-
Neglected Tropical Diseases
Wikipedia
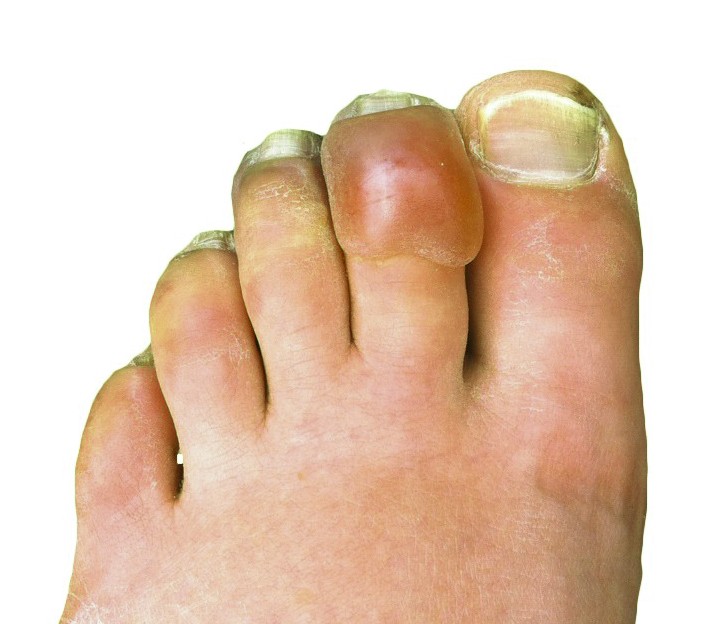
The virus was first isolated from an outbreak in Tanzania in 1952. [27] Chikungunya virus is a member of the genus Alphavirus and family Togaviridae. [27] The word chikungunya is from the Makonde which means "that which bends up", and this refers to the effect of the debilitating joint pain on the patient. [27] Symptoms, generally appearing 5–7 days after exposure, can be confused with dengue and include fever, rash, headache, joint pain, and swelling. [28] The disease mainly occurs in Africa and Asia. [29] Dracunculiasis [ edit ] Main article: Dracunculiasis Dracunculus medinensis larvae Dracunculiasis is also known as Guinea-worm disease.
-
Adult Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Wikipedia
The uptake transporters for dopamine [28] and norepinephrine [29] are overly active and clear these neurotransmitters from the synapse a lot faster than in normal individuals. ... "Evidence-based guidelines for the pharmacological management of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: update on recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology" . Journal of Psychopharmacology . 28 (3): 179–203. doi : 10.1177/0269881113519509 .
-
Auditory Processing Disorder
Wikipedia
Inheritance of Auditory Processing Disorder refers to whether the condition is inherited from your parents or "runs" in families. [28] Central auditory processing disorder may be hereditary neurological traits from the mother or the father. [29] Developmental [ edit ] In the majority of cases of developmental APD, the cause is unknown.
-
Hiv/aids In The United States
Wikipedia
In a survey of doctors in the mid to late 1980s, a substantial number of physicians indicated that they didn't have an ethical obligation to treat and care for those patients with HIV/AIDS. [27] A study of primary care providers showed that half would not care for patients if they were given a choice. [28] In 1990, a national survey of doctors showed that "only 24% believed that office-based practitioners should be legally required to provide care to individuals with HIV infection." [26] However, there were many doctors who chose to care for these patients with AIDS for different reasons: they shared the same sexual orientation as the infected, a commitment to providing care to the diseased, an interest in the mysteries of infectious disease, or a desire to tame the awful threat. [26] Treating patients infected with the AIDS virus changed some doctors' personal lives, as it caused them to have to deal with some of the same stigmas that their patients had. ... Retrieved March 20, 2010 . ^ "Federal Register Volume 52, Issue 167 (August 28, 1987)" . govinfo.gov . Office of the Federal Register. pp. 32540–32544 . ... Retrieved 2009-12-18 . ^ Mutua, Athena (September 28, 2006). Progressive Black Masculinities .
-
Frostbite
Wikipedia
Several notable cases of frostbite include: Captain Lawrence Oates , an English army captain and Antarctic explorer who in 1912 died of complications of frostbite; [23] noted American rock climber Hugh Herr , who in 1982 lost both legs below the knee to frostbite after being stranded on Mount Washington (New Hampshire) in a blizzard; [24] Beck Weathers , a survivor of the 1996 Mount Everest disaster who lost his nose and hands to frostbite; [25] Scottish mountaineer Jamie Andrew , who in 1999 had all four limbs amputated due to sepsis from frostbite sustained after becoming trapped for four nights whilst climbing Les Droites in the Mont Blanc massif . [26] Research directions [ edit ] Evidence is insufficient to determine whether or not hyperbaric oxygen therapy as an adjunctive treatment can assist in tissue salvage. [27] Cases have been reported, but no randomized control trial has been performed on humans. [28] [29] [30] [31] [32] Medical sympathectomy using intravenous reserpine has also been attempted with limited success. [21] Studies have suggested that administration of tissue plasminogen activator (tPa) either intravenously or intra-arterially may decrease the likelihood of eventual need for amputation. [33] References [ edit ] ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w Handford, C; Thomas, O; Imray, CHE (May 2017).
-
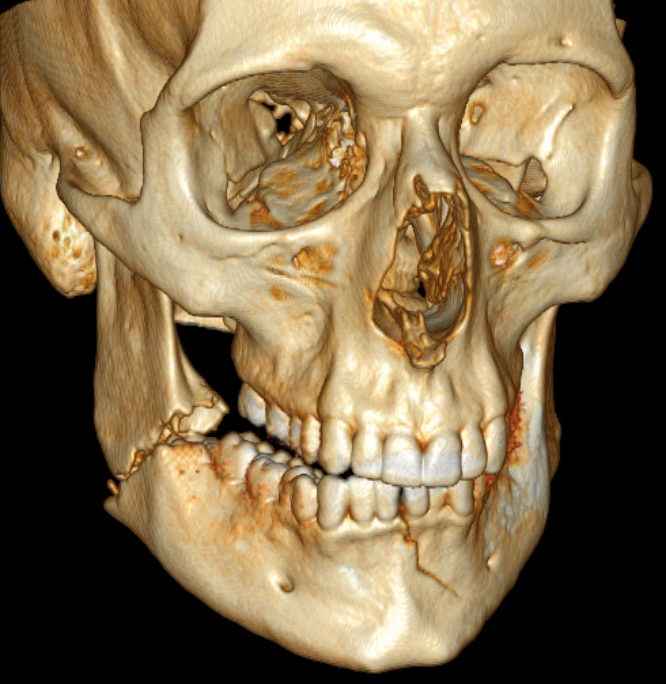
Mandibular Fracture
Wikipedia
In these cases, oral surgeons sometimes opt for external fixation, closed reduction, supraperiosteal dissection or other techniques to maintain the periosteal blood flow. [28] High velocity injuries [ edit ] In high velocity injuries, the soft tissue can be severely damaged far from the bullet wound itself due to hydrostatic shock .
-
Fixation Disparity
Wikipedia
A comparison of subjective versus objective measures revealed a significant correlation (about r = 0.5 – 0.7) for the y-intercept (sFD 0 versus oFD 0 ), but not for the slope. [24] In natural vision without prisms, the vergence state varies as a function of the viewing distance of the target: the subjective fixation disparity may shift towards more exo states from far-vision to near-vision. [25] The effect of proximity is different for objective and subjective fixation disparity. [26] During reading of text material, the objective fixation disparity can be measured with eye trackers in the moments of fixation. [27] [28] This reading fixation disparity has the following properties: Fusion is maintained despite a fixation disparity during a reading fixation [29] The reading fixation disparity reaches a minimum at a certain moment in time during the fixation [30] The reading fixation disparity shifts to more eso conditions in the course of reading a line from left to right [31] Blurring the text makes the reading fixation disparity more exo [32] The reading fixation disparity is smaller when the text characters have a more pronounced periodic spatial structure [33] Clinical diagnostic criteria [ edit ] Fixation disparity can differ considerably between observers with normal binocular vision.
-
Yellow Fever
Wikipedia
In recent years, this has been the most common form of transmission of yellow fever in Africa. [28] Concern exists about yellow fever spreading to southeast Asia, where its vector A. aegypti already occurs. [29] Pathogenesis [ edit ] After transmission from a mosquito, the viruses replicate in the lymph nodes and infect dendritic cells in particular.
-
Coccidioidomycosis
Wikipedia
Greyhound dogs often get coccidioidomycosis as well, and their treatment regimen involves 6–12 months of ketoconazole, to be taken with food. [28] Toxicity [ edit ] Conventional amphotericin B desoxycholate (AmB: used since the 1950s as a primary agent) is known to be associated with increased drug-induced nephrotoxicity (kidney toxicity) impairing kidney function . [29] Other formulations have been developed such as lipid soluble formulations to mitigate such side-effects as direct proximal and distal tubular cytotoxicity . ... Inmates Should Be Tested for Valley Fever Immunity" . California HealthLine . 2014-07-28. ^ Shehab, Ziad M. (2010). "Coccidioidomycosis". ... Archived from the original (PDF) on February 28, 2013 . Retrieved 11 July 2013 . ^ Fisher, M. ... Korean Journal of Internal Medicine . 28 (4): 403–7. doi : 10.3904/kjim.2013.28.4.403 .
-
Gluten-Related Disorders
Wikipedia
To calm itching, dapsone is often recommended as a temporary treatment, during the time it takes for the diet to work, but it has no effect on the gastrointestinal changes and may have important side effects. [25] [28] Gluten ataxia [ edit ] Play media A male with gluten ataxia: previous situation and evolution after three months of gluten-free diet Gluten ataxia is an autoimmune disease triggered by the ingestion of gluten. [2] With gluten ataxia, damage takes place in the cerebellum, the balance center of the brain that controls coordination and complex movements like walking, speaking and swallowing, with loss of Purkinje cells .
-
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Wikipedia
Postinfection, further risk factors are young age, prolonged fever, anxiety, and depression. [24] Psychological factors, such as depression or anxiety, have not been shown to cause or influence the onset of IBS, but may play a role in the persistence and perceived severity of symptoms. [25] Nevertheless, they may worsen IBS symptoms and quality of life. [25] Antibiotic use also appears to increase the risk of developing IBS. [26] Research has found that genetic defects in innate immunity and epithelial homeostasis increase the risk of developing both post-infectious as well as other forms of IBS. [27] Stress [ edit ] Publications suggesting the role of the brain–gut axis appeared in the 1990s [28] and childhood physical and psychological abuse is often associated with the development of IBS. [29] It is believed that psychological stress may trigger IBS in predisposed individuals. [30] Given the high levels of anxiety experienced by people with IBS and the overlap with conditions such as fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome , a potential explanation for IBS involves a disruption of the stress system.IL10, TPSAB1, MAGI2, CRHR1, CRHR2, HTR7, NOS3, MLXIPL, PDIA3, IKBKG, RPSA, TRPV1, ACAD8, TNF, SLC6A4, IL6, TNFSF15, POMC, IL1B, SPATA5, CRH, NOD2, TPH1, HTR3A, GCG, BDNF, CXCL8, COMT, SI, F2RL1, CNR1, NGF, OPN1SW, GNB3, IL1A, C1QL1, IL17A, TAC1, TLR4, IFNG, SCN5A, GLP1R, VCL, IL23R, OR2AG1, GUCY2C, TRPV4, ITGAX, PRSS3, PYY, IL13, MUC1, NLRP6, ETFA, MIR29A, STIN2-VNTR, NR3C1, TPMT, TGFB1, HP, VIP, CXCL12, LINC02210-CRHR1, FAAH, SST, ATG16L1, ZGLP1, GPBAR1, NKX2-3, IL18, IL2RA, KRT8, HTR4, LOC110806262, HTR2A, HLA-B, IL4, FGF19, LCT, TLR2, DLG5, CLDN1, APLN, NR1I2, CXCR4, XDH, TBC1D9, SYNM, NEUROG3, FOXP3, TLR5, TREM1, MPO, EHMT1, S100A10, RET, RARRES2, PTPN2, PTGS2, TPH2, SERPINA1, ABCB1, NPR3, NPY, PRKCD, CLEC11A, GHSR, FGFR4, GDNF, F2R, ESR1, GJA1, FAP, CHGA, CDH1, CNR2, CD14, CRP, MAGEC2, HSPA14, AQP1, GRIN2B, AQP3, IBD5, IBD4, NXPH1, TBX21, SCG3, SETD2, FLVCR1, REM1, AQP6, IL23A, ARSA, GSDMB, LGR6, BIRC2, KIR2DL5A, PELI1, ACKR3, KCNQ5, NSFL1C, LANCL2, NUDT15, GDE1, PACC1, ANO1, SLC52A1, XIAP, TUG1, KRT20, AQP8, TLR9, IGLV5-48, APOL2, PTPN22, BCLAF1, UBD, ABCC4, EBI3, CELA3A, C3, CAD, CALCA, HDAC4, SUMF2, NAPSA, ITM2B, ADIPOQ, SLC9A3R1, CALCR, LPAR2, KCNQ4, CXCR6, TNFSF13B, TRAF3IP2, PLK2, PART1, GAS5, CADM1, LPAR3, SIRT1, BCL2, ACSBG1, TNFRSF17, SSPO, MAST3, DKK1, COPE, AKAP13, BRS3, CCR9, SLC5A7, GORASP1, PROK2, MIR10A, MIR24-1, MIR22, MIR181C, MIR155, MIR150, MIR132, MIR130B, MIR106A, VN1R17P, IRGM, CELIAC2, HTR3E, NEAT1, MRGPRX1, STH, GPRC6A, ADRA1A, GPR166P, CT83, IBD20, ADCY1, MTCO2P12, ADORA2A, CBSL, IFNG-AS1, PSC, OCLN, ADORA2B, MIR148B, KRT8P3, H3P37, LINC00273, MIR510, MIR490, KIR2DL5B, MIR342, LTO1, ADRA2A, PIEZO2, HAVCR2, SSX2IP, FCRL3, NLRP3, PRDM6, MYLK3, FATE1, MYLK2, MAP1LC3B, MRGPRX3, COL18A1, AKR1B1, NLRX1, SLC52A2, WNK1, CLDN2, ANK1, MRGPRX2, MRGPRX4, ADRA2B, CDAN1, OXER1, AGA, KLB, AGER, ANKRD30BP2, AHSG, IL34, PWAR1, EXOSC6, AIF1, SIRPA, RNF183, GPR151, RBM45, NMS, ALCAM, CAMP, CASR, F2RL3, MOS, MYLK, ESR2, MTHFR, COX2, MST1, MSI1, F2, MMP9, LRP5, MMP2, MME, MLH1, MIF, KITLG, MCM6, MBL2, CEACAM6, NCF2, NELL1, NFKBIA, SLC25A3, SLC26A2, CFP, PEPD, PRDX1, P2RY2, P2RY1, OXTR, OXT, OPRK1, EDNRA, EGR1, EPHB2, NOS2, NOS1, CYP4F3, LCN2, PIK3CA, HSD11B1, GLUL, GNRH1, HTR2B, GOT2, HTR1B, HSPD1, HSD11B2, CXCR3, FABP4, HMGB1, HLA-DRB1, GPR42, HIF1A, HGD, GRIA1, GRIN2A, GLI1, GLB1, GJB2, IL1RN, KIF22, KIT, KIR3DS1, KIR2DS5, KIR2DS1, FDXR, ISG20, ING1, FUS, FYN, GATA3, IL9, GFRA3, CBLIF, IL2, DMD, PIK3CB, KALRN, CGA, TST, CD80, CD68, CDC42, TNFRSF1B, CDKN3, CFL1, THOP1, SYT1, THAS, TH, TGFBR2, TG, TFRC, TFF3, TESK1, MS4A1, VEGFA, EZR, BEST1, TRPA1, ENDOU, PER2, CASP3, GRM7, IL18R1, TNFRSF25, CAT, FZD4, CDR3, RUNX3, CBS, XBP1, WNT1, CCK, CHRNA5, STAT6, PIK3CD, PRTN3, CTSL, RAN, MOK, RAC2, CTSS, CX3CR1, CYP2B6, ACE, ST14, PRSS1, DECR1, PON1, DMBT1, PLEK, PKM, PIK3CG, RELA, CTSB, S100A8, S100A9, SSTR4, CLCN5, SOD1, SNRPB, SLC11A1, SLC9A1, SLC6A2, CLDN7, CRHBP, CXCL11, CCL16, CCL11, SCT, ADA, CSF2RA, ACHE
-
Tonsillitis
Wikipedia
., Corynebacterium diphtheriae , Treponema pallidum , and Neisseria gonorrhoeae . [18] [19] [20] [21] Anaerobic bacteria have been implicated in tonsillitis, and a possible role in the acute inflammatory process is supported by several clinical and scientific observations. [22] Sometimes tonsillitis is caused by an infection of spirochaeta and treponema , which is called Vincent's angina or Plaut -Vincent angina. [ non-primary source needed ] [23] Within the tonsils, white blood cells of the immune system destroy the viruses or bacteria by producing inflammatory cytokines like phospholipase A2 , [ non-primary source needed ] [24] which also lead to fever. [25] [26] The infection may also be present in the throat and surrounding areas, causing inflammation of the pharynx . [1] [27] Diagnosis [ edit ] There is no firm distinction between a sore throat that is specifically tonsillitis and a sore throat caused by inflammation in both the tonsils and also nearby tissues. [1] [28] An acute sore throat may be diagnosed as tonsillitis , pharyngitis , or tonsillopharyngitis (also called pharyngotonsillitis), depending upon the clinical findings. [1] Throat swab.GALNS, PAGR1, GAST, MBL3P, VDR, IFNG, IL1B, MBL2, DEFB1, RXRB, TRBV20OR9-2, S100A7, CCL20, CCL24, SKP1, SOD2, BCL2, TNFSF13, TLR4, PRCP, PDLIM7, ANP32B, CCL27, PART1, TLR9, AICDA, RNASE2, LTF, MTHFR, CCNB1, CDKN2A, EGFR, FANCD2, FCN2, GEM, GPX1, HIF1A, HLA-B, HLA-C, IGHG3, IL6, CXCL8, IL10, KIR2DS1, KIR3DL1, KIR3DL2, LTA, FDCSP
-
Prelabor Rupture Of Membranes
Wikipedia
About half of women will give birth within 5 hours, and 95% will give birth within 28 hours without any intervention. [11] The younger the baby, the longer the latency period (time between membrane rupture and start of labor).
-
Osteonecrosis Of The Jaw
Wikipedia
Cancellous bone, with its mesh like structure and spaces filled with marrow tissue is more susceptible to damage by bone infarcts, leading to hypoxia and premature cell apoptosis . [14] [15] [26] [27] The mean life-span of osteocytes has been estimated to be 15 years in cancellous bone, [28] and 25 years in cortical bone. [29] while the average lifespan of human osteoclasts is about 2 to 6 weeks and the average lifespan of osteoblasts is approximately 3 months. [30] In healthy bone these cells are constantly replaced by differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSC). [31] However, in both non-traumatic osteonecrosis and alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head, a decrease in the differentiation ability of mesenchymal stem into bone cells has been demonstrated, [32] [33] and altered osteoblastic function plays a role in ON of the femoral head. [34] If these results are extrapolated to ONJ the altered differentiation potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) combined with the altered osteoblastic activity and premature death of existing bone cells would explain the failed attempts at repair seen in ischaemic-damaged cancellous bone tissue in ONJ. ... "Maxillofacial osteonecrosis in a patient with multiple "idiopathic" facial pains". J. Oral Pathol. Med . 28 (9): 423–32. doi : 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1999.tb02101.x .
-
Hiv And Pregnancy
Wikipedia
However, delay in ART initiation may prove less effective in reducing infection transmission. [28] Antiretroviral therapy is used at the following times in pregnancy to reduce the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV: [29] During pregnancy: pregnant women infected with HIV receive an oral regimen of at least three different anti-HIV medications (such as tenofovir , emtricitabine and efavirenz ). ... "Earlier initiation of ART and further decline in mother-to-child HIV transmission rates, 2000-2011". AIDS . 28 (7): 1049–57. doi : 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000212 .
-
Conversion Disorder
Wikipedia
In neurology clinics, the reported prevalence of unexplained symptoms among new patients is very high (between 30 and 60%). [25] [26] [27] However, diagnosis of conversion typically requires an additional psychiatric evaluation, and since few patients will see a psychiatrist [28] it is unclear what proportion of the unexplained symptoms are actually due to conversion.
-
Cerebral Edema
Wikipedia
In addition to edema, these therapies are associated with microhemorrhages in the brain known as ARIA-H. [27] Familiarity with ARIA can aid radiologists and clinicians in determining optimal management for those affected. [16] Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome [ edit ] Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is a rare clinical disease characterized by cerebral edema. [12] The exact pathophysiology , or cause, of the syndrome is still debated but is hypothesized to be related to the disruption of the blood-brain barrier. [12] The syndrome features acute neurological symptoms and reversible subcortical vasogenic edema predominantly involving the parieto-occipital areas on MR imaging . [28] PRES in general has a benign course, but PRES-related intracranial hemorrhage has been associated with a poor prognosis. [29] Idiopathic delayed-onset edema [ edit ] Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is effective treatment for several neurological and psychiatric disorders, most notably Parkinson's disease . [30] DBS is not without risks and although rare, idiopathic delayed-onset edema (IDE) surrounding the DBS leads have been reported. [14] Symptoms can be mild and nonspecific, including reduction of the stimulation effect, and can be confused for other causes of edema. [14] Thus, imaging is recommended to rule out other causes. [14] The condition is generally self-limiting and the exact mechanism of the cause is unexplained. [14] Early identification can help persons affected avoid unnecessary surgical procedures or antibiotic treatments. [14] Massive Brain Swelling after Cranioplasty [ edit ] Decompressive craniectomy is frequently performed in cases of resistant intracranial hypertension secondary to several neurological conditions and is commonly followed by cranioplasty . [15] Complications, such as infection and hematomas after cranioplasty occur in roughly about a third of cases. [15] Massive brain swelling after cranioplasty (MSBC) is a rare and potentially fatal complication of an uneventful cranioplasty that has recently been elucidated. [15] Preoperative sinking skin flap (SSF) and intracranial hypotension were factors associated with the development of MSBC after cranioplasty. [15] [31] Data suggests that pathologic changes are triggered immediately following the procedure, especially an acute increase in intracranial pressure. [15] Radiation-Induced Brain Edema [ edit ] With the rise of sophisticated treatment modalities such as gamma knife , cyber knife , and intensity modulated radiotherapy , a large number of individuals with brain tumors are treated with radiosurgery and radiotherapy. [13] Radiation-induced brain edema (RIBE) is a potentially life threatening complication of brain tissue radiation and is characterized radiation necrosis, endothelial cell dysfunction, increased capillary permeability, and breakdown of the blood brain barrier . [13] Symptoms include headache, seizure, psychomotor slowing, irritability, and focal neurological deficits. [13] Options for management of RIBE are limited and include corticosteroids , anti platelet drugs, anticoagulants , hyperbaric oxygen therapy , multivitamins, and bevacizumab . [13] Brain tumor-associated cerebral edema [ edit ] This kind of cerebral edema is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with brain tumors and characterized by a disruption of the blood brain barrier and vasogenic edema. [32] The exact mechanism is unclear but hypothesized that cancerous glial cells ( glioma ) of the brain can increase secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which weakens the tight junctions of the blood–brain barrier . [33] Historically, corticosteroids such as dexamethasone were used to reduce brain tumor-associated vascular permeability through poorly understood mechanisms and was associated with systemic side effects. [33] Agents that target the VEGF signaling pathways, such as cediranib , have been promising in prolonging survival in rat models but associated with local and systemic side effects as well. [32] Diagnosis [ edit ] Cerebral edema is commonly present in a variety of neurological injuries. [1] [3] Thus, determining a definitive contribution of cerebral edema to the neurological status of an affected person can be challenging. [3] Close bedside monitoring of a person's level of consciousness and awareness of any new or worsening focal neurological deficits is imperative but demanding, frequently requiring admission into the intensive care unit (ICU). [3] Cerebral edema with sustained increased intracranial hypertension and brain herniation can signify impending catastrophic neurological events which require immediate recognition and treatment to prevent injury and even death. [1] [9] [10] [34] Therefore, diagnosis of cerebral edema earlier with rapid intervention can improve clinical outcomes and can mortality , or risk of death. [34] Diagnosis of cerebral edema relies on the following: Imaging [ edit ] Serial neuroimaging ( CT scans and magnetic resonance imaging ) can be useful in diagnosing or excluding intracranial hemorrhage , large masses, acute hydrocephalus , or brain herniation as well as providing information on the type of edema present and the extent of affected area. [1] [3] CT scan is the imaging modality of choice as it is widely available, quick, and with minimal risks. [1] However, CT scan can be limited in determining the exact cause of cerebral edema in which cases, CT angiography (CTA), MRI , or digital subtraction angiography (DSA) may be necessary. ... The following interventions are more specific treatments for managing cerebral edema and increased ICP: Osmotic Therapy [ edit ] The goal of osmotic therapy is to create a higher concentration of ions within the vasculature at the blood-brain barrier . [3] This will create an osmotic pressure gradient and will cause the flow of water out of the brain and into the vasculature for drainage elsewhere. [3] An ideal osmotic agent produces a favorable osmotic pressure gradient, is nontoxic, and is not filtered out by the blood-brain barrier . [3] Hypertonic saline and mannitol are the main osmotic agents in use, while loop diuretics can aid in the removal of the excess fluid pulled out of the brain. [1] [3] [7] [43] Hypertonic saline is a highly concentrated solution of sodium chloride in water and is administered intravenously . [3] It has a rapid-onset, with reduction of pressures within 5 minutes of infusion, lasting up to 12 hours in some cases, and with negligible rebound pressure. [44] The exact volume and concentration of the hypertonic saline varies between clinical studies. [3] [44] [45] Bolus doses, particularly at higher concentrations, for example 23.4%, are effective at reducing ICP and improving cerebral perfusion pressure. [44] [46] In traumatic brain injuries , a responsiveness to hypertonic saline lasting greater than 2 hours was associated with decreased chance of death and improved neurologic outcomes. [44] The effects of hypertonic saline can be prolonged with combination to agents such as dextran or hydroxyethyl starch , although their use is currently controversial. [44] When compared to mannitol , hypertonic saline has been shown to be as effective as mannitol in decreased ICP in neurocritical care and is more effective in many cases. [44] Hypertonic saline may be preferable to mannitol in persons with hypovolemia or hyponatremia . [44] Mannitol is an alcohol derivative of simple sugar mannose , and is historically the most commonly used osmotic diuretic. [3] Mannitol acts as an inert solute in the blood, decreasing ICP through osmosis as discussed above. [44] Additionally, mannitol decreases ICP and increased cerebral perfusion pressure by increasing reabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid, dilutes and decreased the viscosity of the blood, and can cause cerebral vasoconstriction. [44] Furthermore, mannitol acts in a dose-dependent manner and will not lower ICP if it is not elevated. [44] However, the common limitation of the use of mannitol is its tendency to cause low blood pressure hypotension . [44] Compared to hypertonic saline, mannitol may be more effective at increasing cerebral perfusion pressures and may be preferable in those with hypoperfusion. [44] Loop diuretics , commonly furosemide , act within kidney to increase excretion of water and solutes. [3] Combination with mannitol produces a profound diuresis and increases the risk of systemic dehydration and hypotension. [3] Their use remains controversial. [3] Acetazolamide , a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor , acts as a weak diuretic and modulates CSF production but has not role in the management of cerebral edema from acute brain injuries. [3] It can be used in the outpatient management of cerebral edema caused by idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). [3] Glucocorticoids [ edit ] Glucocorticoids , such as dexamethasone , have been shown to decrease tight-junction permeability and stabilize the blood-brain barrier. [3] Their main use has been in the management of vasogenic cerebral edema associated with brain tumors, brain irradiation, and surgical manipulation. [1] [3] [11] Glucocorticoids have not been shown to have any benefit in ischemic stroke and have been found to be harmful in traumatic brain injury. [3] Due to the negative side effects (such as peptic ulcers, hyperglycemia, and impairment of wound healing), steroid use should be restricted to cases where they are absolutely indicated. [3] Hyperventilation [ edit ] As mentioned previously, hypoxia and hypercapnia are potent vasodilators in the cerebral vasculature, leading to increased cerebral blood flow (CBF) and worsening of cerebral edema. [3] Conversely, therapeutic hyperventilation can be used to lower the carbon dioxide content in the blood and reduce ICP through vasoconstriction . [3] The effects of hyperventilation, although effective, are short-lived and once removed, can often lead to a rebound elevation of ICP. [3] Furthermore, overaggressive hyperventilation and vasoconstriction and lead to severe reduction in CBF and cause cerebral ischemia , or strokes. [3] As a result, standard practice is to slowly reverse hyperventilation while more definitive treatments aimed at the primary cause are instituted. [3] It is important to note that prolonged hyperventilation in those with traumatic brain injuries has been shown to worsen outcomes. [3] Barbiturates [ edit ] Induction of a coma via the use of barbiturates , most notably pentobarbital and thiopental , after brain injury is used for secondary treatment of refractory ICP. [44] Yet their use is not without controversy and it is not clear whether barbiturates are favored over surgical decompression. [3] In patients with traumatic brain injuries, barbiturates are effective in reducing ICP but have failed to show benefit to clinical outcomes. [3] Evidence is limited for their use in cerebral disease that include tumor, intracranial hypertension , and ischemic stroke . [3] There are several adverse effects of barbiturates that limit their use, such as lowering of systemic blood pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure , cardiodepression, immunosuppression , and systemic hypothermia . [3] Hypothermia [ edit ] As discussed previously in the treatment of fever, temperature control has been shown to decrease metabolic demand and reduce further ischemic injury. [47] In traumatic brain injury, induced hypothermia may reduce the risks of mortality, poor neurologic outcome in adults. [48] However, outcomes varied greatly depth and duration of hypothermia as well as rewarming procedures. [47] [48] In children with traumatic brain injury, there was no benefit to therapeutic hypothermia and increased the risk of mortality and arrhythmia. [49] The adverse effects of hypothermia are serious and require clinical monitoring including increased chance of infection, coagulopathy , and electrolyte derangement. [3] The current consensus is that adverse effects outweigh the benefits and its use restricted to clinical trials and refractory increased ICP to other therapies. [3] [38] [48] Surgery [ edit ] The Monroe-Kellie doctrine states that the skull is a fixed and inelastic space and the accumulation of edema will compress vital brain tissue and blood vessels. [8] [38] Surgical treatment of cerebral edema in the context of cerebellar or cerebral infarction is typically done by removing part of the skull to allow expansion of the dura . [38] This will help to reduce the volume constraints inside of the skull. [38] A decompressive hemicraniectomy is the most commonly used procedure. [38] Multiple randomized clinical trials have shown reduced risk of death with hemicraniectomy compared with medical management. [38] [50] [51] However, no individual study has shown an improvement in the percentage of survivors with good functional outcomes. [38] Timing of decompressive craniectomy remains controversial, but is generally suggested that the surgery is best performed before there are clinical signs of brainstem compression . [38] Postoperative complications include wound dehiscence , hydrocephalus , infection, and a substantial proportion of patients may also require tracheostomy and gastrotomy in the early phase after surgery. [38] Outcomes [ edit ] Cerebral edema is a severe complication of acute brain injuries, most notably ischemic stroke and traumatic brain injuries , and a significant cause of morbidity and mortality. [3] [10] [34] Cerebral edema is the cause of death in 5% of all patients with cerebral infarction and mortality after large ischemic strokes with cerebral edema is roughly 20 to 30% despite medical and surgical interventions. [9] [38] Cerebral edema usually occurs between the second and fifth day after onset of symptoms. [9] Large territory ischemic strokes can lead to the rapid development of malignant brain edema and increased intracranial pressure. [52] Cerebral edema in the context of a malignant middle cerebral artery (MCA) infarct has a mortality of 50 to 80% if treated conservatively. [9] Individuals with cerebral edema had a worse 3-month functional outcome than those without edema. [9] These effects were more pronounced with increasing extent of cerebral edema and were independent of the size of the infarct. [9] Mild traumatic brain injury (TBI) represents 70-90% of all reported head injuries. [34] The presence of brain edema on the initial CT scan of those with traumatic brain injuries is an independent prognostic indicator of in-hospital death. [34] The association of brain edema with increased in hospital risk of death was observed in TBI across all level of severity. [34] Edema in the acute and chronic phases were associated with a worse neurologic and clinical outcome. [34] Children with TBI and cerebral edema have worse clinical outcomes as well. [34] Epidemiology [ edit ] As cerebral edema is present with many common cerebral pathologies, the epidemiology of the disease is not easily defined. [1] The incidence of this disorder should be considered in terms of its potential causes and is present in most cases of traumatic brain injury , central nervous system tumors , brain ischemia , and intracerebral hemorrhage . [1] In one study, cerebral edema was found in 28% of those individuals with thrombolysis-treated ischemic strokes, 10% of which occurred in severe forms. [9] A further study detected cerebral edema in 22.7% of cerebral ischemic strokes. [9] A meta-analysis of current studies showed that 31% of those affected by ischemic strokes developed cerebral edema in 31% of cases. [10] In traumatic brain injuries, cerebral edema occurred in greater than 60% of those with mass lesions, and in 15% of those with initial normal CT scans. [53] Research [ edit ] The current understanding of the pathophysiology of cerebral edema after traumatic brain injury is incomplete. [8] Current treatment therapies aimed at cerebral edema and increased intracranial pressure are effective at reducing intracranial hypertension but have unclear impacts on functional outcomes. [53] Additionally, cerebral and ICP treatments have varied effects on individuals based on differing characteristics like age, gender, type of injury, and genetics. [53] There are innumerable molecular pathways that contribute to cerebral edema, many of which have yet to be discovered. [8] Researchers argue that the future treatment of cerebral edema will be based on advances in identifying the underlying pathophysiology and molecular characteristics of cerebral edema in a variety of cases. [8] [53] At the same time, improvement of radiographic markers, biomarkers, and analysis of clinical monitoring data is essential in treating cerebral edema. [53] Many studies of the mechanical properties of brain edema were conducted in the 2010s, most of them based on finite element analysis (FEA), a widely used numerical method in solid mechanics.
-
Hypothyroidism
Wikipedia
It is characterized by infiltration of the thyroid gland with T lymphocytes and autoantibodies against specific thyroid antigens such as thyroid peroxidase , thyroglobulin and the TSH receptor . [7] After women give birth, about 5% develop postpartum thyroiditis which can occur up to nine months afterwards. [26] This is characterized by a short period of hyperthyroidism followed by a period of hypothyroidism; 20–40% remain permanently hypothyroid. [26] Autoimmune thyroiditis is associated with other immune-mediated diseases such as diabetes mellitus type 1 , pernicious anemia , myasthenia gravis , celiac disease , rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus . [7] It may occur as part of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome ( type 1 and type 2 ). [7] Group Causes Primary hypothyroidism [7] Iodine deficiency (developing countries), autoimmune thyroiditis, subacute granulomatous thyroiditis , subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis , postpartum thyroiditis , previous thyroidectomy , acute infectious thyroiditis , [27] previous radioiodine treatment, previous external beam radiotherapy to the neck Medication: lithium -based mood stabilizers , amiodarone , interferon alpha , tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as sunitinib Central hypothyroidism [9] Lesions compressing the pituitary ( pituitary adenoma , craniopharyngioma , meningioma , glioma , Rathke's cleft cyst , metastasis , empty sella , aneurysm of the internal carotid artery ), surgery or radiation to the pituitary, drugs, injury, vascular disorders ( pituitary apoplexy , Sheehan syndrome , subarachnoid hemorrhage ), autoimmune diseases ( lymphocytic hypophysitis , polyglandular disorders), infiltrative diseases (iron overload due to hemochromatosis or thalassemia , neurosarcoidosis , Langerhans cell histiocytosis ), particular inherited congenital disorders, and infections ( tuberculosis , mycoses , syphilis ) Congenital hypothyroidism [28] Thyroid dysgenesis (75%), thyroid dyshormonogenesis (20%), maternal antibody or radioiodine transfer Syndromes: mutations (in GNAS complex locus , PAX8 , TTF-1/NKX2-1 , TTF-2/FOXE1 ), Pendred's syndrome (associated with sensorineural hearing loss ) Transiently: due to maternal iodine deficiency or excess, anti-TSH receptor antibodies, certain congenital disorders, neonatal illness Central: pituitary dysfunction (idiopathic, septo-optic dysplasia , deficiency of PIT1 , isolated TSH deficiency) In consumptive hypothyroidism, high levels of type 3 deiodinase inactivate thyroid hormones and thus lead to hypothyroidism. [29] High levels of type 3 deiodinase generally occur as the result of a hemangioma . [29] The condition is very rare. [29] Pathophysiology [ edit ] Diagram of the hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis. ... Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-12-28. ^ e-Library of Evidence for Nutrition Actions (eLENA) (2014).TSHB, TRHR, TG, APOE, SLC30A10, SHH, KDM5C, TRH, IGF1, NR1D1, BDNF, NCOR1, ATP2A2, UCP2, NOS3, PNPLA3, SERPINA7, SOD1, UCP3, TOMM70, NCAM1, IL10, PCNA, CYP19A1, ADRB2, DCX, ALAD, GPX1, PAX8, CDK5R1, DPYSL2, MTHFR, ND3, ELAVL4, TSHR, GSN, CAV1, F7, NCOA1, TPO, ENTPD1, SLC34A1, MT3, WNT3A, APOA5, COL1A2, COL2A1, SLC2A1, SLC9A1, PLOD3, LIPC, PHKA1, SLC26A5, MAP1B, MSTN, MAP1A, OTOF, GIP, RELN, NKX2-1, NEFL, ARSA, NGF, AQP3, APOC3, NRGN, ANXA5, ANXA2, ANXA1, PLOD2, PLOD1, PAM, PCSK1, PITX2, GRK3, IGFBP2, HSD3B1, NOS2, NEFH, BAD, THRA, SRD5A1, STAR, MYH6, MYH7, L1CAM, NEFM, ATP5PO, SLC5A5, SLC16A2, POU1F1, SLC26A4, FOXE1, DUOX2, IGSF1, PROP1, PIK3CA, FMR1, DUOXA2, IYD, GNAS, IFNG, FOXP3, ADA, HLA-DRB1, IL2RA, THRB, PDE8B, CHD7, STAT1, RET, HESX1, TNFRSF11B, COX2, IFIH1, LHX4, PTPN22, PDE10A, VAV3, CP, SCN4A, DCLRE1C, PTEN, PTCH1, PRL, ALG8, SRD5A3, RNASEH2B, ARID1B, PVT1, NAA25, SRY, TWNK, DCAF17, POLG, PMM2, IQCN, PTPN11, SOX3, RAB5B, PLEKHA1, SIX3, SKI, ATXN2, SBF1, SKIV2L, SALL1, BACH2, SAA1, RREB1, ACP5, PHRF1, ROBO1, RMRP, RFC2, LRRC8A, PRDM16, RAG2, RAG1, RAD51B, RAB5C, ALX4, NFKB1, STAT4, DNM1L, DEAF1, FBLN5, STK25, DLEU1, STUB1, TIMMDC1, SLC25A37, PLXNC1, RASGRP1, GNE, CEP57, SH2B3, TANK, PHF21A, DACT1, TRANK1, ELMO1, KEAP1, PIEZO1, ACAP1, RNASEH2A, CDON, CD226, RAI1, SAMHD1, PANX1, TBL2, PIK3R5, KAT6B, AGO2, TMEM131, GPR161, DLL1, EXOSC2, ADNP, POGZ, IQSEC2, MYH15, TREX1, POLG2, EFEMP2, RRM2B, NEK6, SEMA3E, TTC37, BTNL2, HIRA, ALMS1, ZIC2, XRCC4, FANCI, WFS1, CLIP2, STEAP3, UFD1, TYK2, TSC2, SEC24C, TSC1, TNFRSF1B, TGIF1, RAB20, WDR11, TF, TDGF1, HNF1B, TBX1, KCNAB2, BHLHE40, TP63, PHIP, PTRH2, GTF2IRD1, MPDU1, EIF2AK3, MED7, FADS2, SUFU, TRIP13, BUB3, SH2D2A, BAZ1B, UBASH3A, KYNU, FOXH1, SGPL1, MAGEL2, SLC66A1, CCN4, TNFRSF14, PIK3C2A, DNAH1, CLPB, GATA1, GABRD, ARL6IP6, FYN, FUCA1, FLT3, FLII, FOXI1, FGFR1, FGF8, MB21D2, EXT2, ELN, UBR1, DIO2, HIPK1, JMJD1C, SPATA13, GAS1, GCH1, CPT1C, HORMAD2, EDARADD, HPD, PROKR2, HNF4A, TANGO2, DNAJC19, NRG1, HBB, GTF2I, HT, KCTD19, GPC1, GP1BB, GNB1, ENPP1, GLI2, GH1, FGD2, FOXK1, NKX2-5, RSBN1L, LINC01301, ARVCF, MIR3681HG, PCAT1, ABCC6, IFNG-AS1, LINC01934, LINC00824, PTCSC2, CASC19, APC, SLC25A4, AKT1, LINC02357, LINC02621, ADCY7, ADAR, RERE, LINC00271, LINC01387, CD247, COMT, COL4A1, CDH13, LRBA, HECTD4, CD80, HCG22, CD2, MICOS10, LINC00299, CBLB, CAMK4, C12orf76, FMNL1, BUB1B, BUB1, HSD17B3, HJV, TRNS1, ITK, ARID5B, KARS1, KCNJ10, TRNQ, TRNN, MACIR, TRNL2, TRNL1, TRNH, KCNH7, LIFR, LIG4, LIMK1, TRNF, LPP, ND6, ND5, ND4, ND1, COX3, LRP4, PNPT1, COX1, DISP1, ITCH, MARS1, RNASEH2C, JAK1, MCM8, C1QTNF6, IGHGP, TRNS2, IL12RB2, IL7R, NPHS1, PLVAP, IL2RG, IP6K3, INPP5B, INSR, TRIM8, NODAL, NFATC1, IRF4, IRF5, TRNW, OPA1, LEP, MED12, TNF, CTLA4, CD274, CAT, ALB, PDCD1, DIO3, GPT, SLC20A1, MAPK3, PTH, THRA1/BTR, POMC, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, ACHE, LDLR, SHBG, IL6, IGFBP3, MIR224, GLUL, FSHR, LHX3, PLA2G2A, BRAF, LPA, CST3, BCL2, KCNQ1, GCG, TTF1, GHRHR, NR1I3, GJA1, REN, HLA-DQB1, AGT, PPIG, CRP, SLCO1C1, BRD2, CD68, ACTB, MOK, DECR1, MTTP, ANGPTL3, HAMP, SCGB3A2, SLC2A8, APOBR, GPR151, SLCO6A1, ANTXR2, AMN, COASY, ANGPTL8, USE1, COQ9, SLC16A10, GSTO2, CAMKMT, GSTK1, PCSK9, MAGI3, COPD, TIGIT, NUDT10, GLIS3, DACT2, SLC2A12, SERPINA13P, EHMT1, MIR206, UBE2Z, DNAJC17, IL33, MLXIPL, GSTT2B, POTEF, ZGLP1, CXADRP1, RORA, SMUG1, DPP4, GLP1R, GFAP, XRCC6, FASN, EGR1, EFNA5, DNMT1, LAMP1, DNASE2, DMP1, DIO1, ACE, CYP2B6, CXADR, GPER1, GSTP1, GSTT1, GZMB, HLA-C, HLA-DQA1, HOXD13, HPT, IGFBP1, IGHD, IGHG3, IL2, IL4, IL17A, CXCL10, ISG20, KRT6A, CTNNB1, MAPK14, CRH, BAAT, AGER, JAG1, AHR, APOA1, APOB, APP, AQP4, AR, ARNTL, ARR3, ATM, ATP4A, ATP7B, AVP, BCL6, CNR1, HCN2, BMPR2, C2, CAD, CALM1, CALM2, CALM3, CAPZB, CASP3, CASR, KRIT1, CD28, CD36, CETP, KRT17, LGALS3, SLC39A14, VEGFA, PER2, NR1I2, KSR1, ABCB11, CNBP, XK, TNFSF4, LRP1, TTN, TGFB1, TFAM, TERT, TEF, TRB, HSPB3, ADIPOQ, NCOR2, MED13, KCNE2, MPZL2, TRIM13, NCOA2, TXNRD2, TSBP1, PPARGC1A, RAB40B, METAP2, NLRP1, DKK1, SIRT1, TRAM1, SYT1, STAT3, SST, PPARD, LRPAP1, MAP2, MBL2, MME, MPO, MT1B, CLDN11, PAEP, PDE3B, ATP8B1, PIK3C3, PLIN1, PON1, PPARA, PPARG, SREBF2, PRKAA1, PRKAA2, PRKAB1, PRKAR1A, DNAJC3, PTGS2, PTH1R, RARA, RBP4, SLC2A3, SLC13A1, SOD2, SPG7, SREBF1, MTCO2P12
-
Horse Colic
Wikipedia
Enteroliths are not a common cause of colic, but are known to have a higher prevalence in states with a sandy soil or an abundance of alfalfa hay is fed, such as California, [12] [17] a state where 28% of surgical colics are due to enteroliths. [13] Alfalfa hay is thought to increase the risk due to the high protein content in the hay, which would likely elevate ammonia nitrogen levels within the intestine. [13] They may be more common in horses with diets high in magnesium, [17] and are also seen more often in Arabians , Morgans , American Saddlebreds , miniature horses , and donkeys , and usually occur in horses older than four years of age. [13] [17] Horses with enteroliths typically have chronic, low-grade, recurring colic signs, which may lead to acute colic and distention of the large colon after occlusion of the lumen occurs. ... Horses usually require 3–6 days of treatment before clinical signs improve. [28] Due to the risk of endotoxemia, laminitis is a potential complication for horses suffering from colitis, and may become the primary cause for euthanasia.
-
Sadomasochism
Wikipedia
The report concluded that the Sadomasochism diagnosis were outdated, non scientific, and stigmatizing. [28] [29] In 1995, Denmark became the first European Union country to have completely removed sadomasochism from its national classification of diseases. ... Revise F65 . 2009-09-24 . Retrieved 2018-12-28 . ^ "The ICD-11 Revision: Scientific and political support for the Revise F65 reform Second report to the World Health Organization" . Revise F65 . 2011-11-11 . Retrieved 2018-12-28 . ^ "Fetish and SM diagnoses deleted in Sweden" .