Sinus Tachycardia

Sinus tachycardia (also colloquially known as sinus tach or sinus tachy) is an elevated sinus rhythm characterized by an increase in the rate of electrical impulses arising from the sinoatrial node. In adults, sinus tachycardia is defined as a heart rate greater than 100 beats/min (bpm). The normal resting heart rate is 60–100 bpm in an average male adult and 60-90 bpm in an average female adult. Normal heart rate varies with age, from infants having faster heart rates (110-150 bpm) and the elderly having slower heart rates. Sinus tachycardia is a normal response to physical exercise, when the heart rate increases to meet the body's higher demand for energy and oxygen, but sinus tachycardia can also indicate a health problem. Thus, sinus tachycardia is a medical finding that can be either physiological or pathological.
Signs and symptoms
Tachycardia is often asymptomatic. It is often a resulting symptom of a primary disease state and can be an indication of the severity of a disease. If the heart rate is too high, cardiac output may fall due to the markedly reduced ventricular filling time. Rapid rates, though they may be compensating for ischemia elsewhere, increase myocardial oxygen demand and reduce coronary blood flow, thus precipitating an ischemic heart or valvular disease. Sinus tachycardia accompanying a myocardial infarction may be indicative of cardiogenic shock.
Cause
Sinus tachycardia is usually a response to physiological stress, such as exercise, or an increased sympathetic tone with increased catecholamine release, such as stress, fright, flight, and anger. Other causes include:
- Pain
- Fever
- Anxiety
- Dehydration
- Malignant hyperthermia
- Hypovolemia with hypotension and shock
- Anemia
- Heart failure
- Hyperthyroidism
- Mercury poisoning
- Kawasaki disease
- Pheochromocytoma
- Sepsis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Acute coronary ischemia and myocardial infarction
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Hypoxia
- Intake of stimulants such as caffeine, theophylline, nicotine, cocaine, or amphetamines
- Hyperdynamic circulation
- Electric shock
- Drug withdrawal
- Porphyria
- Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy
- Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome
- Mitral Valve Prolapse
Diagnosis
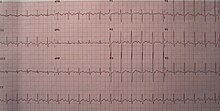
Sinus tachycardia is usually apparent on an ECG, but if the heart rate is above 140 bpm the P wave may be difficult to distinguish from the previous T wave and one may confuse it with a paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia or atrial flutter with a 2:1 block. Ways to distinguish the three are:
- Vagal maneuvers (such as carotid sinus massage or Valsalva's maneuver) to slow the rate and identification of P waves
- administer AV blockers (e.g., adenosine, verapamil) to identify atrial flutter with 2:1 block
Heart sounds should also be listened to.
ECG characteristics
- Rate: Greater than or equal to 100.
- Rhythm: Regular.
- P waves: Upright, in leads I, II and aVL, and negative in lead aVR;
- each P wave is followed by a QRS and T waves
Inappropriate sinus tachycardia
In inappropriate sinus tachycardia (also known as chronic nonparoxysmal sinus tachycardia), patients have an elevated resting heart rate and/or exaggerated heart rate in response to exercise. These patients have no apparent heart disease or other causes of sinus tachycardia. IST is thought to be due to abnormal autonomic control.
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome
Usually, in women with no heart problems, this syndrome is characterized by normal resting heart rate but exaggerated postural sinus tachycardia with or without orthostatic hypotension.
Treatment
Treatment for physiologic sinus tachycardia involves treating the underlying causes of the tachycardia response. Beta blockers may be used to decrease tachycardia in patients with certain conditions, such as ischemic heart disease and rate-related angina. In patients with inappropriate sinus tachycardia, careful titration of beta-blockers, salt loading, and hydration typically reduce symptoms. Patients who are unresponsive to such treatment can undergo catheter ablation to potentially repair the sinus node.
Acute myocardial infarction
Sinus tachycardia can present in more than a third of the patients with AMI but this usually decreases over time. Patients with sustained sinus tachycardia reflects a larger infarct that are more anterior with prominent left ventricular dysfunction, associated with high mortality and morbidity. Tachycardia in the presence of AMI can reduce coronary blood flow and increase myocardial oxygen demand, aggravating the situation. Beta-blockers can be used to slow the rate, but most patients are usually already treated with beta-blockers as a routine regimen for AMI.
IST and POTS
Beta blockers are useful if the cause is sympathetic overactivity. If the cause is due to decreased vagal activity, it is usually hard to treat and one may consider radiofrequency catheter ablation.
Notes
- ^ In this context, the adjectives physiological and pathological are opposites.