Bowel Obstruction

Bowel obstruction, also known as intestinal obstruction, is a mechanical or functional obstruction of the intestines which prevents the normal movement of the products of digestion. Either the small bowel or large bowel may be affected. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, vomiting, bloating and not passing gas. Mechanical obstruction is the cause of about 5 to 15% of cases of severe abdominal pain of sudden onset requiring admission to hospital.
Causes of bowel obstruction include adhesions, hernias, volvulus, endometriosis, inflammatory bowel disease, appendicitis, tumors, diverticulitis, ischemic bowel, tuberculosis and intussusception. Small bowel obstructions are most often due to adhesions and hernias while large bowel obstructions are most often due to tumors and volvulus. The diagnosis may be made on plain X-rays; however, CT scan is more accurate. Ultrasound or MRI may help in the diagnosis of children or pregnant women.
The condition may be treated conservatively or with surgery. Typically intravenous fluids are given, a tube is placed through the nose into the stomach to decompress the intestines, and pain medications are given. Antibiotics are often given. In small bowel obstruction about 25% require surgery. Complications may include sepsis, bowel ischemia and bowel perforation.
About 3.2 million cases of bowel obstruction occurred in 2015 which resulted in 264,000 deaths. Both sexes are equally affected and the condition can occur at any age. Bowel obstruction has been documented throughout history, with cases detailed in the Ebers Papyrus of 1550 BC and by Hippocrates.
Signs and symptoms
Depending on the level of obstruction, bowel obstruction can present with abdominal pain, swollen abdomen, abdominal distension, and constipation. Bowel obstruction may be complicated by dehydration and electrolyte abnormalities due to vomiting; respiratory compromise from pressure on the diaphragm by a distended abdomen, or aspiration of vomitus; bowel ischemia or perforation from prolonged distension or pressure from a foreign body.
In small bowel obstruction, the pain tends to be colicky (cramping and intermittent) in nature, with spasms lasting a few minutes. The pain tends to be central and mid-abdominal. Vomiting may occur before constipation.
In large bowel obstruction, the pain is felt lower in the abdomen and the spasms last longer. Constipation occurs earlier and vomiting may be less prominent. Proximal obstruction of the large bowel may present as small bowel obstruction.
Causes
Small bowel obstruction

Causes of small bowel obstruction include:
- Adhesions from previous abdominal surgery (most common cause)
- Barbed sutures
- Pseudoobstruction
- Hernias containing bowel
- Crohn's disease causing adhesions or inflammatory strictures
- Neoplasms, benign or malignant
- Intussusception
- Volvulus
- Superior mesenteric artery syndrome, a compression of the duodenum by the superior mesenteric artery and the abdominal aorta
- Ischemic strictures
- Foreign bodies (e.g. gallstones in gallstone ileus, swallowed objects such as expandable water toys)
- Intestinal atresia
After abdominal surgery, the incidence of small bowel obstruction from any cause is 9%. In those where the cause of the obstruction was clear, adhesions are the single most common cause (more than half).
Large bowel obstruction

Causes of large bowel obstruction include:
- Neoplasms / cancer
- Diverticulitis / Diverticulosis
- Hernias
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Colonic volvulus (sigmoid, caecal, transverse colon)
- Adhesions
- Constipation
- Fecal impaction
- Fecaloma
- Colon atresia
- Intestinal pseudoobstruction
- Endometriosis
- Narcotic induced (especially with the large doses given to cancer or palliative care patients)
Outlet obstruction
Outlet obstruction is a sub-type of large bowel obstruction and refers to conditions affecting the anorectal region that obstruct defecation, specifically conditions of the pelvic floor and anal sphincters. Outlet obstruction can be classified into four groups.
- Functional outlet obstruction
- Inefficient inhibition of the internal anal sphincter
- Short-segment Hirschsprung's disease
- Chagas disease
- Hereditary internal sphincter myopathy
- Inefficient relaxation of the striated pelvic floor muscles
- Anismus (pelvic floor dyssynergia)
- Multiple sclerosis
- Spinal cord lesions
- Inefficient inhibition of the internal anal sphincter
- Mechanical outlet obstruction
- Internal intussusception
- Enterocele
- Dissipation of force vector
- rectocele
- Descending perineum
- Rectal prolapse
- Impaired rectal sensitivity
- Megarectum
- Rectal hyposensitivity
Diagnosis

| <2.5 cm | Non-dilated |
| 2.5-2.9 cm | Mildly dilated |
| 3-4 cm | Moderately dilated |
| >4 cm | Severely dilated |

The main diagnostic tools are blood tests, X-rays of the abdomen, CT scanning, and ultrasound. If a mass is identified, biopsy may determine the nature of the mass.
Radiological signs of bowel obstruction include bowel distension and the presence of multiple (more than six) gas-fluid levels on supine and erect abdominal radiographs. Ultrasounds may be as useful as CT scanning to make the diagnosis.
Contrast enema or small bowel series or CT scan can be used to define the level of obstruction, whether the obstruction is partial or complete, and to help define the cause of the obstruction. The appearance of water-soluble contrast in the cecum on an abdominal radiograph within 24 hours of it being given by mouth predicts resolution of an adhesive small bowel obstruction with sensitivity of 97% and specificity of 96%.
Colonoscopy, small bowel investigation with ingested camera or push endoscopy, and laparoscopy are other diagnostic options.
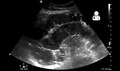 Play media
Play mediaSmall bowel obstruction on ultrasound.
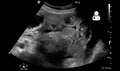 Play media
Play mediaSmall bowel obstruction on ultrasound.

Small bowel obstruction on ultrasound.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnoses of bowel obstruction include:
- Ileus
- Pseudo-obstruction or Ogilvie's syndrome
- Intra-abdominal sepsis
- Pneumonia or other systemic illness.
Treatment
Some causes of bowel obstruction may resolve spontaneously; many require operative treatment. In adults, frequently the surgical intervention and the treatment of the causative lesion are required. In malignant large bowel obstruction, endoscopically placed self-expanding metal stents may be used to temporarily relieve the obstruction as a bridge to surgery, or as palliation. Diagnosis of the type of bowel obstruction is normally conducted through initial plain radiograph of the abdomen, luminal contrast studies, computed tomography scan, or ultrasonography prior to determining the best type of treatment.
Further research is needed to find out if parenteral nutrition is of benefit to people with an inoperable blockage of the bowel caused by advanced cancer.
Small bowel obstruction
In the management of small bowel obstructions, a commonly quoted surgical aphorism is: "never let the sun rise or set on small-bowel obstruction" because about 5.5% of small bowel obstructions are ultimately fatal if treatment is delayed. Improvements in radiological imaging of small bowel obstructions allow for confident distinction between simple obstructions, that can be treated conservatively, and obstructions that are surgical emergencies (volvulus, closed-loop obstructions, ischemic bowel, incarcerated hernias, etc.).
A small flexible tube (nasogastric tube) may be inserted through the nose into the stomach to help decompress the dilated bowel. This tube is uncomfortable but relieves the abdominal cramps, distention, and vomiting. Intravenous therapy is utilized and the urine output is monitored with a catheter in the bladder.
Most people with SBO are initially managed conservatively because in many cases, the bowel will open up. Some adhesions loosen up and the obstruction resolves. The patient is examined several times a day, and X-ray images are made to ensure he or she is not getting clinically worse.
Conservative treatment involves insertion of a nasogastric tube, correction of dehydration and electrolyte abnormalities. Opioid pain relievers may be used for patients with severe pain. Antiemetics may be administered if the patient is vomiting. Adhesive obstructions often settle without surgery. If the obstruction is complete a surgery is usually required.
Most patients improve with conservative care in 2–5 days. When the obstruction is cancer, surgery is the only treatment. Those with bowel resection or lysis of adhesions usually stay in the hospital a few more days until they can eat and walk.
Small bowel obstruction caused by Crohn's disease, peritoneal carcinomatosis, sclerosing peritonitis, radiation enteritis, and postpartum bowel obstruction are typically treated conservatively, i.e. without surgery.
Children
Fetal and neonatal bowel obstructions are often caused by an intestinal atresia, where there is a narrowing or absence of a part of the intestine. These atresias are often discovered before birth via an ultrasound, and treated with using laparotomy after birth. If the area affected is small, then the surgeon may be able to remove the damaged portion and join the intestine back together. In instances where the narrowing is longer, or the area is damaged and cannot be used for a period of time, a temporary stoma may be placed.
Prognosis
The prognosis for non-ischemic cases of SBO is good with mortality rates of 3–5%, while prognosis for SBO with ischemia is fair with mortality rates as high as 30%.
Cases of SBO related to cancer are more complicated and require additional intervention to address the malignancy, recurrence, and metastasis, and thus are associated with poorer prognosis.
All cases of abdominal surgical intervention are associated with increased risk of future small-bowel obstructions. Statistics from U.S. healthcare report 18.1% re-admittance rate within 30 days for patients who undergo SBO surgery. More than 90% of patients also form adhesions after major abdominal surgery. Common consequences of these adhesions include small-bowel obstruction, chronic abdominal pain, pelvic pain, and infertility.



