-
Nephrotic Syndrome
Wikipedia
The first test will be a urinalysis to test for high levels of proteins, [28] as a healthy subject excretes an insignificant amount of protein in their urine. ... A study of a sample's anatomical pathology may then allow the identification of the type of glomerulonephritis involved. [28] However, this procedure is usually reserved for adults as the majority of children suffer from minimal change disease that has a remission rate of 95% with corticosteroids . [30] A biopsy is usually only indicated for children that are corticosteroid resistant as the majority suffer from focal and segmental glomeruloesclerosis. [30] Further investigations are indicated if the cause is not clear including analysis of auto-immune markers ( ANA , ASOT , C3 , cryoglobulins , serum electrophoresis ), or ultrasound of the whole abdomen. ... Retrieved 8 Sep 2008 . ^ a b "Patient information: The nephrotic syndrome (Beyond the Basics)" . Retrieved 2013-06-28 . ^ James W Lohr, MD. "Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis" . Retrieved 2013-06-28 . ^ a b c "Frecuencia de las glomerulonefritis y causas de las glomerulonefritis secundarias" .NPHS2, A2M, SERPINC1, GPC5, HLA-DRB1, ALB, NPHS1, TGFB1, APOA1, ARHGDIA, KANK1, SERPINE1, COL4A1, COL1A1, TNS2, F3, GUCA2B, IL2, LAMA5, HSD11B2, ACE, SOD2, CD2, PODXL, TF, NCK2, FGF2, COL4A2, NCK1, XPO5, NUP37, CTSL, PTGS2, MPV17, IL1B, APOB, ALOX5, ITSN2, FAT1, EDNRA, KCNJ1, ECE1, DDC, GPAM, IL4, NOS1, ACAT1, SCNN1A, MMP1, LIPC, SMAD1, SOAT2, VLDLR, PPARGC1A, DGAT1, CFL1, SCNN1B, PLA2G7, WT1, PLCE1, TRPC6, OSGEP, ITGA3, LAMB2, COQ2, SGPL1, MYO1E, COQ6, MEFV, GATA3, WDR73, SCARB2, NUP107, EMP2, INF2, PTPRO, COL4A5, CRB2, TP53RK, COQ8B, PDSS2, COX2, GSN, CCND1, PAX2, KANK2, ADA, WDR4, DGKE, IL7R, NLRP3, FGA, C3, TBC1D8B, MAGI2, NUP133, ND1, TRNF, TRNH, ND5, ND4, ZFPM2, ND6, PMM2, PTPRD, PARM1, RAG1, COX1, RAG2, MAP3K1, TBX18, RMRP, WWOX, MARS1, ANLN, COX3, TRNS1, TRNL1, IFT27, IFT172, SRY, SLC17A5, SPP1, STAT4, VAMP7, BBS9, TRIM32, SMARCAL1, SERPINA1, SOX9, FOXP3, LAGE3, NPHP1, TPRKB, PRKCD, ZAP70, WDPCP, TRNW, TRNS2, SDCCAG8, LYZ, TRNQ, MKKS, SAA1, MKS1, BBS5, HLA-DQB1, BBS10, CEP290, GLA, GATA4, NR5A1, FN1, ARL6, LMNB2, BBIP1, CHST14, TTC8, LZTFL1, C8orf37, COL4A4, COL4A3, BBS12, CASP10, C1R, C1QA, BTC, BBS4, BBS2, BBS1, B2M, NR0B1, TSBP1-AS1, ACTN4, DCLRE1C, SNAP29, IL2RG, CHD7, BBS7, AHI1, ZNF592, DMRT3, LMX1B, IRAK1, LIG4, LPA, ACTB, CD80, PCSK9, PLG, CD2AP, ABCB1, APOE, NR3C1, APOL1, PLA2R1, TBC1D9, IGAN1, POMC, THSD7A, ANGPTL4, MIF, VEGFA, LEP, MS4A1, AGT, CABIN1, KRT20, IL18, TNF, SOCS3, F9, MIR192, AGTR1, CMIP, CXCL8, IL13, KTWS, HPSE, KIRREL1, BRAF, INS, LPL, MIR30A, REN, RELA, MTHFR, ANGPT2, CFHR5, MIR586, MIR939, MIR146B, AHSA1, HLP, IL21, SQOR, TET1, OLFM1, PPIF, ACE2, DNM1L, CRELD2, SOCS5, IL22, RNF19A, IL23A, LGALSL, PLB1, KANK4, RBM45, GLCCI1, POLDIP2, MLYCD, MUC16, NPNT, ATAD1, NSD3, MIR16-1, APOM, NFASC, MIR23B, HAVCR1, DDN, MZB1, SYNPO, HT, PHB2, TRIM8, FIS1, PIK3CD, GRAP2, ESR1, F2, F5, FKBP5, FLT1, GCG, GLO1, GSTM1, GSTP1, GSTT1, GUCA2A, HDAC2, CFH, HIF1A, HLA-DQA1, HMBS, HP, HPX, HSPA4, HSPB1, IL1A, IL1R1, IL4R, IL6, IL10, IL12B, EXT1, STOM, MAPKAPK2, EDN1, ADCYAP1, APOA4, AQP1, AQP2, AQP4, STS, BCL2, C1S, VPS51, CALR, CD36, CETP, CLU, CNP, CNTN1, COX8A, CLDN7, CRK, MAPK14, CST3, CTSB, CYP2C19, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, HBEGF, IL17A, KDR, KLKB1, LAMP1, RAB5A, RAC1, RYR2, SALL1, CCL2, CCL13, SDC1, SNAI1, STAT3, STAT5A, TFE3, TFPI, TIMP1, TLR4, TP53, TTR, YWHAZ, MANF, AIMP2, FGF23, PDE5A, RAB11A, IQGAP1, CLDN2, CLDN1, PTH, MAPK1, PLCL1, MUC1, LCAT, LDLR, LEPR, LOX, LRP2, LTA4H, MAF, MC1R, MGP, NR3C2, MPO, MYH9, PLAT, MYOC, NOS3, NOTCH1, NPPC, NT5E, PDR, PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PIK3CG, PKD1, PLA2G1B, MTCO2P12
-
Depression In Childhood And Adolescence
Wikipedia
Academic pressure, intrapersonal and interpersonal difficulties, death of loved ones, illnesses, and loss of relationships have shown to be significant stressors in young people. [28] While it is a normal part of development in adolescence to often experience distressing and disabling emotions, there is an increasing incidence of mental illness globally, mainly because of the breakdown in traditional social and family structures. ... People who have low self-esteem, who constantly view themselves and the world with pessimism, or are readily overwhelmed by stress may be especially prone to depression. [28] Community surveys find that women are more likely than men to say they are under stress.
-
Shingles
Wikipedia
Besides the skin, other organs, such as the liver or brain , may also be affected (causing hepatitis or encephalitis , [27] [28] respectively), making the condition potentially lethal. [29] : 380 Pathophysiology [ edit ] Electron micrograph of Varicella zoster virus . ... Multiple studies and surveillance data, at least when viewed superficially, demonstrate no consistent trends in incidence in the U.S. since the chickenpox vaccination program began in 1995. [87] However, upon closer inspection, the two studies that showed no increase in shingles incidence were conducted among populations where varicella vaccination was not as yet widespread in the community. [88] [89] A later study by Patel et al. concluded that since the introduction of the chickenpox vaccine, hospitalization costs for complications of shingles increased by more than $700 million annually for those over age 60. [90] Another study by Yih et al. reported that as varicella vaccine coverage in children increased, the incidence of varicella decreased, and the occurrence of shingles among adults increased by 90%. [91] The results of a further study by Yawn et al. showed a 28% increase in shingles incidence from 1996 to 2001. [92] It is likely that incidence rate will change in the future, due to the aging of the population, changes in therapy for malignant and autoimmune diseases, and changes in chickenpox vaccination rates; a wide adoption of zoster vaccination could dramatically reduce the incidence rate. [8] In one study, it was estimated that 26% of those who contract shingles eventually present complications. ... PMID 24500927 . ^ a b Han Y, Zhang J, Chen N, et al. (28 March 2013). Han Y (ed.). "Corticosteroids for preventing postherpetic neuralgia". ... "The neurotropic herpes viruses: herpes simplex and varicella-zoster". Lancet Neurol. 6 (11): 1015–28. doi : 10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70267-3 . ... "Outbreak of varicella-zoster virus infection among Thai healthcare workers". Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 28 (4): 430–34. doi : 10.1086/512639 .HLA-B, LINC02785, HCP5, TMC7, FAM110B, LRRC32, TNF, CPS1, IL10, HLA-DRB1, HLA-A, ARSA, IFNG, APOE, ESR1, RBM45, CRP, TMPRSS13, TECTA, LMLN, IL33, ENOSF1, GAL, BOD1, PART1, CXCL13, RECQL4, TRPV1, CCR2, THBS1, MIP, STAT3, MUC1, CD34, CCR5, CTLA4, CYP11A1, CYP17A1, EGFR, ETFA, GP2, IL5, IL6, IL7, IL17A, MBL2, MECP2, MSMB, MST1, MTX1, LINC02605
-
Arsacs
Gene_reviews
Features of ARSACS View in own window Organ System Feature % of Persons with Feature Neurologic Ataxia, kinetic 96% (135/140) 1-6 Ataxia, static 95% (140/146) 1-6 Cognitive decline 5% (3/51) 1, 3 Dysarthria 74% (37/50) (at age 18 yrs) 2 Dysphagia 13% (11/84) 3, 5, 6 Dystonia 7% (5/70) 3, 6 Epilepsy 7% (5/70) 3, 6 Extension plantar response 86% (119/138) 1-5 Linear hypointensities pons (FLAIR) on brain MRI 49% (19/39) 3 Nystagmus 74% (89/120) 1-5 Sensorimotor polyneuropathy 97% (36/37) (axonal 25%; demyelinating 53%; both 14%) 3 Vermis atrophy w/upper predominance on brain MRI 83% (39/47) 3 Neuromuscular/ Developmental Muscle wasting, lower limb 51% (28/54) 3, 4 Muscle wasting, upper limb 19% (8/43) 3, 4 Spasticity, lower limb 75% (77/103) 1-6 Spasticity, upper limb 15% (9/58) 1-6 Stiff legs, isolated, at disease onset 5% 3 Unsteadiness at disease onset 96% (43/45) (isolated 82%; w/stiff legs 11%) 3 Weakness, lower limb 60% (74/124) 1-5 Weakness, upper limb 3% (21/60) 1-5 Wheelchair bound after age 30 yrs 25% (6/24) 3 Ophthalmologic Hypertrophy of retinal myelinated fibers 33% (19/58) 1, 3-6 Hearing Hearing loss 13% (8/62) 1, 4 Other Intellectual disability / school difficulties 29% (28/95) 1-3 Pes cavus 61% (75/123) 1-3 Scoliosis 15% (9/62) 3, 4 Urinary dysfunction 34% (38/111) 1-6 1.
-
Turner Syndrome
Wikipedia
Strangely, Turner syndrome seems to be associated with unusual forms of partial anomalous venous drainage. [24] [28] In a patient with Turner syndrome, these left-sided cardiovascular malformations can result in an increased susceptibility to bacterial endocarditis. ... Aortic dilation, dissection, and rupture [ edit ] Two studies have suggested aortic dilatation in Turner syndrome, typically involving the root of the ascending aorta and occasionally extending through the aortic arch to the descending aorta, or at the site of previous coarctation of the aorta repair. [29] A study that evaluated 28 girls with Turner syndrome found a greater mean aortic root diameter in people with Turner syndrome than in the control group (matched for body surface area).GH1, SOD1, SOD2, NOS2, CAT, NR5A1, SRY, SHOX, IGF1, GHR, IGFBP3, AMH, AR, WT1, HTC2, TP53, EFHC2, BRD2, XIC, RPS4X, TPO, ESR1, DMRT1, MTHFR, ZFY, XIST, VDR, SOX9, KDM6A, TG, MAP3K1, PTPN22, CD38, HLA-A, SSRP1, ARSL, PWAR1, HT, SLC52A2, SHBG, NT5E, GAPDH, TNFRSF11B, RPS4Y1, RPS2, TIMP1, NIPBL, NR0B1, PTPN1, F2R, DMD, POMC, DAZ1, NR1I2, STATH, TSHR, TSHB, TYMS, SULT2A1, STAR, TIMP3, UTY, VAMP7, AFP, VEGFA, ZFAT, PHPT1, LGALS13, SOX8, FOXP3, PPP2R3C, LHX9, DHX37, VWF, VSPA, WDR34, RBM45, NDUFS7, POU5F1P3, POU5F1P4, SPIDR, ZFPM2, MLC1, DMRT2, PAICS, MAMLD1, BCL2L11, ADIPOQ, PPIG, SMC3, MBD2, SOCS2, SLC4A4, SMC1A, USP9X, MOGS, ZFX, SRD5A2, RAD21, SOX3, CYP19A1, H2AX, NR3C1, GRB10, GNAS, GLS, GDF9, GCH1, GCG, GART, FGF9, FANCA, EGFR, CYP21A2, CTLA4, HLA-DRB1, CSF2RA, CSF2, CRP, COX8A, CDX2, CDK4, SERPING1, BGN, BDNF, ASAH1, APOA1, XIAP, AMELX, HLA-C, IFNA1, SOS2, MTR, SOS1, SLC6A8, SCN5A, RS1, RFC1, RARRES2, PTH, POU5F1, PGD, PCYT1A, PAPPA, MYOD1, MYO9B, MMP1, IFNA13, MCL1, MBL2, MAOB, LPA, KRAS, KIT, ANOS1, INPPL1, INS, IL3RA, IL3, IGFALS, IGF2, CERNA3
-
Auditory Hallucination
Wikipedia
Transverse temporal gyri (Heschl's gyri) : found within the primary auditory cortex . [28] Left temporal lobe : processes semantics in speech and vision, includes primary auditory cortex. [10] Broca's area : speech and language comprehension. [10] Superior temporal gyrus : contains primary auditory cortex. [10] Primary auditory cortex : processes hearing and speech perception. [10] Globus pallidus : Regulation of voluntary movement. [11] Treatments [ edit ] Medication [ edit ] The primary means of treating auditory hallucinations is antipsychotic medications which affect dopamine metabolism . ... "Spontaneous perception of melodies – hallucination or epilepsy?". Nervenheilkunde . 28 : 217–221. ISSN 0722-1541 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j Hugdahl K, Løberg EM, Nygård M (May 2009).
-
Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Wikipedia
The treatment may be repeated 6–12 months after initial treatment of metastatic disease where disease recurs or has not fully responded. [28] Patients are administered hormone replacement levothyroxine for life after surgery, especially after total thyroidectomy. ... Coauthors: Silvia Gagliardi and Andrew Scott Kennedy. Updated: Sep 28, 2010 ^ "New York Thyroid Center: Prognosis Staging for Thyroid Cancer" .BRAF, NKX2-1, CCDC6, RET, FOXE1, NCOA4, PPARG, KRAS, PAX8, NTRK1, NRAS, DIRC3, NTRK3, ETV6, ALK, GAS8-AS1, PTCSC3, HRAS, MIR485, EIF1AX, SNAI1, ERC1, TPR, TFG, DIO3, MIR431, MIR381, MIR409, MIR369, MIR376C, MIR758, PCM1, TRIM27, MIR299, MIR539, MIR136, TRIM33, LPAR4, MIR654, TRIM24, MIR379, MIR382, WARS1, WDR20, MIR380, BEGAIN, NDUFA13, MIR377, MIR376A1, MIR127, MIR370, MIR134, MIR337, MIR323A, MIR433, MIR154, DIO3OS, MIR329-1, MIR496, MIR323B, MIR376A2, MIR487B, MIR411, MIR655, MIR656, MIR770, MIR300, MIR543, DYNC1H1, MIR889, MIR1247, MIR1197, MIR1193, ZEB1, GOLGA5, MIR487A, MIR493, MIR410, PPP2R5C, MIR412, MIR432, MIR494, SNAI2, MIR376B, ZEB2, MIR495, APC, HABP2, PTEN, NRG1, DICER1, TAS2R38, PTCH1, MINPP1, MAPK1, PIK3CG, TPCN1, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, CTNNB1, PIK3CA, PCNX2, ESR1, EGFR, F9, VAV3, TP53, BRCA2, MIR146B, BCL2, CCND1, TGFB1, HT, AKT1, JAG1, TG, LINC02454, TERT, LOC110806263, LGALS3, MIR222, SEC23B, MMP9, CXCR4, LIG4, TPM3, TPO, TSHR, SLC5A5, MIR221, VEGFA, EPHB2, MIR146A, COX2, FN1, CD274, MET, KRT19, MIR21, PTGS2, TIMP1, GABPA, SPP1, NCAM1, MTCO2P12, ATM, MUC1, MAP2K7, IGF1, KIT, TNF, ESR2, CD44, HIF1A, RASSF1, SLC2A1, CXCL12, HGF, VEGFC, NFE2L2, MAPK3, TTF1, MIR204, PRPF31, VDR, DUSP6, CDKN1B, MIR451A, XIAP, TFF3, PDGFRA, CYP24A1, THBS1, KDR, RUNX2, PTH, LEP, CHEK2, STAT3, ERBB2, MMP2, MIR144, PCNA, RAF1, VIM, CDKN2A, PTCH2, MDK, IRAK1, MTOR, MT1G, ROCK1, SOX2, IGF1R, CITED1, S100A4, GDF1, MYC, NOTCH1, LEPR, MDM2, TACSTD2, H3P10, ICAM1, FOXP3, MIR30A, CRK, ACKR3, TGFA, NOB1, NEAT1, MIR141, SMUG1, MIR155, MIR15A, HTC2, AKT3, DPP4, SPHK1, CENPJ, UCA1, HMGA2, TIMP3, EDN1, MIR486-1, XRCC1, AR, SNHG12, MIR613, IL6, SLC5A8, PTCSC2, MT1A, MMP11, WNK1, ORI6, SPHK2, MALAT1, MIR34B, IL10, MIR150, MIR96, MLH1, MIR199A1, MIR199A2, MCL1, MIR200A, SYTL2, MIR497, MIR29A, MIR206, SP1, KRT20, AIMP2, AHSA1, GRAP2, RAP1A, TP63, TTF2, RNH1, RPE65, KLK7, S100A11, WNT5A, VHL, UVRAG, SLC2A3, TWIST1, PPP1R13L, PROX1, TERF2IP, SGSM3, SHC3, GDE1, SIRT6, IL22, STOML2, PDGFRB, RABGEF1, CKAP4, PDCD4, POLDIP2, RNF19A, DKK1, ZHX2, MAP2K1, YAP1, ABL1, MS4A1, COL1A1, VEGFD, CCR7, HLA-G, MAPK14, DIO2, CDH1, HLA-DRB1, DIO1, EZH2, HOXD13, EDNRA, FOXO1, FAS, EGF, HMGB1, GSTM1, GPI, HSP90AA1, MIR122, MIR139, DCTN6, EBP, SOX11, GLI1, NNMT, TNFSF10, MIR202, MIR137, MIRLET7E, CDKN1A, NRP1, HOPX, TENM1, ITCH, PLAU, AKAP9, PLG, EIF4E, SLPI, DNMT1, SERPINA1, PGR, DDR2, NRCAM, P2RX7, MIR126, PAK1, ZNRD2, FGF2, PDPN, NT5E, CIB1, PCBP4, POSTN, FGFR1, CRNDE, FASLG, POLR2E, ZNRF3, KIDINS220, NOTCH3, MIR10A, PDPK1, ARNTL, MIR509-1, MIR149, MIR145, DUSP5, RAC1, CAV1, MIR7-2, RARA, MIR34A, RARG, NAPSA, MIR195, OPN1LW, RELA, CCK, ABCG2, SLIT2, MIR363, FOS, FLT3, CCL21, FLT1, RPL36A, CLDN10, MIR199B, CLDN1, S100A6, FOXO3, TMSB10, LPAR2, MIAT, MIR183, CXCL14, PTN, CDK4, PAG1, PRKAA1, PRKAA2, PRKAB1, DNMT3A, CA12, GAS5, FOXM1, MIR375, GAS1, CDH6, KEAP1, CASP3, EIF4A3, RAPGEF5, GORASP1, MIR335, PSMD9, E2F1, SFTPB, GABRB2, NECTIN4, SELL, FRTS1, NCL, C3, SYT1, TOP2A, TRAF6, JAK1, JUN, CXXC5, IL27, CASC2, HOXA@, LAMB3, LAMC2, IL17D, CREBBP, ITGA3, LINC00313, HAGLR, LGALS1, CPSF2, LMNA, MIR2861, TLR4, ERRFI1, LRP4, CRABP1, ITGA5, ITGA2, SIRT1, IL1B, H3P23, YY1, CLIP2, KLB, IFI27, DEUP1, IGFBP5, CTSC, IHH, IL1A, ZCCHC12, FALEC, HSPA5, CXCL8, CXCR2, ABHD11-AS1, LIPH, IL13RA2, IL17A, TMED7, CXCL10, INSR, EPCAM, LPAR3, ANGPT1, MTDH, PTK2B, TMED10, MT1X, MIR933, AHR, AKT2, CISH, TMED7-TICAM2, TMED10P1, GSTT1, TICAM2, TEK, ALDH1A1, MST1, DCN, MSH2, FOXD2-AS1, UNC5B-AS1, HOTAIR, HLA-C, HOXA-AS2, MCM5, CYP27B1, ETV5, MDM4, HLA-DQB1, CYTOR, THRB, RASAL1, KDM1A, KLLN, PDCD1LG2, NT5C1A, STON2, DCSTAMP, SLCO6A1, PROK1, GPR151, ADAT2, E2F7, PROSER3, CLPTM1L, AFAP1L2, LIMD2, SPZ1, RTN4IP1, LMLN, CHEK1, TMEM139, FSD1L, ECRG4, XKR4, AHNAK2, FOXQ1, FAM83F, HTRA3, ABHD11, TMPRSS13, PKHD1L1, MCM3AP-AS1, SH3BGRL3, HSDL2, MAL2, ARL11, RBM45, MRGPRX3, TLR10, MRGPRX4, PRAP1, LINC01278, CYP2R1, ACBD5, CPT1C, TRIM8, HOOK3, KLF17, CHI3L1, HSPD1, WNT10A, IL17RB, LARP7, CRKL, RAB23, CREM, FXYD5, DUOX1, TLR9, CREB1, DLL4, CROT, SLC35F2, XAF1, TRIM44, GATAD2A, CPOX, PGPEP1, ELOVL2, PINX1, TUG1, PIWIL2, THAP1, RMDN3, ZNF654, LAPTM4B, IMPACT, CRY2, MBIP, IL23A, DUOX2, SETD2, DROSHA, PYCARD, CTLA4, UHRF1, TFCP2L1, CERS2, PSAT1, EHD2, CSNK1G2, CD207, NOX4, SIRT7, CSF2, TAS2R3, F11R, CSF1R, CSF1, RMDN1, HSPA14, TCEAL9, MZB1, TNFRSF12A, REV1, LGR4, SYBU, NAA15, IWS1, CXCL16, IL22RA1, ACE2, LGR6, SCOC, PROK2, MYO1G, ERAP2, SOX17, HHIP, MRPL41, CDK15, MRPL44, CCR3, TRAK2, OTUB2, MAPKAP1, FSD1, MUL1, TNFAIP8L2, LIN28A, E2F8, CKS2, TRPM3, ZNF703, C6orf47, ANKRD36B, NCOA5, TCIM, RUFY2, WDR11, ATF7IP, CHFR, AGK, COX8A, PBK, MYDGF, PDGFC, TMPRSS4, KLF6, EMSY, TNRC6C, SMYD2, CTNNBIP1, TWSG1, CEMIP, DANCR, SRGAP1, MIB1, SEMA6A, MRTFA, CNGB1, RELCH, TEKT4, MIR130A, RMDN2, GGTLC4P, MIR622, MIR625, MIR630, AMPD1, AMFR, MIR663A, LINC00460, GGTLC3, GGT2, CCR2, ALOX5, ALDH1A3, MIR608, MIR766, MIR675, ALCAM, VTRNA2-1, MIR744, MIR922, MIR940, MIR885, TNRC6C-AS1, LINC00271, CD24, ANGPT2, MIR599, MIR1915, ARAF, BMI1, BGN, BGLAP, BAX, B2M, ATP5F1E, ATF1, ARR3, MIR520A, MIR524, MIR506, RASSF10, MIR584, NORAD, CXADRP1, GGTLC5P, PAX8-AS1, APRT, APOA4, ANXA5, ANXA1, MIR564, MIR574, MIR577, MIR1183, NR0B1, CCDC80, LOC102723407, MIR4516, MIR4429, MIR5189, BANCR, ADRA2B, COMETT, NAMA, BLACAT1, SAMMSON, LINC01186, ADRA1A, LOC102724971, MIR4728, CCND2-AS1, BISPR, PARP1, CERNA3, LOC105379528, RNU1-55P, ADCYAP1R1, ADCYAP1, ADCY1, LNCRNA-ATB, H3P17, MIR4500, COMMD3-BMI1, MIR1270, MIR320E, MIR1266, MIR1271, MIR1261, MIR1179, MIR1304, AFM, MIR718, MIR761, HOTTIP, AP2A1, MIR4316, MIR3144, SNHG16, MIR3151, LINC00673, MIR3619, MIR3663, PROX1-AS1, APTR, LINC01672, LUCAT1, HOTAIRM1, TTN-AS1, DLG1-AS1, BMP4, BMPR1A, BRCA1, LINC01061, SCAI, UBAC2, RSPO2, ZNF677, GSTK1, AGRN, CDX2, KMT5A, CCL4L1, IYD, LOC390714, MIRLET7B, SNHG15, MIR106A, MIR106B, MIR125A, CDKN3, HIPK2, MIR130B, CDKN1C, CDK8, MIR143, CDK7, MIR148A, SLC26A4-AS1, RPL34-AS1, BRS3, USF3, PAQR3, C8orf37, CBLL2, OXER1, DACT2, GLIS3, NLRP6, EMX2OS, TIGIT, PRSS55, ANO5, SKA1, RSPO1, HOXA11-AS, JAZF1, GPRC6A, ZNRF2, TTTY10, FNDC5, MRGPRX1, MAGEA2B, CEBPB, B4GALNT3, LINC00514, CDK2, CDH2, MIR18A, MIR361, ZFAS1, GPR166P, MIR148B, CASR, MIR324, CASP9, MIR339, MIR346, CASP8, CASP6, MIR196B, CASP2, MIR181A2, CAMP, CALCA, CAD, CA9, MIR384, MIR422A, RGMB-AS1, MIR20B, TMEM50B, MPPED2, BUB1B, VN1R17P, NRARP, NR2F1-AS1, PRDM16-DT, MIR182, MIR190A, CD74, CD68, MIR20A, CD63, MIR203A, CD38, CD34, MIR211, MIR212, MIR214, MIR215, MIR219A1, MIR22, CD247, CD1A, MIR23A, CCNG1, MIR296, CBL, MIR31, RUNX3, ATAD2, AKAP13, CTNNA1, PTGDS, MAPK8, LRRC32, PRL, PRLR, GAPDH, GAP43, HTRA1, KLK10, PSG1, PSMD8, GAGE5, GAGE4, PTGIS, FLVCR1, GAGE1, G6PD, PTPRJ, NECTIN1, PVT1, RAD52, FUT4, FUCA1, RAP1GAP, RARB, RARRES2, RBP2, GCGR, GGT1, PRKCE, PRKAR1A, SLC26A4, PECAM1, PGM1, PHB, SERPINB5, SERPINE2, GCLC, GPC3, GLA, PIN1, PITX2, PKM, PLA2G1B, PLA2G2A, PLD2, PLK1, PMP22, PMS2, POMC, POU5F1B, PPARA, GJB2, GH1, PRKACA, PRKACG, FPR2, FOSB, RGS4, FKBP5, SLC6A9, SLC16A2, FKBP4, SOD2, SOD3, FGFR4, SOX9, SOX12, SPARC, SPG7, SPINT1, SRC, SRF, SRY, SST, SSTR4, STAT1, FGF1, STK11, STRN, SYPL1, MAP3K7, TBX1, TCF4, TBX3, SLC6A2, FOXF1, RNASE2, SLC1A5, BRD2, ROS1, RRAS, RXRG, S100A1, FLI1, S100A13, S100B, SERPINB3, SCD, SCN4B, CCL2, CCL3, CCL4, CCL5, CCL20, CXCL11, CXCL5, SDC4, SDHB, SELE, SFRP1, SHH, SHMT1, SKP2, ENPP2, GLI2, GLP1R, JUNB, CD82, KCNJ2, HOXD10, KIF5B, HOXA9, HOXA3, LAIR1, LASP1, LBR, LCN2, LDHA, HNF4A, FOXA2, HMGB2, LMO7, LOX, LOXL1, BCAM, HMBS, SMAD3, SMAD4, MAGEA2, MARK1, MC1R, MCM3, JUND, ITGB4, MAP3K5, ITGB2, TNC, HSP90AB1, ID1, ID3, IDH1, IFNG, HSPA9, IGFBP1, IGFBP7, IL1R1, IL2, IL2RA, IL4, HPRT1, IL11, IL11RA, IL13, IL18, IDO1, INS, INPPL1, IRS1, ISG20, ITGAV, ITGB1, MCM7, MEN1, PDCD1, GSN, GPX3, GRK6, NFKB1, NGF, NGFR, NNAT, NME1, NOS2, NOS3, GPR42, UTS2R, CXCR3, ROR2, NUCB2, PEBP1, PRDX1, SERPINE1, PRKN, PAX6, PC, SERPINA5, GNAS, GLS, CDK16, PCYT1A, MYH9, MMUT, MFAP1, MUC4, MGMT, CXCL9, MKI67, HLA-B, MME, MMP1, HLA-A, HK2, HIC1, MMP13, MOG, MPZ, MRC1, ABCC1, HBB, MSH3, MSMB, GUSB, MT1E, MT1F, MT1M, MT2A, MTF1, MTHFR, GSR, TCF7L2, FCGR3B, TERC, TAB1, CFD, ATG7, ARFGEF1, NPC2, TXNRD2, DECR1, PDLIM5, CXCR6, CLDN16, CERS1, POLQ, PTGES3, CHL1, FRS2, AKR1C2, HPSE, HCP5, EHD1, RAB40B, DCT, COPS6, OGFR, WDR5, ACE, HUS1, GPNMB, NQO1, ANKRD26, RAPGEF3, WSCD2, NUP93, RAB11FIP3, SART3, HDAC9, HDAC4, TRIM14, DPT, PJA2, TLK1, WDR1, FGF19, NR1I3, RBX1, SCO2, NAALADL1, PLXNC1, PSME3, TRIM13, SPRY2, STUB1, PAK4, TLR6, NDRG1, RACK1, TUSC2, CILK1, DUSP2, CYP1A1, LRIG1, DNM3, CYLD, CXADR, DGCR5, PHGDH, FGF21, EHF, BEX3, LAT, TSPAN13, DKK3, SNX5, SERP1, CUX1, HPGDS, RBMX, CTSL, CTSB, EML4, IGHV3OR16-7, IGHV3-69-1, TRBV2, TRBJ1-2, TRBJ1-1, WWTR1, BRMS1, DCK, QPCT, MMRN1, ATF6, RPIA, DAPK1, USP33, SMG1, RRS1, KAZN, CUX2, USP22, CYP19A1, ANGPTL2, HEY1, BRD4, PES1, SRRM2, PSD4, CYP2D6, AMACR, LDOC1, SNHG1, TRIM29, SLC7A11, IL17RA, RASGRP3, PRDX6, CCL4L2, FCGR3A, EPHB4, SUMO1, UGCG, USF1, EPHB1, VAV2, EPAS1, ENG, EMX2, ELK3, ELF3, TRPV1, ELAVL2, WIPF1, WNT1, EIF4EBP1, WNT7A, XRCC3, ZIC1, CNBP, TRIM26, EPHA2, EGR2, NTT, EDNRB, LPAR1, EPHB3, EPS15, ACP3, TSG101, TFAP2A, TFE3, FCER2, FBN1, FASN, TGFBR1, TGFBR2, EZH1, EWSR1, TK1, TLR1, TLR2, TLR3, TM7SF2, ETV4, ETS1, TP53BP1, TPI1, ERCC5, ERBB4, ERBB3, TPT1, CRISP2, HSP90B1, CCT3, SLC7A5, CND, TP53I3, TNFRSF10B, TNFRSF10A, E2F4, IQGAP1, SOCS2, PROM1, KSR1, CDK5R1, PER2, CCNA1, BTRC, MAP3K14, SOCS3, USP6, OSMR, BUB3, AURKB, PTTG1, CRLF1, DHRS3, STK17B, KLF4, COX5A, ATG5, ADAMTS1, PTGES, SCEL, CDC23, NAA10, BECN1, TKTL1, BAP1, CDC45, FZD1, FZD4, PLA2G6, TAGLN2, RECK, CAVIN2, CUL3, TYMP, MAP4K3, PARG, APOL1, LMO4, LGR5, CDC14B, KHSRP, PSMG1, ECE1, EIF4EBP3, E2F6, SOCS1, PDE5A, IRS2, CDR3
-
Atrial Septal Defect
Wikipedia
In a large randomized controlled trial , the higher prevalence of PFO in migraine patients was confirmed, but migraine headache cessation was not more prevalent in the group of migraine patients who underwent closure of their PFOs. [27] Causes [ edit ] Down syndrome – patients with Down syndrome have higher rates of ASDs, especially a particular type that involves the ventricular wall . [28] As many as one half of Down syndrome patients have some type of septal defect. [28] Ebstein's anomaly [29] – about 50% of individuals with Ebstein anomaly have an associated shunt between the right and left atria, either an atrial septal defect or a patent foramen ovale . [30] Fetal alcohol syndrome – about one in four patients with fetal alcohol syndrome has either an ASD or a ventricular septal defect . [31] Holt–Oram syndrome – both the osteium secundum and osteum primum types of ASD are associated with Holt–Oram syndrome [32] Lutembacher's syndrome – the presence of a congenital ASD along with acquired mitral stenosis [6] Mechanisms [ edit ] In unaffected individuals, the chambers of the left side of the heart are under higher pressure than the chambers of the right side because the left ventricle has to produce enough pressure to pump blood throughout the entire body, while the right ventricle needs only to produce enough pressure to pump blood to the lungs . ... PMID 31547797 . ^ "Atrial Septal Defect Types – Mayo Clinic" . Archived from the original on 28 September 2007 . Retrieved 2007-10-14 . ^ Fix, James D.; Dudek, Ronald W. (1998).NKX2-5, PQBP1, GATA4, MYH6, GABRQ, MYT1L, TRIP12, CCN1, NTF3, ACTC1, FOXC1, TBX5, TLL1, PTPN11, PTEN, BMPR1A, SALL4, COMT, NODAL, EVC, B3GLCT, MAP2K1, GATA6, TTN, SHANK3, TRIP13, ABL1, BUB3, SMC3, BAZ1B, CDC45, ARID1A, NAA10, SMC1A, CDK13, SEC24C, EFTUD2, LONP1, ZMPSTE24, GPC6, MED12, RBM8A, WASHC5, FIG4, ZEB2, KIAA0586, TMEM94, SEMA3E, CEP57, TTC37, USP9X, GTF2IRD1, TBX4, RBM10, WT1, MKKS, KMT2D, SOS1, SON, SNRPB, SMN1, SMARCE1, SKIV2L, SCN4A, SALL1, RREB1, RPS17, RPL27, RPL5, RIT1, RFC2, RAF1, STK4, ABCC8, TALDO1, NELFA, SHOC2, KAT6A, PCGF2, ZIC3, XRCC2, CITED2, NSD2, TBX1, CLIP2, KDM6A, UFD1, HIRA, NKX2-1, TBX2, TRAIP, MRAS, MAD2L2, UPF3B, UBE3B, TMEM87B, SLX4, PHF6, BRIP1, CEP290, PALB2, NXN, VAC14, NSD1, STRA6, XYLT2, FANCM, ARHGAP31, ARID1B, KIF15, NEK9, G6PC3, CHST14, MMP21, TTN-AS1, RNU4ATAC, DIPK1A, CTU2, KANSL1, JMJD1C, UBR1, ASXL1, ESCO2, CEP120, CCBE1, GATA5, AMER1, EVC2, B3GALT6, HDAC8, CHD7, SLC19A2, PIGN, TBL2, VPS33B, AUTS2, SETBP1, C2CD3, SH2B1, NIPBL, KAT6B, ASXL2, HAAO, TGDS, SIK3, SPECC1L, RAD51, TXNL4A, KDM5B, NPHP3, CCDC22, UBE2T, SLC25A24, FANCI, SETD5, RFWD3, FANCL, AGGF1, BCOR, NDUFB11, TMCO1, RAB23, OTUD6B, DYNC2LI1, LARP7, DACT1, ZDHHC9, TBX22, RAD51C, STIM1, RAD21, FOXF1, ERCC4, FANCA, FANCC, FANCD2, FANCE, FANCB, FANCF, FANCG, FBN2, FKTN, GPC4, FGFR1, PEX19, FGFR2, FLNB, LETM1, GDF1, GJA1, GPC3, GLI1, GLI3, GP1BB, GPX4, GTF2I, HCCS, HNRNPK, HRAS, HSPA9, HSPG2, KIF11, EP300, ELN, ECE1, DNMT3A, ACTL6A, JAG1, ANK1, ARSD, ARVCF, ATIC, RERE, ATP6V1A, ATP6V1E1, BCR, BMP2, BRCA1, BRAF, BRCA2, BUB1, BUB1B, MYRF, TMEM258, LYST, CHRM3, COL1A1, COL5A1, COL5A2, COX7B, CREBBP, CRKL, CYP11A1, DHCR7, DMD, KRAS, FGFR3, MYH7, MASP1, KMT2A, MMP2, MAP2K2, MMP14, MAPK1, MMUT, NFIX, NOTCH2, LMNA, POR, ROR2, POLA1, PAX3, PCNT, PIGA, PIK3R2, LIMK1, MEIS2, PITX2, SMS, RSS, TBX20, CYP11B2, ACTA2, IL1B, IL18, CRP, WNT1, CNTNAP2, BMP4, CYP1B1, MTHFR, STX18, BDNF, MSX1, SHANK2, ASNS, ACTB, CNTNAP3, MIR499A, ELMOD3, PITX3, SOD1, SIL1, SNAP25, ARSA, MIR486-1, CACNA1C, CAPG, EBPL, LGALS7B, CAT, CCNA2, CDH11, SHROOM3, NUFIP2, POMC, FOXL2, ADO, TARP, ANGPT2, PSD, SLFN14, MAPK3, PTH, SAA1, SAA2, ACTN4, OSR1, RBM45, MIRLET7B, OPN1SW, ACTA1, MIR139, SCN2A, MIR27A, SYTL4, PPP3CA, NEXN, BMPR2, LBX2, RELN, MDD1, LGALS7, CYP2E1, RTN4, COL4A1, HEY2, ZFPM2, MSX2, FOXE3, KDM4C, FMR1, PHB2, WDHD1, MMP3, DGCR6, LZTR1, TSHZ1, GRM5, GRM7, MEFV, MECP2, HLA-DRB1, SMAD4, LRPAP1, AXIN1, HTC2, IL1A, IL4, IL6, CXCL8, ISL1, KLRC2, MYBPC3, VEGFA, NOS3, TGFB1, PCDHGA4, CFC1, CDKL5, PCYT1A, SYN2, CHDH, NRP1, PAX6, HYDIN, PCSK6, DMPK, ARID4B, DPYSL3, PHGDH, TGFBR2, EFNB1, ELK3, PLAC8, OPRD1, TNF, F2, TNFRSF1A, INTU, NPPA, NOTCH3, SUMO1, CERNA3
-
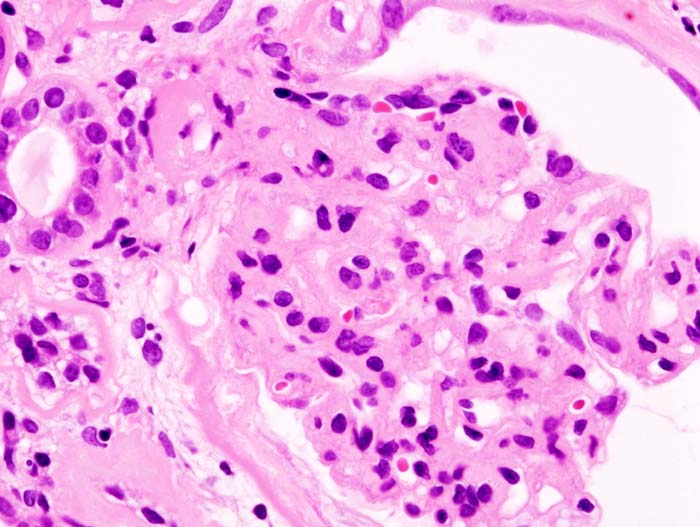
Hepatorenal Syndrome
Wikipedia
These include the use of intravenous albumin infusion, medications (for which the best evidence is for analogues of vasopressin , which causes splanchnic vasoconstriction), radiological shunts to decrease pressure in the portal vein , dialysis , and a specialized albumin-bound membrane dialysis system termed molecular adsorbents recirculation system (MARS) or liver dialysis . [2] Medical therapy [ edit ] Many major studies showing improvement in kidney function in patients with hepatorenal syndrome have involved expansion of the volume of the plasma with albumin given intravenously. [2] [25] [26] The quantity of albumin administered intravenously varies: one cited regimen is 1 gram of albumin per kilogram of body weight intravenously on the first day, followed by 20 to 40 grams daily. [27] Notably, studies have shown that treatment with albumin alone is inferior to treatment with other medications in conjunction with albumin; most studies evaluating pre-transplant therapies for HRS involve the use of albumin in conjunction with other medical or procedural treatment. [2] [28] Midodrine is an alpha-agonist and octreotide is an analogue of somatostatin , a hormone involved in regulation of blood vessel tone in the gastrointestinal tract . ... "Hepatorenal syndrome" . Clin Biochem Rev . 28 (1): 11–7. PMC 1904420 . PMID 17603637 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Ginès P, Arroyo V (1999). ... Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther . 25 (9): 1017–28. doi : 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2007.03303.x . ... "Prostaglandins for the treatment of hepatorenal syndrome". Ann Pharmacother . 28 (1): 54–5. doi : 10.1177/106002809402800112 .
-
Frontal Lobe Epilepsy
Wikipedia
Laws restricting driving privileges vary greatly in the United States as well as across the world. In the United States, 28 states require a patient to be seizure free for fixed periods of time ranging from 3–12 months. [15] However, research done by Johns Hopkins University showed that there was no difference in seizure-related fatal crash rates in states with 3-month restrictions versus states with 6-12 month seizure-free restrictions. ... People with frontal lobe epilepsy show decreased cognitive capabilities in the following areas: humor appreciation, recognition of emotional expressions, response selection/initiation and inhibition, hyperactivity, conscientiousness, obsession, addictive behavior , motor coordination and planning, attention span, performance speed, continuous performance without intrusion and interference errors, copying and recall, concept formation, anticipatory behavior, memory span , working memory , executive planning, visuo-spatial organization, mental flexibility, conceptual shift, problem solving, programming of complex motor sequences, impulse control , judgment and forecasting of consequences. [9] [23] [24] [25] Physical health and risk of other conditions Patients with epilepsy face a greater risk of accidents, injury and other medical conditions than the general population. [22] A European study showed that people with epilepsy were at greater risk for accidental injuries related to seizures such as concussions, abrasions and wounds and reported more hospitalizations and medical action than the general population. [26] Other studies have shown that people with epilepsy are at a greater risk of seizure related drowning, suffocation, broken bones and burns and more likely to die in a fatal automobile crash. [27] Epilepsy Ontario reports that people with epilepsy are also more likely to have other conditions than the general population such as: 30% of autistic children have epilepsy, 33% of cerebral palsy patients have epilepsy, 15-20% of fragile X syndrome patients have epilepsy, 50% of children with learning disabilities will have some form of epilepsy, 3-10% of patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome will have epilepsy, 80% of children with Rett syndrome will have epilepsy and 80% of patients with Tuberous Sclerosis will have epilepsy. [28] Mental and emotional health Epileptic patients are more prone to suffer psychological and social dysfunction than individuals that do not have epilepsy. ... Retrieved 2009-12-01 . [ dead link ] ^ Schachter SC, Shafer PO (2008-03-28). "Treatment" . epilepsy.com . Retrieved 2009-10-24 . ^ Weiner HL (2004-03-08).
-
Oral And Maxillofacial Pathology
Wikipedia
It is a science that investigates the causes, processes and effects of these diseases." [28] In some parts of the world, oral and maxillofacial pathologists take on responsibilities in forensic odontology . ... ISBN 978-0721690032 . ^ a b c d W., Odell, E. (2017-06-28). Cawson's essentials of oral pathology and oral medicine .
-
Thrombophilia Due To Activated Protein C Resistance
Omim
The heterozygous mother developed a DVT of the left leg during her most recent pregnancy at the age of 37. Two daughters, aged 28 and 33 years, who were homozygous for the mutation, and the father, who was heterozygous, had not developed thrombosis. ... Kerlin et al. (2003) found that 4.1% of 65 patients with sepsis were heterozygous carriers of the factor V Leiden mutation. The 28-day mortality was lower in heterozygous carriers (13.9%) compared to those without the mutation (27.9%, p = 0.013).
-
Histiocytosis-Lymphadenopathy Plus Syndrome
Omim
Spiegel et al. (2010) reported an Israeli Moslem Arab family in which 2 sisters and their nephew were affected. The 28-year-old sister had clinical features consistent with classic PHID, consisting of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus that developed at 12 years of age and the onset of hyperpigmented hypertrichotic sclerodermatous skin lesions at 14 years of age. ... In an Israeli Moslem Arab family in which a 28-year-old woman had PHID, her 5-year-old nephew had H syndrome, and her 23-year-old sister had a more severe phenotype combining features from both syndromes, as well as the additional features of severe seronegative polyarthritis and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, Spiegel et al. (2010) identified mutations in the SLC29A3 gene: the sisters were compound heterozygous for the G427S and G437R mutations, whereas their nephew was homozygous for the G437R mutation.
-
Osteochondritis Dissecans
Wikipedia
OCD in humans most commonly affects the knees, [8] ankles, and elbow but can affect any joint. [28] In skeletally immature individuals, the blood supply to the epiphyseal bone is good, supporting both osteogenesis and chondrogenesis . ... X-rays are usually taken three months after the start of non-operative therapy; if they reveal that the lesion has healed, a gradual return to activities is instituted. [48] [50] Those demonstrating healing by increased radiodensity in the subchondral region, or those whose lesions are unchanged, are candidates to repeat the above described three-month protocol until healing is noted. [28] Surgery [ edit ] Arthroscopic image of OATS surgery on the medial femoral condyle of the knee The choice of surgical versus non-surgical treatments for osteochondritis dissecans is controversial. [51] Consequently, the type and extent of surgery necessary varies based on patient age, severity of the lesion, and personal bias of the treating surgeon—entailing an exhaustive list of suggested treatments. ... Retrieved 17 September 2008 . ^ a b c "Osteochondritis dissecans of the knee" (PDF) . Orthogate. 28 July 2006 . Retrieved 16 November 2008 . ^ "Osteochondritis dissecans" (PDF) . ... PMID 8590122 . ^ Jacobs B, Ertl JP, Kovacs G, Jacobs JA (28 July 2006). "Knee Osteochondritis dissecans: treatment & medication" . eMedicine .
-
Minamata Disease
Wikipedia
The certification committee convened on 29 November 1962 and agreed that the two dead children and the sixteen children still alive should be certified as patients, and therefore liable for "sympathy" payments from Chisso, in line with the 1959 agreement. [28] Outbreak of Niigata Minamata disease [ edit ] Further information: Niigata Minamata disease Minamata disease broke out again in 1965, this time along the banks of the Agano River in Niigata Prefecture . ... One of the Chisso trade unions held an eight-hour strike in protest at the poor treatment of the arbitration group by their own company. [32] The litigation group, representing 41 certified patients (17 already deceased) in 28 families, submitted their suit against Chisso in the Kumamoto District Court on 14 June 1969.
-
Variant Angina
Wikipedia
National Heart Lung and Blood Institute . Retrieved April 28, 2010 . ^ "Prinzmetal's Angina, Variant Angina and Angina Inversa" . ... PMID 8626956 . ^ Sun, Hongtao; Mohri, Masahiro; Shimokawa, Hiroaki; Usui, Makoto; Urakami, Lemmy; Takeshita, Akira (28 February 2002). "Coronary microvascular spasm causes myocardial ischemia in patients with vasospastic angina".
-
Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
Wikipedia
More specifically, adrenal stimulation by the sympathetic nervous system has been noted in cases ranging from physical events such as ischemic stroke, to emotional events such as depression or loss of a loved-one. [24] How these increased levels of catecholamines act in the body to produce the changes seen with TTS is not clearly understood. [5] [10] [11] [14] Research supports the widely-held understanding that microvascular dysfunction and coronary vasospasm caused by a rapid influx of catecholamines to cardiac myocytes results in apical stunning and transient cardiomyopathy. [5] [10] [11] Microvascular dysfunction/Transient vasospasm: Some of the original researchers of takotsubo suggested that multiple simultaneous spasms of coronary arteries could cause enough loss of blood flow to cause transient stunning of the myocardium. [25] Other researchers have shown that vasospasm is much less common than initially thought. [26] [27] [28] It has been noted that when there are vasospasms, even in multiple arteries, that they do not correlate with the areas of myocardium that are not contracting. [29] However, the idea of coronary artery vasospasm is still believed to contribute to the TTS disease process. ... Once a patient has recovered from the acute stage of the syndrome, they can expect a favorable outcome and the long-term prognosis is excellent for most. [1] [19] [35] Even when ventricular systolic function is heavily compromised at presentation, it typically improves within the first few days and normalises within the first few months. [1] [26] [27] [28] Although infrequent, recurrence of the syndrome has been reported and seems to be associated with the nature of the trigger. [1] [13] Stress cardiomyopathy is now a well-recognized cause of acute congestive heart failure , lethal abnormal heart rhythms , and rupture of the heart wall . [12] Epidemiology [ edit ] Takotsubo cardiomyopathy is rare, affecting between 1.2% and 2.2% of people in Japan and 2% to 3% in Western countries who suffer a myocardial infarction.
-
Meningitis
Wikipedia
In these cases, the persons are more likely to be infected with Staphylococci , Pseudomonas , and other Gram-negative bacteria. [8] These pathogens are also associated with meningitis in people with an impaired immune system . [2] An infection in the head and neck area, such as otitis media or mastoiditis , can lead to meningitis in a small proportion of people. [8] Recipients of cochlear implants for hearing loss are more at risk for pneumococcal meningitis. [27] Tuberculous meningitis , which is meningitis caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis , is more common in people from countries in which tuberculosis is endemic, but is also encountered in persons with immune problems, such as AIDS . [28] Recurrent bacterial meningitis may be caused by persisting anatomical defects, either congenital or acquired, or by disorders of the immune system . [29] Anatomical defects allow continuity between the external environment and the nervous system . ... It may identify bacteria in bacterial meningitis and may assist in distinguishing the various causes of viral meningitis ( enterovirus , herpes simplex virus 2 and mumps in those not vaccinated for this). [21] Serology (identification of antibodies to viruses) may be useful in viral meningitis. [21] If tuberculous meningitis is suspected, the sample is processed for Ziehl-Neelsen stain , which has a low sensitivity, and tuberculosis culture, which takes a long time to process; PCR is being used increasingly. [28] Diagnosis of cryptococcal meningitis can be made at low cost using an India ink stain of the CSF; however, testing for cryptococcal antigen in blood or CSF is more sensitive. [52] [53] A diagnostic and therapeutic difficulty is "partially treated meningitis", where there are meningitis symptoms after receiving antibiotics (such as for presumptive sinusitis ). ... While tuberculosis of the lungs is typically treated for six months, those with tuberculous meningitis are typically treated for a year or longer. [28] Steroids [ edit ] Additional treatment with corticosteroids (usually dexamethasone ) has shown some benefits, such as a reduction of hearing loss , and better short term neurological outcomes [71] in adolescents and adults from high-income countries with low rates of HIV. [72] Some research has found reduced rates of death [72] while other research has not. [71] They also appear to be beneficial in those with tuberculosis meningitis, at least in those who are HIV negative. [73] Professional guidelines therefore recommend the commencement of dexamethasone or a similar corticosteroid just before the first dose of antibiotics is given, and continued for four days. [45] [46] Given that most of the benefit of the treatment is confined to those with pneumococcal meningitis, some guidelines suggest that dexamethasone be discontinued if another cause for meningitis is identified. [8] [45] The likely mechanism is suppression of overactive inflammation. [74] Additional treatment with corticosteroids have a different role in children than in adults.C8B, C8A, CRP, HCN1, HCN2, IL10, PRF1, BTK, TLR4, HLA-B, CYBB, WIPF1, LAMC2, JAK3, FOXP3, IL12A, IGLL1, SH2D1A, IGHM, IGH, ERAP1, HLA-DRB1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DPA1, NDE1, ICOS, PTPN22, BLNK, TBK1, CXCR4, TLR3, KLRC4, TCF3, STAT4, RAG2, RAG1, PRTN3, PIK3R1, STAG2, NCF4, NCF2, TNFRSF13B, NLRC4, MEFV, LRRC8A, WAS, CR2, CD79B, CTLA4, CSF2, C4A, NLRP3, CCR1, TNFRSF13C, FAS, DNASE1L3, CD79A, IL23R, BCL2, CD19, UBAC2, BCL6, CYBA, C4B, XIAP, IL12A-AS1, CYBC1, NCF1, VANGL1, TNF, IL6, MBL2, MMP9, CADM1, CXCL8, ST11, TLR2, BPI, GAST, NOD2, CXCL11, BDNF, CD248, MYD88, RECQL4, VIM, BATF, EGF, ENOSF1, LINC01672, IL2RG, TGFB1, CXCL10, ICAM1, IL1B, GALNS, TCF12, PAGR1, MECP2, TNFSF10, PER2, CNTNAP1, MARCO, ARTN, RIPK2, SAMM50, NEURL1, IRAK4, CARD9, ARHGEF28, CARD14, DDX56, TLR9, MARCHF9, IL23A, AADAT, SLC46A1, LRG1, MSC, LAMP3, SUMF2, NCOA6, IFNL3, WDHD1, CYCSP51, FST, UBAC1, ABCB6, PARP1, NEU1, HSP90B1, IGFBP2, PRMT1, HLA-G, HLA-A, CFH, GYPC, CXCL1, GDNF, GC, FN1, FCGR3A, FCGR2A, FCGR1A, ESR1, ERBB2, EGFR, CSF3, COX8A, CHI3L1, CDS1, CD47, CAT, CAMP, C4BPA, AQP4, KLK3, APRT, AMBP, IFNG, IL1RN, TIMP1, IL17A, THBS1, PRDX2, STAT3, SLC11A1, CCL8, CCL3, PRNP, PDE7A, SERPINE1, OMP, OGG1, OAS3, OAS2, NTF3, NOS3, AGRP, MPO, MMP12, MMP8, MMP3, CXCL9, MFAP1, MDK, MAPT, LYZ, LSAMP, IL18, LOC108281177
-
Actinic Keratosis
Wikipedia
The HPV virus has been detected in AKs, with measurable HPV viral loads (one HPV-DNA copy per less than 50 cells) measured in 40% of AKs. [28] Similar to UV radiation, higher levels of HPV found in AKs reflect enhanced viral DNA replication. ... Histopathologic exam remains the gold standard Polarized contact dermoscopy of AKs occasionally reveals a "rosette sign," described as four white points arranged in a clover pattern, often localized to within a follicular opening. [40] It is hypothesized that the "rosette sign" corresponds histologically to the changes of orthokeratosis and parakeratosis known as the "flag sign." [40] Non-pigmented AKs: linear or wavy vascular patterning, or a "strawberry pattern," described as unfocused vessels between hair follicles, with white-haloed follicular openings. [41] Pigmented AKs: gray to brown dots or globules surrounding follicular openings, and annular-granular rhomboidal structures; often difficult to differentiate from lentigo maligna. [42] Prevention [ edit ] Ultraviolet radiation is believed to contribute to the development of actinic keratoses by inducing mutations in epidermal keratinocytes, leading to proliferation of atypical cells. [43] Therefore, preventive measures for AKs are targeted at limiting exposure to solar radiation, including: Limiting extent of sun exposure Avoid sun exposure during noontime hours between 10:00 AM and 2:00 PM when UV light is most powerful Minimize all time in the sun, since UV exposure occurs even in the winter and on cloudy days [44] Using sun protection Applying sunscreens with SPF ratings 30 or greater that also block both UVA and UVB light, at least every 2 hours and after swimming or sweating [44] Applying sunscreen at least 15 minutes before going outside, as this allows time for the sunscreen to be absorbed appropriately by the skin [44] Wearing sun protective clothing such as hats, sunglasses, long-sleeved shirts, long skirts, or trousers Recent research implicating human papillomavirus (HPV) in the development of AKs suggests that HPV prevention might in turn help prevent development of AKs, as UV-induced mutations and oncogenic transformation are likely facilitated in cases of active HPV infection. [28] A key component of HPV prevention includes vaccination , and the CDC currently recommends routine vaccination in all children at age 11 or 12. [45] There is some data that in individuals with a history of non-melanoma skin cancer, a low-fat diet can serve as a preventative measure against future actinic keratoses. [37] Management [ edit ] This section needs more medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources .TP53, XPA, CDKN2A, BCL2, PTGS2, MAL, H3P10, AK1, HRAS, BRAF, AK3, PPARA, AK4, VDR, MC1R, SMAD4, INPP5A, TNC, CCL27, H2AX, GSTM1, CD274, EGFR, MAPK1, FOXP3, TLR7, TNFSF10, AIMP2, XPC, SMIM10L2B, VIM, MIR204, TYR, TP53BP1, TMX2-CTNND1, TNF, TLR4, TAC1, STAT3, SSTR2, SSTR1, SST, TMC8, SMARCA2, ENDOV, SLC2A1, SDHD, RPE65, MTCO2P12, KRT72, MIR31, SLC24A4, AHSA1, TLR8, HPLH1, PDCD4, POLDIP2, RNF19A, PART1, SIRT1, MIB1, UBA5, TXNDC5, ZMPSTE24, CLDN1, MAPK3, KNSTRN, PRRT2, ABCB6, SMIM10L2A, BCAR1, AIM2, GRAP2, RPS6KA5, PTTG1, SCO2, AHR, PRKCB, MAPK14, GHR, MLANA, FLG, FHL1, FGFR3, FAP, ERCC1, EGF, TYMP, CYP24A1, CTNND1, CSE1L, CRK, HK2, CLDN7, COL17A1, CKS1B, CDKN2B, CDKN1A, CDK4, CD40LG, CFB, AR, AQP3, FASLG, AK2, CFH, HOXC4, PRKCA, CD200, PPT1, PPP5C, PLXNA2, PIK3CA, PI3, PCNA, PEBP1, CLDN11, MYC, MMUT, COX2, MSH2, MMP12, IRF4, MMP3, MMP2, MMP1, MKI67, MCM2, LMNA, LIG4, LBR, KRT17, KRT16, IVL, ITGB4, PLD2
-
Gallstone
Wikipedia
Risk factors for pigment stones include hemolytic anemias (such as from sickle-cell disease and hereditary spherocytosis ), cirrhosis , and biliary tract infections. [25] People with erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP) are at increased risk to develop gallstones. [26] [27] Additionally, prolonged use of proton pump inhibitors has been shown to decrease gallbladder function, potentially leading to gallstone formation. [28] Cholesterol modifying medications can affect gallstone formation. ... November 2013. Archived from the original on 28 July 2016 . Retrieved 27 July 2016 . ^ a b c d e f g Lee, JY; Keane, MG; Pereira, S (June 2015).ABCB4, ASPG, ABCG8, UGT1A4, UGT1A10, UGT1A8, UGT1A7, UGT1A6, ABCB11, UGT1A9, UGT1A5, UGT1A3, HBB, ABCG5, BAZ2B, DELEC1, GCGR, GDF2, GP1BB, GPR35, CA10, FRMD4A, TNC, GTF2I, GYPC, UGT1A1, HK1, SMAD4, LIMK1, STX12, TBL2, MYPN, ZNF28, UROS, UFD1, HIRA, TPI1, TCF4, TBX1, BAZ1B, SPTB, SPTA1, SMPD1, SLC4A1, GTF2IRD1, GNA14, SEC24C, RREB1, GNE, PEX19, SEC23B, PKLR, PFKM, MYO10, MST1, HMCN1, RFC2, TANC1, SH2D4B, CYP27A1, SGCZ, JMJD1C, COMT, TMEM114, MIR646HG, C22orf34, BPGM, DMPK, BLVRA, ARVCF, APOE, AIRE, ANK1, ALDOA, ACVRL1, DACH1, CLIP2, EPB41, EPB42, FECH, ENG, ELN, GUSBP11, L3MBTL4, SLC10A2, UGT1A, CCK, APOB, NR1H4, NPC1L1, CYP7A1, UGGT1, SLC35A2, LDLR, PNPLA3, CCKAR, SERPINA1, TNF, MUC5AC, HNF4A, IL6, CRP, LRP2, SLCO1B1, ALB, TLR4, CYP17A1, GUSB, SLCO1A2, AR, LRPAP1, ACAT2, PTGS2, PPARG, EGFR, OGG1, CETP, G6PD, LEPR, SLC22A7, XPC, MIR372, CXCL16, CLDN2, OPN1MW2, PART1, ZGLP1, ABCC3, POT1, PLA2G10, GLP2R, RETN, ST8SIA4, OR10A4, MICA, CCL28, PPARGC1B, OPN1MW3, BMF, XRCC1, XPR1, MIR210, NRXN3, PCSK9, CDHR5, GSTK1, DDX53, SLCO6A1, NR1H3, PPARGC1A, LINC01194, SLC51B, IFIH1, FGF19, GGTLC1, FAIM2, ATP11A, CHD1L, EHMT1, ABCG2, LIX1, ADIPOQ, SMUG1, MIR122, NAT2, VIPR1, OPN1MW, ESR1, ESR2, FABP2, FABP6, FEN1, FGFR4, FMO3, GCG, GLP1R, DPEP1, GPER1, GPT, GPX1, GPX3, GSTM1, GSTT1, HBA1, HBA2, EGF, CYP8B1, HIF1A, CCT, ADCYAP1, ADRB3, APC, APEX1, APOBEC1, APOC1, ARSA, CAT, CD36, CTLA4, CDK4, CDX2, CLIC1, CCR5, ABCC2, MAP3K8, CLDN3, CR1, HHEX, HLA-A, VEGFA, SLC11A1, RBP4, RNASEL, RPL4, SORT1, S100A8, SHBG, SHH, SLC10A1, SOD1, PLA2G2A, SPINK1, SPP1, SST, SULT1E1, TGFB1, TLR2, TP53, TRAF3, MAP2K5, SERPINB5, HMGB1, LCN2, HMGCR, HMOX1, IL1B, IL1RN, IL10, IL13, IL18, KRT18, LEP, ABCB1, MBNL1, MC4R, MECP2, MMP2, MMP9, MUC1, MUC2, NOS2, LOC102724197