-
Acromegaly
Orphanet
Assessment of tumor volume and extension is based on imaging studies. Echocardiography and sleep apnea testing are used to determine the clinical impact of acromegaly.GH1, AIP, IGF1, GNAS, GPR101, SST, GHR, MEN1, PTPRF, GHRH, SSTR2, SSTR5, PRL, IGFBP3, AHR, PPARG, IGF1R, POU1F1, SOCS2, PRKAR1A, SLC20A1, CDKN1B, BRAF, REN, CST3, SSTR1, AGT, MTHFR, RET, SMS, VDR, ARRB1, FGF21, GIPR, KL, TRIM21, GDNF, POMC, ESRP1, CALR, TP53, ACE, CDKN2A, TRH, TWIST1, TP73, TXN, SLPI, VEGFA, TNFSF11, TRHR, ZHX2, DGCR2, ABCB6, ZGLP1, MIR660, MIR21, ZACN, RSS, ARHGAP24, ASRGL1, EHMT1, FTO, MIB1, NDRG2, NPDC1, GPRC5C, GPRC5D, NAT10, UGT1A1, GHRL, SOST, PDLIM3, ATRNL1, RAB18, CCL2, CHEK2, UTS2, CCL27, CIB1, NAMPT, SLC5A2, GRK2, SRL, CYP11B2, GSTP1, GNAI2, GLP1R, GIP, GHRHR, GCG, FLNA, FGF2, E2F1, DPP4, DMBT1, CTSB, IGSF1, CRP, CISH, CALCA, CA1, BTF3P11, BAX, ATHS, APOE, AMH, ALPP, AGTR1, HSD11B1, INS, S100A1, OGG1, RORC, BRD2, RENBP, RAF1, PTPN4, PTPN3, PTH, AGRP, PRKACB, PLAGL1, TNFRSF11B, NRAS, EIF6, NPPB, NCAM1, MYC, MTRR, MTR, MMP2, MKI67, LPL, LGALS3, LEP, JAK2, H3P10
-
Catathrenia
Wikipedia
Find sources: "Catathrenia" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR ( March 2015 ) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message ) Catathrenia is a sleep-related breathing disorder , consisting of end-inspiratory apnea (breath holding) and expiratory groaning during sleep . ... The main characteristics are: Vocal sound: Sounds are usually a short or long vocalisation of the same letter (mainly an [a], [e], [o] sound or something in between). [6] Contrary to snoring which has only formants , catathrenia has also harmonics and show more regular and similar patterns between nights. [10] Onset of groanings: Groanings tend to begin in childhood, adolescence or early adulthood. [11] The ICSD-2 established the age of onset ranging from 5 to 36 years. [12] Consistency from night to night. ... "Sleep-related groaning: Prevalence and characteristics in a cohort of patients with suspected obstructive sleep apnea". Acta Oto-Laryngologica . 132 (1): 90–95. doi : 10.3109/00016489.2011.624119 . ... External links [ edit ] neurology.org - Catathrenia (nocturnal groaning): A new type of parasomnia European Respiratory Journal - Bringing light to the sirens of night: laryngoscopy in catathrenia during sleep Catathrenia: Parasomnia or Uncommon Feature of Sleep Disordered Breathing? ... (PDF available) [ permanent dead link ] v t e Sleep and sleep disorders Stages of sleep cycles Rapid eye movement (REM) Non-rapid eye movement Slow-wave Brain waves Alpha wave Beta wave Delta wave Gamma wave K-complex Mu rhythm PGO waves Sensorimotor rhythm Sleep spindle Theta wave Sleep disorders Dyssomnia Excessive daytime sleepiness Hypersomnia Insomnia Kleine–Levin syndrome Narcolepsy Night eating syndrome Nocturia Sleep apnea Catathrenia Central hypoventilation syndrome Obesity hypoventilation syndrome Obstructive sleep apnea Periodic breathing Sleep state misperception Circadian rhythm disorders Advanced sleep phase disorder Cyclic alternating pattern Delayed sleep phase disorder Irregular sleep–wake rhythm Jet lag Non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder Shift work sleep disorder Parasomnia Bruxism Nightmare disorder Night terror Periodic limb movement disorder Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder Sleepwalking Somniloquy Benign phenomena Dreams Exploding head syndrome Hypnic jerk Hypnagogia / Sleep onset Hypnopompic state Sleep paralysis Sleep inertia Somnolence Nocturnal clitoral tumescence Nocturnal penile tumescence Nocturnal emission Treatment Sleep diary Sleep hygiene Sleep induction Hypnosis Lullaby Somnology Polysomnography Other Sleep medicine Behavioral sleep medicine Sleep study Daily life Bed Bunk bed Daybed Four-poster bed Futon Hammock Mattress Sleeping bag Bed bug Bedding Bedroom Bedtime Bedtime story Bedtime toy Biphasic and polyphasic sleep Chronotype Dream diary Microsleep Mouth breathing Nap Nightwear Power nap Second wind Siesta Sleep and creativity Sleep and learning Sleep deprivation / Sleep debt Sleeping while on duty Sleepover Snoring
-
Sleep Disorders
Mayo_clinic
Some common types of sleep disorders include: Insomnia, in which you have difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep throughout the night. Sleep apnea, in which you experience abnormal patterns in breathing while you are asleep. There are several types of sleep apnea. Restless legs syndrome (RLS), a type of sleep movement disorder. ... Symptoms Symptoms of sleep disorders include being very sleepy during the daytime and having trouble falling asleep at night. Some people may fall asleep at inappropriate times, such as while driving.SLC6A3, CHRNA4, IL1B, POMC, HTR7, BHLHE41, CHRNB2, LRRK2, SNCA, MECP2, MAPT, RAI1, PRNP, ASXL3, ATXN2, SLC2A1, ATXN10, SATB2, GNAO1, CDKL5, PROKR2, MBD5, TFAP2B, ATXN3, USP8, HESX1, CC2D1A, GATAD2B, SLC6A5, PROP1, AIFM1, NSUN2, C12orf4, PPT1, SMC3, POU1F1, LINS1, KMT2A, NAGLU, NR4A2, SETD5, PIGC, PIGQ, NDP, ATAD3A, VPS35, PNKP, NEUROD2, HDAC8, FMN2, CRADD, FRRS1L, OTX2, FBXO7, RAD21, ATXN8OS, RSRC1, TSHB, THRB, NKX2-1, REM1, PRSS12, NIPBL, TRHR, TRIO, BSCL2, TSHR, CLIP1, RTTN, HIBCH, EZR, SMC1A, WFS1, GIGYF2, LHX3, EPM2A, THRA, TCF20, TBP, STXBP1, PIGP, SARS1, EPG5, CRBN, SEPSECS, SCN2A, NSDHL, SLC45A1, SGSH, ST3GAL3, SLC18A2, SMARCC2, SOX2, SOX3, SPR, CASK, DCPS, CHD8, MED23, KCNA1, SARDH, B3GALNT2, HGSNAT, DEAF1, CTNNB1, DBH, DNAJC13, DCTN1, DDC, SLC9A6, HDAC4, METTL23, WARS2, EIF4G1, WASHC4, EML1, SLITRK1, AIMP1, ARNT2, SIK1, CORIN, VPS13A, STAG2, ADH1C, MAN1B1, TNIK, WDR45, AGA, CISD2, LIAS, IQSEC2, SPART, ASPA, SEPTIN9, NHLRC1, WDR4, KDM5B, MFSD8, STOX1, ARX, FGFR1, GPHN, LHX4, SLC25A22, ZC3H14, ATAD1, EHMT1, HCRT, FBXO31, GABBR2, HDC, HNMT, GNS, MBOAT7, NDST1, ADNP, IDUA, TECR, CDH23, TUSC3, PGAP1, GRIK2, GBA, LMAN2L, FLII, TRAPPC9, FLT1, SNCAIP, MED25, TRIM8, GLUD2, SIN3A, GCH1, EDC3, GLRB, CLOCK, GLRA1, IL6, PER3, APOE, HLA-DQB1, CRP, SLC6A4, MTNR1B, PDSS2, BDNF, PER2, ARNTL, IGLON5, TIMELESS, COPD, MCF2L, TPTEP2-CSNK1E, HCRTR2, MT2A, COMT, TMPRSS6, CSNK1E, OPN4, FMR1, GH1, VIP, LRP2, MAOA, HRH3, ATXN1, ZC4H2, GPRC6A, GPR151, TAAR1, ACAD8, HT, HAVCR1, SLC17A5, OXER1, NALCN, MRGPRX4, MRGPRX1, CCL4L1, VN1R17P, GPR166P, PLF, NPS, SNORD116@, PTLS, CD200R1, MRGPRX3, NPDC1, LGR6, ARNTL2, PLXNA3, ACKR3, MOCOS, SIAE, SMUG1, LPAR3, SEC14L2, DBA2, PROK2, MPPE1, ASPSCR1, NLGN3, MAP3K20, TRIM47, KCNIP3, CNTNAP2, ACHE, PSIP1, EIF6, DRD4, EDNRA, ELF3, SLC29A1, ESR1, FANCC, FKBP4, FKBP5, FLG, FLNB, MTOR, GAD1, GC, GDF1, GLI2, GPR42, GRN, NR3C1, HCRTR1, HLA-DQB2, HLA-DRB5, HRAS, IDS, IFNA2, IGF1, DRD3, DRD1, DPP6, BID, ADORA1, ADRA1A, ADRA2B, AGRP, AHR, ALDH2, ARSD, AVP, AVPR1A, BBS2, BCHE, BRS3, ACE, CA1, CACNA1C, CCT, CDR1, CECR, CRH, CSE1L, CSF1R, CSF2, CSN1S1, CST3, IL17A, KCNJ11, PRSS21, LAMC2, STAC, TNF, TPI1, TPO, ACP5, UMOD, VEGFA, XPO1, PAX8, ARHGEF5, FZD4, SRPX, USO1, BTRC, ARTN, LPAR2, LGI1, KL, CCL4L2, IGSF6, NXF1, KAT5, CXCR6, CERS1, MALT1, SSTR4, CCL4, SCN5A, ABCB1, LEP, LY6E, SMCP, MEIS1, NBN, NFKB2, NHS, OAT, P2RX7, PAX6, PER1, SLC25A3, SCN1A, PLXNA2, PNN, PPARA, PRL, PSG2, PSG3, PSG5, REN, BRD2, ACSM3, SCD, TSC1
-
Excessive Daytime Sleepiness
Wikipedia
EDS can be considered as a broad condition encompassing several sleep disorders where increased sleep is a symptom, or as a symptom of another underlying disorder like narcolepsy , circadian rhythm sleep disorder , sleep apnea or idiopathic hypersomnia . Some persons with EDS, including those with hypersomnias like narcolepsy and idiopathic hypersomnia , are compelled to nap repeatedly during the day; fighting off increasingly strong urges to sleep during inappropriate times such as while driving, while at work, during a meal, or in conversations. ... Some are: insufficient quality or quantity of night time sleep; misalignments of the body's circadian pacemaker with the environment (e.g., jet lag , shift work , or other circadian rhythm sleep disorders ); another underlying sleep disorder , such as narcolepsy , sleep apnea , [2] idiopathic hypersomnia , or restless legs syndrome ; disorders such as clinical depression or atypical depression ; tumors, head trauma, anemia, kidney failure , hypothyroidism , or an injury to the central nervous system ; drug abuse; genetic predisposition; vitamin deficiency , such as biotin deficiency ; and particular classes of prescription and over-the-counter medication. ... PMID 11459741 . ^ "How to Stop Snoring" . Sleep Apnea . Archived from the original on 4 March 2016 . ... External links [ edit ] Classification D ICD - 10 : F51.1 , G47.1 ICD - 9-CM : 291.82 , 292.85 , 307.43 - 307.44 , 327.1 , 780.53 - 780.54 MeSH : D006970 External resources eMedicine : med/3129 v t e Sleep and sleep disorders Stages of sleep cycles Rapid eye movement (REM) Non-rapid eye movement Slow-wave Brain waves Alpha wave Beta wave Delta wave Gamma wave K-complex Mu rhythm PGO waves Sensorimotor rhythm Sleep spindle Theta wave Sleep disorders Dyssomnia Excessive daytime sleepiness Hypersomnia Insomnia Kleine–Levin syndrome Narcolepsy Night eating syndrome Nocturia Sleep apnea Catathrenia Central hypoventilation syndrome Obesity hypoventilation syndrome Obstructive sleep apnea Periodic breathing Sleep state misperception Circadian rhythm disorders Advanced sleep phase disorder Cyclic alternating pattern Delayed sleep phase disorder Irregular sleep–wake rhythm Jet lag Non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder Shift work sleep disorder Parasomnia Bruxism Nightmare disorder Night terror Periodic limb movement disorder Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder Sleepwalking Somniloquy Benign phenomena Dreams Exploding head syndrome Hypnic jerk Hypnagogia / Sleep onset Hypnopompic state Sleep paralysis Sleep inertia Somnolence Nocturnal clitoral tumescence Nocturnal penile tumescence Nocturnal emission Treatment Sleep diary Sleep hygiene Sleep induction Hypnosis Lullaby Somnology Polysomnography Other Sleep medicine Behavioral sleep medicine Sleep study Daily life Bed Bunk bed Daybed Four-poster bed Futon Hammock Mattress Sleeping bag Bed bug Bedding Bedroom Bedtime Bedtime story Bedtime toy Biphasic and polyphasic sleep Chronotype Dream diary Microsleep Mouth breathing Nap Nightwear Power nap Second wind Siesta Sleep and creativity Sleep and learning Sleep deprivation / Sleep debt Sleeping while on duty Sleepover SnoringHCRT, HLA-DRB1, LARGE1, P2RY11, SLC12A3, CLCNKB, TNFSF4, MOG, TBC1D24, FKRP, HLA-DQB1, ZNF365, POMT1, FKTN, SYNGAP1, DNMT1, DMPK, CTSH, POMT2, REM1, TNF, CENPJ, SLC17A5, SAR1A, ZFYVE9, LRRK2, UBXN2B, PATJ, AMOT, PDSS2, BDNF, PAX8, VWF, VDR, SOD2, PSG5, PDE4A, OPHN1, NOS1, MUC1, MAOA, IL1B, HLA-DQA1, HCRTR2, ETFA, WDR27
-
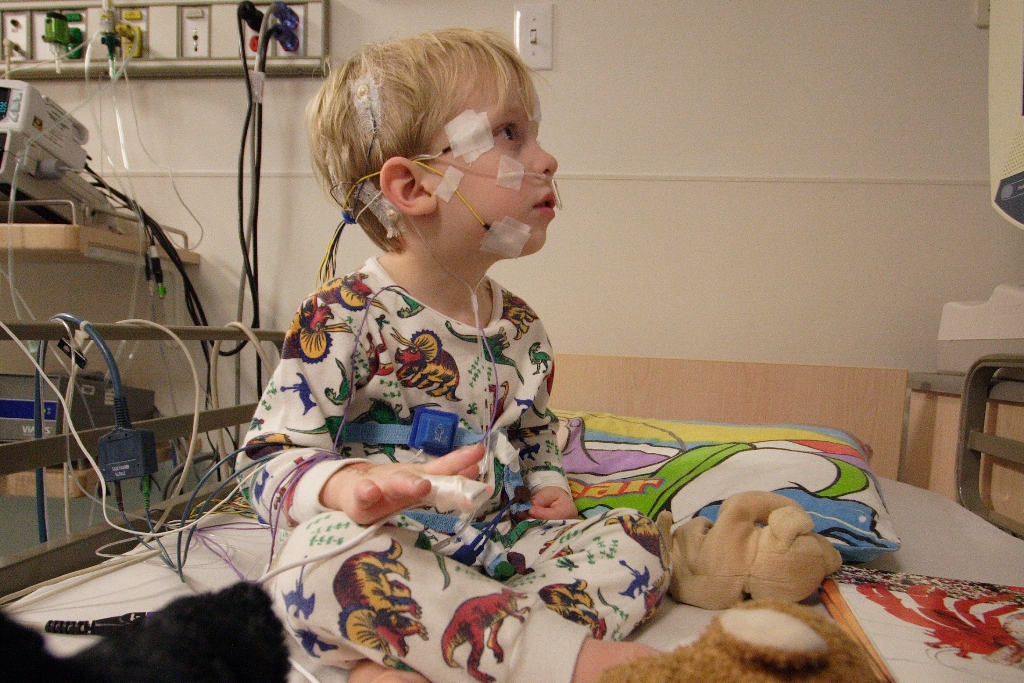
Xia-Gibbs Syndrome
Gard
People with this syndrome usually present with developmental delay (especially delays in speech), low muscule tone (hypotonia), failure to thrive, mildly unusual facial features (broad forehead, widely-spaced eyes (hypertelorism), big and low-set ears, flat nasal bridge, and thin upper lip), and breathing difficulties when sleeping (sleep apnea). The sleep apnea may be due to a collapse of the airway when breathing ( tracheomalacia ). ... This may include careful monitoring of the airways, continuous positive airway pressure at night, frequent growth assessments, physical therapy and early interventions to maximize developmental potential.
-
Dyssomnia
Wikipedia
Patients may complain of difficulty getting to sleep or staying asleep, intermittent wakefulness during the night, early morning awakening, or combinations of any of these. ... The major three groups, along with the group types, include: [1] : 15 Intrinsic sleep disorders [1] : 15 idiopathic hypersomnia , narcolepsy , periodic limb movement disorder , restless legs syndrome , obstructive sleep apnea , central sleep apnea syndrome , sleep state misperception , psychophysiologic insomnia, recurrent hypersomnia, post-traumatic hypersomnia, central alveolar hypoventilation syndrome, Extrinsic sleep disorders – 13 disorders recognized, including [1] : 16 alcohol-dependent sleep disorder, food allergy insomnia , inadequate sleep routine. ... External links [ edit ] Classification D ICD - 9-CM : 307.47 , 780.56 MeSH : D020920 v t e Mental and behavioral disorders Adult personality and behavior Gender dysphoria Ego-dystonic sexual orientation Paraphilia Fetishism Voyeurism Sexual maturation disorder Sexual relationship disorder Other Factitious disorder Munchausen syndrome Intermittent explosive disorder Dermatillomania Kleptomania Pyromania Trichotillomania Personality disorder Childhood and learning Emotional and behavioral ADHD Conduct disorder ODD Emotional and behavioral disorders Separation anxiety disorder Movement disorders Stereotypic Social functioning DAD RAD Selective mutism Speech Stuttering Cluttering Tic disorder Tourette syndrome Intellectual disability X-linked intellectual disability Lujan–Fryns syndrome Psychological development ( developmental disabilities ) Pervasive Specific Mood (affective) Bipolar Bipolar I Bipolar II Bipolar NOS Cyclothymia Depression Atypical depression Dysthymia Major depressive disorder Melancholic depression Seasonal affective disorder Mania Neurological and symptomatic Autism spectrum Autism Asperger syndrome High-functioning autism PDD-NOS Savant syndrome Dementia AIDS dementia complex Alzheimer's disease Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease Frontotemporal dementia Huntington's disease Mild cognitive impairment Parkinson's disease Pick's disease Sundowning Vascular dementia Wandering Other Delirium Organic brain syndrome Post-concussion syndrome Neurotic , stress -related and somatoform Adjustment Adjustment disorder with depressed mood Anxiety Phobia Agoraphobia Social anxiety Social phobia Anthropophobia Specific social phobia Specific phobia Claustrophobia Other Generalized anxiety disorder OCD Panic attack Panic disorder Stress Acute stress reaction PTSD Dissociative Depersonalization disorder Dissociative identity disorder Fugue state Psychogenic amnesia Somatic symptom Body dysmorphic disorder Conversion disorder Ganser syndrome Globus pharyngis Psychogenic non-epileptic seizures False pregnancy Hypochondriasis Mass psychogenic illness Nosophobia Psychogenic pain Somatization disorder Physiological and physical behavior Eating Anorexia nervosa Bulimia nervosa Rumination syndrome Other specified feeding or eating disorder Nonorganic sleep Hypersomnia Insomnia Parasomnia Night terror Nightmare REM sleep behavior disorder Postnatal Postpartum depression Postpartum psychosis Sexual dysfunction Arousal Erectile dysfunction Female sexual arousal disorder Desire Hypersexuality Hypoactive sexual desire disorder Orgasm Anorgasmia Delayed ejaculation Premature ejaculation Sexual anhedonia Pain Nonorganic dyspareunia Nonorganic vaginismus Psychoactive substances, substance abuse and substance-related Drug overdose Intoxication Physical dependence Rebound effect Stimulant psychosis Substance dependence Withdrawal Schizophrenia , schizotypal and delusional Delusional Delusional disorder Folie à deux Psychosis and schizophrenia-like Brief reactive psychosis Schizoaffective disorder Schizophreniform disorder Schizophrenia Childhood schizophrenia Disorganized (hebephrenic) schizophrenia Paranoid schizophrenia Pseudoneurotic schizophrenia Simple-type schizophrenia Other Catatonia Symptoms and uncategorized Impulse control disorder Klüver–Bucy syndrome Psychomotor agitation Stereotypy v t e Diseases of the nervous system , primarily CNS Inflammation Brain Encephalitis Viral encephalitis Herpesviral encephalitis Limbic encephalitis Encephalitis lethargica Cavernous sinus thrombosis Brain abscess Amoebic Brain and spinal cord Encephalomyelitis Acute disseminated Meningitis Meningoencephalitis Brain / encephalopathy Degenerative Extrapyramidal and movement disorders Basal ganglia disease Parkinsonism PD Postencephalitic NMS PKAN Tauopathy PSP Striatonigral degeneration Hemiballismus HD OA Dyskinesia Dystonia Status dystonicus Spasmodic torticollis Meige's Blepharospasm Athetosis Chorea Choreoathetosis Myoclonus Myoclonic epilepsy Akathisia Tremor Essential tremor Intention tremor Restless legs Stiff-person Dementia Tauopathy Alzheimer's Early-onset Primary progressive aphasia Frontotemporal dementia / Frontotemporal lobar degeneration Pick's Dementia with Lewy bodies Posterior cortical atrophy Vascular dementia Mitochondrial disease Leigh syndrome Demyelinating Autoimmune Inflammatory Multiple sclerosis For more detailed coverage, see Template:Demyelinating diseases of CNS Episodic/ paroxysmal Seizures and epilepsy Focal Generalised Status epilepticus For more detailed coverage, see Template:Epilepsy Headache Migraine Cluster Tension For more detailed coverage, see Template:Headache Cerebrovascular TIA Stroke For more detailed coverage, see Template:Cerebrovascular diseases Other Sleep disorders For more detailed coverage, see Template:Sleep CSF Intracranial hypertension Hydrocephalus Normal pressure hydrocephalus Choroid plexus papilloma Idiopathic intracranial hypertension Cerebral edema Intracranial hypotension Other Brain herniation Reye syndrome Hepatic encephalopathy Toxic encephalopathy Hashimoto's encephalopathy Both/either Degenerative SA Friedreich's ataxia Ataxia–telangiectasia MND UMN only: Primary lateral sclerosis Pseudobulbar palsy Hereditary spastic paraplegia LMN only: Distal hereditary motor neuronopathies Spinal muscular atrophies SMA SMAX1 SMAX2 DSMA1 Congenital DSMA Spinal muscular atrophy with lower extremity predominance (SMALED) SMALED1 SMALED2A SMALED2B SMA-PCH SMA-PME Progressive muscular atrophy Progressive bulbar palsy Fazio–Londe Infantile progressive bulbar palsy both: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis v t e Sleep and sleep disorders Stages of sleep cycles Rapid eye movement (REM) Non-rapid eye movement Slow-wave Brain waves Alpha wave Beta wave Delta wave Gamma wave K-complex Mu rhythm PGO waves Sensorimotor rhythm Sleep spindle Theta wave Sleep disorders Dyssomnia Excessive daytime sleepiness Hypersomnia Insomnia Kleine–Levin syndrome Narcolepsy Night eating syndrome Nocturia Sleep apnea Catathrenia Central hypoventilation syndrome Obesity hypoventilation syndrome Obstructive sleep apnea Periodic breathing Sleep state misperception Circadian rhythm disorders Advanced sleep phase disorder Cyclic alternating pattern Delayed sleep phase disorder Irregular sleep–wake rhythm Jet lag Non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder Shift work sleep disorder Parasomnia Bruxism Nightmare disorder Night terror Periodic limb movement disorder Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder Sleepwalking Somniloquy Benign phenomena Dreams Exploding head syndrome Hypnic jerk Hypnagogia / Sleep onset Hypnopompic state Sleep paralysis Sleep inertia Somnolence Nocturnal clitoral tumescence Nocturnal penile tumescence Nocturnal emission Treatment Sleep diary Sleep hygiene Sleep induction Hypnosis Lullaby Somnology Polysomnography Other Sleep medicine Behavioral sleep medicine Sleep study Daily life Bed Bunk bed Daybed Four-poster bed Futon Hammock Mattress Sleeping bag Bed bug Bedding Bedroom Bedtime Bedtime story Bedtime toy Biphasic and polyphasic sleep Chronotype Dream diary Microsleep Mouth breathing Nap Nightwear Power nap Second wind Siesta Sleep and creativity Sleep and learning Sleep deprivation / Sleep debt Sleeping while on duty Sleepover SnoringRAI1, ATXN3, CDKL5, ASXL3, PRNP, MBD5, PIGQ, USP8, VPS35, EPM2A, SLC6A5, TUSC3, AIFM1, SMC3, LHX3, SMC1A, PRSS12, CASK, WFS1, CRADD, HESX1, ATAD3A, SETD5, CISD2, HDAC8, LINS1, TFAP2B, SNCA, SOX2, SOX3, SPR, GATAD2B, STXBP1, TBP, TCF20, THRA, EZR, THRB, NKX2-1, TRHR, TRIO, TSHB, TSHR, C12orf4, FMN2, AIMP1, MED23, SLC18A2, TECR, IQSEC2, SPART, VPS13A, SATB2, DNAJC13, WASHC4, ADNP, FRRS1L, FBXO7, ATXN10, NIPBL, RTTN, SIN3A, GIGYF2, HIBCH, BSCL2, CRBN, DCPS, SLC45A1, TNIK, PNKP, MAN1B1, SLC9A6, NSUN2, GABBR2, SNCAIP, HDAC4, ARNT2, GPHN, CC2D1A, WARS2, DEAF1, WDR45, CORIN, RSRC1, STAG2, KDM5B, WDR4, SEPTIN9, PIGP, LIAS, SMARCC2, SLC2A1, SEPSECS, TRAPPC9, FLT1, METTL23, GBA, GCH1, LRRK2, SLITRK1, GLRA1, GLRB, GLUD2, GNAO1, GNS, GRIK2, LHX4, HDC, HNMT, ST3GAL3, IDUA, FLII, PROKR2, FGFR1, CTNNB1, ADH1C, AGA, ASPA, NHLRC1, MFSD8, STOX1, ARX, DBH, HGSNAT, SIK1, DCTN1, DDC, SARDH, EIF4G1, EML1, B3GALNT2, ATAD1, NDST1, FBXO31, ZC3H14, EHMT1, POU1F1, PPT1, KCNA1, PROP1, SLC25A22, MBOAT7, RAD21, CLIP1, SARS1, CDH23, ATXN2, ATXN8OS, EPG5, SCN2A, CHD8, SGSH, PIGC, NSDHL, PGAP1, OTX2, NR4A2, EDC3, MED25, NEUROD2, NDP, MAPT, LMAN2L, MECP2, TRIM8, NAGLU, KMT2A, CRP, HCRT, COMT, COPD, TIMELESS, APOE, MAOA, IL6, MPPE1, ASPSCR1, NALCN, PLXNA3, PDSS2, CCL4L1, PLF, OPN4, ACHE, REM1, PRSS21, NFKB2, NBN, MEIS1, LAMC2, IL1B, IFNA2, HCRTR2, GLI2, GH1, GDF1, FMR1, FLG, FANCC, ESR1, ACE, CSN1S1, CSF2, CSF1R, CSE1L, CECR, CCT, BBS2, AGRP, NHS, PAX6, PER1, VEGFA, CERS1, IGSF6, CCL4L2, KL, ARTN, PER3, SRPX, ACP5, XPO1, VIP, UMOD, PNN, TNF, STAC, CCL4, SCD, ATXN1, BRD2, REN, PSG3, PSG2, PRL, PAX8
-
Night Sweats
Wikipedia
repeated occurrence of excessive sweating during sleep This article is about the medical condition. For the television series, see Night Sweats . Night sweats Other names Sleep sweats, nocturnal hyperhidrosis Specialty Infectious disease , oncology Night sweats , or also referred to as nocturnal hyperhidrosis (Hyperhidrosis - a medical term for excessive sweating [1] + nocturnal - night) is the repeated occurrence of excessive sweating during sleep . [2] The person may or may not also perspire excessively while awake. ... Retrieved 29 October 2020 . ^ a b "Night sweats - Mayo Clinic" . www.mayoclinic.org . ... PMID 31001050 . ^ a b Mold, James W.; Holtzclaw, Barbara J.; McCarthy, Laine (November–December 2012). "Night sweats: a systematic review of the literature" . ... McGraw-Hill Professional. p. 74. ISBN 978-0-07-147058-2 . ^ "Night sweats : Causes" . Mayo Clinic. 22 March 2011 . ... "Understanding the pathophysiology of vasomotor symptoms (hot flushes and night sweats) that occur in perimenopause, menopause, and postmenopause life stages".
-
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
Wikipedia
Adenoid cystic carcinoma Other names Adenocyst , Malignant cylindroma , Adenocystic , Adenoidcystic Micrograph of an adenoid cystic carcinoma of a salivary gland (right of image): Normal serous glands, typical of the parotid gland , are also seen (left of image), H&E stain . Specialty Oncology Adenoid cystic carcinoma is a rare type of cancer that can exist in many different body sites. ... Coronal MRI showing right parotid adenoid cystic carcinoma with perineural spread of tumor along the facial nerve extending to the stylomastoid foramen Histopathological image of adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary gland infiltrating a nerve (center), H&E stain Histopathological image of adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary gland, immunostain for S-100 protein Micrograph of adenoid cystic carcinoma, fine needle aspiration specimen, Pap stain Adenoid cystic carcinoma with comedonecrosis See also [ edit ] Primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma Collagenous spherulosis References [ edit ] ^ Marchiò C, Weigelt B, Reis-Filho JS (Mar 2010). ... "Novel MYBL1 Gene Rearrangements with Recurrent MYBL1-NFIB Fusions in Salivary Adenoid Cystic Carcinomas Lacking t(6;9) Translocations" . ... "Targeting the Oncogenic Transcriptional Regulator MYB in Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma by Inhibition of IGF1R/AKT Signaling" .TP53, NOTCH1, PIK3CA, MYBL1, FBXW7, BCOR, HRAS, MYB, NFIB, CREBBP, CDH1, PTEN, CCND1, SOX4, DAPK1, BRCA1, AQP1, IGFBP2, ATM, ESPL1, SRCAP, HOMER3, TLK1, MAGI2, SMARCA2, MORF4L1, KDM6B, MLC1, FGF16, DTX4, H1-4, GUCY1A1, MGA, RBFOX2, GAS6, GAS2, MAGI1, KAT6A, H2AC16, INSRR, SERPINF1, PRKDC, MAP2K2, MYCN, PYGB, ST3GAL4, SMARCE1, SON, SOX11, MARCKS, TOP2A, KDM6A, KRT15, SMC1A, KRT5, ARID1A, ITGB4, ZIM2, BRD1, MYCBP, NSD1, STAG3L1, CNTN6, MIER2, IL17RD, MAML3, CMTR2, ERBIN, SLC24A3, KMT2C, BCORL1, EFHD1, BCL11A, WNT5B, NETO2, ARID5B, ATRX, FOXP2, JMJD1C, JAG1, ASPM, KANSL1, XAGE1A, VCAN, PDZK1, FAT1, PCSK1N, ARID4B, GINS2, SETD2, FOXO3, DTL, UHRF1, FGFR4, IRX4, ISYNA1, FANCA, MARK2, EN1, EP300, KRAS, KIT, ARID2, SF3B1, CYLD, IDH1, EGFR, CTNNB1, CDKN2A, SOX10, CXCR4, ERBB2, HIF1A, VEGFA, ACCS, SOX2, SMUG1, H3P10, NOS2, BCL2, NOS1, RUNX3, FN1, BCL2A1, MIR21, ACACB, SNAI1, MMP2, MIF, MDM2, TBX1, KRT14, ILK, TP63, BECN1, BMS1, ID1, MMP9, CD274, CTSD, ANO1, MYB-AS1, CD44, BTBD7, SLC2A1, ACACA, PCNA, NOTCH4, MAPK1, PSMD7, CTSB, CTAG1B, CCR5, CENPF, CDK2, CDH5, PECAM1, CDH4, PAX3, DNMT1, KRIT1, PA2G4, CCL28, TMPRSS4, ACKR3, CALM3, NDRG2, MTUS1, CALM2, NNMT, EPHA2, BUB1, BBC3, USP22, GPC3, GJA1, GATA1, FZD2, MTOR, SULT4A1, FOLH1, DKK2, LEF1, PIK3CB, FGF2, FABP7, NGF, EWSR1, OBP2A, ERBB3, TMED7, CALM1, CAMKMT, HOXB7, MIR17HG, MIR125A, MIR140, MIR150, MIR181A2, NTF3, MIR222, MIR320A, MIR93, MIR338, SBSN, MIR375, MIR455, ASIC1, MIR1234, TMED7-TICAM2, ADAMTS9-AS2, H3P23, H3P28, MIRLET7B, TICAM2, BSG, ATF1, PDCD1LG2, CD276, BNIP3, NTRK3, REG4, NTRK1, MINDY4, MAML2, AQP5, MACC1, WDR66, AQP3, SKA1, ALCAM, CTAG1A, ADK, ADAM10, ARMH1, SFN, HES1, PSMD9, HSPB1, SRY, STAT3, PPP2R2B, TFE3, TGFB1, ICAM5, TNF, EPCAM, LYZ, TRAF6, TXN, TYMS, LMNA, UVRAG, LGALS3, VEGFC, VIM, NSD2, RPSA, SPN, SMAD4, MCAM, SDC1, PTCH1, MYC, PTGS2, MMP15, RAC1, RPE65, S100A1, S100B, SGTA, PTPA, PROX1, SKP2, NCAM1, SMARCA1, MAPK3, MMP7, NFKB1, PRKD1, PRRX1, KRT7, KIF22, AGR2, IFI27, PIM1, MFN2, AKT3, RABEPK, NOTCH2, HOXB13, ZNRD2, DCTN6, PIK3CD, HSPG2, SMR3B, HSPB2, MLLT11, EBNA1BP2, CKAP4, PTP4A3, RASSF1, ZEB2, IGF1R, PLAG1, NRP2, RECK, GEMIN2, PPM1D, PIN1, PIK3CG, TNFSF10, ADAM9, IL9, PROM1, ATG5, HSPB3, SCAF11, ARHGEF2, IL2, SLC9A3R2, LHX2, DDX23, CCN1, LANCL1
-
Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
Wikipedia
The syndrome is often associated with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), which causes periods of absent or reduced breathing in sleep, resulting in many partial awakenings during the night and sleepiness during the day. [1] The disease puts strain on the heart, which may lead to heart failure and leg swelling . Obesity hypoventilation syndrome is defined as the combination of obesity and an increased blood carbon dioxide level during the day that is not attributable to another cause of excessively slow or shallow breathing . [2] The most effective treatment is weight loss , but this may require bariatric surgery to achieve. [3] Weight loss of 25 to 30% is usually required to resolve the disorder. [3] The other first line treatment is non-invasive positive airway pressure (PAP), usually in the form of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) at night. [4] [5] The disease was known initially in the 1950s, as "Pickwickian syndrome" in reference to a Dickensian character. [5] Contents 1 Signs and symptoms 2 Mechanism 3 Diagnosis 3.1 Classification 4 Treatment 4.1 Positive airway pressure 4.2 Other treatments 5 Prognosis 6 Epidemiology 7 History 8 References 9 Further reading Signs and symptoms [ edit ] Most people with obesity hypoventilation syndrome have concurrent obstructive sleep apnea , a condition characterized by snoring , brief episodes of apnea (cessation of breathing) during the night, interrupted sleep and excessive daytime sleepiness . ... In OHS, this effect is reduced. [5] [10] Furthermore, episodes of nighttime acidosis (e.g. due to sleep apnea) lead to compensation by the kidneys with retention of the alkali bicarbonate . ... The first is OHS in the context of obstructive sleep apnea; this is confirmed by the occurrence of 5 or more episodes of apnea, hypopnea or respiratory-related arousals per hour (high apnea-hypopnea index ) during sleep. ... This relieves the features of obstructive sleep apnea and is often sufficient to remove the resultant accumulation of carbon dioxide.
-
Sleep Terrors (Night Terrors)
Mayo_clinic
Overview Sleep terrors are episodes of screaming, intense fear and flailing while still asleep. Also known as night terrors, sleep terrors often are paired with sleepwalking. ... Sleep terrors generally occur in the first third to first half of the night, and rarely during naps. A sleep terror may lead to sleepwalking. ... If the sleep terrors are associated with an underlying medical or mental health condition or another sleep disorder, such as obstructive sleep apnea, treatment is aimed at the underlying problem. ... To help prevent injury, close and lock all windows and exterior doors at night. You might even lock interior doors or put alarms or bells on them. ... If your child has sleep terrors, keep a sleep diary. For several nights, note how many minutes after bedtime a sleep terror episode occurs.
-
Insomnia
Mayo_clinic
You don't have to put up with sleepless nights. Simple changes in your daily habits can often help. ... Examples of conditions linked with insomnia include chronic pain, cancer, diabetes, heart disease, asthma, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), overactive thyroid, Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease. Sleep-related disorders. Sleep apnea causes you to stop breathing periodically throughout the night, interrupting your sleep. ... A lack of activity can interfere with a good night's sleep. Also, the less active you are, the more likely you may be to take a daily nap, which can interfere with sleep at night. ... Sleep apnea and restless legs syndrome become more common with age. ... If the cause of your insomnia isn't clear, or you have signs of another sleep disorder, such as sleep apnea or restless legs syndrome, you may need to spend a night at a sleep center.MEIS1, ADORA2A, LMX1B, GABRB3, HCRT, PRNP, TUBB3, TBL2, GTF2I, GTF2IRD1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRB1, HMBS, PINK1, LIMK1, DNAJC6, MEN1, VPS13C, HTRA2, PRKN, CLIP2, SIN3A, PODXL, SLC25A13, ZNF365, QARS1, RFC2, PARK7, SLC12A3, SNCA, FARS2, UCHL1, LRRK2, BAZ1B, CPOX, ELN, DCTN1, CRY1, CLCNKB, UNC80, NAGS, CLOCK, CRP, OPN1SW, SLC6A4, BDNF, REM1, ACTG2, POTEM, POTEKP, COPD, ACOT7, ACTG1, ACTBL2, FHL5, GAD1, SERPINA3, SLC17A5, MDD1, HTR2A, PSG5, VIP, SDHD, IL6, PER3, CELIAC6, RLS1, MIR182, CD200R1, GSC, TPPP, FREM3, UTS2, PPARGC1A, CTCF, IGSF6, SEMA4D, MARCHF11, EBPL, UBE2Z, ABCB6, RLS3, PCSK9, PPP2R3C, MIR146A, MOCOS, MSTO1, ARSI, TMED9, SIAE, GAL, PYCARD, ADIPOQ, CHDH, CENPJ, FBXO3, PPARGC1B, PART1, DDAH1, USE1, DDAH2, PLEKHM2, NDUFS7, ZC4H2, GTF2H5, IS1, STAC, PKD2L1, ELK3, LEPR, LCN2, IL1B, IARS1, HRES1, HCRTR2, HCRTR1, GSR, GSK3B, PRLHR, FSHMD1A, FLT4, FLNA, ERCC2, DRD2, MAP6, CYP19A1, CYP3A4, CYP2C9, CYP2B6, CASP9, STS, ARNTL, AR, AMT, AMPD1, ALB, AHR, JAG1, ADRA2A, MXD1, SMCP, WASF1, ROM1, TIMELESS, PER2, CDK5R1, TP63, MADD, TAM, PAX8, TST, TPO, TPH1, TNF, STAR, ACHE, CCL11, PSMD9, MET, PRL, POMC, PIGR, PDC, PAX6, PAEP, OPRM1, OPRK1, OAT, NDUFS4, MTNR1B, MTNR1A, MPST, MAP3K10, OCLN
-
Sleep Disorder
Wikipedia
The most common sleep disorder is insomnia . [2] Others are sleep apnea , narcolepsy and hypersomnia (excessive sleepiness at inappropriate times), sleeping sickness (disruption of sleep cycle due to infection), sleepwalking , and night terrors . ... About 70% of those who have narcolepsy also have cataplexy , a sudden weakness in the motor muscles that can result in collapse to the floor while retaining full conscious awareness. [8] Night terror , Pavor nocturnus , sleep terror disorder, an abrupt awakening from sleep with behavior consistent with terror . [9] Nocturia , a frequent need to get up and urinate at night. ... Other forms of sleep apnea are less common. [12] Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a medical disorder that is caused by repetitive collapse of the upper airway (back of the throat) during sleep. ... The algorithm that incorporated a combination of structured and unstructured variables identified more than 36,000 individuals with physician-documented insomnia. [75] Obstructive sleep apnea [ edit ] Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) affects around 4% of men and 2% of women in the United States. [76] In general, this disorder is more prevalent among men. ... Retrieved 27 July 2016 . ^ "Sleep Apnea Diagnosis" . SingularSleep . Retrieved 27 April 2018 . ^ MeSH 68020920 ^ Melinda Smith, M.A., Lawrence Robinson, Robert Segal, M.A.
-
Automatic Behavior
Wikipedia
ISBN 978-0-521-40150-0 . v t e Sleep and sleep disorders Stages of sleep cycles Rapid eye movement (REM) Non-rapid eye movement Slow-wave Brain waves Alpha wave Beta wave Delta wave Gamma wave K-complex Mu rhythm PGO waves Sensorimotor rhythm Sleep spindle Theta wave Sleep disorders Dyssomnia Excessive daytime sleepiness Hypersomnia Insomnia Kleine–Levin syndrome Narcolepsy Night eating syndrome Nocturia Sleep apnea Catathrenia Central hypoventilation syndrome Obesity hypoventilation syndrome Obstructive sleep apnea Periodic breathing Sleep state misperception Circadian rhythm disorders Advanced sleep phase disorder Cyclic alternating pattern Delayed sleep phase disorder Irregular sleep–wake rhythm Jet lag Non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder Shift work sleep disorder Parasomnia Bruxism Nightmare disorder Night terror Periodic limb movement disorder Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder Sleepwalking Somniloquy Benign phenomena Dreams Exploding head syndrome Hypnic jerk Hypnagogia / Sleep onset Hypnopompic state Sleep paralysis Sleep inertia Somnolence Nocturnal clitoral tumescence Nocturnal penile tumescence Nocturnal emission Treatment Sleep diary Sleep hygiene Sleep induction Hypnosis Lullaby Somnology Polysomnography Other Sleep medicine Behavioral sleep medicine Sleep study Daily life Bed Bunk bed Daybed Four-poster bed Futon Hammock Mattress Sleeping bag Bed bug Bedding Bedroom Bedtime Bedtime story Bedtime toy Biphasic and polyphasic sleep Chronotype Dream diary Microsleep Mouth breathing Nap Nightwear Power nap Second wind Siesta Sleep and creativity Sleep and learning Sleep deprivation / Sleep debt Sleeping while on duty Sleepover Snoring This medical symptom article is a stub .
-
Somniloquy
Wikipedia
It can be quite loud, ranging from simple mumbling sounds to loud shouts and long, frequently inarticulate speeches, and can occur many times during a sleep cycle. [1] As with sleepwalking and night terrors , sleeptalking usually occurs during delta-wave NREM sleep stages or during temporary arousals therefrom. ... It often occurs in association with other sleep disorders such as confusional arousals, sleep apnea, and REM sleep behavior disorder. ... About half of the children have sleep-talking episodes at least once a year but less than 10% of children present somniloquy every night whereas 20%-25% talk in their sleep at least once a week. ... I do not give much heed to such dreaming now; but she has never yet said anything, while in this state, that has not proved in a manner true; though she can discern nothing, by night or day, more than others may do when they are in their senses. ... ISBN 9780965993036 External links [ edit ] OSF Healthcare The Sleep Well Somniloquies in the form of albums and books by Bryan Lewis Saunders Filmmaker Adam Rosenberg's four-minute film of himself sleeptalking v t e Sleep and sleep disorders Stages of sleep cycles Rapid eye movement (REM) Non-rapid eye movement Slow-wave Brain waves Alpha wave Beta wave Delta wave Gamma wave K-complex Mu rhythm PGO waves Sensorimotor rhythm Sleep spindle Theta wave Sleep disorders Dyssomnia Excessive daytime sleepiness Hypersomnia Insomnia Kleine–Levin syndrome Narcolepsy Night eating syndrome Nocturia Sleep apnea Catathrenia Central hypoventilation syndrome Obesity hypoventilation syndrome Obstructive sleep apnea Periodic breathing Sleep state misperception Circadian rhythm disorders Advanced sleep phase disorder Cyclic alternating pattern Delayed sleep phase disorder Irregular sleep–wake rhythm Jet lag Non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder Shift work sleep disorder Parasomnia Bruxism Nightmare disorder Night terror Periodic limb movement disorder Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder Sleepwalking Somniloquy Benign phenomena Dreams Exploding head syndrome Hypnic jerk Hypnagogia / Sleep onset Hypnopompic state Sleep paralysis Sleep inertia Somnolence Nocturnal clitoral tumescence Nocturnal penile tumescence Nocturnal emission Treatment Sleep diary Sleep hygiene Sleep induction Hypnosis Lullaby Somnology Polysomnography Other Sleep medicine Behavioral sleep medicine Sleep study Daily life Bed Bunk bed Daybed Four-poster bed Futon Hammock Mattress Sleeping bag Bed bug Bedding Bedroom Bedtime Bedtime story Bedtime toy Biphasic and polyphasic sleep Chronotype Dream diary Microsleep Mouth breathing Nap Nightwear Power nap Second wind Siesta Sleep and creativity Sleep and learning Sleep deprivation / Sleep debt Sleeping while on duty Sleepover Snoring
-
Central Hypoventilation Syndrome
Wikipedia
Not to be confused with Central sleep apnea . Central hypoventilation syndrome Other names Ondine's curse, primary alveolar hypoventilation, alveolar hypoventilation secondary to neurologic disease, idiopathic acquired central hypoventilation syndrome Ondine by John William Waterhouse (1849–1917) Specialty Neurology Central hypoventilation syndrome ( CHS ) is a sleep-related breathing disorder that causes ineffective breathing, apnea , or respiratory arrest during sleep (and during wakefulness in severe cases). ... As of 2008, only 1000 total cases were known. [2] The diagnosis may be delayed because of variations in the severity of the manifestations or lack of awareness in the medical community, particularly in milder cases. [3] However, as there have been cases where asymptomatic family members also were found to have CCHS, it may be that these figures only reflect those found to require mechanical ventilation. In all cases, episodes of apnea occur in sleep, but in a few patients, at the most severe end of the spectrum, apnea also occurs while awake. ... Other symptoms include darkening of skin color from inadequate amounts of oxygen, drowsiness, fatigue, headaches, and an inability to sleep at night. Patients with CHS also have a sensitivity to sedatives and narcotics, which makes respiration even more difficult. ... The sequence of PHOX2B reveals mutations in 91% of the cases. [7] As in many disorders that are very rare, an infant with this unusual form of sleep apnea suffers from the probability that their physician has most likely never seen another case and will not recognize the diagnosis. ... External links [ edit ] Classification D ICD - 10 : G47.35 ICD - 9-CM : 327.25 OMIM : 209880 MeSH : D020182 DiseasesDB : 32976 External resources MedlinePlus : 000078 eMedicine : article/1002927 GeneReviews : Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome v t e Sleep and sleep disorders Stages of sleep cycles Rapid eye movement (REM) Non-rapid eye movement Slow-wave Brain waves Alpha wave Beta wave Delta wave Gamma wave K-complex Mu rhythm PGO waves Sensorimotor rhythm Sleep spindle Theta wave Sleep disorders Dyssomnia Excessive daytime sleepiness Hypersomnia Insomnia Kleine–Levin syndrome Narcolepsy Night eating syndrome Nocturia Sleep apnea Catathrenia Central hypoventilation syndrome Obesity hypoventilation syndrome Obstructive sleep apnea Periodic breathing Sleep state misperception Circadian rhythm disorders Advanced sleep phase disorder Cyclic alternating pattern Delayed sleep phase disorder Irregular sleep–wake rhythm Jet lag Non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder Shift work sleep disorder Parasomnia Bruxism Nightmare disorder Night terror Periodic limb movement disorder Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder Sleepwalking Somniloquy Benign phenomena Dreams Exploding head syndrome Hypnic jerk Hypnagogia / Sleep onset Hypnopompic state Sleep paralysis Sleep inertia Somnolence Nocturnal clitoral tumescence Nocturnal penile tumescence Nocturnal emission Treatment Sleep diary Sleep hygiene Sleep induction Hypnosis Lullaby Somnology Polysomnography Other Sleep medicine Behavioral sleep medicine Sleep study Daily life Bed Bunk bed Daybed Four-poster bed Futon Hammock Mattress Sleeping bag Bed bug Bedding Bedroom Bedtime Bedtime story Bedtime toy Biphasic and polyphasic sleep Chronotype Dream diary Microsleep Mouth breathing Nap Nightwear Power nap Second wind Siesta Sleep and creativity Sleep and learning Sleep deprivation / Sleep debt Sleeping while on duty Sleepover Snoring
-
Irregular Sleep–wake Rhythm
Wikipedia
Other ways to monitor the sleep schedule are actigraphy [4] [5] or use of a Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machine that can log sleeping times The following are possible warning signs: sleeping off and on in a series of naps during the day and at night, with no regular pattern but with normal total sleep time, difficulty getting restorative sleep, and excessive daytime sleepiness. [4] [5] Because of the changes in sleep/wake time, and because this is a rare disorder, initially it can seem like another circadian rhythm sleep disorder such as non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder or like insomnia. ... An overnight sleep study is usually not needed to detect this disorder, but may be indicated if other sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea and periodic limb movement disorder, seem likely. ... Management [ edit ] Treatment for irregular sleep–wake rhythm tries to enable the body clock in the brain, such that a normal long sleep period at night can be achieved. Education about sleep hygiene is important, and counseling can be helpful. ... External links [ edit ] Classification D ICD - 10 : G47.23 ICD - 9-CM : 327.33 MeSH : D021081 External resources MedlinePlus : 000806 eMedicine : neuro/655 v t e Sleep and sleep disorders Stages of sleep cycles Rapid eye movement (REM) Non-rapid eye movement Slow-wave Brain waves Alpha wave Beta wave Delta wave Gamma wave K-complex Mu rhythm PGO waves Sensorimotor rhythm Sleep spindle Theta wave Sleep disorders Dyssomnia Excessive daytime sleepiness Hypersomnia Insomnia Kleine–Levin syndrome Narcolepsy Night eating syndrome Nocturia Sleep apnea Catathrenia Central hypoventilation syndrome Obesity hypoventilation syndrome Obstructive sleep apnea Periodic breathing Sleep state misperception Circadian rhythm disorders Advanced sleep phase disorder Cyclic alternating pattern Delayed sleep phase disorder Irregular sleep–wake rhythm Jet lag Non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder Shift work sleep disorder Parasomnia Bruxism Nightmare disorder Night terror Periodic limb movement disorder Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder Sleepwalking Somniloquy Benign phenomena Dreams Exploding head syndrome Hypnic jerk Hypnagogia / Sleep onset Hypnopompic state Sleep paralysis Sleep inertia Somnolence Nocturnal clitoral tumescence Nocturnal penile tumescence Nocturnal emission Treatment Sleep diary Sleep hygiene Sleep induction Hypnosis Lullaby Somnology Polysomnography Other Sleep medicine Behavioral sleep medicine Sleep study Daily life Bed Bunk bed Daybed Four-poster bed Futon Hammock Mattress Sleeping bag Bed bug Bedding Bedroom Bedtime Bedtime story Bedtime toy Biphasic and polyphasic sleep Chronotype Dream diary Microsleep Mouth breathing Nap Nightwear Power nap Second wind Siesta Sleep and creativity Sleep and learning Sleep deprivation / Sleep debt Sleeping while on duty Sleepover Snoring
-
Nocturia
Wikipedia
Nocturia Other names Nycturia Specialty Urology Nocturia is defined by the International Continence Society (ICS) as “the complaint that the individual has to wake at night one or more times for voiding ( i.e. to urinate ).” [1] The term is derived from Latin nox, night , and Greek [τα] ούρα, urine . Causes are varied and can be difficult to discern. [2] Although not every patient needs treatment, most people seek treatment for severe nocturia, waking up to void more than 2–3 times per night. Contents 1 Prevalence 2 Impact 3 Diagnosis 4 Causes 4.1 Polyuria 4.1.1 Global polyuria 4.1.2 Nocturnal polyuria 4.2 Bladder storage 4.3 Mixed cause 5 Management 5.1 Lifestyle changes 5.2 Medications 5.3 Surgery 6 See also 7 References 8 External links Prevalence [ edit ] Studies show that 5–15% of people who are 20–50 years old, 20–30% of people who are 50–70 years old, and 10–50% of people 70+ years old, urinate at least twice a night. [3] Nocturia becomes more common with age. ... Nocturnal polyuria [ edit ] Nocturnal polyuria is defined as an increase in urine production during the night but with a proportional decrease in daytime urine production that results in a normal 24-hour urine volume. ... Other causes of nocturnal polyuria include diseases such as congestive heart failure nephritic syndrome liver failure lifestyle patterns such as excessive nighttime drinking sleep apnea increasing obstructive airway resistance. Obstructive sleep apnea sufferers have shown to have increases in renal sodium and water excretion that are mediated by elevated plasma atrial natriuretic hormone (ANH) levels. [14] [17] ANH is released by cardiac muscle cells in response to high blood volume.
-
Hypnic Jerk
Wikipedia
Involuntary twitches Hypnic jerk Other names Hypnagogic jerk, sleep start, sleep twitch, myoclonic jerk, night start Specialty Sleep medicine Causes caffeine, dreams, anxiety A hypnic jerk , hypnagogic jerk , sleep start , sleep twitch , myoclonic jerk , or night start is a brief and sudden involuntary contraction of the muscles of the body which occurs when a person is beginning to fall asleep, often causing the person to jump and awaken suddenly for a moment. ... "Hypnic Jerks: How To Avoid Waking With A Jolt" . No Sleepless Nights . Retrieved 3 July 2019 . Classification D v t e Sleep and sleep disorders Stages of sleep cycles Rapid eye movement (REM) Non-rapid eye movement Slow-wave Brain waves Alpha wave Beta wave Delta wave Gamma wave K-complex Mu rhythm PGO waves Sensorimotor rhythm Sleep spindle Theta wave Sleep disorders Dyssomnia Excessive daytime sleepiness Hypersomnia Insomnia Kleine–Levin syndrome Narcolepsy Night eating syndrome Nocturia Sleep apnea Catathrenia Central hypoventilation syndrome Obesity hypoventilation syndrome Obstructive sleep apnea Periodic breathing Sleep state misperception Circadian rhythm disorders Advanced sleep phase disorder Cyclic alternating pattern Delayed sleep phase disorder Irregular sleep–wake rhythm Jet lag Non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder Shift work sleep disorder Parasomnia Bruxism Nightmare disorder Night terror Periodic limb movement disorder Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder Sleepwalking Somniloquy Benign phenomena Dreams Exploding head syndrome Hypnic jerk Hypnagogia / Sleep onset Hypnopompic state Sleep paralysis Sleep inertia Somnolence Nocturnal clitoral tumescence Nocturnal penile tumescence Nocturnal emission Treatment Sleep diary Sleep hygiene Sleep induction Hypnosis Lullaby Somnology Polysomnography Other Sleep medicine Behavioral sleep medicine Sleep study Daily life Bed Bunk bed Daybed Four-poster bed Futon Hammock Mattress Sleeping bag Bed bug Bedding Bedroom Bedtime Bedtime story Bedtime toy Biphasic and polyphasic sleep Chronotype Dream diary Microsleep Mouth breathing Nap Nightwear Power nap Second wind Siesta Sleep and creativity Sleep and learning Sleep deprivation / Sleep debt Sleeping while on duty Sleepover Snoring
-
Rem Sleep Behavior Disorder
Mayo_clinic
You normally don't move during REM sleep, a normal stage of sleep that occurs many times during the night. About 20 percent of your sleep is spent in REM sleep, the usual time for dreaming, which occurs primarily during the second half of the night. ... The onset can be gradual or sudden, and episodes may occur occasionally or several times a night. The disorder often worsens with time. ... REM sleep behavior disorder may have symptoms similar to other sleep disorders, or it may coexist with other sleep disorders such as obstructive sleep apnea or narcolepsy. Talking with your sleeping partner. ... Clonazepam may cause side effects such as daytime sleepiness, decreased balance and worsening of sleep apnea. Doctors continue to study several other medications that may treat REM sleep behavior disorder. ... In the morning, record as much as you know of your (or your partner's) sleep issues that occurred the previous night. Before your appointment, make a list of: All medications, vitamins, herbs or other supplements you're taking, as well as dosages and any recent changes Any symptoms you're experiencing, including any that may seem unrelated to the reason for the appointment Key personal information, including any major stresses or recent life changes Questions to ask your doctor to make the most of your time together Some questions to ask your doctor may include: What's likely causing my symptoms or condition?SLC6A3, REM1, SNCA, GBA, LRRK2, PSG5, PAFAH1B1, MAPT, YWHAE, SF3B1, TET2, ASXL1, LAMC2, CSF2, SNCB, SNCG, PDSS2, SCARB2, APOE, RNH1, SMUG1, OPN1MW2, DGKQ, BEAN1, GAK, TMEM175, PPP1R2C, OPN1MW, GDF1, SHC3, UTS2R, FBXO7, HCRT, PRNP, CIT, PPP1R13L, CPLX1, CLOCK, SLC14A2, IL10, TPO, TK2, MC1R, PRKN, POR, OPN1MW3
-
Hypotonia, Hypoventilation, Impaired Intellectual Development, Dysautonomia, Epilepsy, And Eye Abnormalities
Omim
Description Hypotonia, hypoventilation, impaired intellectual development, dysautonomia, epilepsy, and eye abnormalities (HIDEA) is an autosomal recessive neurodevelopmental syndrome characterized by global developmental delay, poor or absent speech, hypotonia, variable ocular movement and visual abnormalities, and respiratory difficulties, including hypoventilation, and sleep apnea. Patients may have significant breathing problems during respiratory infections that may lead to early death (summary by Rahikkala et al., 2019). ... The patients had common respiratory difficulties, including bradypnea and hypoventilation, and obstructive or restrictive sleep apnea, often requiring BiPAP at night. ... INHERITANCE - Autosomal recessive GROWTH Height - Short stature (in some patients) Weight - Obesity (in some patients) HEAD & NECK Head - Small head circumference (in some patients) Face - Coarse facial features (in some patients) - Prominent forehead - Prominent chin Eyes - Poor visual fixation - Strabismus - Exotropia - Amblyopia - Hyperopia - Myopia - Astigmatism - Rotating eye movements - Pendular nystagmus - Optic atrophy - Achromic fundi - Abnormal eye movements - Cortical blindness Nose - Low nasal bridge Mouth - Thick lips RESPIRATORY - Hypoventilation - Bradypnea - Sleep apnea - BiPAP at night - Pneumonia, recurrent ABDOMEN Gastrointestinal - Constipation SKELETAL Spine - Scoliosis - Kyphosis Pelvis - Hip flexion Limbs - Knee deformities - Elbow contractures Hands - Finger joint hypermobility Feet - Planovalgus deformities SKIN, NAILS, & HAIR Hair - Thick coarse hair MUSCLE, SOFT TISSUES - Hypotonia NEUROLOGIC Central Nervous System - Global developmental delay - Delayed walking - Unsteady gait - Inability to walk - Intellectual disability, severe to profound - Poor or absent speech - Seizures - EEG abnormalities - Multifocal spikes - Slowed background activity Behavioral Psychiatric Manifestations - Abnormal sleep behavior METABOLIC FEATURES - Poor temperature regulation - Hyperthermia - Hypothermia MISCELLANEOUS - Onset in infancy - Death due to respiratory insufficiency may occur MOLECULAR BASIS - Caused by mutation in the prolyl 4-hydroxylase, transmembrane gene (P4HTM, 614584.0001 ) ▲ Close