Heterochromia Iridum

Heterochromia is a variation in coloration. The term is most often used to describe color differences of the iris, but can also be applied to color variation of hair or skin. Heterochromia is determined by the production, delivery, and concentration of melanin (a pigment). It may be inherited, or caused by genetic mosaicism, chimerism, disease, or injury. It occurs in humans and certain breeds of domesticated animals.
Heterochromia of the eye is called heterochromia iridum or heterochromia iridis. It can be complete or sectoral. In complete heterochromia, one iris is a different color from the other. In sectoral heterochromia, part of one iris is a different color from its remainder. In central heterochromia, there is a ring around the pupil or possibly spikes of different colors radiating from the pupil.
Though multiple causes have been posited, the scientific consensus is that a lack of genetic diversity is the primary reason behind heterochromia, at least in domestic animals. This is due to a mutation of the genes that determine melanin distribution at the 8-HTP pathway, which usually only become corrupted due to chromosomal homogeneity. Though common in some breeds of cats, dogs, cattle and horses, due to inbreeding, heterochromia is uncommon in humans, affecting fewer than 200,000 people in the United States, and is not associated with lack of genetic diversity.
The affected eye may be hyperpigmented (hyperchromic) or hypopigmented (hypochromic). In humans, an increase of melanin production in the eyes indicates hyperplasia of the iris tissues, whereas a lack of melanin indicates hypoplasia. The term is from Ancient Greek: ἕτερος, héteros 'different' and χρῶμα, chrôma 'color'.
Background - how eye color is determined
Eye color, specifically the color of the irises, is determined primarily by the concentration and distribution of melanin. Although the processes determining eye color are not fully understood, it is known that inherited eye color is determined by multiple genes. Environmental or acquired factors can alter these inherited traits.
The color of the mammalian, including human, iris is very variable. However, there are only two pigments present, eumelanin and pheomelanin. The overall concentration of these pigments, the ratio between them, variation in the distribution of pigment in the layers of the stroma of the iris and the effects of light scattering all play a part in determining eye color.
Classification

Heterochromia is classified primarily by onset: as either genetic or acquired. Although a distinction is frequently made between heterochromia that affects an eye completely or only partially (sectoral heterochromia), it is often classified as either genetic (due to mosaicism or congenital) or acquired, with mention as to whether the affected iris or portion of the iris is darker or lighter. Most cases of heterochromia are hereditary, or caused by genetic factors such as chimerism, and are entirely benign and unconnected to any pathology, however, some are associated with certain diseases and syndromes. Sometimes one eye may change color following disease or injury.
Sectoral or partial heterochromia
In sectoral heterochromia, sometimes referred to as partial heterochromia, areas of the same iris contain two completely different colors. It is unknown how rare sectoral heterochromia is in humans.
Abnormal iris darker
- Lisch nodules – iris hamartomas seen in neurofibromatosis.
- Ocular melanosis – a condition characterized by increased pigmentation of the uveal tract, episclera, and anterior chamber angle.
- Oculodermal melanocytosis (nevus of Ota)
- Pigment dispersion syndrome – a condition characterized by loss of pigmentation from the posterior iris surface which is disseminated intraocularly and deposited on various intraocular structures, including the anterior surface of the iris.
- Sturge–Weber syndrome – a syndrome characterized by a port-wine stain nevus in the distribution of the trigeminal nerve, ipsilateral leptomeningeal angiomas with intracranial calcification and neurologic signs, and angioma of the choroid, often with secondary glaucoma.
Abnormal iris lighter
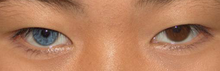
- Simple heterochromia – a rare condition characterized by the absence of other ocular or systemic problems. The lighter eye is typically regarded as the affected eye as it usually shows iris hypoplasia. It may affect an iris completely or only partially.
- Congenital Horner's syndrome – sometimes inherited, although usually acquired
- Waardenburg syndrome – a syndrome in which heterochromia is expressed as a bilateral iris hypochromia in some cases. A Japanese review of 11 children with albinism found that the condition was present. All had sectoral/partial heterochromia.
- Piebaldism – similar to Waardenburg's syndrome, a rare disorder of melanocyte development characterized by a white forelock and multiple symmetrical hypopigmented or depigmented macules.
- Hirschsprung's disease – a bowel disorder associated with heterochromia in the form of a sector hypochromia. The affected sectors have been shown to have reduced numbers of melanocytes and decreased stromal pigmentation.
- Incontinentia pigmenti
- Parry–Romberg syndrome
Acquired heterochromia

Acquired heterochromia is usually due to injury, inflammation, the use of certain eyedrops that damage the iris, or tumors.
Abnormal iris darker
- Deposition of material
- Siderosis – iron deposition within ocular tissues due to a penetrating injury and a retained iron-containing, intraocular foreign body.
- Hemosiderosis – long standing hyphema (blood in the anterior chamber) following blunt trauma to the eye may lead to iron deposition from blood products
- Certain eyedrops – prostaglandin analogues (latanoprost, isopropyl unoprostone, travoprost, and bimatoprost) are used topically to lower intraocular pressure in glaucoma patients. A concentric heterochromia has developed in some patients applying these drugs. The stroma around the iris sphincter muscle becomes darker than the peripheral stroma. A stimulation of melanin synthesis within iris melanocytes has been postulated.
- Neoplasm – Nevi and melanomatous tumors.
- Iridocorneal endothelium syndrome
- Iris ectropion syndrome
Abnormal iris lighter
- Fuchs heterochromic iridocyclitis – a condition characterized by a low grade, asymptomatic uveitis in which the iris in the affected eye becomes hypochromic and has a washed-out, somewhat moth eaten appearance. The heterochromia can be very subtle, especially in patients with lighter colored irides. It is often most easily seen in daylight. The prevalence of heterochromia associated with Fuchs has been estimated in various studies with results suggesting that there is more difficulty recognizing iris color changes in dark-eyed individuals.
- Acquired Horner's syndrome – usually acquired, as in neuroblastoma, although sometimes inherited.
- Neoplasm – Melanomas can also be very lightly pigmented, and a lighter colored iris may be a rare manifestation of metastatic disease to the eye.
- Parry–Romberg syndrome – due to tissue loss.
Heterochromia has also been observed in those with Duane syndrome.
- Chronic iritis
- Juvenile xanthogranuloma
- Leukemia and lymphoma
Central heterochromia

Central heterochromia is an eye condition where there are two colors in the same iris; the central (pupillary) zone of the iris is a different color than the mid-peripheral (ciliary) zone, with the true iris color being the outer color.
Central heterochromia appears to be prevalent in irises containing low amounts of melanin.
History
Heterochromia of the eye was described by Aristotle, who termed it heteroglaucos. Notable historical figures thought to have heterochromia include Anastasius the First, dubbed dikoros (Greek for 'having two irises'), and Alexander the Great, as noted by the historian Plutarch.
In other animals
Although infrequently seen in humans, complete heterochromia is more frequently observed in other species, where it almost always involves one blue eye. The blue eye occurs within a white spot, where melanin is absent from the skin and hair (see Leucism). These species include the cat, particularly breeds such as Turkish Van, Turkish Angora, Khao Manee and (rarely) Japanese Bobtail. These so-called odd-eyed cats are white, or mostly white, with one normal eye (copper, orange, yellow, green), and one blue eye. Among dogs, complete heterochromia is seen often in the Siberian Husky and few other breeds, usually Australian Shepherd and Catahoula Leopard Dog and rarely in Shih Tzu. Horses with complete heterochromia have one brown and one white, gray, or blue eye—complete heterochromia is more common in horses with pinto coloring. Complete heterochromia occurs also in cattle and even water buffalo. It can also be seen in ferrets with Waardenburg syndrome, although it can be very hard to tell at times as the eye color is often a midnight blue.
Sectoral heterochromia, usually sectoral hypochromia, is often seen in dogs, specifically in breeds with merle coats. These breeds include the Australian Shepherd, Border Collie, Collie, Shetland Sheepdog, Welsh Corgi, Pyrenean Shepherd, Mudi, Beauceron, Catahoula Cur, Dunker, Great Dane, Dachshund and Chihuahua. It also occurs in certain breeds that do not carry the merle trait, such as the Siberian Husky and rarely, Shih Tzu. There are examples of cat breeds that have the condition such as Van cat.
Gallery

Complete heterochromia in a child.

Actress Alice Eve has heterochromia: her left eye is blue and right eye is green.

Former cricketer Shane Warne has complete heterochromia.

Washington Nationals pitcher Max Scherzer has complete heterochromia.

A young adult human exhibiting sectoral heterochromia in the form of an orange segment in blue eye.

Actress Kate Bosworth has sectoral heterochromia.

Actor Dominic Sherwood has sectoral heterochromia.

Actor Henry Cavill has sectoral heterochromia.

Human example of central heterochromia showing an orange to blue iris.
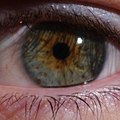
Human example of central heterochromia in green eye with speckled brown pigment.

Complete heterochromia in a female sled dog

Complete heterochromia in a Siberian Husky: one eye blue, one eye brown.

Sectoral hypochromia in a blue merle Border Collie.

Sectoral heterochromia in a mutt dog.

A cat with complete heterochromia.

Central heterochromia in a bicolor tabby cat.
Trivia
- English singer David Bowie exhibited anisocoria (one pupil was larger than the other), owing to a teenage injury. This was sometimes mistaken for heterochromia iridum.
See also
- Brushfield spots
- Coloboma
- Erythrism
- Leucism
- List of systemic diseases with ocular manifestations
- Piebaldism
- List of people with heterochromia















