- Hypotonia, Infantile, With Psychomotor Retardation And Characteristic Facies 2 Omim
-
Neurodevelopmental Disorder With Hypotonia, Neuropathy, And Deafness
Omim
The mutation, which was found by a combination of autozygosity mapping and whole-exome sequencing, was confirmed by Sanger sequencing and segregated with the disorder in the family.
-
Joubert Syndrome 3
Omim
The missense mutation was found by homozygosity mapping and whole-exome sequencing. Functional studies of the S761L variant were not performed, but structural modeling predicted that it would cause detrimental structural changes.
-
Skewed X-Inactivation
Wikipedia
A mouse cell with the Xce genotype ad will have a greater number of the a -carrying than d -carrying X chromosomes inactivated, because the d -carrying X chromosome is less likely to be inactivated. [5] There are two theories on the mechanism Xce uses to affect inactivation. The first is that genomic differences in the Xce alleles alter the sequence of the long non-coding RNA that is an integral part of X chromosome inactivation. ... At the turn of the 21st century, ratio detection moved to more direct methods by using mRNA or protein levels, and whole exome sequencing . With the exception of escaped genes, only the active X chromosome will transcribe mRNA and produce protein. [9] The exome sequencing provides a dataset that shows target sequences, giving an indication of disease-related protein coding regions. mRNA sequencing is then used on these regions to focus on the X chromosome and find single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) that are associated with the disease. ... "Characterization of X Chromosome Inactivation Using Integrated Analysis of Whole-Exome and mRNA Sequencing" . PLOS One . 9 (12): e113036.
-
Wheat Allergy
Wikipedia
A study of mothers and infants on an allergen-free diet demonstrated that these conditions can be avoided if wheat sensitive cohort in the population avoid wheat in the first year of life. [22] As with exercise induced anaphylaxis, aspirin (also: tartrazine, sodium benzoate, sodium glutamate (MSG), sodium metabisulfite, tyramine) may be sensitizing factors for reactivity. [23] Studies of the wheat-dependent exercise induced anaphylaxis demonstrate that atopy and EIA can be triggered from the ingestion of that aspirin and probably NSAIDs allow the entry of wheat proteins into the blood, where IgE reacts within allergens in the dermal tissues. ... The published data on this approach are sparse, with the only double-blind study reporting negative results. [29] Diagnosis [ edit ] Diagnoses of wheat allergy may deserve special consideration. [17] Omega-5 gliadin, the most potent wheat allergen, cannot be detected in whole wheat preparations; it must be extracted and partially digested (similar to how it degrades in the intestine) to reach full activity. ... If multiple symptoms associated with wheat allergies are present in the absence of immunosuppressants then a wheat allergy is probable. [17] Prevention and treatment [ edit ] Main article: Gluten-free diet Management of wheat allergy consists of complete withdrawal of any food containing wheat and other gluten-containing cereals ( gluten-free diet ). [30] [31] Nevertheless, some patients can tolerate barley, rye or oats. [32] In people suffering less severe forms of wheat-dependent exercise induced anaphylaxis (WDEIA), may be enough completely avoiding wheat consumption before exercise and other cofactors that trigger disease symptoms, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and alcohol . [31] Wheat is often a cryptic contaminant of many foods; more obvious items are bread crumbs, maltodextrin , bran , cereal extract, couscous , cracker meal, enriched flour , gluten , high-gluten flour, high-protein flour, seitan , semolina wheat, vital gluten, wheat bran, wheat germ, wheat gluten, wheat malt, wheat starch or whole wheat flour . Less obvious sources of wheat could be gelatinized starch , hydrolyzed vegetable protein , modified food starch, modified starch , natural flavoring, soy sauce , soy bean paste, hoisin sauce, starch, vegetable gum , specifically beta-glucan , vegetable starch.
-
Nail Low-Sulfur Protein
Omim
Nails - Low-sulfur nail proteins Inheritance - Autosomal dominant ▲ Close
-
Proteolytic Capacity Of Plasma
Omim
Jacobsen (1968) concluded that low proteolytic capacity is inherited as an autosomal dominant. Increased tendency to thrombosis did not occur in these persons.
-
Epiblepharon Of Upper Lid
Omim
Eyes - Upper eyelid epiblepharon Inheritance - Autosomal dominant ▲ Close
- Ureter, Cancer Of Omim
-
Glaucoma 1, Open Angle, P
Omim
Bennett et al. (1989) stated that the 3 Norwegian families segregating autosomal dominant low-tension glaucoma described by Sandvig (1961) and which the author designated 'pseudoglaucoma,' appeared to have the same or a similar condition to the family they studied. Fingert et al. (2011) studied 10 affected individuals from a 4-generation African American pedigree segregating autosomal dominant normal tension glaucoma (NTG). ... The CNVs segregated with NTG in all 4 families, showing an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. No CNVs were detected in 1,045 Australian patients with HTG or in 254 unaffected controls. INHERITANCE - Autosomal dominant HEAD & NECK Eyes - Cupping of optic nerve head - Increased cup-to-disc ratio - Thin central cornea - Visual field defects MISCELLANEOUS - Early age of onset (mean age at diagnosis, 36 years) Most patients have intraocular pressures within the normal range (21 mmHg or less) MOLECULAR BASIS - Caused by duplication of 300kb (Chr12:64,803,839-65,098,981 (GRCh37)) on 12q14 ▲ Close
-
Dermatopathia Pigmentosa Reticularis
Wikipedia
Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis Other names Dermatopathic pigmentosa reticularis [1] : 511 Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis has an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance Specialty Medical genetics Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis is a rare, autosomal dominant [2] congenital disorder that is a form of ectodermal dysplasia . ... "Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis: a report of a family demonstrating autosomal dominant inheritance". J Am Acad Dermatol . 26 (2 pt. 2): 298–301. doi : 10.1016/0190-9622(92)70039-I . ... "Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome and dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis: two allelic ectodermal dysplasias caused by dominant mutations in KRT14" . Am. J. Hum.
-
Hypogammaglobulinemia
Wikipedia
Unfortunately, the diagnosis of hypogammaglobulinemia is often significantly delayed. [3] Research [ edit ] In 2015, a journal article by McDermott et al. reported on a case in which chromothripsis , normally a catastrophic event in which chromosomes undergo massive deletion and rearrangement within a single stem cell's DNA, cured a patient with WHIM syndrome , a primary immunodeficiency disease. WHIM is autosomal dominant and is caused by a gain-of-function mutation of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. ... She has fulfilled none of the criteria for WHIM syndrome except for mild hypogammaglobulinemia since then. WHIM-09 was the first patient ever described with myelokathexis, the "M" in WHIM syndrome, and her parents and siblings showed no sign of the syndrome. Therefore, the evidence is compatible with a WHIM mutation occurring de novo in patient WHIM-09, an autosomal dominant transition to two of her three daughters, and a spontaneous and complete remission in WHIM-09. This provides the first evidence that chromothripsis may result in clinical benefit, in particular, the cure of a genetic disease.
-
Monophalangy Of Great Toe
Omim
Limbs - Monophalangy of great toe Inheritance - Autosomal dominant ▲ Close
- Lentigines Omim
-
Parotidomegaly, Hereditary Bilateral
Omim
Neck - Bilateral parotid gland enlargement Inheritance - Autosomal dominant ▲ Close
-
Trichorhinophalangeal Syndrome, Type I
Omim
Description Trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type I is a malformation syndrome characterized by distinctive craniofacial and skeletal abnormalities and is inherited as an autosomal dominant (Momeni et al., 2000). TRPS I patients have sparse scalp hair, bulbous tip of the nose, long flat philtrum, thin upper vermilion border, and protruding ears. ... While showing that in most instances inheritance is autosomal dominant, Giedion et al. (1973) concluded that a recessive form probably exists. Gonadal mosaicism is a frequent phenomenon, however, and it is probably noteworthy that there was so little evidence for a recessive form. Autosomal dominant inheritance seemed unequivocal in light of a family in which affected grandfather, son, and grandson were observed (Murdoch, 1969; McKusick, 1972). ... Three Japanese families with 19 affected persons in a clear autosomal dominant pedigree pattern were reported by Sugiura et al. (1976). ... Although Giedion et al. (1973) concluded that a recessive form of TRPS I probably exists, the isolation of TRPS1, a putative transcription factor zinc finger protein that shows its effects in single dose, indicates that haploinsufficiency of this gene causes the condition which, therefore, is inherited as an autosomal dominant. Of the 6 patients in whom mutations were identified by Momeni et al. (2000), 3 were familial and 3 were sporadic; all 6 showed heterozygosity for a mutation.
-
Hyperthyroidism
Wikipedia
PPT typically has several phases, the first of which is hyperthyroidism. This form of hyperthyroidism usually corrects itself within weeks or months without the need for treatment. ... This includes those that cannot tolerate medicines for one reason or another, people that are allergic to iodine, or people that refuse radioiodine. [27] If people have toxic nodules treatments typically include either removal or injection of the nodule with alcohol. [28] Radioiodine [ edit ] In iodine-131 ( radioiodine ) radioisotope therapy , which was first pioneered by Dr. Saul Hertz , [29] radioactive iodine-131 is given orally (either by pill or liquid) on a one-time basis, to severely restrict, or altogether destroy the function of a hyperactive thyroid gland. ... People not responding sufficiently to the first dose are sometimes given an additional radioiodine treatment, at a larger dose. ... In the United States, up to 10% of cats over ten years old have hyperthyroidism. [42] The disease has become significantly more common since the first reports of feline hyperthyroidism in the 1970s. ... Retrieved 10 May 2010 . ^ Differential diagnosis by laboratory medicine: a quick reference for physicians; Vincent Marks, Dušan Meško, page 156 ^ Biondi B1, Cooper DS (2008).CAT, GPX1, SOD1, GSR, TSHR, PON1, CARTPT, SOD2, AQP1, NR1D1, SERPINA7, PPARGC1A, UCP3, CP, PCSK1, CTSL, MTHFR, VIM, UGT1A1, CAB39, MCM7, HMOX1, IGF1R, ADIPOQ, BDH1, IL10, ANXA1, ANXA5, SLC34A1, ANXA2, APOC3, STK11, SLC9A1, APOA1, APOA2, THRB, AKT1, KCNJ18, GNAS, FOXP3, HLA-DRB1, ND6, TRNL1, TRNF, TRNH, RRM2B, TRNQ, TRNS1, ND5, RREB1, ND4, ND1, SLC25A4, MICOS10, COX3, COX2, COX1, POLG2, POLR3A, PDE10A, PDE8B, SEC24C, PTCSC2, GP1BB, TRNS2, MSTO1, TPO, JMJD1C, ARVCF, FAM227B, CACNA1S, TMEM71, TBX1, POLG, COMT, PIK3CA, LINC00511, PTEN, PRDM11, HIRA, TRNW, UFD1, BTNL2, TWNK, SLC16A2, HT, TG, SHBG, IGF1, REN, GH1, DIO2, VDR, VWF, SLC5A5, PAX8, MOK, LEP, PTH, PRL, TH, IL13, CLOCK, SST, RNH1, UCP2, NOS3, IL6, BCL2, CS, CST3, IL4, CTLA4, DIO1, EDN1, SHC3, SOST, F3, FN1, CD40, COX8A, PTPN22, BGLAP, GDF1, AHSG, AGT, PPP1R13L, AGTR1, AZGP1, MAGI3, WNK1, EHMT1, PGR-AS1, TM7SF2, GPR174, ZGLP1, THRA, CGB5, TGFB1, POTEF, MIR206, BCAR4, SYT1, LINC01193, CGB8, TXNRD3, COPD, PPARGC1B, NRG4, TNF, BACH2, GORASP1, DKK1, RAPGEF5, GDF15, ATG5, NAMPT, RNASET2, ATP6AP2, CPQ, LOH19CR1, FGF23, TXNRD2, STAT5B, TRPV1, SMG1, TRH, LMOD1, FGF21, MAT2B, SETD2, CD274, ICOS, CMAS, COQ9, RNF213, UCP1, TTN, TSHB, STAT6, ACP3, STAT5A, CGB3, CTH, CYP7A1, ACE, DIO3, DMD, DMP1, DNMT1, EGFR, EGR1, ELANE, EPHA3, F2, FCGRT, FLNB, XRCC6, GABPA, GCG, GIP, GJA1, GLP1R, GPX4, CPB2, CGA, STAT4, CETP, ADA, ADCY1, ADRB2, AGTR2, ALB, ANGPT1, APOB, APOD, APP, ARNTL, ATP2A2, BAAT, HCN2, BRCA1, C6, CA1, CALCA, SERPINA6, CBS, CD34, CD40LG, GSK3B, HIF1A, HLA-A, HLA-C, ACTB, NPY, NT5E, SERPINE1, PC, PDCD1, PDE3B, ENPP2, SLC26A4, ABCB1, PITX2, PPARA, PPARG, PRKAA1, PRKAA2, PRKAB1, RELA, RPS19, SLC2A1, SLC2A3, SLC2A4, NFE2L2, MYD88, MPST, IL2RA, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, HOXD13, HSPA4, HTC2, IFNG, IGFBP1, IGFBP3, IL2, CXCL8, MEN1, IL12B, ISG20, KNG1, KRT19, LDLR, LHB, LIPE, LPA, MBL2, CBSL
-
Citrullinemia Type I
Gene_reviews
Sign and symptoms classically occur within the first week of life while on a full protein diet: Increasing lethargy Somnolence Refusal to feed Vomiting Tachypnea Stroke Increased intracranial pressure (secondary to hyperammonemia) resulting in increased neuromuscular tone, spasticity, and ankle clonus Non-classic presentation. ... Sequence analysis of ASS1 is performed first and followed by gene-targeted deletion/duplication analysis if only one or no pathogenic variant is found. ... Pathogenic variants may include small intragenic deletions/insertions and missense, nonsense, and splice site variants; typically, exon or whole-gene deletions/duplications are not detected. ... Classic citrullinemia type I shares the phenotype of the typical acute neonatal hyperammonemia displayed by other defects in the first four steps in the urea cycle pathway. ... Evaluations can include: Molecular genetic testing if the pathogenic variants in the family are known; in utero diagnosis (which permits appropriate oral therapy beginning with first feeds), if possible, is preferred.
-
Histiocytosis-Lymphadenopathy Plus Syndrome
Omim
In a 13-year-old girl and her 11-year-old brother, born of first-cousin parents, Hamadah and Banka (2006) described well-demarcated, nontender, hyperpigmented induration over the inner aspects of both thighs, extending to the pubic area and to the knees, with mild hypertrichosis over the thigh plaques. ... Hussain et al. (2009) described 2 sisters, born of first-cousin Pakistani parents, who had autoantibody-negative diabetes mellitus, severe pancreatic exocrine deficiency, hyperpigmentation, hypertrichosis, hepatosplenomegaly with lymphadenopathy, and persistently elevated inflammatory markers. ... Jonard et al. (2012) reported a 17-year-old Moroccan girl, born of first-cousin parents, who presented with a single cervical node at age 12 years, biopsy of which revealed proliferation of histiocytes with destruction of the follicles, consistent with the massive sinus histiocytosis of Rosai-Dorfman disease. ... In a 17-year-old Moroccan girl, born of first-cousin parents, who had sensorineural hearing loss and sinus histiocytosis limited to a single cervical node (SHML), Jonard et al. (2012) identified homozygosity for the R363Q mutation (612373.0010) in the SLC29A3 gene. In 2 sibs from a consanguineous Moroccan family with nasal granulomatous histiocytosis, originally reported by de Pontual et al. (2008), Bolze et al. (2012) combined genomewide linkage analysis and whole-exome sequencing and identified a single pathologic variant in the chromosome 10 linkage region: a homozygous 1-bp deletion in the SLC29A3 gene (243delA; 612373.0012).
-
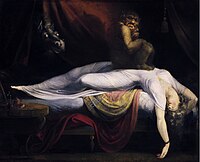
Sleep Paralysis
Wikipedia
Further studies must be conducted to determine whether there is a mistake in the signaling pathway for arousal as suggested by the first theory presented, or whether the regulation of melatonin or the neural populations themselves have been disrupted. ... Episode disruption techniques [30] are first practiced in session and then applied during actual attacks. ... Only 3% of individuals experiencing sleep paralysis that is not associated with a neuromuscular disorder have nightly episodes. [32] Sleep paralysis is more frequent in students and psychiatric patients. [4] Society and culture [ edit ] Etymology [ edit ] A 19th century version of Füssli's The Nightmare (1781) The original definition of sleep paralysis was codified by Samuel Johnson in his A Dictionary of the English Language as nightmare , a term that evolved into our modern definition. The term was first used and dubbed by British neurologist, S.A.K. ... Going to bed before the usual hour is a frequent cause of night-mare, as it either occasions the patient to sleep too long or to lie long awake in the night. Passing a whole night or part of a night without rest likewise gives birth to the disease, as it occasions the patient, on the succeeding night, to sleep too soundly. ... ISBN 978-1-4438-9107-3 . ^ "Watch: First Trailer for Creepy Sleep Paralysis Doc 'The Nightmare ' " . firstshowing.net .