-
Tetralogy Of Fallot
Wikipedia
Retrieved 2009-01-02 . ^ Russell, Mark W.; Chung, Wendy K.; Kaltman, Jonathan R.; Miller, Thomas A. ... PMID 29523523 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Munoz R, Morell V, Cruz E, Vetterly C (2010). ... PMID 14517948 . ^ Lambrechts D, Devriendt K, Driscoll DA, Goldmuntz E, Gewillig M, Vlietinck R, et al. ... PMC 325224 . PMID 7787464 . ^ Farouk A, Zahka K, Siwik E, Erenberg F, Al-Khatib Y, Golden A, et al.ZFPM2, NKX2-5, JAG1, GATA4, TBX1, GATA6, GDF1, GJA5, CITED2, FLT4, GATA5, NKX2-6, FOXC2, FOXH1, HAND2, FGF8, FOXC1, HEY2, MKS1, BMP10, NTF3, INVS, DNAH5, PHC1, DOCK1, NRP1, HIRA, UFD1, NOTCH1, COMT, PTPN11, FN1, TAB2, MKKS, RFC2, RET, NOTCH2, NODAL, UBE2T, INTU, ROR2, CCDC22, SPECC1L, RAD51C, RAD51, DLL1, PTCH1, PIGN, NIPBL, RPH3A, TBL2, PAH, HIBCH, ATXN2, CERS1, RPL5, TDGF1, GTF2IRD1, PIGL, NR2F2, TGIF1, TPM1, UBE2A, SLC35A2, BAZ1B, CLIP2, WT1, XRCC2, ZIC2, CXCR4, ALX1, SEC24C, TTC37, SEMA3E, SIX3, RREB1, MAD2L2, SF3B4, SALL1, CDON, SHH, SKI, TMEM94, SKIV2L, PQBP1, SH2B3, RBM8A, WASHC5, FIG4, NID1, LINC02676, DACT1, STRA6, DDX59, NAA25, EHMT1, PALB2, CRELD1, NXN, ELN, SLX4, EPHB4, ERCC4, PRDM16, FANCM, FANCA, COX3, BRIP1, DISP1, FANCE, BRAF, ZFPM2-AS1, RNU4ATAC, ALX3, ARVCF, RERE, BRCA1, BRCA2, COL2A1, EOGT, MYRF, HECTD4, JMJD1C, CHD4, CHRM3, FANCD2, FANCC, FANCB, SALL4, COX2, COX1, SUFU, RAB23, DLL4, KCNAB2, FANCL, RFWD3, FANCI, CHD7, LIMK1, VAC14, FANCF, HDAC8, RBPJ, RBM10, FOXF1, FANCG, GTF2I, ARID1B, DOCK6, GP1BB, GLI2, ARHGAP31, FGFR1, GPC5, GAS1, GABRD, VEGFA, TBX20, CHDH, HAND1, GJA1, KDR, TGFB1, VANGL2, MIR421, MIR1233-1, SULT1E1, MTHFR, APOE, HIF1A, REN, PVR, PITX2, MMP9, NPPB, MEIS2, FBN2, MAVS, GPR42, HAS2, MMP3, HOXA1, ACKR3, DGCR8, MMP2, HTC2, JARID2, FBN1, LPA, LRPAP1, LSAMP, MAP4, MBNL1, FEZF2, SLC50A1, IQGAP1, F5, TSPYL2, ADRA2B, AGT, ALDH2, MIR625, MIR424, BRS3, CAD, CD48, CRKL, CRP, CYBA, ACE, DMD, FSD1L, DNAH8, DNMT1, DNMT3B, DNTT, CORO7, FSD1, DVL2, EDNRA, EGF, F2, MYL4, CHMP5, TCF21, SLN, SNAI2, SCO2, REC8, SMN1, SMN2, SSTR4, ADRA1A, TADA2A, TBX5, RGS6, WNT11, TFAP2B, CHD1L, TFAP2C, TTN, VIM, LPAR2, BEST1, MBD2, AVSD1, ALDH1A2, MBNL2, ACSM3, RYR2, RXRA, NTRK3, OPRD1, PBX1, PBX3, PDGFA, LAMP3, PECAM1, AATF, PFKL, SUN2, PLN, PTH, DICER1, RASA1, MMRN1, ROBO1, BVES, WWP2, PPARGC1A, ROCK1, CXCR6, ACTC1
-
Agoraphobia
Wikipedia
Towards the end of his life, he acquired some control over the condition. [ citation needed ] Daryl Hannah (b. 1960), American actress [51] Howard Hughes (1905–1976), American aviator , industrialist , film producer and philanthropist [52] Olivia Hussey (b. 1951), Anglo-Argentine actress [53] [54] Shirley Jackson (1916–1965), American writer – her agoraphobia is considered to be a primary inspiration for the novel We Have Always Lived in the Castle . [55] [56] Elfriede Jelinek (b. 1946), Austrian writer, Nobel Prize laureate in Literature in 2004 [57] Bolesław Prus (1847–1912), Polish journalist and novelist [58] Peter Robinson (b. 1962), British musician known as Marilyn [59] Brian Wilson (b. 1942), American singer and songwriter, primary songwriter of the Beach Boys, a former recluse and agoraphobic who has schizophrenia [60] See also [ edit ] Hikikomori List of phobias References [ edit ] ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x American Psychiatric Association (2013), Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.) , Arlington: American Psychiatric Publishing, pp. 217–221, 938 , ISBN 978-0890425558 ^ a b c "Agoraphobia" . ... PMID 2886145 . ^ Cosci F, Schruers KR, Abrams K, Griez EJ (June 2007). "Alcohol use disorders and panic disorder: a review of the evidence of a direct relationship". ... PMID 17592911 . ^ Cosci F, Knuts IJ, Abrams K, Griez EJ, Schruers KR (May 2010). ... Attachment and Loss (Vol. 2: Separation). ^ Jacobson K (2004). "Agoraphobia and Hypochondria as Disorders of Dwelling".
-
Tracheobronchial Injury
Wikipedia
PMID 17767714 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x Chu CP, Chen PP (2002). ... PMID 12002920 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u Johnson SB (2008). ... PMID 18420127 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Stark P (1995). "Imaging of tracheobronchial injuries". ... PMID 3283046 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y Karmy-Jones R, Wood DE (2007). ... PMID 11463564 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Euathrongchit J, Thoongsuwan N, Stern EJ (2006).
-
Viral Disease
Wikipedia
University of South Carolina School of Medicine. ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg ch ci cj ck cl cm cn co cp cq cr cs ct cu cv cw cx cy cz da db dc dd de df dg dh di dj dk dl dm dn do dp dq dr ds dt du dv dw dx dy dz ea eb ec ed ee ef eg eh ei ej ek el em en eo ep eq er es et eu ev ew ex ey ez fa fb fc fd fe ff fg fh fi fj fk fl fm fn fo fp fq fr fs ft fu fv fw fx fy fz ga gb gc gd ge gf gg gh gi Fisher, Bruce; Harvey, Richard P.; Champe, Pamela C. (2007). ... Retrieved 7 September 2020 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am Table 1 in: Dimitrov, Dimiter S. (2004). ... PMID 21994671 . ^ Cook, S.; Moureau, G.; Harbach, R. E.; Mukwaya, L.; Goodger, K.; Ssenfuka, F.; Gould, E.; Holmes, E. ... PMID 25183845 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p "Herpesviridae" . ViralZone .
-
Medical Abortion
Wikipedia
ISSN 0010-7824 . PMID 23756114 . ^ Gambir, K; Kim, C; Necastro, KA; Ganatra, B; Ngo, TD (March 9, 2020). ... CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list ( link ) 20.237% Mifegyne + 3.021% Medikamentöser Abbruch = 23.257% medical abortions ^ a b Jones, Rachel K.; Witwer, Elizabeth; Jerman, Jenna (2019). ... Helsinki: Suomen virallinen tilasto (Official Statistics of Finland), Terveyden ja hyvinvoinnin laitos (National Institute for Health and Welfare), Finland. ^ Jones, Rachel K.; Jerman, Jenna (January 17, 2017). ... This study could end the debate" . April 17, 2019. ^ Jones, Rachel K.; Kooistra, Kathryn (March 2011). ... The Washington Post . p. A3. ^ Jones, Rachel K.; Finer, Lawrence B.; Singh, Shusheela (May 4, 2010).
-
Vocal Cord Dysfunction
Wikipedia
An overall prevalence of 2.5% has been reported in patients presenting with asthma. [19] Among adults with asthma considered "difficult to control", 10% were found to have VCD while 30% were found to have both VCD and asthma. [6] Among children with severe asthma, a VCD prevalence rate of 14% has been reported. [6] However, higher rates have also been reported; among one group of schoolchildren thought to suffer from exercise-induced asthma, it was found that 26.9% actually had VCD and not asthma. [4] Among intercollegiate athletes with exercise-induced asthma, the VCD rate has been estimated at 3%. [4] In patients presenting with symptoms of dyspnea, prevalence rates ranging from 2.8% to 22% have been reported in various studies. [6] [4] [19] It has been reported that two to three times more females than males suffer from VCD. [6] [4] [25] VCD is especially common in females who suffer from psychological problems. [4] There is an increased risk associated with being young and female. [4] Among patients suffering from VCD, 71% are over the age of 18. [6] In addition, 73% of those with VCD have a previous psychiatric diagnosis. [6] VCD has also been reported in newborns with gastroesophageal reflux disorder (GERD). [4] See also [ edit ] Puberphonia References [ edit ] ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Colton RH, Casper JK, Leonard R (2011). ... Retrieved 26 September 2018 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac Ibrahim WH, Gheriani HA, Almohamed AA, Raza T (March 2007). ... PMID 17344570 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Deckert J, Deckert L (2010). ... PMID 20082511 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y Gimenez LM, Zafra H (April 2011).
-
Sunburn
Wikipedia
. ^ Premi S, Han L, Mehta S, Knight J, Zhao D, Palmatier MA, Kornacker K, Brash DE. Genomic sites hypersensitive to ultraviolet radiation. ... PMC 3232447 . PMID 21734176 . ^ a b c d e Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra A (2013). Fitzpatrick's color atlas and synopsis of clinical dermatology (7th ed.). ... ISBN 978-0-07-179302-5 . OCLC 813301093 . ^ Wolff, K, ed. (2017). "PHOTOSENSITIVITY, PHOTO-INDUCED DISORDERS, AND DISORDERS BY IONIZING RADIATION" . ... Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJ, Stephens K, Amemiya A (eds.). GeneReviews® . ... PMID 17914160 . S2CID 22417600 . ^ Schagen, S. K.; Zampeli, V. A.; Makrantonaki, E.; Zouboulis, C.
-
Cystocele
Wikipedia
More recently, the use of stem cells, robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery are being used to treat cystocele. [37] See also [ edit ] Hysterectomy Fecal incontinence Sigmoidocele Urethropexy References [ edit ] ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab "Cystocele (Prolapsed Bladder)" . ... Archived from the original on 2017-10-25. ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Williams, J. Whitridge (2012). ... PMID 29214325 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Henry, Norma Jean E (2016). RN adult medical surgical nursing review module (10th ed.). ... OCLC 779244257 . ^ a b Rahn, David D.; Ward, Renée M.; Sanses, Tatiana V.; Carberry, Cassandra; Mamik, Mamta M.; Meriwether, Kate V.; Olivera, Cedric K.; Abed, Husam; Balk, Ethan M. (2015-01-01). ... J. M.; Withagen, M. I. J.; Kluivers, K. B.; Milani, A. L.; Vierhout, M. E. (2013-10-01).
-
Vertebral Artery Dissection
Wikipedia
The ball struck Hughes on the base of the skull just behind his left ear which caused a vertebral artery dissection complicated by subarachnoid hemorrhage . [22] References [ edit ] ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq Kim YK, Schulman S (April 2009). ... PMID 19269682 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Debette S, Leys D (July 2009). ... PMID 19539238 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Campos-Herrera CR, Scaff M, Yamamoto FI, Conforto AB (December 2008). ... PMID 24300790 . ^ a b c Haynes MJ, Vincent K, Fischhoff C, Bremner AP, Lanlo O, Hankey GJ (2012).
-
Transmission And Infection Of H5n1
Wikipedia
Avian influenza – epidemiology of human H5N1 cases reported to WHO The regression curve for deaths is y = a + e k x , and is shown extended through the end of April, 2007. ... A Colour Atlas and Text on Avian Influenza : 13–20. ^ S. Bano S; K. Naeem K; S.A. Malik (2003). "Evaluation of pathogenic potential of avian influenza virus serotype H9N2 in chicken" . ... Archived from the original on 2007-10-17. ^ C Li; K Yu; G TiaG; D Yu; L Liu; B Jing; J Ping; H.
-
Hyperthymesia
Wikipedia
It is also open to question how far it is an all-or-none condition, or whether people can have the condition to different degrees. K. Anders Ericsson of Florida State University does not believe that sufficient evidence exists to suggest that the skills of AJ and Williams need additional explanation: "Our work has pretty much concluded that differences in memory don't seem to be the result of innate differences, but more the kinds of skills that are developed." [39] McGaugh rejects the idea that hyperthymestic syndrome can be explained away so easily; he argues that nothing explains how subjects are able to memorize so much: "You'd have to assume that every day they rehearse it... ... His hyperthymesia memories are visually depicted in the movie as "screens" appearing to Keegan, often in an overwhelming and distressing manner. [44] See also [ edit ] Daniel McCartney Hypermnesia Eidetic memory References [ edit ] ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Parker ES, Cahill L, McGaugh JL (February 2006). ... PMID 16806314 . ^ a b Patihis, L.; Frenda, S. J.; LePort, A. K. R.; Petersen, N.; Nichols, R. M.; Stark, C. ... Ceci Susan Clancy Hermann Ebbinghaus Sigmund Freud Patricia Goldman-Rakic Jonathan Hancock Judith Lewis Herman HM (patient) Ivan Izquierdo Marcia K. Johnson Eric Kandel KC (patient) Elizabeth Loftus Geoffrey Loftus Chris Marker James McGaugh Paul R.
-
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Wikipedia
CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list ( link ) ^ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 601104 ^ Josephs, K. A.; Ishizawa, T.; Tsuboi, Y.; Cookson, N.; Dickson, D. ... PMID 11912113 . ^ Amano N, Iwabuchi K, Yokoi S, Yagishita S, Itoh Y, Saitoh A, et al. ... S2CID 20275104 . ^ Hattori M, Hashizume Y, Yoshida M, Iwasaki Y, Hishikawa N, Ueda R, Ojika K (August 2003). "Distribution of astrocytic plaques in the corticobasal degeneration brain and comparison with tuft-shaped astrocytes in the progressive supranuclear palsy brain". ... PMID 20129321 . S2CID 33349776 . ^ Abe K (January 2008). "Zolpidem therapy for movement disorders". ... Retrieved 2020-12-09 . ^ https://www.independent.ie/life/health-wellbeing/health-features/i-dont-want-to-believe-i-have-an-incurable-brain-disease-but-i-know-i-have-former-rte-presenter-kieron-wood-38614857.html ^ Tomita S, Oeda T, Umemura A, Kohsaka M, Park K, Yamamoto K, et al. (August 13, 2015).MAPT, STX6, MOBP, EIF2AK3, SRSF2, TRA2B, SLCO1A2, TRIM11, SP1, PSPH, REG1A, SNCA, RIDA, STXBP3, MSMB, PSPN, TPO, CD8B, ASAP1, RUNX2, BPIFA2, PIK3C2G, IRF4, APOE, SLC6A3, TARDBP, LRRK2, NEFL, SOD1, CIT, C9orf72, CSF2, MAOB, GRN, LAMC2, DCTN1, STH, SMUG1, PRKN, UBB, PYCARD, NPC1, APP, TYMS, CRHR1, TH, TGM2, SLC25A38, ATXN2, GFAP, IGLON5, CST3, NPEPPS, VEGFA, RAB35, YWHAE, OGA, CXCR4, PICALM, NPC2, SNCAIP, BSN, MAP3K14, OPN1MW3, DUSP10, ARL17B, ROCK2, SCRN1, MAP4K4, NF1P1, UNC13A, DNAJB1P1, FLAD1, UBASH3B, SPECC1, FOXP2, RMDN2, ASXL1, MCIDAS, SETX, MIR132, MIR518E, GGTLC5P, GGTLC3, GGT2, OPN1MW2, CTNNBL1, SYBU, PSPC1, RMDN3, LRRC37A4P, TET2, TMEM106B, TREM2, LCMT1, PPME1, RMDN1, GGTLC4P, PSAT1, TBK1, CSDC2, LMOD1, SF3B1, MINK1, NAT1, TPI1, OPN1MW, FMR1, MTOR, FUS, GABPA, GABRG2, GBA, GGT1, EGFR, GLDC, GSTM1, NRG1, HSPA4, DNAJB1, IFNG, ERBB4, DLX1, IGFALS, CASP3, AP2A2, ANXA6, KLK3, BDNF, BNIP1, BRCA1, CBS, ACE, CDK5, CHI3L1, CLU, CRP, CTSS, CYP2D6, IGF1, IL2, TP53BP1, MAP2K4, PSEN2, PTEN, PTPRC, RAPSN, ROCK1, ATXN8OS, NAT2, PROS1, SPOCK1, SPP1, TCOF1, TGFB1, TGM1, TNF, PSEN1, PRNP, IL6, NR4A2, IRS1, MUSK, NFE2L2, NGF, NOS1, NSF, PAEP, PTPA, PAFAH1B1, PDK1, PIN1, PLAG1, PLCG2, PLXNA2, ATXN2-AS
-
Helminthiasis
Wikipedia
PMID 23285307 . ^ a b Lustigman S.; Prichard R. K.; Gazzinelli A.; Grant W. N.; Boatin B. ... ISBN 978-9241547109 . ^ Prichard R. K.; Basáñez M. G.; Boatin B. A.; McCarthy J. ... PMID 26063472 . ^ a b Lustigman S.; Prichard R. K.; Gazzinelli A.; Grant W. N.; Boatin B. ... PMID 22325616 . ^ Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Foreman, K.; Lim, S.; Shibuya, K.; Aboyans, V.; Abraham, J.; Adair, T.; et al. (15 December 2012). ... "Helminths" . In Kayser, F. H.; Bienz, K. A.; Eckert, J.; Zinkernagel, R. M.IL4, IL13, IL5, IL10, IL33, IL9, IFNG, IL25, IL17A, FOXP3, MYDGF, CCL11, BCL11B, NELFCD, GREM1, PRDX5, NMUR1, ADIPOQ, IL1RL1, ABO, FBXW7, EOMES, SUCNR1, RETN, CYSLTR2, CLEC7A, NBEAL1, FUZ, SETD7, NLRP3, LINGO2, SERPINA13P, SUCLA2, STAT6, TYROBP, FCER2, AGXT, ARNTL, TNFRSF8, TNFSF8, CD38, CRP, CSF2, CTSB, EGFR, MS4A2, GAMT, TNFRSF4, GLB1, IL1A, IL1B, IL4R, ITGAX, LTBR, SERPINA1, ADCY9, TGFB1, TNFSF4, MIR155
-
Lassa Fever
Wikipedia
The chip model has been used to show the therapeutic effects of FX-06 for Lassa virus disease. [45] References [ edit ] ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af "Lassa fever" . ... S2CID 31217913 . ^ a b c d Richmond, J. K.; Baglole, D. J. (2003). "Lassa fever: Epidemiology, clinical features, and social consequences" . ... C.; Imomeh, P.; Odike, M. A.; Gire, S.; Andersen, K.; Sabeti, P. C.; Happi, C. T.; Akpede, G. ... A.; Scribner, C. L.; Craven, R. B.; Johnson, K. M.; Elliott, L. H.; Belmont-Williams, R. (2 January 1986).
-
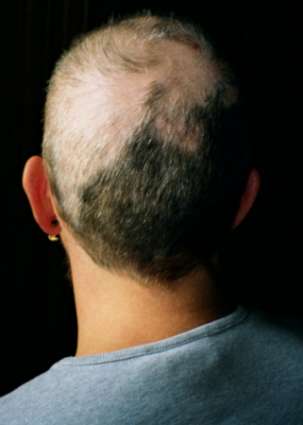
Trichotillomania
Wikipedia
Trichotillomania Other names Trichotillosis, hair pulling disorder, [1] compulsive hair pulling A pattern of incomplete hair loss on the scalp of a person with trichotillomania Pronunciation / ˌ t r ɪ k ə ˌ t ɪ l ə ˈ m eɪ n i ə / TRIK -ə- TIL -ə-MAY-NEE-ə Specialty Dermatology , psychiatry Symptoms Visible hair loss , distress [1] [2] Usual onset Childhood or adolescence [2] Risk factors Family history, anxiety , obsessive compulsive disorder [1] Diagnostic method Based on symptoms, seeing broken hairs [1] Differential diagnosis Body dysmorphic disorder [1] Medication Cognitive behavioral therapy , clomipramine [3] Frequency ~2% [2] [3] Trichotillomania ( TTM ), also known as hair pulling disorder or compulsive hair pulling , is a mental disorder characterized by a long-term urge that results in the pulling out of one's hair . [2] [4] This occurs to such a degree that hair loss can be seen. [2] A brief positive feeling may occur as hair is removed. [5] Efforts to stop pulling hair typically fail. ... ISBN 9780520255678 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z Chamberlain SR, Menzies L, Sahakian BJ, Fineberg NA (April 2007). ... PMID 17403968 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa Sah, Deborah E; Koo, John; Price, Vera H (January 2008). ... PMID 19505779 . ^ a b c d e Tay, Y.-K.; Levy, M. L.; Metry, D. W. (30 April 2004).
-
Lichen Sclerosus
Wikipedia
Br J Dermatol . 150 (1): 168–169. doi : 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.05707.x . PMID 14746647 . ^ Eisendle, K; Grabner, TG; Kutzner, H (2008). "Possible Role of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato Infection in Lichen Sclerosus" . ... PMID 26070005 . ^ Fistarol, Susanna K.; Itin, Peter H. (2012). "Diagnosis and Treatment of Lichen Sclerosus" . ... PMID 23329078 . ^ Smith, Yolanda R; Haefner, Hope K (2004). "Vulvar Lichen Sclerosus". ... PMID 16831147 . ^ Fistarol, Susanna K (2013). "Diagnosis and treatment of lichen sclerosus: an update" .TP53, CDKN2A, ECM1, H3P10, TNF, IL1B, CAT, RBP2, S100A7, CCL4, CCL4L2, SOD1, TRBV20OR9-2, THBS1, RARB, PTGS1, CRISP2, ARHGEF1, FSCN1, RASSF2, SERPINA1, MMRN1, CADM1, KRT20, MIB1, SPZ1, MIR155HG, PRSS55, CXCL17, CCL4L1, MIR155, LINC01191, DEFB4B, PTCH1, AFM, PCNA, IL1A, CCND1, CALCA, MS4A1, CRABP2, CCN2, DEFB4A, FLG, GATA3, CXCR3, GZMB, HLA-B, HSPA4, IL1RN, AR, IL13, CXCL10, IRF6, KRAS, KRT1, KRT17, SMAD3, MAL, MGMT, MKI67, MMP9, COX1, MUC2
-
Aspirin Exacerbated Respiratory Disease
Wikipedia
. ^ Kalaria RN, Maestre GE, Arizaga R, Friedland RP, Galasko D, Hall K, Luchsinger JA, Ogunniyi A, Perry EK, Potocnik F, Prince M, Stewart R, Wimo A, Zhang ZX, Antuono P (September 2008). ... PMID 12421891 . ^ Cowburn AS, Sladek K, Soja J, Adamek L, Nizankowska E, Szczeklik A, Lam BK, Penrose JF, Austen FK, Holgate ST, Sampson AP (February 1998). ... August 3, 2018. ^ Glicksman JT, Parasher AK, Doghramji L, Brauer D, Waldram J, Waters K, Bulva J, Palmer JN, Addapa ND, White AA, Bosso JV (July 2018). ... S2CID 12166132 . ^ Bochenek G, Bánska K, Szabó Z, Nizankowska E, Szczeklik A (March 2002).
-
Birt–hogg–dubé Syndrome
Wikipedia
Homozygotes die in utero. [3] References [ edit ] Citations ^ a b c Genetics Home Reference . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Andrews 2011 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Reese et al. 2009 . ^ a b c d e f Palmirotta et al. 2010 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y Toro 2008 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Menko et al. 2009 . ^ a b Chan-Smutko 2012 , p. 345. ^ a b c d e f g Coleman & Russo 2009 , p. 482. ^ a b Furuya & Nakatani 2012 . ^ Grant, Babar & Griffin 2009 , p. 442. ^ Devine & Garcia 2012 , p. 4. ^ Coleman & Russo 2009 , p. 481. ^ Nickerson et al. 2002 . ^ a b c d e Toro et al. 2008 . ^ a b Maher 2011 . ^ Sudarshan et al. 2013 . ^ Napolitano G, Di Malta C, Esposito A, de Araujo MEG, Pece S, Bertalot G, Matarese M, Benedetti V, Zampelli A, Stasyk T, Siciliano D, Venuta A, Cesana M, Vilardo C, Nusco E, Monfregola J, Calcagnì A, Di Fiore PP, Huber LA, Ballabio A (September 2020).
-
Diffuse Panbronchiolitis
Wikipedia
S2CID 23668839 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Poletti V, Casoni G, Chilosi M, Zompatori M (October 2006). ... PMID 17012632 . ^ a b c d e Yanagihara K, Kadoto J, Kohno S (2001). "Diffuse panbronchiolitis--pathophysiology and treatment mechanisms". ... The major histocompatibility complex: its genes and their roles in antigen presentation . 15 . Pergamon. ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Keicho N, Hijikata M (May 2011). "Genetic predisposition to diffuse panbronchiolitis" . ... PMID 8977613 . ^ Yamanaka A, Saiki S, Tamura S, Saito K (March 1969). "[Problems in chronic obstructive bronchial diseases, with special reference to diffuse panbronchiolitis]".
-
Coeliac Disease
Wikipedia
Autoimmune disorder that results in a reaction to gluten Coeliac disease Other names Celiac sprue, nontropical sprue, endemic sprue, gluten enteropathy Biopsy of small bowel showing coeliac disease manifested by blunting of villi , crypt hypertrophy , and lymphocyte infiltration of crypts Pronunciation / ˈ s iː l i æ k / SEE -lee-ak Specialty Gastroenterology , internal medicine Symptoms None or non-specific , abdominal distention , diarrhoea , constipation , malabsorption , weight loss, dermatitis herpetiformis [1] [2] Complications Iron-deficiency anemia , osteoporosis , infertility , cancers , neurological problems , other autoimmune diseases [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] Usual onset Any age [1] [8] Duration Lifelong [6] Causes Reaction to gluten [9] Risk factors Genetic predisposition , type 1 diabetes , autoimmune thyroid disease , Down and Turner syndromes , Diagnostic method Family history , blood antibody tests, intestinal biopsies , genetic testing , response to gluten withdrawal [10] [11] Differential diagnosis Inflammatory bowel disease , intestinal parasites , irritable bowel syndrome , cystic fibrosis [12] Treatment Gluten-free diet [13] Frequency ~1 in 135 [14] Coeliac disease or celiac disease is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the small intestine . [10] Classic symptoms include gastrointestinal problems such as chronic diarrhoea , abdominal distention , malabsorption , loss of appetite , and among children failure to grow normally . [1] This often begins between six months and two years of age. [1] Non-classic symptoms are more common, especially in people older than two years. [8] [15] [16] There may be mild or absent gastrointestinal symptoms, a wide number of symptoms involving any part of the body or no obvious symptoms. [1] Coeliac disease was first described in childhood; [6] [8] however, it may develop at any age. [1] [8] It is associated with other autoimmune diseases , such as Type 1 diabetes mellitus and Hashimoto's thyroiditis , among others. [6] Coeliac disease is caused by a reaction to gluten , a group of various proteins found in wheat and in other grains such as barley and rye . [9] [17] [18] Moderate quantities of oats , free of contamination with other gluten-containing grains, are usually tolerated. [17] [19] The occurrence of problems may depend on the variety of oat. [17] [20] It occurs in people who are genetically predisposed . [10] Upon exposure to gluten, an abnormal immune response may lead to the production of several different autoantibodies that can affect a number of different organs . [4] [21] In the small bowel, this causes an inflammatory reaction and may produce shortening of the villi lining the small intestine ( villous atrophy ). [10] [11] This affects the absorption of nutrients, frequently leading to anaemia . [10] [18] Diagnosis is typically made by a combination of blood antibody tests and intestinal biopsies , helped by specific genetic testing . [10] Making the diagnosis is not always straightforward. [22] Frequently, the autoantibodies in the blood are negative, [23] [24] and many people have only minor intestinal changes with normal villi. [25] People may have severe symptoms and they may be investigated for years before a diagnosis is achieved. [26] [27] Increasingly, the diagnosis is being made in people without symptoms , as a result of screening . [28] Evidence regarding the effects of screening, however, is not sufficient to determine its usefulness. [29] While the disease is caused by a permanent intolerance to gluten proteins, [10] it is distinct from wheat allergy , which is much more rare. [30] The only known effective treatment is a strict lifelong gluten-free diet , which leads to recovery of the intestinal mucosa, improves symptoms and reduces the risk of developing complications in most people. [13] If untreated, it may result in cancers such as intestinal lymphoma and a slightly increased risk of early death. [3] Rates vary between different regions of the world, from as few as 1 in 300 to as many as 1 in 40, with an average of between 1 in 100 and 1 in 170 people. [14] It is estimated that 80% of cases remain undiagnosed, usually because of minimal or absent gastrointestinal complaints and lack of knowledge of symptoms and diagnostic criteria. [5] [26] [31] Coeliac disease is slightly more common in women than in men. [32] Contents 1 Signs and symptoms 1.1 Gastrointestinal 1.2 Malabsorption-related 1.3 Miscellaneous 2 Cause 2.1 Other grains 2.2 Risk modifiers 3 Pathophysiology 3.1 Genetics 3.2 Prolamins 3.3 Tissue transglutaminase 3.4 Villous atrophy and malabsorption 4 Diagnosis 4.1 Blood tests 4.2 Endoscopy 4.3 Pathology 4.4 Other diagnostic tests 4.5 Gluten withdrawal 5 Screening 6 Treatment 6.1 Diet 6.2 Refractory disease 7 Epidemiology 8 History 9 Social and culture 9.1 Christian churches and the Eucharist 9.1.1 Roman Catholic position 9.2 Passover 9.3 Spelling 10 Research directions 11 References 12 External links Signs and symptoms [ edit ] The classic symptoms of untreated coeliac disease include pale, loose, or greasy stools ( steatorrhoea ), and weight loss or failure to gain weight. ... Whether or not a gluten-free diet brings this risk back to baseline is not clear. [39] Long-standing and untreated disease may lead to other complications, such as ulcerative jejunitis (ulcer formation of the small bowel) and stricturing (narrowing as a result of scarring with obstruction of the bowel). [40] Malabsorption-related [ edit ] The changes in the bowel make it less able to absorb nutrients, minerals, and the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K. [18] [41] Malabsorption of carbohydrates and fats may cause weight loss (or failure to thrive or stunted growth in children) and fatigue or lack of energy. ... Selenium malabsorption in coeliac disease, combined with low selenium content in many gluten-free foods, confers a risk of selenium deficiency , [42] Copper and zinc deficiencies have also been associated with coeliac disease. [42] A small proportion have abnormal coagulation due to vitamin K deficiency and are slightly at risk for abnormal bleeding. ... Other intestinal disorders may have biopsy that look like coeliac disease including lesions caused by Candida. [86] Villous atrophy and malabsorption [ edit ] The inflammatory process, mediated by T cells , leads to disruption of the structure and function of the small bowel's mucosal lining and causes malabsorption as it impairs the body's ability to absorb nutrients , minerals, and fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K from food. Lactose intolerance may be present due to the decreased bowel surface and reduced production of lactase but typically resolves once the condition is treated.MYO9B, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DQA1, BACH2, THEMIS, IL15, ZMIZ1, IFNG, CTLA4, HLA-DPB1, TGM2, ICOSLG, IL21, ETS1, MMP3, CXCL10, FCGR3A, MAGI2, UBD, CXCL11, MMP12, CD80, TFF1, APOB, TNFRSF9, ASAH2, CD36, CXCL9, LRAT, LPL, LCN2, CAPN8, TNFRSF14, CCR4, UGT1A4, IFI27, UPB1, SLC6A14, ACE, PIWIL2, VNN1, SOAT2, PCK1, RUNX3, GBP5, APOC3, S100A9, IL2, CD28, IL12A, SH2B3, ICOS, TAGAP, LPP, HLA-DQA2, IL23R, KIAA1109, CCR3, IL2RA, CIITA, ATG16L1, IL18R1, SMAD3, FUT2, PPP1R12B, FRMD4B, CD247, PUS10, MMEL1, ZNF335, PLEK, YDJC, NFIA, NCF2, POU2AF1, NKAIN2, IRF1-AS1, MST1, HECTD4, LURAP1L, SLC9A4, LINC02649, C1orf141, LINC01185, PTEN, CRB1, MROH3P, PTPRK, LINC01934, LINC00993, IL12A-AS1, IL6, IL10, LINC00824, IL12RB1, LINC01250, IL17A, INS-IGF2, MICA, IRF4, IRF5, AFF3, NONOP2, UQCRC2P1, C6orf99, ADCY7, ATXN2, RBM45, TNPO3, ELMO1, MYNN, SMG7, TNFSF15, INAVA, DLEU1, UBASH3A, SRCAP, IGF2-AS, ATXN2L, FNBP1, FOXP3, CNTNAP2, PHLDB1, ADGRL2, NRXN1, ARHGAP31, ERAP2, RMI2, LRRK2, SPIB, STAT3, STAT4, SUOX, TCF4, TNF, CARD9, WNT3, ANKRD30A, GATD3A, TMEM187, NKD1, ANKRD55, ACACA, PTPN2, DAG1, ABCC6, RUNX1, ZFP36L1, HLA-DRB1, GPR35, ACAD8, HP, PTPN22, IL18, LINC01193, IL18RAP, CFTR, PREP, CELIAC2, CXCL8, TLR4, AGA, HLA-A, IL1B, HT, HFE, IL4, IL22, NXF1, USO1, TLR2, TOR1A, FLNB, SEC14L2, FCGR2A, KIR3DL1, CD14, NOS2, INS, IL1A, TRBV20OR9-2, NLRP3, STAT1, HLA-C, ICAM1, MMP1, TGM6, IBD5, MBL2, PON1, VDR, GOT2, CXCR3, TPO, DMD, HSPA1A, EGFR, KLRK1, TAP2, DEFB1, GEM, KLRC4-KLRK1, NTS, CCR9, SLC11A2, HSPA1B, BEST1, TGFB1, IRF1, HMGB1, HLA-G, MYD88, ISYNA1, HLA-DRB4, NFKB1, RGS1, CRP, CCK, SCHIP1, TNFRSF8, VEGFA, TSLP, CD19, TXN, TNFAIP3, REG1A, CD38, TJP1, CD59, CX3CL1, SDC1, PARD3, TG, TFRC, TLR9, CDR3, HIF1A, CNR2, DLG5, HLA-DRB3, FAS, ISG20, PAEP, ATP12A, CTNNB1, ATP4A, HLA-DPA1, IL15RA, KLRC2, MLH1, MIF, DEFA5, IFNA13, IFNA1, IL12B, MTHFR, IL5, CLDN2, GHRL, TOLLIP, NELFCD, IL23A, ISCU, TBC1D9, COX8A, GINS2, ACSL5, CLDN3, CTSB, CX3CR1, CLEC16A, CCN2, TRDC, CADM1, B3GAT1, TRDD3, TRAV26-1, TRDJ1, DLL1, CD209, PGPEP1, IGHV5-51, HPGDS, SPINK4, LAMP3, CLDN15, GBGT1, CSN2, IBD6, ULK3, CR2, CPOX, TBC1D7, CHMP2B, QPCT, TLR7, IGF1, ODR4, BCL2, ATD, BAK1, BAX, GSTK1, IRGM, BCKDHB, STPG4, OR10A4, TICAM1, NAPEPLD, SLC30A8, OLIG3, TMPRSS6, CST13P, NKX2-3, BDNF, MIR155, DEFB103A, HCG14, KIR2DL5B, PARP1, ADRA1A, AHR, ALB, ALK, OCLN, LINC01672, AMELX, AD12, AMH, ANPEP, ZGLP1, CCR2, ANXA11, APC, CFB, TRIM69, CCR5, KIR2DL5A, CD34, IFIH1, CD44, CD48, C6orf47, ZFAT, CDKN2A, CDKN2D, SLCO6A1, PNPLA2, DEFB103B, CHI3L1, CLC, IFT122, SLC30A10, CCR1, FTO, VTCN1, CD86, EHMT1, ADAD1, IL17RE, CD1D, CD3E, CD3G, CD4, MTG1, CD8A, IL33, ATAD1, NCALD, PNPLA3, TRABD, NLRP1, BTNL8, CCDC33, FCGRT, DMRT1, NHS, SERPINF1, PDGFB, GRINA, PBX3, TNFRSF11B, NT5E, NOS1, NFKBIB, DUSP10, GTF2A1, NDUFA2, GZMB, NCAM1, MUC1, MSH5, MSH2, ABCB1, SERPINA1, PI3, SERPINE2, GNAO1, PTH, PSMB6, PRL, PRKCQ, PRKCD, PPP6C, PON3, PON2, PML, PLA2G4A, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, PIK3CA, HLA-B, MME, MLN, KIR3DL2, KCNJ11, IRF2, IRAK1, INSR, HNRNPD, IL13, IL12RB2, HSPA2, HSPD1, IL9, IL6R, IDDM3, IL5RA, IL2RB, IGHA1, KIR2DS1, L1CAM, HLA-DMB, LCT, MICB, HLA-DOA, MGMT, MEFV, MCL1, SMAD7, SMAD2, LYZ, LTBR, LTA, LSAMP, HLA-DQB2, LMO2, LMO1, LGALS1, PTPRC, GLS, RAC2, NCR1, COX5A, F2, HSPB3, F9, FAAH, TNFSF13, MADD, IGFALS, MTOR, SCG2, ZFP36, YY1, FUT4, VIP, UBE2L3, ETFA, ERBB2, TPMT, ELN, LILRA3, BTNL3, DNAH8, TNFSF13B, GNA13, CD226, DPP4, KAT5, CLEC10A, SEMA3A, PRSS16, OPTN, ABCB6, EGF, ELAVL2, TSHR, TNFRSF1A, RAG1, GH1, GLB1, SOX9, SOD1, SLC22A4, SLC6A4, SGK1, SELL, SELE, GLI1, CCL5, CCL2, GLI2, S100B, GLP1R, SNORA73A, SPINK1, STAT6, GABBR1, GCG, CLDN5, TLR3, TIMP1, TIA1, GAD1, TGM1, TGFB3, TGFA, TFF3, GAD2, TRD, TCN2, GATA3, TBX1, TAP1, H3P13