-
Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Wikipedia
A few popular antibiotics include tetracycline , minocycline , and clindamycin . [27] Topical clindamycin has been shown to have an effect in double-blind placebo controlled studies. [28] Corticosteroid injections. Also known as intralesional steroids: can be particularly useful for localized disease, if the drug can be prevented from escaping via the sinuses. ... Retrieved 27 October 2017 . ^ a b c d e f "Hidradenitis suppurativa" . rarediseases.info.nih.gov . 2017. Archived from the original on 28 July 2017 . Retrieved 27 October 2017 . ^ Jemec G, Revuz J, Leyden JJ (2006). ... ISBN 9783540331018 . Archived from the original on 28 October 2017. ^ Medline Plus (2012). ... "Hidradenitis suppurativa associated with use of oral contraceptives" . BMJ . 298 (6665): 28–9. doi : 10.1136/bmj.298.6665.28 .NCSTN, PSENEN, NLRP3, MEFV, NOD2, PSTPIP1, GJB2, PSEN1, IL17A, TNF, HYOU1, KDF1, IL1B, IL1A, IFNG, CRP, IL23A, IL10, IL22, CXCL8, PAPPA, IL6, IL20, GLI3, IL36RN, IL17B, DCD, IL37, IL13, AGO1, YME1L1, ADIPOQ, IL32, ACAD8, ADM, SND1, AGO2, C5AR2, SULT1B1, KRT20, IL26, RETN, ELOVL7, IL1F10, MTDH, RBM45, TET3, IL1RL2, SAA1, TLR4, IFNA1, BCL2, CAMP, MS4A1, CD27, CHI3L1, CTNNB1, CTNND1, EPHB2, ERBB4, HLA-A, HLA-DRB1, IDH1, IDH2, IDH3B, IFNA13, TIE1, IL12RB1, ITGAL, ITGB2, KLRB1, LCN2, CYP4F3, NHS, P2RX7, PDE4A, ANXA5, SAA2, SULT1E1, TARBP2, TGFB1, MIR21
-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Wikipedia
Both correlate with NAFLD presence and severity, but their roles for diagnosis remain unclear. [18] [24] Although NAFLD has a genetic component, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) does not recommend screening family members as there is not enough confirmation of heritability, [4] although there is some evidence from familial aggregation and twin studies . [18] Diet [ edit ] According to the Asia-Pacific Working Group (APWG) on NAFLD, overnutrition is a major factor of NAFLD and NASH, particularly for lean NAFLD. [5] Diet composition and quantity, in particular omega-6 fatty acid and fructose , have important roles in disease progression from NAFL to NASH and fibrosis. [25] [26] Choline deficiency can lead to the development of NAFLD. [27] Pathophysiology [ edit ] The primary characteristic of NAFLD is the accumulation of lipids in the liver, largely in the form of triglycerides . [13] However, the mechanisms by which triglycerides accumulate and the reasons that accumulation can lead to liver dysfunction are complex and incompletely understood. [13] [28] [29] [30] NAFLD can include steatosis along with varied signs of liver injury: either lobular or portal inflammation (a form of liver injury) or ballooning degeneration . ... Although fibrosis improves with lifestyle interventions and weight loss, there is limited evidence for cirrhosis improvement. [5] [8] [51] [53] A combination of improved diet and exercise, rather than either alone, appears to best help manage NAFLD and reduce insulin resistance. [4] [9] [12] [54] [55] Motivational support, such as with cognitive behavioral therapy , is helpful, as most people with NAFLD do not perceive their condition as a disease, and thus have a low motivation to change. [4] [7] [10] [12] [28] Higher-intensity behavioral weight loss therapies (diet and exercise combined) may produce more weight loss than lower-intensity ones. ... Reviews reported the use of probiotics and synbiotics (combinations of probiotics and prebiotics ) were associated with improvement in liver-specific markers of hepatic inflammation, measurements of liver stiffness, and steatosis in persons with NAFLD. [65] [66] Physical activity [ edit ] Weight loss may improve NAFLD and is recommended particularly for obese or overweight people; [67] [68] [69] similar physical activities and diets are advisable for overweight people with NAFLD as for other obese and overweight people. [10] [55] Although physical activity is less important for weight loss than dietary adaptations (to reduce caloric intake), [28] the NICE advises physical activity to reduce liver fat even if there is no overall bodyweight reduction. [7] [10] Weight loss, through exercise or diet, is the most effective way to reduce liver fat and help NASH and fibrosis remission. [28] Exercise alone can prevent or reduce hepatic steatosis, but it remains unknown whether it can improve all other aspects of the liver; hence a combined approach with diet and exercise is advised. [4] [9] Aerobic exercise may be more effective than resistance training, although there are contradictory results. [7] [70] Vigorous training is preferable to moderate training, as only the high-intensity exercise reduced the chances of NASH developing into steatohepatitis or advanced fibrosis. [7] [71] The EASL recommends between 150 and 200 min/week in 3 to 5 sessions of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity or resistance training. ... Bariatric surgery is an effective method for obese and diabetic individuals with NAFLD to induce weight loss and reduce or resolve NASH inflammation, including fibrosis, and improve longevity. [7] [8] [12] [28] [77] [78] For the AASLD, bariatric surgery can be considered only for NASH on a case-by-case basis by an experienced bariatric surgery program. [4] Indeed, some individuals might develop new or worsened features of NAFLD. [78] About 92% of people with NAFLD saw an improvement in steatosis and 70% a complete resolution after bariatric surgery. [79] A preoperative diet such as a low-calorie diet or a very-low-calorie diet is usually recommended to reduce liver volume by 16–20%. ... Thus, people suffering from NAFLD deserve consideration for treatment regardless of the presence or absence of obesity. [5] [18] [28] [88] In children ages 1 to 19, the prevalence was found to be approximately 8% in the general population up to 34% in studies with data from child obesity clinics. [100] The majority of cryptogenic cirrhosis is believed to be due to NASH. [5] NAFLD prevalence is expected to increase steadily, [101] from 25% in 2018 to a projected 33.5% of people with NAFLD globally in 2030, and from 20% to a projected 27% of those with NAFLD will progress to NASH. [102] History [ edit ] The first acknowledged case of obesity-related non-alcoholic fatty liver was observed in 1952 by Samuel Zelman. [103] [104] Zelman started investigating after observing a fatty liver in a hospital employee who drank more than twenty bottles of Coca-Cola a day.TM6SF2, PNPLA3, NFE2L2, LEP, CYP2E1, PPARA, SIRT1, NR1H4, FGF21, ADIPOQ, PPARD, SREBF1, XBP1, LDLR, CAT, FAS, GNMT, CPT1A, PEMT, NR5A2, TGFB1, AHR, GSTP1, GSTM1, PRKCA, IL1A, JAK2, ACE, CD14, KLB, GSTT1, ALDH2, ABCC2, PTEN, PDK4, GSTA1, IL4, LIF, PRKCE, VLDLR, NQO1, PRKCD, FOLR2, EIF2AK1, TNFRSF1B, CYP17A1, CSF2, ALDH4A1, SCARB1, RDX, F2, STC2, LAMA1, IKBKG, CYP1A2, PRKACA, RAG2, B3GAT1, ALDH1B1, ADH1A, IL3, MMP1, ABCB4, TRIB3, ADH4, ADH1B, PRF1, SERPINB2, AHCY, ALDH1A1, GCKR, ATP5F1B, NCAN, PARVB, SAMM50, FDFT1, PTPRD, PLPP7, KRT18, MIR122, TLR4, ZNF512, IGF1, LEPR, MBOAT7, MIR21, SREBF2, CRP, MTTP, IL1B, SP4, ACTR5, IL6, CRACR2A, PRKAA2, SLC5A2, HFE, PRKAA1, COL13A1, GLP1R, GPT, GGT1, GCG, PPARG, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, GATAD2A, OSBPL5, DPP4, RBP4, NLRP3, EHBP1L1, PIK3CA, SCD, FBL, ERBB4, DDX60L, SHBG, PWWP3A, PRKAB1, EHMT1, LIPA, APOC3, GGTLC3, CREB5, PPARGC1A, ZGLP1, GGTLC4P, CD36, SLC17A5, CNBP, XPR1, GGT2, TNF, FGF19, TP63, GGTLC5P, ALB, MIR34A, AHSG, GH1, GABPA, LBP, HAMP, FASN, REN, LGALS3BP, CCL2, FABP1, NR1H3, IL17A, MLXIPL, HSD17B13, HNF4A, CYP3A4, SIRT3, AGTR1, APOE, PON1, RARRES2, RETN, MTOR, LOC102724197, FETUB, UCP2, GGTLC1, NR0B2, DECR1, MTHFR, IL10, PCSK9, ACACA, TP53, ANGPTL8, SERPINE1, MIR192, SOD1, APOB, VDR, IRS2, HMGB1, LPL, RCBTB1, NR1I2, APRT, CNR1, SERPINA1, SOD2, TRIB1, FADS2, STAT3, IRS1, FOXO1, PPP1R3B, NR3C2, MFAP1, SELENOP, PLIN2, GOLGA6A, AKT1, PNPLA2, MIR33A, TXNIP, ABCD1, CYBB, HIF1A, FGL1, IL18, FLII, APP, SLC27A5, TNFSF10, APOA5, HSD11B1, TMC4, NRG4, IFNG, HP, CCR2, GCK, KLF6, CHPT1, ABCB11, EGFR, EPAS1, CASP1, MAP3K5, CETP, SPP1, FTO, VEGFA, IFNL3, CEBPA, FABP4, INSR, MIR29A, BGLAP, TLR2, COL1A1, MIR140, GDF15, CYP7A1, ABCA1, SMN2, ANPEP, ACLY, BCO2, SMN1, CXCL16, HMOX1, PRRT2, FST, NTS, NR1I3, TIMP2, TIMP1, CPT2, CMKLR1, HPGDS, MIR155, TERT, BMS1, NPC1L1, CTNNB1, GPX1, CYP4F3, SMUG1, BCL2A1, PARP1, MIR451A, BNIP3, NEAT1, MT1B, MMP2, OR10A4, PRL, MAPK8, MIR378A, NAMPT, SLC10A2, SAV1, AFP, BCO1, GIP, FGFR4, ARNTL, CXCL10, PRKCB, CAV1, AGER, BCL2, GOT2, DLAT, ADIPOR2, AGT, ACE2, GPBAR1, MMP13, CORIN, FAM3A, MC4R, YAP1, POSTN, ABCG5, IL25, MAS1, NLRC4, TLR6, MUC1, CCN4, CCN3, ADIPOR1, SCP2, TNFSF11, FAM3B, CCL20, LUC7L3, SELPLG, GDE1, HSD17B7, SLC2A1, SLC2A2, MLYCD, SLPI, TNFRSF11B, IL22, TRPV1, SPARC, SPTBN1, ATRNL1, STAT5A, STAT5B, TBK1, SETD2, TEK, PDLIM3, S100A8, ROCK1, SOCS1, UGT1A1, MYDGF, CCL27, ENPP1, MTMR11, PPIG, CD163, MEG3, NAT10, PTPA, ECD, USP10, SOCS3, SELENBP1, APLN, MAPK1, PRTN3, SIRT2, ELOVL2, RIPK1, PTGS1, PTPN1, LPIN1, MOK, CRNKL1, SPINK1, CEACAM1, CBR1, MIR375, CASP8, CASP3, FOXO3, FOS, CALCR, MIR146B, GC, GCGR, HCC, BCAT1, GLUL, NCF1, GPR119, AZGP1, BHLHE23, LYPLAL1, GRN, NR3C1, PDIA3, AVP, ATHS, ATF3, C1QTNF1, AR, MLKL, FCGR2B, FOXA1, FAT1, MIR20A, MIR222, MIR149, CYBA, CYP1A1, COX8A, MAP3K8, CYP2D6, MIR126, CHIT1, CES1, ENHO, IRGM, ATN1, PLIN5, FFAR4, ELANE, ELAVL2, CD68, SLC13A5, ESR1, ESRRA, CD5L, FNDC5, ACSL4, AQP9, MIR200C, HSP90AA1, STEAP4, ALPP, ALOX15, ALOX5, ALOX12, LCN2, LINC01672, CXCL8, FAS-AS1, IDH2, INS, ACOX1, ACACB, IGFALS, LECT2, DHRS11, ORAI1, HSPA1A, HSPA1B, GRK2, ASRGL1, PSC, ERLIN1, CXCR6, MIR331, TRPC4AP, PRPF31, RNF19A, CAMKK2, SIRT1-AS, EIF2AK4, WWTR1, TOR1AIP1, POLDIP2, MIR330, APPL1, TIPARP, OSBPL3, LINC01684, HULC, MIR30C1, FGF20, AHSA1, MIR206, MIR212, RBMS3, PRDX4, LNCARSR, MIR223, MIR23B, IL37, MIR24-1, MIR27A, NAAA, SORBS1, INTU, MIR27B, LOC110806263, MIR29B1, SIGLEC7, NOX1, MIR29B2, MIR29C, AATF, MIR30B, PRDX5, LATS2, MIR30C2, B4GALT1-AS1, TMEFF2, MIR367, PHLPP2, LOC100505909, MCF2L, TMED2, MIR1224, MPRIP, SLC27A2, LILRB4, SARM1, RIPK3, CD24, MIR190B, DKK1, TNFSF13B, SNHG20, ZHX2, MIR33B, MLXIP, MGLL, MIR590, DNLZ, VSIG4, ADAMTS13, MIR873, DUSP12, MIR205, OCLN, MIR193B, NMU, EBP, IFNL4, CISD2, IL17RA, TREH, YME1L1, MKRN1, DAPK2, MIR361, DDAH1, PARTICL, MMD, SRRM2, BRD4, ERVK-2, ANGPTL2, PLK4, HPSE, PGRMC1, SIRT4, MIR423, MIR20B, CRTC1, DUSP26, NOX4, MAT2B, ERBIN, PAG1, ACOT13, ZNF300, TIMD4, TBL1Y, WNT3A, FAM83A, MIR200B, LGALS14, UBQLN4, PNO1, CARD6, DGAT2, ADAMTS9, ALLC, TXNRD3, C1QTNF3, TWIST2, TRERF1, NLRP2, IFTAP, CHDH, FBXW7, CWF19L1, SLC47A1, CYP2R1, CPT1C, PPARGC1B, NADK2, FGFBP3, SLC38A8, PCBP4, MAK16, SMURF1, NCOA2, FRTS1, ELOVL6, WNK1, APOO, ARV1, GORASP1, XPO4, NSD1, ABCG8, NLRX1, KCTD17, TMBIM1, SMOC2, GSDMD, DHDDS, LRRC7, CIDEC, HKDC1, CPEB4, TRPV4, PGAP6, COASY, SPX, SESN2, TRAPPC9, ITCH, ANGPTL6, ARRDC3, SEMA6A, CHCHD6, ZFP90, CILP2, HJV, MIR142, MBTPS2, IRF2BP2, INSIG2, ABHD5, RTL1, C1QL3, LINC01194, MIR130A, MIR132, SOST, MIR136, MIR141, IL20, AACS, MIR143, ISYNA1, MIR144, MIR146A, DUOX2, SLC40A1, SLC2A8, DMGDH, CERS2, MIR150, MIR15B, MIR17, MIR185, REPIN1, CTNNA3, MYLIP, MOGAT3, CPP, APPL2, EGLN1, NUDT11, PDIK1L, PIWIL2, SIK1, SLC52A1, HORMAD2, SLC2A12, TMPRSS6, TET2, CROT, LINC01554, UNC5B, MARCHF8, UGT1A4, JAZF1, SIRT6, UGT1A6, UGT1A7, UGT1A8, UGT1A10, CCHCR1, ZBTB38, TREM1, BTBD8, DUOX1, BPIFA4P, HCAR2, C1QTNF9, ARID4B, STING1, ATG7, A2M, STK25, GCLC, FGF1, FGR, FOSB, FOSL2, G6PC, GALR1, GDNF, GPC3, GLB1, GLI2, SLC26A3, GLRX, GNA12, GNAI3, GNAO1, GPI, GPR31, FFAR2, GPS2, GSK3B, GPC4, FCGR3B, FCGR3A, FBN1, DUSP9, EDA, S1PR1, EEF1A1, EGF, EGR1, EIF4E, ENO3, EPHB2, EPHB6, EPO, ERN1, ESRRB, EZH2, F2RL1, FABP2, FABP5, ACSL1, PTK2B, GSTM2, H2AX, HADHB, IGF2, IGFBP2, IGFBP4, IGFBP7, IKBKB, IL2, CXCR2, INPP5D, INSIG1, IRF3, ITGAM, ITGB1, ITIH4, ITPR2, JAK1, JUN, JUNB, JUND, CD82, KRT8, IGFBP1, IFNA13, HADH, IFNA2, HCFC1, HLA-A, HLA-C, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DQB2, HLA-DRB1, NR4A1, FOXA2, HOXD13, HRG, PRMT1, HSPA4, HSPA5, HSPA8, HSPG2, HTR2A, TNC, IFNA1, DSPP, DPYSL3, LCP1, BMP4, ARG2, ARNT, ARRB1, ASNS, ATF4, BAAT, BAX, BCHE, BLVRA, BMP8B, DMD, TSPO, C3, CALCA, RUNX2, CCNC, CD44, CDC42, CDH1, CDK4, AREG, AQP7, KLK3, APOA2, ABO, ACAT1, ACTB, ADM, ADRB2, AEBP1, JAG1, AKT2, ALDOB, AKR1B1, AMD1, AMD1P2, ANGPT1, ANGPT2, AOX1, APOF, AIRE, XIAP, APOA1, CDK8, CDKN2A, CEL, CTNNA1, CTSB, CTSD, CTSG, CTSS, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2B7P, CYP2D7, CYP2J2, CYP4A11, CYP8B1, CYP19A1, CYP27B1, CYP51A1, DBP, DDOST, TIMM8A, DHCR7, DIO3, CTRL, CCN2, CHRM3, CTF1, CHUK, CIDEA, CLCN2, CNR2, COL3A1, SLC31A1, CP, CPN1, CPOX, CPS1, CREB1, ATF2, CREBBP, CRK, CRMP1, MAPK14, CSF3, CSF3R, CTAA1, LCAT, LGALS3, CAP1, VEGFC, UCP1, UCP3, SLC35A2, UGT1A, UGT2B4, USP4, UROD, UTRN, VCAM1, VIP, STAT1, BEST1, YY1, ZBTB16, LAP, PLA2G7, TFEB, AIMP2, STAM, FOSL1, TRAF3, TPO, TP53BP1, TNFRSF1A, SULT1E1, STK11, SYT1, ADAM17, MAP3K7, TAZ, TCF7L2, TFAM, TFF3, TG, TGFB1I1, THRSP, TIMP3, TLL1, TLR1, NR2E1, TM7SF2, TMPO, TNFAIP3, FGF23, SLC7A5, BAS, TMPRSS11D, GGPS1, ATG5, LITAF, CLOCK, ABCG1, KEAP1, PLPPR4, MFN2, PARP2, DNM1L, PPIF, LRPPRC, SLC25A13, PRMT3, PLIN3, FSTL3, ZNF267, AKR1A1, MERTK, EIF2AK3, GRAP2, PLA2G6, COX5A, PIK3R3, CYP4F2, DENR, RTCA, DGAT1, ABCC3, MBTPS1, TNFSF14, DLK1, TRIM24, CES2, HDAC3, SQSTM1, MBD2, CCRL2, MYOM2, HACD1, NOG, GLP2R, STAT6, STAR, LIPE, P2RX5, NBN, NEU1, NHS, NNMT, NOS2, NOS3, NOTCH1, NRF1, NUCB2, P4HA1, AKR1D1, PAPPA, PC, PCK1, PDGFRB, SERPINA4, SERPINB6, PIGR, PITX3, PKM, HNRNPM, MYD88, MYC, ND6, FADS1, LNPEP, LOXL2, LRP6, LTF, LUM, SMAD7, MAT1A, DNAJB9, MEFV, MET, MIF, CXCL9, MMP9, MPI, MPO, MPST, MRC1, MST1, PKNOX1, PLCG1, PLG, CCL19, SELL, SELP, SETMAR, SFRP4, SFRP5, SRSF3, ST3GAL4, SLC2A4, SLC3A2, SLC6A2, SLC10A1, SLC13A1, SMPD1, SIGLEC1, SNAI1, SORD, SP1, SPRR2A, SQLE, CXCL5, CCL17, PLTP, CCL5, PMCH, PPP1R3C, PRKDC, MAPK3, MAP2K7, PRLR, PTBP1, PTGFRN, PTPN6, PTPRC, PTX3, RARA, OPN1LW, RELA, RLN2, BRD2, RPS6KB1, SORT1, S100A4, H3P10
-
Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis
Wikipedia
Preliminary results report the drug has completely cleared away storage material from the white blood cells of the first six patients, as well as slowing down the rapid neurodegeneration of infantile NCL.Currently, two drug trials are underway for infantile NCL, both using Cystagon. [ citation needed ] Gene therapy [ edit ] A gene therapy trial using an adenoassociated virus vector called AAV2CUhCLN2 began in June 2004 in an attempt to treat the manifestations of late infantile NCL. [25] The trial was conducted by Weill Medical College of Cornell University [25] and sponsored by the Nathan's Battle Foundation. [26] In May 2008, the gene therapy given to the recipients reportedly was "safe, and that, on average, it significantly slowed the disease's progression during the 18-month follow-up period" [27] and "suggested that higher doses and a better delivery system may provide greater benefit". [28] A second gene therapy trial for late infantile NCL using an adenoassociated virus derived from the rhesus macaque (a species of Old World monkey ) called AAVrh.10 began in August 2010, and is once again being conducted by Weill Medical College of Cornell University. [28] Animal models of late infantile NCL showed that the AAVrh.10 delivery system "was much more effective, giving better spread of the gene product and improving survival greatly". [28] A third gene therapy trial, using the same AAVrh.10 delivery system, began in 2011 and has been expanded to include late infantile NCL patients with moderate tosevere impairment or uncommon genotypes, and uses a novel administration method that reduces general anesthesia time by 50% to minimize potential adverse side effects. [29] Flupirtine [ edit ] Flupirtine A painkiller available in several European countries, flupirtine , has been suggested to possibly slow down the progress of NCL, [30] particularly in the juvenile and late infantile forms. ... Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=5538&ordinalpos=28&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Gene.Gene_ResultsPanel.Gene_RVDocSum ^ a b Sharp, J.; et al. (1997).TPP1, CLN6, CLN3, CLN8, PPT1, MFSD8, CLN5, ATP13A2, KCTD7, ARSG, CTSD, PPT2, CLCN3, CLCN6, DNAJC5, GRN, FBXL3, NCL, CTSF, ATP5MC1, TARDBP, CAPN3, CLN9, PSAP, CPQ, AGER, TMEM106B, TBCK, SLC39A7, ZDHHC15, CAPN8, TFEB, PPP5C, TAC1, SOD2, CALD1, DPYSL2, GAD1, GAD2, KCNMA1, LGALS1, MAS1, MECP2, TRPM1, PKD1, POLG, POU4F1, APP, MAPK13, SNCA, PRCD
-
Ceroid Lipofuscinosis, Neuronal, 2
Omim
Seitelberger et al. (1957) collected 28 cases from the world's literature. ... In total, 52 patients from 34 families were identified clinically. Of the 28 families with available DNA, 18 had 5 different mutations in the CLN2 gene (see, e.g., 607998.0007).
-
Episodic Ataxia, Type 1
Omim
McGuire et al. (1984) described the syndrome of continuous muscle fiber activity in a 3-year-old boy and his 28-year-old mother. The boy had shown persistent fisting from the age of 4 months. ... She was still taking phenytoin at age 28 and showed toxic effects with a serum level of 36 mg/L.
-
Sirenomelia
Wikipedia
Other hypotheses involve an insult to the embryo between 28–32 days affecting the caudal mesoderm , a teratogen exposure affecting the neural tube during neurulation , and a defect in the twinning process that either stops the process of caudal differentiation or generates a second primitive streak . [1] Maternal diabetes mellitus has been associated with caudal regression syndrome and sirenomelia, [5] [6] although a few sources question this association. [7] Prenatal cocaine exposure has also been suggested as an association with sirenomelia. [1] Genetics [ edit ] In animal models, several genes have been found to cause or be associated with sirenomelia. ... (Tweet) – via Twitter . ^ a b " " Mermaid" girl takes first steps" . BBC News. 28 September 2006. ^ a b " " Mermaid" girl's legs separated" .
-
Noma (Disease)
Wikipedia
Archived from the original on 2007-05-28 . Retrieved 2007-07-12 . ^ Srour ML, Marck K, Baratti-Mayer D (February 2017). ... PMID 10522217 . ^ Fondation Winds of Hope ^ Medical care Archived 2009-04-28 at the Wayback Machine at Project Harar ^ "Make Me a New Face: Hope for Africa's Hidden Children" .
-
Irlen Syndrome
Wikipedia
Archived from the original on 25 January 2014 . Retrieved 2014-03-28 . CS1 maint: archived copy as title ( link ) ^ "Archived copy" . Archived from the original on 25 January 2014 . Retrieved 2014-03-28 . CS1 maint: archived copy as title ( link ) ^ "Society for Coloured Lens Prescribers" . www.s4clp.org . ^ "The University of Newcastle, Australia" . www.newcastle.edu.au . 13 November 2015.
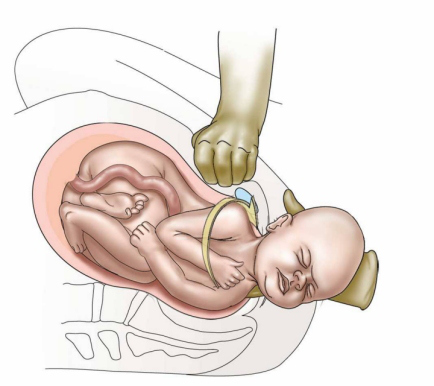
- Shoulder Dystocia Wikipedia
-
2011 Turkish Riviera Mass Alcohol Poisoning
Wikipedia
Three women died, others were hospitalized in Antalya and Denizli , with six placed in intensive care stations in critical condition. [2] [3] [4] On May 30, Marina Sheveleva ( Russian : Марина Шевелева ), born in 1989, died as the first victim at a hospital in her country, after her condition worsened during the flight to Moscow . [1] [6] [7] Two other Russian citizens, Maria Shalyapina ( Russian : Мария Шаляпина ), born in 1983, and Aigul Zalayeva ( Russian : Айгуль Залаева ), born in 1991, died in the following days at the hospital of Akdeniz University in Antalya. [6] [7] On the night of June 5, 2011, 28-year-old Alexandr Zhuchkov ( Russian : Алекса́ндр Жучков ) died in the hospital of Pamukkale University in Denizli, where he had been in intense supportive care since May 28.
-
Influenza-Like Illness
Wikipedia
Archived from the original on 10 February 2009 . Retrieved 28 April 2009 . ^ Moore C, Corden S, Sinha J, Jones R (November 2008). ... "Dosing regimens and main adverse events of bisphosphonates". Semin Oncol . 28 (4 Suppl 11): 49–53. doi : 10.1016/S0093-7754(01)90232-5 .
-
Fistula
Wikipedia
(subscription required) ^ a b c d "Definition of Fistula" . www.merriam-webster.com . Retrieved 28 December 2020 . ^ a b c d e f "What Is A Fistula? ... Urinary incontinence education; National Association for Continence . Retrieved 28 December 2020 . ^ Garefalakis, Maria; Hickey, Martha; Johnson, Neil (2016).LAMC2, CSF2, TNF, NOD2, AKT1, CRP, ALB, IL6, IL10, IL13, TGFB1, SULT1E1, A1BG, SST, SNAI1, ZIC2, SLC22A4, SLC25A1, RASA1, RAF1, SLC22A5, TBC1D9, ZHX2, MIXL1, C20orf181, MIR340, DNAAF3, PTCRA, IL23R, ACCS, TET1, DKK1, MYH14, ACSS2, DNAI1, PLA2G15, ATP6V0A2, MAPK3, PTS, PCBD1, PLEC, F11, B2M, TSPO, CAV1, CHRM3, MAP3K8, SLC25A10, CTF1, CTLA4, ACE, DNAH5, DPEP1, EFNB2, ETS1, FAAH, ABCB1, GH1, HNF4A, HSPA1B, HSPA5, IGFBP3, IL17A, MMP2, MMP3, MMP9, NF1, NHS, PCNT, PCYT1A, CERNA3
-
Obesity In India
Wikipedia
Due to genetic tendency of Indians towards abdominal obesity and its associated risk of related lifestyle diseases such as diabetes and heart disease , guidelines for diagnosis of obesity and abdominal obesity for India have been published in JAPI (2009) that a BMI over 23 kg/m2 is considered overweight. [5] Further definitions: Normal BMI: 18.0-22.9 kg/m2, Overweight: 23.0-24.9 kg/m2, Obesity: >25 kg/m2. [5] Contents 1 NFHS data 2 See also 3 References 4 Further reading NFHS data [ edit ] This is a list of the states of India ranked in order of percentage of people who are overweight or obese , based on data from the 2007 National Family Health Survey. [6] States Males (%) Males rank Females (%) Females rank India 12.1 14 16 15 Delhi 45.5 - 49.8 - Punjab 30.3 1 37.5 1 Kerala 24.3 2 34 2 Goa 20.8 3 27 3 Tamil Nadu 19.8 4 24.4 4 Andhra Pradesh 17.6 5 22.7 5 Sikkim 17.3 6 21 6 Mizoram 16.9 7 20.3 7 Himachal Pradesh 16 8 19.5 8 Maharashtra 15.9 9 18.1 9 Gujarat 15.4 10 17.7 10 Haryana 14.4 11 17.6 11 Karnataka 14 12 17.3 12 Manipur 13.4 13 17.1 13 Uttarakhand 11.4 15 14.8 14 Arunachal Pradesh 10.6 16 12.5 15 Uttar Pradesh 4.9 17 12 16 Jammu and Kashmir 8.7 18 11.1 17 Bihar 8.5 19 10.5 18 Nagaland 8.4 20 10.2 19 Rajasthan 8.4 20 9 20 Meghalaya 8.2 22 8.9 21 Odisha 6.9 23 8.6 21 Assam 6.7 24 7.8 23 Chhattisgarh 6.5 25 7.6 27 West Bengal 6.1 26 7.1 25 Madhya Pradesh 5.4 27 6.7 26 Jharkhand 5.3 28 5.9 27 Telangana 5.2 29 5.3 28 Tripura 5.1 30 5.2 29 See also [ edit ] Malnutrition in India References [ edit ] ^ "India facing obesity epidemic: experts" .
-
Menkes Disease
Wikipedia
"Screening for Menkes disease using the urine HVA/VMA ratio" . J. Inherit. Metab. Dis . 28 (1): 89–93. doi : 10.1007/s10545-005-5083-6 . ... "A survey of Japanese patients with Menkes disease from 1990 to 2003: incidence and early signs before typical symptomatic onset, pointing the way to earlier diagnosis" . J. Inherit. Metab. Dis . 28 (4): 473–8. doi : 10.1007/s10545-005-0473-3 .
-
Clinical Vampirism
Wikipedia
London Review of Books (book review). Vol. 28 no. 16. pp. 23–26. Archived from the original on 9 June 2013 . ... Archived from the original on 2008-02-28 . Retrieved 2007-12-18 . Kenny Valdez is in the Seclusion Room, strapped to a bed in a five-point restraint system, claiming he can "smell it!"
-
Alexander Disease
Wikipedia
Archived from the original on 2010-04-28 . Retrieved 2010-06-14 . CS1 maint: archived copy as title ( link ) ^ a b c "Mutation in common protein triggers tangles, chaos inside brain cells" . news.wisc.edu . ... "Alexander's disease: reassessment of a neonatal form". Childs Nerv Syst . 28 (12): 2029–31. doi : 10.1007/s00381-012-1868-8 .
-
Neurogenic Inflammation
Wikipedia
Smith, "Preventive treatment of migraine in adults" UpToDate 2019 [25] Additional CGRP blockers are progressing through clinical trials. [26] Anticipating later botox therapy for migraine, early work by Jancsó et al. found some success in treatment using denervation or pretreatment with capsaicin to prevent uncomfortable symptoms of neurogenic inflammation. [27] A 2010 study of the treatment of migraine with CGRP blockers had shown promise for CGRP blockers. [28] In early trials, the first oral nonpeptide CGRP antagonist, MK-0974 ( Telcagepant ), was shown effective in the treatment of migraine attacks, [29] but elevated liver enzymes in two participants were found. ... "Skeletal and hormonal effects of magnesium deficiency". J Am Coll Nutr . 28 (2): 131–41. doi : 10.1080/07315724.2009.10719764 .
-
Squamous-Cell Carcinoma Of The Lung
Wikipedia
National Cancer Institute . 1980-01-01 . Retrieved 2019-02-28 . ^ a b Kenfield SA, Wei EK, Stampfer MJ, Rosner BA, Colditz GA (June 2008). ... PMID 26629421 . ^ "Browse the Tables and Figures - SEER Cancer Statistics Review (CSR) 1975-2012" . SEER . Retrieved 2019-02-28 . v t e Glandular and epithelial cancer Epithelium Papilloma / carcinoma Small-cell carcinoma Combined small-cell carcinoma Verrucous carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Basal-cell carcinoma Transitional cell carcinoma Inverted papilloma Complex epithelial Warthin's tumor Thymoma Bartholin gland carcinoma Glands Adenomas / adenocarcinomas Gastrointestinal tract: Linitis plastica Familial adenomatous polyposis pancreas Insulinoma Glucagonoma Gastrinoma VIPoma Somatostatinoma Cholangiocarcinoma Klatskin tumor Hepatocellular adenoma / Hepatocellular carcinoma Urogenital Renal cell carcinoma Endometrioid tumor Renal oncocytoma Endocrine Prolactinoma Multiple endocrine neoplasia Adrenocortical adenoma / Adrenocortical carcinoma Hürthle cell Other/multiple Neuroendocrine tumor Carcinoid Adenoid cystic carcinoma Oncocytoma Clear-cell adenocarcinoma Apudoma Cylindroma Papillary hidradenoma Adnexal and skin appendage sweat gland Hidrocystoma Syringoma Syringocystadenoma papilliferum Cystic, mucinous, and serous Cystic general Cystadenoma / Cystadenocarcinoma Mucinous Signet ring cell carcinoma Krukenberg tumor Mucinous cystadenoma / Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma Pseudomyxoma peritonei Mucoepidermoid carcinoma Serous Ovarian serous cystadenoma / Pancreatic serous cystadenoma / Serous cystadenocarcinoma / Papillary serous cystadenocarcinoma Ductal, lobular, and medullary Ductal carcinoma Mammary ductal carcinoma Pancreatic ductal carcinoma Comedocarcinoma Paget's disease of the breast / Extramammary Paget's disease Lobular carcinoma Lobular carcinoma in situ Invasive lobular carcinoma Medullary carcinoma Medullary carcinoma of the breast Medullary thyroid cancer Acinar cell Acinic cell carcinoma v t e Cancer involving the respiratory tract Upper RT Nasal cavity Esthesioneuroblastoma Nasopharynx Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma Larynx Laryngeal cancer Laryngeal papillomatosis Lower RT Trachea Tracheal tumor Lung Non-small-cell lung carcinoma Squamous-cell carcinoma Adenocarcinoma ( Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma ) Large-cell lung carcinoma Rhabdoid carcinoma Sarcomatoid carcinoma Carcinoid Salivary gland–like carcinoma Adenosquamous carcinoma Papillary adenocarcinoma Giant-cell carcinoma Small-cell carcinoma Combined small-cell carcinoma Non- carcinoma Sarcoma Lymphoma Immature teratoma Melanoma By location Pancoast tumor Solitary pulmonary nodule Central lung Peripheral lung Bronchial leiomyoma Pleura Mesothelioma Malignant solitary fibrous tumorFGFR2, EGFR, DDR2, KRAS, EPHA2, FGFR1, IGF1R, TTN, PLK1, NOTCH1, FYN, PRKDC, DDR1, MAST4, EPHA3, MYLK4, EPHA5, ANKK1, WNK3, ACVR1C, GUCY2F, DCLK3, MAP3K15, AURKC, BMP2K, TRIM24, MYO18B, ERBB4, MAP2K4, MAP4K3, CSF1R, ATR, TP53, CDKN2A, PIK3CA, BRAF, FGFR3, NFE2L2, STK11, FBXW7, HLA-A, CHRNA3, CLPTM1L, HRAS, PTEN, EP300, HLA-DQA1, CYP2A6, HNF1B, DCLK1, KRT8, BRCA2, H2AC6, TNXB, HLA-B, DCUN1D4, PDS5B, THRB, ATXN2, TRIM26, DBH, HLA-DMB, GBAP1, FRY, RALY, ESM1, SH2B3, MORF4L1, HCP5, SOX2, ZSCAN12, SCGN, BTN3A3, ZNF623, GSTM1, PKD2L1, MED12, HLA-DQA2, NEB, LCORL, MORN5, GPX6, LINC-PINT, CENPP, PC, B2M, NF1, FAM155A, PPP6C, ALK, CDKN2B-AS1, ZSCAN16-AS1, MTX1, EGFR-AS1, MUC22, PTCSC2, TSBP1-AS1, CYP1A1, NEK10, BTBD9, VARS2, BABAM1, CD274, ZNRD1, RAD51B, LRRC8D, CARMIL1, CREBBP, PTPN11, REXO4, NPAS3, TUBA1C, WNK1, ZNF322, CHRNB4, USHBP1, PGBD1, KCNH1, APOM, PIK3CB, PIK3CD, PIK3CG, H3P10, TP63, NME1, GPC3, PTHLH, MIR205, MET, CEACAM5, VEGFA, RARB, GATA6, CCND1, MKS1, MAP2K7, MAPK3, BDNF, CDK4, SFTA1P, DSG3, MIR93, MYC, AKT1, CTNNB1, TYMS, RAD52, ME1, TOP2A, TGFBR2, ELAVL2, PDPN, OGG1, SOX2-OT, MALAT1, MIR145, MIR150, ZEB1, PDCD1, MIR21, MBD2, NAPSA, PARP1, PROM1, SUMO1P3, MIR375, MIR590, CXCR4, MPO, MMP9, MLH1, CCNB2, CKAP4, FGF19, RET, TPX2, TRIM58, DGCR5, HPGDS, SGSM3, RPE65, ROS1, RFC4, SLC2A2, UVRAG, SKP2, XAF1, PTPN13, ACKR3, PTK2, SST, DMRT3, PSG2, STAT3, PDCD1LG2, PRKCI, TIMP1, BMP4, CLDN3, COL11A2, ERBB2, CYP1A2, CYP2E1, FHIT, STMN1, IL6, FGFR4, LGALS8, CAV1, LOXL2, CDH1, EIF4G1, GABPA, BCL2, GSTP1, IFNG, DUSP6, CEACAM3, CEACAM7, MCL1, MDM2, SMAD4, AGER, CTLA4, GLI1, BIRC6, SOX17, AICDA, MYDGF, METTL3, COL17A1, SPC25, RAD18, SYT13, CLDN7, CCAR2, METTL14, COX8A, KIF15, MRTFA, CNOT6, NSD1, MEOX1, ZMAT3, DENND2D, ZNF503, CDKN1B, MAP1LC3A, HOPX, CHRNA4, FSD1L, DOCK8, MAP1LC3B, CHRNA7, CHUK, TBL1XR1, P2RY12, AP2M1, IRX1, FSD1, MAPKAP1, FTO, BRD9, CLU, CCR4, MRPL41, IL25, FRTS1, CRK, CPOX, LMO3, IL17C, LHX6, FBXO5, DAXX, PRPF31, POLDIP2, RNF19A, AKR1C2, NOCT, CIZ1, SNHG1, CORO1C, MMD, NCS1, SIRT1, COBL, GRAMD4, GADD45A, PEG10, DIO3, DMRT1, MMRN1, DNAH5, TUSC2, WIF1, IL17B, GPR78, RBMS3, CSNK2A1, BRK1, CACNA2D3, CHFR, HHAT, ATG4D, MAPK14, CSF1, BRF2, CSF2, CSF3, ALKBH5, EGLN1, TMEM97, CYTL1, SOX18, GPR87, IL17D, BCL11A, ANAPC11, GOLM1, GMNN, CSNK2A2, CTSB, EML4, RIOX2, IL17F, CDKN1A, MNX1-AS1, MIR193B, MIR452, MIR448, AQP5, ARG2, MIR372, MIR342, MIR324, MIR135B, MAP1LC3C, C5orf17, PRR26, MIR9-3, BCHE, MIR31, MIR29B2, MIR29B1, MIR29A, MIR28, MIR224, MIR223, MIR206, BMI1, MIR203A, MIR20A, MIR486-1, IGF2BP2-AS1, MIR195, LINC00273, SEC62-AS1, LINC01419, ADRA1A, ADRA2B, LINC01206, MIR5682, COMMD3-BMI1, LINC00968, AGTR1, PCAT6, MIR1911, ALB, GATA6-AS1, VPS9D1-AS1, MIR944, MIR541, ALDH1A1, MIR671, ANG, LINC00460, MIR662, ANGPT1, MIR588, MIR579, NME1-NME2, MIR198, MIR192, TRIM15, CD14, STXBP4, FAM83B, ADGRF4, CD44, FBXO45, PLPP4, FEZF1-AS1, APCDD1L-DT, IL23R, FAM163A, HJV, PIWIL4, LINC00261, ADHFE1, CD109, CDK2, PODN, LRRK2, CDK7, AZIN2, PRDM5, MUC16, MTDH, IL33, ERVH48-1, MS4A3, CCNE1, MIR185, TBX5-AS1, MIR183, MIR182, MIR15A, FOXL2, MIR144, MIR141, MIR140, MIR125A, MIRLET7I, BRS3, USP17L7, SERPING1, CCL4L1, KMT5A, CA9, CASP3, CASR, CBR1, GADL1, CELIAC2, STPG4, CXCL17, HCCAT5, SBF2-AS1, CCK, FSTL1, AHSA1, DSC3, S100A10, RRM2, RPS14, FOXA2, HNRNPU, RGS3, HOXA10, HSPB1, HTC2, IRF8, MOK, IFIT2, PVT1, PTPRA, IGF2R, TWF1, PTK7, IHH, PTGS2, IL10, IL17A, MASP1, IDO1, MAPK8, IRF1, MAPK1, S100A6, HLA-C, DUSP1, SERPINB3, GSTM2, STAT1, SSTR4, SRPK2, SRPK1, SQLE, SPARC, SOX4, GZMB, HLTF, HBE1, SLC2A1, HIC1, SIM1, SIAH2, SHH, SFTPB, TRA2B, SRSF2, SRSF1, HK2, SELENOP, SELP, CCL4, CCL2, IRF4, ITGB4, KIF5B, PPBP, NME2, NGFR, NFYC, NFKBIA, NFIX, LRP6, LRP5, EPCAM, NCAM1, MYO10, MYH10, MYCN, SMAD3, MYBPH, MUC4, MUC1, ND5, MSR1, MSH2, MMP14, MCM2, MMP7, MCM5, MIF, MIA2, LIPA, LGALS1, CLDN11, SERPINA1, POU4F2, POU3F2, KIT, PLG, PLAU, PKP1, PIK3R2, KRT19, KRT81, LCK, SERPINB5, ABCB1, OVOL1, PDGFRB, LCN2, PCNA, LDHA, PAX7, PARN, PAK1, SERPINE1, PAEP, PEBP1, P2RY1, AURKA, GSPT1, GSK3B, BECN1, CCL4L2, TP53I3, BAG4, EIF2AK3, GRAP2, COX5A, PLAA, KL, SOCS6, PIWIL1, ERCC1, LPAR2, ESRRA, CLDN1, CLDN12, PRC1, ETV4, H3C7, EZH2, SQSTM1, F2R, INPP4B, FAP, TNFRSF10B, DLK1, EPHX1, KMT2B, KEAP1, HCG9, E2F1, CHL1, CXCR6, ECT2, SPAG5, EDNRA, TACC3, YAP1, PIAS3, DLC1, EEF2, GPHN, EPHB3, WASF2, PDIA6, EIF4E, ARL4C, ARPC5, BCL2L11, HDAC5, ENO1, EPAS1, GAB2, ZEB2, TNFSF10, FGF1, MAP3K7, GAS7, FUS, FUT1, TTF1, NR2C2, TPD52, TOP3A, GATA3, GATA4, TNNI3, TNF, CLDN5, TK1, TIAL1, TIA1, GPR42, THOP1, THBS2, GPX2, TGFBI, TGFB1, TFF3, TFAM, TERC, GRN, GRM8, SUMO1, SCGB1A1, USP4, FGF9, FGF3, HYAL3, H3C2, H3C10, H3C12, H3C8, H3C11, H3C6, H3C3, H3C4, H3C1, FXR1, FOXO3, KMT2D, AIMP2, USP7, YWHAZ, XRCC3, XRCC1, XPC, WNT5A, VIM, FOXM1, VDAC3, ABL2
-
Microphthalmia, Syndromic 2
Omim
All 34 patients had congenital cataract, and microphthalmia and/or microcornea were present in 28 (82%). Twenty-five (96%) of 26 patients for whom a facial phenotype was observed had septate nasal cartilage, and 8 (31%) had palatal abnormalities, including cleft palate, high-arched palate, and bifid uvula. ... Skeletal anomalies were observed in 28 (97%) of 29 patients examined, with 2-3 toe syndactyly in 16 (57%) and hammertoes in 15 (54%).
-
Fetal Akinesia Deformation Sequence 1
Omim
Hageman et al. (1987) observed a variety of brain pathology in 6 unrelated new cases and in a review of 28 previously reported cases. Katzenstein and Goodman (1988) reported a case of survival to the age of 20 months. Out of about 60 reported cases, only 5 others surviving beyond 28 days were found. Lammer et al. (1989) described affected brothers who were unusual because they had macrocephaly and normal intrauterine growth.