receive consolidation therapy (p<0.01). Likewise in the 2000 US APL study, the survival rates in those receiving ATRA maintenance was 61% compared to just 36% without ATRA maintenance.
However, recent research on consolidation therapy following ATRA-ATO, which became the standard treatment in 2013, has found that maintenance therapy in low-risk patients following this therapy may be unnecessary, although this is controversial.
Relapsed or refractory disease
Arsenic trioxide (As2O3) is currently being evaluated for treatment of relapsed / refractory disease. Remission with arsenic trioxide has been reported. Studies have shown arsenic reorganizes nuclear bodies and degrades the mutant PML-RAR fusion protein. Arsenic also increases caspase activity which then induces apoptosis. It does reduce the relapse rate for high risk patients. In Japan a synthetic retinoid, tamibarotene, is licensed for use as a treatment for ATRA-resistant APL.
Investigational agents
Some evidence supports the potential therapeutic utility of histone deacetylase inhibitors such as valproic acid or vorinostat in treating APL. According to one study, a cinnamon extract has effect on the apoptotic process in acute myeloid leukemia HL-60 cells.
Prognosis
Prognosis is generally good relative to other leukemias. Because of the acuteness of onset compared to other leukemias, early death is comparatively more common. If untreated, it has median survival of less than a month. It has been transformed from a highly fatal disease to a highly curable one. The cause of early death is most commonly severe bleeding, often intracranial hemorrhage. Early death from hemorrhage occurs in 5–10% of patients in countries with adequate access to healthcare and 20–30% of patients in less developed countries. Risk factors for early death due to hemorrhage include delayed diagnosis, late treatment initiation, and high white blood cell count on admission. Despite advances in treatment, early death rates have remained relatively constant, as described by several groups including Scott McClellan, Bruno Medeiros, and Ash Alizadeh at Stanford University.
Relapse rates are extremely low. Most deaths following remission are from other causes, such as second malignancies, which in one study occurred in 8% of patients. In this study, second malignancies accounted for 41% of deaths, and heart disease, 29%. Survival rates were 88% at 6.3 years and 82% at 7.9 years.
In another study, 10-year survival rate was estimated to be approximately 77%.
Epidemiology
Acute promyelocytic leukemia represents 10–12% of AML cases. The median age is approximately 30–40 years, which is considerably younger than the other subtypes of AML (70 years). Incidence is higher among individuals of Latin American or South European origin. It can also occur as a secondary malignancy in those that receive treatment with topoisomerase II inhibitors (such as the anthracyclines and etoposide) due to the carcinogenic effects of these agents, with patients with breast cancer representing the majority of such patients. Around 40% of patients with APL also have a chromosomal abnormality such as trisomy 8 or isochromosome 17 which do not appear to impact on long-term outcomes.