-
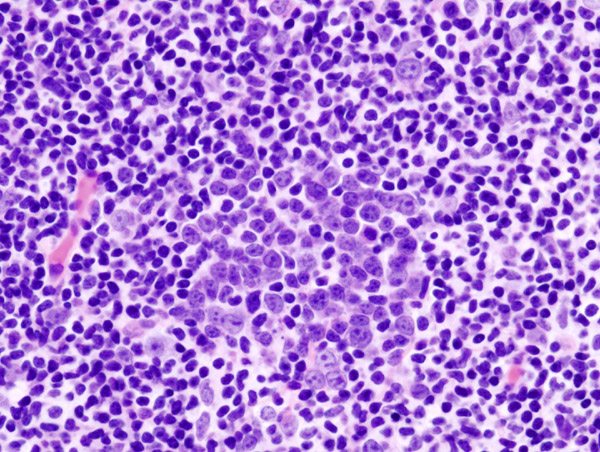
Aggressive Lymphoma
Wikipedia
Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology . 28 (2): 167–177. doi : 10.1053/j.semdp.2011.04.001 .BCL2, MYC, SMUG1, BCL6, ALK, CD44, IL10, CD274, TP53, CD19, PARP9, SLC27A5, EPM2A, P2RX6, PDLIM7, ESPL1, CASP8AP2, HMGB1P5, RAD51AP1, CTCF, MIR17HG, RAPH1, P2RX2, CLEC4D, ACSBG1, AURKA, SAMD14, KRT20, PPP1R9A, RHOJ, IGHV3-48, P2RX7, PDCD1, HMGB1, PRDM1, BTK, MS4A1, TNFRSF8, CDKN2A, CEL, CYLD, DDIT3, FH, HK2, NR4A1, P2RY2, LIG4, NOS1, NOS2, NPM1, P2RX1, P2RX3, P2RX4, P2RX5, ATM, P2RY1, P2RX5-TAX1BP3
- Kaposi Sarcoma, Susceptibility To Omim
-
Peeling Skin Syndrome 1
Omim
Other familial cases in the offspring of consanguineous parents were reported by Levy and Goldsmith (1982) and Heid et al. (1983). Mevorah et al. (1987) reported a 28-year-old Caucasian woman with variably pruritic ichthyosiform dermatosis.CDSN, CHST8, PHF21A, SERPINB8, TGM5, PSORS1C1, IFNG, IL17A, CXCL10, HLA-C, PSS, TNFSF13B, FLG2, TNF, TRAF6, VIP, TLR4, VIPR2, TLR3, TLR2, SSNA1, CNTRL, BTG3, SPINK5, STAT5A, CDC42EP1, SS18L1, RBMS3, IL22, TLR9, DIABLO, FCRL4, FAM167A, TUBA1C, IFNL1, STAT5B, NR0B1, STAT3, SSB, BST2, CD28, CCR8, CST3, CST4, ATN1, EDA, GPI, GTF2I, HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRB1, IFNA1, IFNA13, IL2, IL6, IL10, IL11, IL13, IRAK1, KLRB1, MMP9, MPZ, PMP22, BLK, RO60, CCL25
-
Pilocytic Astrocytoma
Wikipedia
"Pilocytic astrocytoma: A disease with evolving molecular heterogeneity". Journal of Child Neurology . 28 (5): 625–32. doi : 10.1177/0883073813476141 .KRAS, BRAF, NF1, KIAA1549, FGFR1, HIF1A, NTRK2, PTPN11, HEY2, HGF, MMP3, ESR2, ESR1, NOTCH1, NOTCH2, MET, MMP9, ACVR1, HEY1, LATS2, NCOA3, LATS1, TP53, NDRG1, AR, DLL3, SDHA, IDH1, IDH2, FLCN, CDKN2A, RAF1, EPHB2, MAPK1, VEGFA, PTEN, OLIG2, H3P10, ATRX, EGFR, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, ZHX2, ABCB1, PIK3CA, PIK3CB, IGF2BP3, SGSM3, CD99, MGMT, AKT1, SOX10, ERBB3, FAM131B, KDR, GTF2I, TXN, MAP2K7, DCX, TBC1D9, HIPK2, PNKP, CIT, GSTP1, ALDH1L1, AQP4, AHSA1, TARDBP, RAMP3, RAMP2, VPS51, MVP, GIT2, AKAP12, ONECUT2, GRAP2, LGI1, CD34, SOCS3, MPRIP, POLDIP2, AQP1, ARHGAP24, MIR24-1, MIR15A, NDUFS7, GADL1, ZAR1, PARP1, DACT2, ASPRV1, AZIN2, ATP23, DCLK3, COL18A1, APOD, GOLPH3, MIB1, LHX9, SAGE1, IMP3, PHF20, ATP6V0A4, ANGPT2, ABCC3, RNF19A, PRDX5, PROM1, TP73, CD63, LRP1, PCNA, PBX3, ERBB2, ERBB4, ETV1, MYB, ETV5, FABP7, MKI67, FGFR3, MATN2, LGALS3, AIMP2, RPSA, FLT1, KIT, IL13RA2, IL1B, FN1, GFAP, HES1, HRAS, GLB1, GCLC, PMP22, MAPK8, CTSL, PTPRA, COL1A1, TYROBP, TWIST1, TTF1, COL2A1, TNR, NR2E1, NKX2-1, TIMP4, TIMP1, ZEB1, SST, SOX2, SMARCB1, SNAI2, CRK, S100B, S100A1, RNASE3, RASA1, MAPK14, ADM, PTPRZ1, PXMP2
-
X-Linked Acrogigantism
Gene_reviews
Other frequently observed clinical features of GH excess: acral enlargement, coarse facial features, and increased appetite (~1/3 of cases) Laboratory findings GH excess as demonstrated by: Elevated levels of GH that do not suppress during an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) (1.75 g/kg of anhydrous glucose; maximum 75 g) Increased circulating age-adjusted IGF-1 levels Hyperprolactinemia (seen in 26/28 reported individuals for whom data were available) Imaging findings consistent with either of the following: Pituitary macroadenoma (>10 mm in diameter) with or without associated hyperplasia (in 24 of 30 reported individuals with available data) Diffusely (even slightly) enlarged pituitary gland secondary to pituitary hyperplasia without an adenoma (in 6 of 30 reported individuals with available data) Note: Although none of the reported individuals presented with a microadenoma, this presentation is theoretically possible. ... The diagnosis of X-linked acrogigantism was made at age 28 years [Iacovazzo et al 2016]. From Moran et al [1990].
-
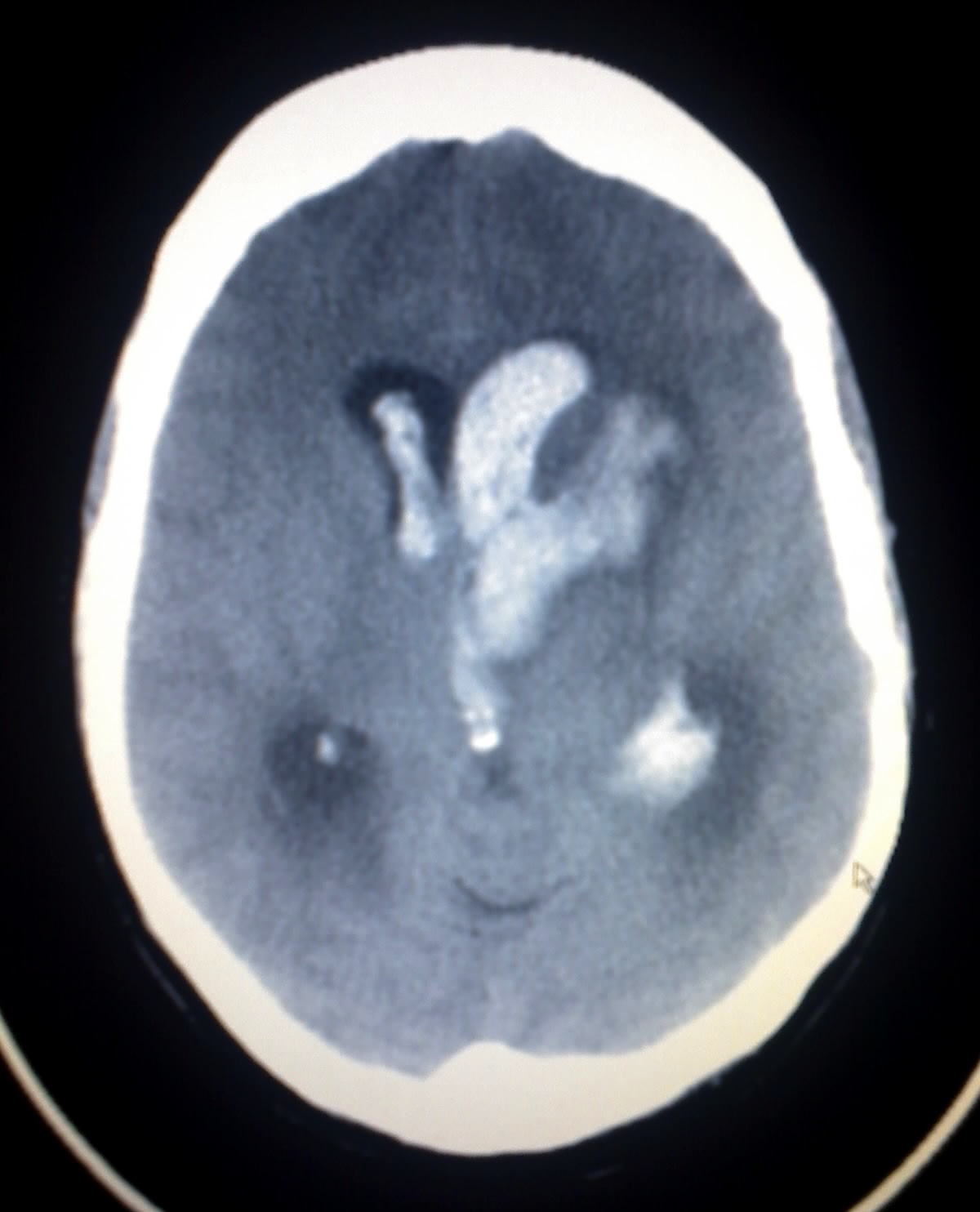
Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Wikipedia
However, in large controlled studies, corticosteroids have been found to increase mortality rates and are no longer recommended. [26] [27] Surgery [ edit ] Surgery is required if the hematoma is greater than 3 cm (1 in), if there is a structural vascular lesion or lobar hemorrhage in a young patient. [19] A catheter may be passed into the brain vasculature to close off or dilate blood vessels , avoiding invasive surgical procedures. [28] Aspiration by stereotactic surgery or endoscopic drainage may be used in basal ganglia hemorrhages, although successful reports are limited. [19] A craniectomy may take place, where part of the skull is removed to allow a swelling brain room to expand without being squeezed. ... Further reading [ edit ] Hemphill JC, 3rd; Greenberg, SM; Anderson, CS; Becker, K; Bendok, BR; Cushman, M; Fung, GL; Goldstein, JN; Macdonald, RL; Mitchell, PH; Scott, PA; Selim, MH; Woo, D (28 May 2015). "Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association" .CASP8, CASP3, FLT1, PLAT, COL4A1, S100B, ACE, F7, MMP3, COL4A2, MMP9, MMP2, VEGFA, SPP1, ITGB3, ITGAV, ITGA2B, HMOX2, KDR, CNTF, HMOX1, NPPB, BCL2L1, BCL2, BAX, SERPINC1, POMC, PLAU, IL1RN, RELB, RELA, SQSTM1, PTGS2, BECN1, MT2A, NPY, NFKBIA, MT1A, THBS2, THBS1, MMP12, NFKB2, NFKB1, SLC24A1, CXCR4, MTOR, CD14, MAP1LC3A, SLC8B1, C3, DAG1, DCX, NQO1, BNIP3L, AQP4, CASP9, CASP12, APEX1, ANXA1, APP, CST3, SDHD, SMARCB1, CCM2, PMF1-BGLAP, SDHC, SDHB, HELLPAR, FCGR2C, SLC25A44, COLGALT1, TMEM127, VHL, SDHAF2, SUFU, SLC25A11, PARVB, KIF1B, USP18, PMF1, PDCD10, SH2B3, TMEM94, SDHA, LINC02444, RET, GDNF, ABCC6, KRIT1, DLST, ENG, F13A1, F13B, FGA, FGB, FGG, FH, PTCH1, GDF2, FN1, PROS1, CFI, JAK2, SMAD4, MAX, CD46, MDH2, ACVRL1, CFH, NF2, PDGFB, APOE, SERPINA3, AGTR1, APOB, APOH, HCRT, TUBB1, MTHFR, HSPB8, IGFBP3, ESR1
-
Spastic Paraplegia 3, Autosomal Dominant
Omim
In the 12 probands and 24 affected family members, age of onset was before 10 years of age, except in 1 family with mean onset of 14 years and notable variability (range, 8 to 28 years). In addition to typical features of SPG, 6 (17%) of 36 affected individuals had an axonal, predominantly motor peripheral polyneuropathy, confirmed by pathologic and electrophysiologic studies. ... Varga et al. (2013) also identified heterozygosity for the R415W mutation in 1 of 83 Spanish patients with apparent sporadic HSP and in 2 of 28 Russian patients with dominant HSP.
-
Abortion In Spain
Wikipedia
According to Trinidad Jimenez , then Minister for Health and Social Policy of Spain, the decline was due to over-the-counter sales in pharmacies for the so-called morning-after pill which was liberalized in late September 2009. [25] [26] In Spain, the evolution of the number of abortions, according to statistics from the Ministry of Health, [27] is as follows: Year Notifiable centres of Induced abortion Number of abortions Rate per 1,000 women 1995 49,367 [28] 1996 51,002 1997 49,578 1998 117 53,847 6.00 1999 123 58,399 6.52 2000 121 63,756 7.14 2001 121 69,857 7.66 2002 124 77,125 8.46 2003 128 79,788 8.77 2004 133 84,985 [29] 8.94 2005 134 91,664 [30] 9.60 2006 135 101,592 10.62 2007 137 112,138 [31] 11.49 [32] 2008 137 115,812 11.78 2009 141 111,482 [25] [33] 11.41 2010 147 113,031 [27] [34] [35] 11.49 2011 172 118,359 [36] 12.44 2012 [27] 189 113,419 12.44 2013 [27] 198 108,690 12.12 2014 [27] 191 94,796 10.46 2015 [27] 200 94,188 10.40 2016 [27] 201 93,131 10.36 Surgical and medical abortions in Spain [ edit ] Induced abortion or termination of unwanted pregnancy can be performed by two methods: Medical abortion - Using drugs or medications such as mifepristone and misoprostol . ... Archived from the original on 2019-03-28 . Retrieved 2016-02-06 . ^ José María Garat (12 May 1937).
-
Hypophosphatasia
Wikipedia
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may improve pain-associated physical impairment and can help improve walking distance [25] ] Bisphosphonate (a pyrophosphate synthetic analog) in one infant had no discernible effect on the skeleton, and the infant’s disease progressed until death at 14 months of age. [26] Bone marrow cell transplantation in two severely affected infants produced radiographic and clinical improvement, although the mechanism of efficacy is not fully understood and significant morbidity persisted. [27] [28] Enzyme replacement therapy with normal, or ALP-rich serum from patients with Paget’s bone disease, was not beneficial. [29] [30] Phase 2 clinical trials of bone targeted enzyme-replacement therapy for the treatment of hypophosphatasia in infants and juveniles have been completed, and a phase 2 study in adults is ongoing. [31] [32] Pyridoxine, or Vitamin B6 may be used as adjunctive therapy in some cases, which may be referred to as Pyridoxine responsive seizures. [10] [33] History [ edit ] It was discovered initially in 1936 but was fully named and documented by a Canadian Pediatrician, John Campbell Rathbun (1915-1972) while examining and treating a baby boy with very low levels of alkaline phosphatase in 1948. ... "Hypophosphatasia: molecular testing of 19 prenatal cases and discussion about genetic counseling". Prenatal Diagnosis . 28 (11): 993–8. doi : 10.1002/pd.2088 .
-
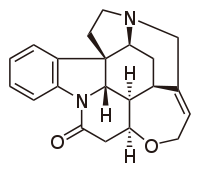
Strychnine Poisoning
Wikipedia
Retrieved 27 July 2017 . ^ Sandall, Leondard, (28 March 1896). "AN OVERDOSE OF STRYCHNINE." ... "These Old Bones" – via Slate. ^ Today's Zaman , 20 June 2013, Independent expert evaluation casts doubt on Özal report Archived 2016-03-05 at the Wayback Machine ^ Rogers, David (February 28, 2008), "Suspect in poisoned-mayor case has been arrested" , Wiener Zeitung , archived from the original on March 19, 2008 (dead link) ^ Dennis Covington, Salvation on Sand Mountain: Snake Handling and Redemption in Southern Appalachia (Reading, MA.: Addison-Wesley, 1995). ^ "The Poison That Killed A Major Game Of Thrones Character Is Real" .
-
Antenatal Depression
Wikipedia
These results are not independent of any effects of prenatal depression on infants. [28] Connection to postpartum depression and parenting stress [ edit ] Studies have found a strong link between antenatal depression and postpartum depression in women. ... "Antenatal depression: a rationale for studying exercise" . Depression and Anxiety . 28 (3): 234–42. doi : 10.1002/da.20777 .
-
Benzodiazepine Dependence
Wikipedia
The number dependent on the benzodiazepines in the UK from 1960 to 1977 has been estimated to be 28 persons. This is equivalent to a dependence rate of 5-10 cases per million patient months. ... "Testing the abuse liability of anxiolytic and hypnotic drugs in humans". Drug and Alcohol Dependence . 28 (1): 83–111. doi : 10.1016/0376-8716(91)90054-3 . ... "Benzodiazepine use, abuse, and dependence". J Clin Psychiatry . 66 (Suppl 2): 28–33. PMID 15762817 . ^ a b c d e f Allison C; Pratt JA (May 2003). ... The number dependent on the benzodiazepines in the UK from 1960 to 1977 has been estimated to be 28 persons. This is equivalent to a dependence rate of 5-10 cases per million patient months. ^ a b c Haddad P; Deakin B; Dursun S (27 May 2004). ... S2CID 20715355 . ^ a b Puri BK; Tyrer P (28 August 1998). "Clinical psychopharmacology" .
-
Abortion In Louisiana
Wikipedia
At the time the law was passed, only one doctor had this privileges, effectively leaving only one legal abortion clinic in the state. [27] The state had a law on the books in August 2018 that would be triggered if Roe v. Wade was overturned. [28] Nationally, 2019 was one of the most active years for state legislatures in terms of trying to pass abortion rights restrictions. ... That year, 63% of women in the state aged 15 – 44 lived in a county without an abortion clinic. [28] In 2017, there were two Planned Parenthood clinics in a state with a population of 1,089,684 women aged 15 – 49 of which zero offered abortion services. [38] North Dakota, Wyoming, Mississippi, Louisiana and Kentucky were the only five states as of July 21, 2017 not to have a Planned Parenthood clinic that offered abortion services. [38] Statistics [ edit ] In the period between 1972 and 1974, the state had an illegal abortion mortality rate per million women aged 15 – 44 of between 0.1 and 0.9. [39] In 1990, 489,000 women in the state faced the risk of an unintended pregnancy. [36] In 2010, the state had zero publicly funded abortions. [40] In 2001, Arizona, Florida, Iowa, Louisiana, Massachusetts, and Wisconsin did not provide any residence related data regarding abortions performed in the state to the Centers for Disease Control . [41] In 2013, among white women aged 15–19, there were abortions 290, 640 abortions for black women aged 15–19, zero abortions for Hispanic women aged 15–19, and 60 abortions for women of all other races. [42] In 2014, 39% of adults said in a poll by the Pew Research Center that abortion should be legal in all or most cases. [43] Number of reported abortions, abortion rate and percentage change in rate by geographic region and state in 1992, 1995 and 1996 [44] Census division and state Number Rate % change 1992–1996 1992 1995 1996 1992 1995 1996 US Total 1,528,930 1,363,690 1,365,730 25.9 22.9 22.9 –12 West South Central 127,070 119,200 120,610 19.6 18 18.1 –8 Arkansas 7,130 6,010 6,200 13.5 11.1 11.4 –15 Louisiana 13,600 14,820 14,740 13.4 14.7 14.7 10 Oklahoma 8,940 9,130 8,400 12.5 12.9 11.8 –5 Texas 97,400 89,240 91,270 23.1 20.5 20.7 –10 Number, rate, and ratio of reported abortions, by reporting area of residence and occurrence and by percentage of abortions obtained by out-of-state residents, US CDC estimates Location Residence Occurrence % obtained by out-of-state residents Year Ref No.
-
Streptococcal Pharyngitis
Wikipedia
Cause Strep throat is caused by group A β-hemolytic Streptococcus (GAS or S. pyogenes ). [13] Humans are the only known natural reservoir for group A streptococcus. [14] Other bacteria such as non–group A β-hemolytic streptococci and fusobacterium may also cause pharyngitis . [10] [12] It is spread by direct, close contact with an infected person; thus crowding, as may be found in the military and schools, increases the rate of transmission. [12] [15] Dried bacteria in dust are not infectious, although moist bacteria on toothbrushes or similar items can persist for up to fifteen days. [12] Contaminated food can result in outbreaks, but this is rare. [12] Of children with no signs or symptoms, 12% carry GAS in their pharynx, [7] and, after treatment, approximately 15% of those remain positive, and are true "carriers". [16] Diagnosis Modified Centor score Points Probability of Strep Management 1 or fewer <10% No antibiotic or culture needed 2 11–17% Antibiotic based on culture or RADT 3 28–35% 4 or 5 52% Empiric antibiotics A number of scoring systems exist to help with diagnosis; however, their use is controversial due to insufficient accuracy. [17] The modified Centor criteria are a set of five criteria; the total score indicates the probability of a streptococcal infection. [10] One point is given for each of the criteria: [10] Absence of a cough Swollen and tender cervical lymph nodes Temperature >38.0 °C (100.4 °F) Tonsillar exudate or swelling Age less than 15 (a point is subtracted if age >44) A score of one may indicate no treatment or culture is needed or it may indicate the need to perform further testing if other high risk factors exist, such as a family member having the disease. [10] The Infectious Disease Society of America recommends against routine antibiotic treatment and considers antibiotics only appropriate when given after a positive test. [8] Testing is not needed in children under three as both group A strep and rheumatic fever are rare, unless a child has a sibling with the disease. [8] Laboratory testing A throat culture is the gold standard [18] for the diagnosis of streptococcal pharyngitis, with a sensitivity of 90–95%. [10] A rapid strep test (also called rapid antigen detection testing or RADT) may also be used. ... However, in children a throat culture is recommended to confirm the result. [8] Asymptomatic individuals should not be routinely tested with a throat culture or RADT because a certain percentage of the population persistently "carries" the streptococcal bacteria in their throat without any harmful results. [20] Differential diagnosis See also: Acute pharyngitis As the symptoms of streptococcal pharyngitis overlap with other conditions, it can be difficult to make the diagnosis clinically. [10] Coughing, nasal discharge, diarrhea , and red, irritated eyes in addition to fever and sore throat are more indicative of a viral sore throat than of strep throat. [10] The presence of marked lymph node enlargement along with sore throat, fever, and tonsillar enlargement may also occur in infectious mononucleosis . [21] Other conditions that may present similarly include epiglottitis , Kawasaki disease , acute retroviral syndrome , Lemierre's syndrome , Ludwig's angina , peritonsillar abscess , and retropharyngeal abscess . [5] Prevention Tonsillectomy may be a reasonable preventive measure in those with frequent throat infections (more than three a year). [22] However, the benefits are small and episodes typically lessen in time regardless of measures taken. [23] [24] [25] Recurrent episodes of pharyngitis which test positive for GAS may also represent a person who is a chronic carrier of GAS who is getting recurrent viral infections. [8] Treating people who have been exposed but who are without symptoms is not recommended. [8] Treating people who are carriers of GAS is not recommended as the risk of spread and complications is low. [8] Treatment Untreated streptococcal pharyngitis usually resolves within a few days. [10] Treatment with antibiotics shortens the duration of the acute illness by about 16 hours. [10] The primary reason for treatment with antibiotics is to reduce the risk of complications such as rheumatic fever and retropharyngeal abscesses . [10] Antibiotics prevent acute rheumatic fever if given within 9 days of the onset of symptoms. [13] Pain medication Pain medication such as NSAIDs and paracetamol (acetaminophen) helps in the management of pain associated with strep throat. [26] Viscous lidocaine may also be useful. [27] While steroids may help with the pain, [13] [28] they are not routinely recommended. [8] Aspirin may be used in adults but is not recommended in children due to the risk of Reye syndrome . [13] Antibiotics The antibiotic of choice in the United States for streptococcal pharyngitis is penicillin V , due to safety, cost, and effectiveness. [10] Amoxicillin is preferred in Europe. [29] In India, where the risk of rheumatic fever is higher, intramuscular benzathine penicillin G is the first choice for treatment. [13] Appropriate antibiotics decrease the average 3–5 day duration of symptoms by about one day, and also reduce contagiousness. [20] They are primarily prescribed to reduce rare complications such as rheumatic fever and peritonsillar abscess . [30] The arguments in favor of antibiotic treatment should be balanced by the consideration of possible side effects, [12] and it is reasonable to suggest that no antimicrobial treatment be given to healthy adults who have adverse reactions to medication or those at low risk of complications. [30] [31] Antibiotics are prescribed for strep throat at a higher rate than would be expected from how common it is. [32] Erythromycin and other macrolides or clindamycin are recommended for people with severe penicillin allergies . [10] [8] First-generation cephalosporins may be used in those with less severe allergies [10] and some evidence supports cephalosporins as superior to penicillin. [33] [34] These late-generation antibiotics show a similar effect when prescribed for 3–7 days in comparison to the standard 10-days of penicillin when used in areas of low rheumatic heart disease. [35] Streptococcal infections may also lead to acute glomerulonephritis ; however, the incidence of this side effect is not reduced by the use of antibiotics. [13] Prognosis The symptoms of strep throat usually improve within three to five days, irrespective of treatment. [20] Treatment with antibiotics reduces the risk of complications and transmission; children may return to school 24 hours after antibiotics are administered. [10] The risk of complications in adults is low. [8] In children, acute rheumatic fever is rare in most of the developed world.
-
Frailty Syndrome
Wikipedia
Researchers tested this model for signal in routinely collected hospital data, [25] and then used this signal in the development of a frailty model, finding even predictive capability across 3 outcomes of care. [26] In the care home setting, one study indicated that not all four domains of frailty were routinely assessed in residents, giving evidence to suggest that frailty may still primarily be viewed only in terms of physical health. [27] SHARE Frailty Index [ edit ] The SHARE-Frailty Index (SHARE-FI) was originally developed by Romero-Ortuno (2010) [28] and researchers as part of the Survey of Healthy Ageing and Retirement in Europe. ... Journal of the American College of Surgeons . 210 (6): 901–8. doi : 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2010.01.028 . PMID 20510798 . Lay summary (28 December 2010). ^ Fried LP, Ferrucci L, Darer J, Williamson JD, Anderson G (March 2004).
-
Overjet
Wikipedia
There appears to be no other advantage for providing early treatment'. [5] Epidemiology [ edit ] Class II Div I [ edit ] This malocclusion is common, with an estimated prevalence of 15−20%. [28] There is racial variation with Class II division 1 more common in Caucasian than Latin American, Middle Eastern and Asian populations, and lowest in Black racial groups. [5] History [ edit ] Class II div 1 [ edit ] Functional appliances: The first reported use of a mandibular positioning device was the 'Monobloc' by Dr Robin, in France in 1902, for neonates with under-developed mandibles. ... [viewed 7 January 2018] Available from https://www.bos.org.uk ^ Mandal, Ananya (28 June 2019). "What is Orthodontics?"
-
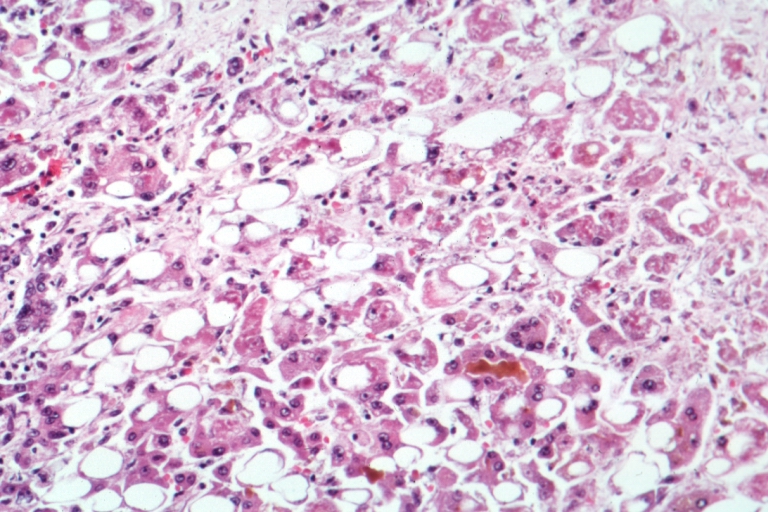
Alcoholic Liver Disease
Wikipedia
"Alcoholic liver disease: AASLD Practice Guidelines" (PDF) . Hepatology . 51 (1): 307–28. doi : 10.1002/hep.23258 . PMID 20034030 . ... PMID 17045579 . ^ a b c Suk, KT; Kim, MY; Baik, SK (28 September 2014). "Alcoholic liver disease: treatment" .PNPLA3, SPP1, PPARD, RBP4, CYP2E1, TNF, HFE, IL1B, HIF1A, CXCL1, MIF, EIF2S1, CXCL6, CD59, CD27, CAV1, CXCL2, LPL, MMP9, SLC39A13, PSMD14, IGF2, UCHL5, TBXAS1, OTC, ALDH2, TLR4, HAMP, CD14, GSTM1, AKR1A1, ADH1B, IL10, IL6, SIRT1, TM6SF2, ADH1C, GPT, HLA-A, CCL2, NFE2L2, HPGDS, TGFB1, STAT3, AVP, PPARA, IL1RN, ABCD1, IL1A, MIR21, AKT1, ADIPOQ, GOLM1, AFP, CXCL8, IL22, RIPK3, MPRIP, ST8SIA4, HMGB1, ELANE, ACTB, SOD2, GSTT1, HSD17B13, CNR1, NR1H4, GABPA, SIRT3, PPIG, ZEB2, TRPV1, XPR1, CHST3, YME1L1, NAMPT, MYOM2, FST, NR1I2, ABCB11, ARID1A, AKT3, XBP1, NAT2, SF3B3, MIR155, DOCK11, CERS6, PCSK9, HCAR2, FFAR4, GSTK1, MIR122, MIR200A, CLEC4E, MIR203A, MIR212, MIR223, MIR30E, MIR34A, MIR570, KRT8P3, SLCO6A1, REG3G, TNFRSF13C, IL33, FGF21, IL37, IL19, NOX4, DERL2, UROD, PIWIL2, RETN, SPHK2, NXN, DEPTOR, MBOAT7, LIN28A, HDAC11, PPP1R2C, VLDLR, PPARG, UCP2, UCHL1, NCAN, CCN2, CTLA4, CYP1A1, ACE, DDIT3, EGR1, EPHX1, MTOR, FUT1, GLS, GSTA4, GSTP1, HK2, HLA-DOA, MAPK14, CEACAM5, CDKN2A, AKT2, PLIN2, ADH1A, ADH4, ADH5, ADM, AGTR1, ALDH1A1, CASP1, ALDH1B1, AKR1B1, ALOX15, APOA1, ARNTL, ARRB2, HSPA5, HSPG2, IL1R1, CCL5, PMS2, PSMC5, ROS1, S100A4, SAA1, SAA2, SELE, PIK3CD, SFRP5, ST6GAL1, SKP2, STIM1, TGFA, TLR2, PIK3CG, PIK3CB, IL2, LEP, IL6ST, IL12B, IL16, IRF3, KRT8, KRT18, MAT1A, PIK3CA, MIP, MSH2, MUC2, NFE2, NFKB1, P2RX7, PSC
-
Delirium Tremens
Wikipedia
. ^ Summary and analysis of novel Archived 2011-06-28 at the Wayback Machine ^ Bailey, Blake. ... Archived 2016-04-13 at the Wayback Machine , Vanity Fair (magazine) , February 28, 2013. Accessed February 15, 2017.
-
Uterine Atony
Wikipedia
If the bleeding has not stopped or physical exam does not show signs of restored uterine function within 30 minutes of medication administration, immediate invasive interventions are recommended. [28] [1] Tamponade techniques include uterine packing (extending into the vagina) with gauze that also has a Foley catheter in place to allow for bladder drainage. It is inexpensive and readily available. [1] [16] Balloon tamponade is the suggested method of tamponade in guidelines for management of PPH. [29] A bakri balloon to tamponade (also with vaginal packing) can be used with Foley catheter insertion to facilitate bladder drainage. [1] [30] Vacuum-induced uterine tamponade is newer technique that uses low-level vacuum to evacuate blood from the uterine cavity and facilitate uterine contraction [31] Surgical management techniques include: Compression sutures such as the B-Lynch [1] [28] Uterine curettage to remove retained placental products [1] [32] Uterine artery ligation, with or without ligation of the tubo-ovarian vessels. [1] [33] Ligation of the uterine and utero-ovarian arteries can decrease uterine bleeding by reducing the pressure of arterial blood flow in the uterus.
-
Spectrum Disorder
Wikipedia
Schizophrenia-like personality disorders [ edit ] Schizoid personality disorder , schizotypal personality disorder and paranoid personality disorder can be considered 'schizophrenia-like personality disorders' because of their links to the schizophrenia spectrum. [27] Mood [ edit ] A mood disorder ( affective ) spectrum [28] or bipolar spectrum [2] or depressive spectrum. [29] These approaches have expanded out in different directions. ... "Autism spectrum disorders". Neuron . 28 (2): 355–63. doi : 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)00115-X .