-
Tk2-Related Mitochondrial Dna Maintenance Defect, Myopathic Form
GeneReviews
Clinical Manifestations of TK2 -Related Mitochondrial DNA Maintenance Defect View in own window Age of Onset Prevalence Manifestation Frequency Age <2 years (infantile onset) 61/89 (69%) Hypotonia 55/57 (96%) Elevated serum CK 56/59 (95%) Respiratory difficulties 48/53 (91%) Loss of previously acquired motor skills 43/49 (88%) mtDNA depletion 33/40 (83%) Hyporeflexia 31/39 (79%) Lactic acidemia 28/42 (67%) Motor developmental delay 18/49 (37%) Seizures 11/34 (32%) Cognitive impairment 4/43 (9%) Age 2-18 years (juvenile/ childhood onset) 14/89 (16%) Muscle weakness 8/9 (89%) mtDNA depletion 9/14 (64%) Respiratory failure 7/12 (58%) Age >18 years (adult onset) 14/89 (16%) Dysphagia 5/5 (100%) mtDNA multiple deletions 4/4 (100%) Muscle weakness 8/8 (100%) Ptosis 7/7 (100%) Ragged red fibers 8/8 (100%) Infantile onset (<2 years).
-
Scn9a Neuropathic Pain Syndromes
GeneReviews
Pathogenic missense variants in SCN9A were reported in eight of 28 adults (age ≥18 years) with inherited small fiber neuropathy (I-SFN) in whom other known causes for small fiber neuropathy (e.g., diabetes mellitus, impaired glucose tolerance, hyperlipidemia) were excluded, and who met strict diagnostic criteria for I-SFN with reduced intraepidermal nerve fiber density on skin biopsy or abnormal quantitative sensory testing [Faber et al 2012].
-
Primary Hyperoxaluria Type 3
GeneReviews
Nephrocalcinosis of prematurity occurs in a significant proportion of infants born prior to 28 weeks' gestation and is characterized by both nephrocalcinosis and nephrolithiasis [Habbig et al 2011].
-
16p12.2 Recurrent Deletion
GeneReviews
Pizzo et al [2018] showed that among parents with the 16p12.2 deletion, 53% (17/32) had exhibited learning difficulties in school, 52% (11/21) exhibited depressive behaviors, 13% (2/15) alcohol or drug addiction, 19% (3/16) schizophrenic-like behaviors, 28% epilepsy, and 13% (2/16) bipolar disorder.
-
Glycogen Storage Disease Ia
OMIM
Obara et al. (1993) described the renal histology in 2 adult patients with type I glycogen storage disease, a 37-year-old woman and a 28-year-old man. Smit (1993) studied retrospectively 41 patients over 10 years of age from 5 different European centers.
- Wolfram Syndrome 1 OMIM
-
Peri-Implantitis
Wikipedia
Journal of Clinical Periodontology . 28 (6): 517–523. doi : 10.1034/j.1600-051x.2001.028006517.x .IL1A, IL1B, TNF, TNFRSF11B, MMP8, IL6, IL1RN, OLR1, IL23A, IL22, TNFSF11, VEGFA, TLR4, TLR2, IL17A, BOP, CD14, DKK2, CPA1, CCR5, CD68, CD44, WNT5A, CD38, TNFSF12, HERPUD1, PARK7, HIF1A, CXCR3, SOST, CALR, IL21, MTG1, IL34, BRINP3, MIR27A, TNFSF12-TNFSF13, DEFB4B, TIMP2, TGFB1, TERT, SPP1, FUT4, IL1R1, FN1, IL4, FGF2, CXCL8, IL10, DEFB4A, MIP, MMP2, DEFB1, MMP9, MPO, CAD, CSF1, PPIA, CCL2, SFRP1, SNAP25, BTF3P11
-
Heterochromia Iridum
Wikipedia
Notable historical figures thought to have heterochromia include Anastasius the First , dubbed dikoros (Greek for 'having two irises'), [28] [29] and Alexander the Great , as noted by the historian Plutarch . [11] [30] In other animals [ edit ] See also: Odd-eyed cat Although infrequently seen in humans, complete heterochromia is more frequently observed in other species, where it almost always involves one blue eye. [ citation needed ] The blue eye occurs within a white spot, where melanin is absent from the skin and hair (see Leucism ).
-
Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
Wikipedia
(In atrial fibrillation, this additional 20% filling volume is lost and the patient may experience systolic heart failure symptoms). [28] Complete left ventricular filling is essential to maintain maximum cardiac output. ... European journal of heart failure, 13(1), 18-28. ^ González-López E, Gallego-Delgado M, Guzzo-Merello G, de Haro-Del Moral FJ, Cobo-Marcos M, Robles C, Bornstein B, Salas C, Lara-Pezzi E, Alonso-Pulpon L, Garcia-Pavia P (7 October 2015).
-
Virtual Reality Sickness
Wikipedia
Galvanic vestibular stimulation , which creates the illusion of motion by electric stimulation of the vestibular system, is another technique being explored for its potential to mitigate or eliminate the visual-vestibular mismatch. [28] Newest technology [ edit ] With the integration of virtual reality into the more commercial mainstream, issues have begun to arise in relation to VR sickness in head-mounted gaming devices. [29] While research on head-mounted VR for gaming dates back to the early 1990s, [30] the potential for mass usability has only become recently realized.
-
Sotos Syndrome 1
OMIM
There was a strong correlation between presence of an NSD1 alteration and clinical phenotype, as 28 of 37 patients (76%) in group 1 had NSD1 mutations or deletions, whereas none of the patients in group 4 had alterations in NSD1.
-
Anomic Aphasia
Wikipedia
The studies show that verbs are harder to recall or repeat, even with rehabilitation. [24] [28] Other methods in treating anomic aphasia include circumlocution-induced naming therapy (CIN), wherein the patient uses circumlocution to assist with his or her naming rather than just being told to name the item pictured after given some sort of cue.
-
Hyperhidrosis
Wikipedia
] [23] [24] A microwave -based device has been tried for excessive underarm perspiration and appears to show promise. [25] Tap water iontophoresis as a treatment for palmoplantar hyperhidrosis was originally described in the 1950s. [26] Studies showed positive results and good safety with tap water iontophoresis. [27] One trial found it decreased sweating by about 80%. [28] Surgery [ edit ] Sweat gland removal or destruction is one surgical option available for axillary hyperhidrosis (excessive underarm perspiration).BIRC3, SCN11A, SRCAP, AGPAT2, GNA14, PLAA, CRLF1, AIP, PHOX2B, BCL10, SUCLG1, SERPINB7, CDK13, ELP1, IKBKG, CUL4B, VHL, UCP2, TP53, THPO, TERT, TERC, MLX, HNF1A, TAT, ABCC8, SPR, MALT1, KIF1B, ASCL1, CLCF1, CAVIN1, NLRP3, LONP2, GPR101, CTC1, USB1, WNK1, KLC2, CDH23, NLRC4, SLURP1, NGLY1, TMEM127, NHP2, NOP10, WRAP53, MAGEL2, RETREG1, RTEL1, SEPSECS, FOXP1, BSCL2, TINF2, PTPN22, FLRT1, SLCO2A1, SLC18A2, SLC12A3, SDHD, IGH, HPGD, HNF4A, HMBS, HLA-B, HINT1, HEXB, GDNF, GABRA3, FUCA1, FOS, FGFR3, EDN3, DKC1, DDC, CTSB, COL6A3, COL6A2, COL6A1, CLCNKB, CAV1, CACNA1S, DST, BLM, KIF1A, IGHMBP2, IL12B, JAK2, MEN1, SDHC, SDHB, SCN9A, RET, PSMB8, PRNP, MAP2K2, MAP2K1, PPARG, PARN, MPL, MAX, JUP, LIFR, KRT17, KRT16, KRT14, KRT9, KRT6B, KRT6A, KRT5, KRT1, KCNJ11, KCNA1, KCNJ18
-
Anosmia
Wikipedia
Loss of smell has also been found to be more predictive of COVID-19 than all other symptoms, including fever, cough or fatigue, based on a survey of 2 million participants in the UK and US. [16] Google searches for "smell", "loss of smell", "anosmia", and other similar terms increased since the early months of the pandemic, and strongly correlated with increases in daily cases and deaths. [17] Research into the mechanisms underlying these symptoms are currently ongoing. [18] Many countries list anosmia as an official COVID-19 symptom, and some have developed "smell tests" as potential screening tools. [19] [20] In 2020, the Global Consortium for Chemosensory Research, a collaborative research organization of international smell and taste researchers, formed to investigate loss of smell and related chemosensory symptoms. [21] List of causes [ edit ] Upper respiratory tract infection (such as sinusitis , the common cold ) [22] COVID-19 [23] [24] Nasal polyps [25] Idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism Hypothyroidism Head trauma, damage to the ethmoid bone [26] Dementia with Lewy bodies Tumors of the frontal lobe Antibiotics Fibromyalgia Multiple sclerosis Hypoglycaemia Diabetes Asthma or allergy Hayfever Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Long term alcoholism Cushing's syndrome Exposure to a chemical that burns the inside of the nose Stroke Epilepsy Radiation therapy to the head and neck Liver or kidney disease Parkinson's disease [27] Alzheimer's disease [28] Toxins (especially acrylates , methacrylates [29] and cadmium [30] [31] ) Old age [32] Kallmann syndrome Primary ciliary dyskinesia Post-perfusion syndrome Laryngectomy with permanent tracheostomy Esthesioneuroblastoma is an exceedingly rare cancerous tumor that originates in or near the olfactory nerve .
-
Infection
Wikipedia
A review of chronic wounds in the Journal of the American Medical Association's "Rational Clinical Examination Series" quantified the importance of increased pain as an indicator of infection. [28] The review showed that the most useful finding is an increase in the level of pain [likelihood ratio (LR) range, 11–20] makes infection much more likely, but the absence of pain (negative likelihood ratio range, 0.64–0.88) does not rule out infection (summary LR 0.64–0.88). ... Antimicrobial stewardship is the concept that healthcare providers should treat an infection with an antimicrobial that specifically works well for the target pathogen for the shortest amount of time and to only treat when there is a known or highly suspected pathogen that will respond to the medication. [47] Epidemiology [ edit ] Deaths due to infectious and parasitic diseases per million persons in 2012 28–81 82–114 115–171 172–212 213–283 284–516 517–1,193 1,194–2,476 2,477–3,954 3,955–6,812 Disability-adjusted life year for infectious and parasitic diseases per 100,000 inhabitants in 2004. [48] no data ≤250 250–500 500–1000 1000–2000 2000–3000 3000–4000 4000–5000 5000–6250 6250–12,500 12,500–25,000 25,000–50,000 ≥50,000 In 2010, about 10 million people died of infectious diseases. [49] The World Health Organization collects information on global deaths by International Classification of Disease (ICD) code categories .MBL2, TNF, CRP, G6PD, POMC, SAMD9, PEPD, IL18, IFNG, CXCL8, IL1B, TGFB1, IL10, TLR4, CCR5, TP53, TLR3, IRF3, APOBEC3G, TLR2, TRIM5, IL6, GHRL, BCL2, IL4, IFNA1, CD81, CXCL10, CD209, HLA-DRB1, CCL5, PTGS2, CXCL12, STAT1, PDCD1, MIF, CCL2, MX1, MAPK1, CLEC4M, CD14, CDKN2A, TLR9, PML, IFNB1, IRF1, MMP9, ACE2, EGFR, CXCR4, DEFB4A, CFTR, EIF2AK2, GZMB, DDX58, MAPK3, ICAM1, CD274, SCARB1, DAXX, IFNGR1, CAMP, IL2, BIRC5, OAS1, CD4, IL12B, IL13, TNFSF10, DEFA1, VEGFA, LTA, LEP, TNFRSF10B, CXCR3, SFTPD, CXCL5, MUC1, HLA-E, MICB, HLA-G, IDO1, SOCS3, ABL1, VDR, NFKB1, CTLA4, FAS, CD1D, CASP3, APOE, TNFRSF8, FOXP3, MAVS, CXADR, IL1RL1, CD80, TAP1, IL7, TAP2, SERPINA1, IL4R, IFNAR1, BAG3, IL1RN, PLA2G5, SSTR3, IGF2, CD38, MMP2, APOBEC3F, PON1, DEFB103B, PPIA, SP110, PRF1, IL12RB1, PCNA, IL15, APOB, MPO, TNFRSF1B, MSN, CEACAM1, BPI, EZR, FASLG, LMAN1, IFIH1, TP53AIP1, NOS2, IL16, KLRC1, CYLD, CALCA, OGG1, IRF7, IL21, CASP9, CAV1, TERT, SOD2, CD63, CD44, CDH1, AKT1, EFNB2, MAPK14, SLC11A1, GSTP1, IL22, IFNL1, PTHLH, TBK1, SLAMF1, PTPRC, PTX3, EIF4G1, KLRK1, FHIT, NECTIN1, SFTPB, EMD, F10, CTTN, SAA1, SLPI, ADAR, HLA-DQB1, HSPA8, SOD1, HMOX1, DEFA5, HMGB1, DEFB1, TLR7, HLA-A, IRAK4, CX3CR1, RNASEL, HLA-DQA1, HLA-B, TLR1, DCD, MIR21, NLRP3, IL33, MIR155, TIA1, TOP1, SAT2, CCL24, TIRAP, TIAL1, TLR5, TNFRSF1A, CCL21, TIMP1, GAB3, TG, SELE, SIGLEC1, SPI1, SPP1, REXO1L1P, RICTOR, SRPK1, SRPK2, IFNL2, APOBEC3H, STAT3, STAT6, SYK, SMN1, SMARCB1, NFAM1, SLC4A1, TRD, SLC2A1, TRG, SP1, H19, TFF2, SFTPC, SELL, LRRC15, MAATS1, SH3KBP1, TP73, APOM, TNFSF13B, CTCF, KHDRBS1, CXCL13, NOD1, TRIM22, IL23A, CCL26, TLR6, KLRG1, DHRS9, NAMPT, BCL2L11, HDAC6, TANK, THOC1, CCL20, DERL2, MASP2, LILRB1, SIGLEC7, TBX21, PILRA, ICOS, IL20, FLVCR1, APOBEC3C, BBC3, PTPN22, YWHAQ, LY96, NUP62, SWAP70, ATF5, SP140, RASSF1, PSIP1, NUP153, NR1H4, TPO, HS3ST2, RIPK1, GBF1, IRS4, CYREN, IL1R2, RNASEH2B, ZNF175, XDH, VIPR1, VIM, PDCD1LG2, VCAM1, UBE3A, TNFRSF4, HSP90B1, ANTXR1, MAP1LC3A, TNFRSF14, RIPK2, FADD, RETN, TBKBP1, IKBKE, GKN1, EIF2AK3, CCL28, ADIPOQ, CD83, AICDA, TNFRSF10A, CLDN1, RPTOR, AP3D1, HAMP, IER3, HDAC3, IL18R1, TNFRSF10D, ABCA4, CCL19, FLT3LG, FCGR3A, FCGR2A, FCAR, FASN, FAP, F3, F2R, ESR1, ENG, EIF4E, E2F1, DPP4, DNMT3B, DNM2, CD55, CYP2D6, CTNNB1, CTNNA1, CTBP1, FLNA, FOS, IFNAR2, FTH1, IFN1@, IFIT1, IFIT2, IFI16, DNAJB1, HSPD1, HSPB1, HRAS, HNRNPA1, HLA-C, HIF1A, HFE, CFH, HCK, GZMA, FUT3, FUT2, GAST, FTL, CSF3, COL2A1, CCR7, CCR1, BAX, BAD, ATM, RHOA, APP, APOH, APOC1, APOA1, XIAP, BIRC3, APEX1, APCS, ANPEP, ALOX5, ALAD, AHSG, ADRB2, PARP1, ADM, BCL2A1, BCL2L1, CXCR5, CD27, CHUK, CHIT1, CEBPB, CD59, CD40, CD36, CD33, CD86, CD2, C1QBP, RUNX3, CAV2, CASP8, CASP1, CACNA1C, C6, C4A, C2, IFNA4, IFNGR2, CCL3L1, PMAIP1, PLAUR, PLAU, PLAT, PIK3CG, PIK3CA, PI3, SLC26A4, PDGFRA, PDGFB, PAK1, OSM, NTRK1, NMT1, NFKBIA, NFIB, NFATC3, NEFL, MYD88, MYC, PLEC, PPARA, IGF2R, PPARG, CCL3, S100B, RYR1, RELA, RBBP8, RB1, RAF1, PVR, PTPN11, PTH1R, PTGS1, PTBP1, PSMB8, PROS1, PRNP, PRKDC, PRKCQ, PRKCE, PRKCA, MUC6, MTHFR, MT1A, MSI1, KPNB1, KLRD1, KIR3DL1, KIR2DL1, JAK1, ITGB2, ITGA5, ITGA6, ILF3, IL17A, IL12RB2, IL10RA, IL9, IL5, IL2RA, IL1R1, IGHG2, IGH, CCN1, KPNA2, LAMA5, LBP, MDM2, MRE11, MPL, MMP3, MLH1, CXCL9, CIITA, MGMT, RAB8A, CD46, LDLR, MAPT, SMAD5, SMAD3, M6PR, SH2D1A, LTF, LPL, LGALS3, PNPP1
- Nightmare Disorder Wikipedia
-
Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia
Wikipedia
Another consideration goes to hospital referral; although more severe pneumonia requires admission to an acute care facility, this also predisposes to hazards of hospitalization such as delirium , urinary incontinence , depression , falls , restraint use, functional decline, adverse drug effects and hospital infections . [26] Therefore, mild pneumonia might be better dealt with inside the long-term care facility. [27] [28] [29] In patients with a limited life expectancy (for example, those with advanced dementia), end-of-life pneumonia also requires recognition and appropriate, palliative care . [30] Prognosis [ edit ] Healthcare-associated pneumonia seems to have fatality rates similar to hospital-acquired pneumonia, worse than community-acquired pneumonia but less severe than pneumonia in ventilated patients. [31] Besides clinical markers like tachypnea (fast breathing) or a high white cell count ( leukocytosis ), the prognosis seems to be influenced by the underlying associated diseases ( comorbidities ) and functional capacities (for example, the ADL score ). [32] [33] [34] Many patients have a decreased health condition after the episode. [35] Epidemiology [ edit ] Several studies found that healthcare-associated pneumonia is the second most common type of pneumonia, occurring less commonly than community-acquired pneumonia but more frequently than hospital-acquired pneumonia and ventilator-associated pneumonia.
- Photoinhibition Wikipedia
-
Burning Mouth Syndrome
Wikipedia
International Headache Society. Archived from the original on 28 September 2013 . Retrieved 7 May 2013 . ^ Porter, R.A.
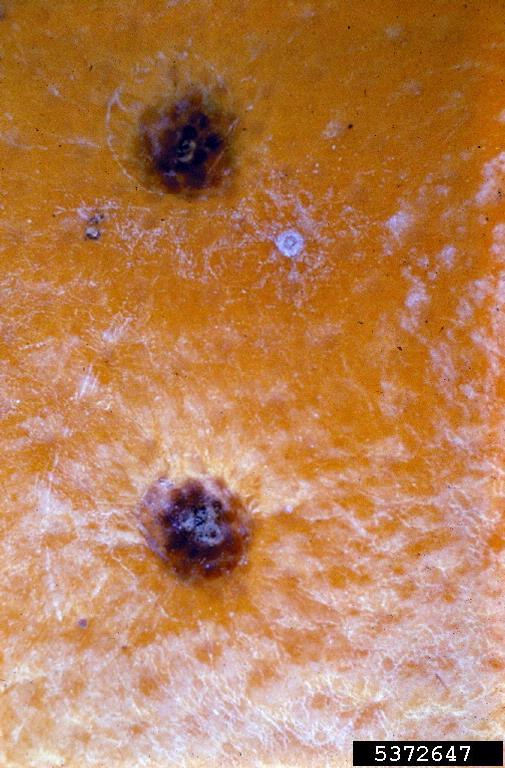
- Citrus Black Spot Wikipedia