Wilson Disease
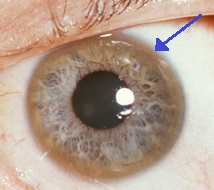
Wilson disease is a rare inherited disorder that is characterized by the accumulation of copper in the body. Because high levels of copper are toxic to tissues and organs, this buildup can lead to damage of the liver, brain and eyes. Signs and symptoms of Wilson disease include chronic liver disease, central nervous system abnormalities, and psychiatric (mental health-related) disturbances. It is caused by a mutation of the ATP7B gene and is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. Although there is no cure for Wilson disease, therapies exist that aim to reduce or control the amount of copper that accumulates in the body.