-
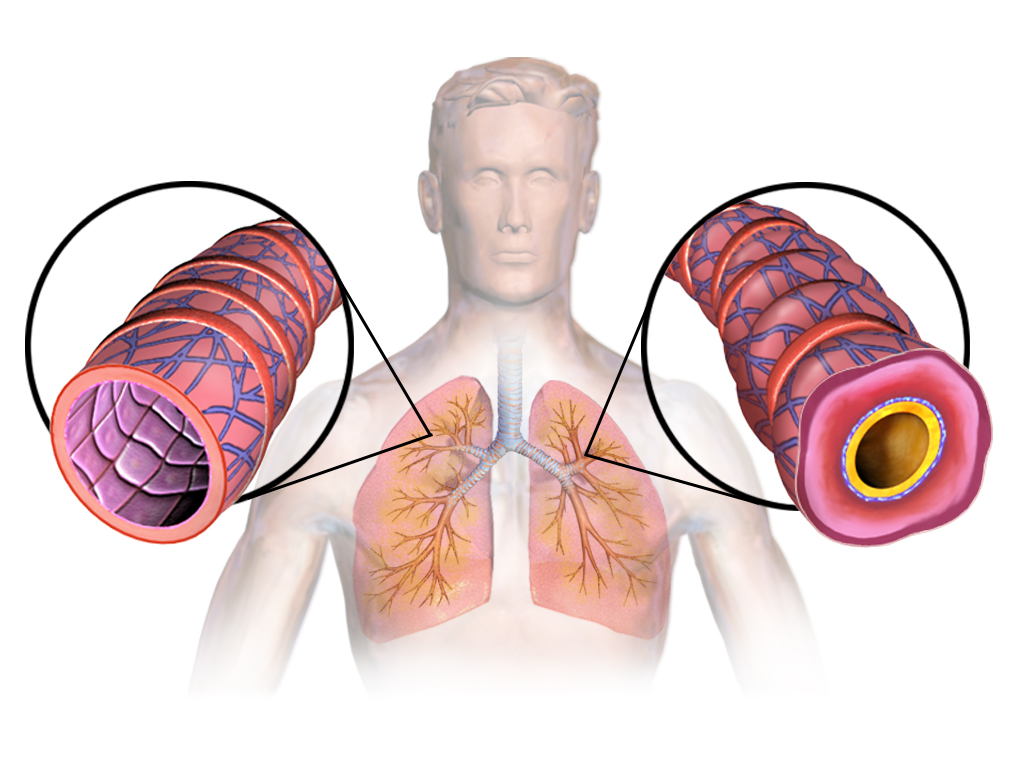
Axial Spondyloarthritis
Wikipedia
History [ edit ] In 1984, a joint effort led to the definition of specific classification criteria for ankylosing spondylitis, called the “Modified New York Criteria”. [4] One of the central New York criteria was the existence of radiographically visible changes in the sacroiliac joints and/or spine , which have formed due to bone fusion, erosion and/or formation caused by the disease. [5] Even though these criteria helped to improve uniformly define ankylosing spondylitis, such radiologic changes often only manifested several years after the first disease symptoms appeared. [5] In order to be able to study also patients with early and less typical forms, new criteria were needed that could identify the disease already at an early stage.HLA-B, CRP, IL17A, TNF, IL23A, CD74, ESR1, SOST, TNFRSF11B, IL37, HLA-C, BTF3P11, COLEC10, EBNA1BP2, LANCL1, RABEPK, WDHD1, MMRN1, DKK1, TSKU, SEC16A, IL22, ACR, IL17F, SCLY, NSG2, ARHGEF2, MAMDC4, ARMH1, CPP, IL31, MIR126, MIR146A, MIR17, MIR27A, MIR29A, MTCO2P12, CD163, VIM, TP63, TNFSF11, CSF2, CTSK, DMD, FCN2, HLA-DRB1, IL9, JAK3, KRT7, RPSA, MRC1, COX2, NFKB1, MAPK1, PSMD7, PTGS2, SFTPD, SH3BP2, STAT4, TAL1, TLR2, TLR4, TNFAIP3, BMP2, BEST1, FGF23, H3P28
-
Lamaze Technique
Wikipedia
Modern Lamaze childbirth classes teach expectant mothers many ways to work with the labor process to reduce the pain associated with childbirth and promote normal (physiological) birth including the first moments after birth. Techniques include allowing labour to begin on its own, movement and positions, massage, aromatherapy, hot and cold packs , breathing techniques, the use of a "birth ball" (yoga or exercise ball), spontaneous pushing, upright positions for labour and birth, breastfeeding techniques, and keeping mother and baby together after childbirth.
-
Hypertrophic Osteoarthropathy, Primary, Autosomal Recessive, 2
Omim
In a Han Chinese male proband with primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy, who was born of first-cousin parents and was negative for mutation in HPGD, Zhang et al. (2012) performed exome sequencing and identified 28 genes that contained homozygous missense, nonsense, or splicing variants.
- Interstitial Nephritis, Karyomegalic Omim
-
Brenner Tumour
Wikipedia
The same crystals were also noted under high power view in Brenner tumors. [1] [6] Eponym [ edit ] It is named for Fritz Brenner (1877–1969), a German surgeon who characterized it in 1907. [7] The term "Brenner tumor" was first used by Robert Meyer , in 1932. [8] Additional images [ edit ] Micrograph of a Walthard cell nest , the entity Brenner tumours are thought to arise from.
- Neovascularization Wikipedia
-
Aspartylglucosaminuria
Wikipedia
Once an individual hits the age of 25-30 the decrease begins again, including: learned skills become lost which result in severe learning disabilities motor skills deteriorate individuals become less mobile and more dependent (Children are physically uncoordinated, but remain able to play sports and do everyday activities until they reach adulthood.) During the first year of life inguinal and umbilical hernias are common.
-
Brittle Asthma
Wikipedia
The cardinal symptoms of an asthma attack are shortness of breath ( dyspnea ), wheezing , and chest tightness. [8] Individuals with type 1 suffer chronic attacks in spite of ongoing medical therapy, while those with type 2 experience sudden, acute and even potentially life-threatening attacks even though otherwise their asthma seems well managed. [9] When first defined by Margaret Turner-Warwick in 1977, the term brittle asthma was used specifically to describe type 1, but as studies into the phenotype were conducted the second type was also distinguished. [10] Treatment [ edit ] In addition to any issues of treatment compliance , and maximised corticosteroids (inhaled or oral) and beta agonist , brittle asthma treatment also involves for type 1 additional subcutaneous injections of beta2 agonist and inhalation of long acting beta-adrenoceptor agonist , [11] whilst type 2 needs allergen avoidance and self-management approaches. [12] Since catastrophic attacks are unpredictable in type 2, patients may display identification of the issue, such as a MedicAlert bracelet, and carry an epinephrine autoinjector . [7] Epidemiology [ edit ] The condition is rare. 1999's Difficult Asthma estimates a prevalence of approximately 0.05% brittle asthma sufferers among the asthmatic population. [13] Though found in all ages, it is most commonly found in individuals between the ages of 18 and 55; it is present in both sexes, though type 1 has been diagnosed in three times as many women as men. [13] Hospitalization is more frequent for type 1 than type 2. [13] References [ edit ] ^ Holgate, Stephen T.; Homer A.
-
Clinically Isolated Syndrome
Wikipedia
A clinically isolated syndrome ( CIS ) is a clinical situation of an individual's first neurological episode, caused by inflammation or demyelination of nerve tissue.IFNB1, NEFL, CISH, MS, CSF2, LAMC2, CHI3L1, IL10, MIR181C, MARCHF11, CX3CL1, SMPD1, SPP1, STAT3, SYN1, TGFBI, THBD, TNFRSF1A, TP53BP1, IL17F, VDR, PRB1, TCL1B, TOB1, CXCL13, LDB3, CSAD, HRH4, MIR20A, NR4A3, AQP4, PLXNA2, H2AX, SERPING1, CD1C, CD27, CD38, CCR6, DDT, GH1, GLA, GRN, NR4A1, NCAM1, HRH1, HRH2, IFNG, IGHG3, IL17A, KIR2DL2, KIR2DL3, MOG, ARG2, KIR2DS2
-
Lupus Vulgaris
Wikipedia
Queen Alexandra of Great Britain, (1844–1925), consort to Edward the VII , as the inscription on the bronze statue of her at the London Hospital, notes, "Introduced to England the Finsen light cure for Lupus, and presented the first lamp to this hospital". Etymology [ edit ] The term "lupus" (meaning "wolf" in Latin) to describe an ulcerative skin disease dates to the late thirteenth century, though it was not until the mid-nineteenth that two specific skin diseases were classified as lupus erythematosus and lupus vulgaris.CR2, C2, DNMT1, IL10, TNF, TLR7, IL6, IL2, TLR9, IL21, IFNA13, CD40LG, TRIM21, FCGR2B, IFNA1, IL17A, IRF5, CD70, TNFSF13B, MTOR, TREX1, TLR5, ESR1, RO60, ITGAM, BTK, IL1B, CTLA4, TP53BP1, FLI1, MAPK1, IL22, BLK, TRBV20OR9-2, CD28, EPHB2, IFIH1, HLA-DRB1, IFNG, RNPC3, FCGR3A, EZH2, RAB4A, ACE, SPP1, PRL, ICOS, ITGAL, CCL2, FOXP3, FCGR3B, MECP2, PBX1, C1QA, C3, KIR3DL2, PTPN22, IL2RA, IL4, AIM2, STAT4, CRP, CXCL12, RFX1, F5, FCGR2A, HDAC6, F3, STAT1, STAT3, TLR4, VEGFA, FLII, ISG20, GEM, BANK1, DECR1, IRAK1, IL18, ITGB2, KIR3DL1, F11R, MBL2, CBLIF, IFN1@, IFI16, HRES1, IRF7, BTG3, MAVS, MYDGF, IGHG3, CREM, BCR, APOH, MIR146A, MIR21, CASP1, CAMK4, CALR, CD44, CYBB, P2RX7, SLAMF1, KIR2DS1, FASLG, PRKAR1A, TLR8, MIR663A, CASR, PTPA, MIR155, CXCL10, MIR148A, IL17D, TNFRSF17, CXADRP1, MBD2, CD19, MS4A1, PPARD, SLEB4, IL1A, TREM1, CD38, KRT20, IFNAR1, CD40, CAMP, PDCD1, IRAK4, NR1I3, CXCL13, NOS3, NCF2, MYD88, MTHFR, SIRT1, TRIM13, PADI4, ARR3, PRDM1, MMP9, REN, PRKCB, CXCR5, AR, HDAC9, SH2D1A, RPS19, IL21R, LGALS9, LGALS3, TNFSF13, LEP, MIR31, CD274, MIR125A, TLR2, CTNNB1, TGFB1, TGFB3, GATA3, XRCC6, VSIR, IL27, CD69, ADAM10, ACTB, EMB, ETS1, IGAN1, RBM45, SRCIN1, FAM167A, CXADR, UBASH3B, TRPM2, TNFSF4, VCAM1, SLAMF6, CXCR4, NEAT1, BCL2, APOL1, CDR1, SPG7, ANXA6, SSB, STING1, HMGB1, CD72, H4C1, TRIM38, TNIP1, H4C13, SIGLEC14, ANP32B, H4C4, MAEA, H4C6, ZNRD2, H3C13, PROCR, TNFSF9, DGAT1, AHSA1, H4C9, TAM, SH2B2, AIMP2, TNFSF12, LOC102723971, DCTN6, PSME3, IER3, H3C9P, KLK4, MIR633, EIF2AK3, KLRC4-KLRK1, XPR1, ATG5, H4C14, NR0B2, ATG12, OASL, MACROH2A1, H4C5, BECN1, H4C2, GRAP2, FCGR2C, ERVK-20, ERVW-4, H4C8, H4C3, SPATA2, RPL17-C18orf32, TNFSF15, H4C11, TMED7-TICAM2, H4C12, HNRNPDL, MBTPS1, H3C14, C1QL1, PHRF1, SGMS1, IFNL3, ERVK-6, BACH2, RFH1, HIVEP3, RSPO1, HAMP, MRTFA, LARP6, SCYL1, SLC12A9, BDH2, H3C15, SPHK2, IFNK, TICAM2, APOM, TIGIT, CENPV, BTLA, IL23R, CTHRC1, CGAS, NLRP3, IL17F, PRRT2, ORMDL3, DNER, IL33, ELOF1, LBH, CD276, VTCN1, DOCK11, WNK1, IL25, GORASP1, IL34, CHST12, VGLL3, LILRB4, ZNF423, PDCD4, PHGDH, POLDIP2, RNF19A, TNFRSF13B, BRD4, NBEAL2, KDM6B, DKK1, LBX1-AS1, ATF6, PLA2R1, KLRK1, SYNPO, H4C15, PADI2, CORO1A, LILRA3, H4-16, WG, TBX21, ERVW-1, VIP, MIR142, MIR145, RIPK4, DUOX1, MIR150, CD244, MIR224, IL23A, MIR23B, MIR29B1, MIR29B2, NT5C3A, TMED7, MIR17HG, DUOX2, TNFSF12-TNFSF13, VWF, ABCA1, VIM, CX3CR1, FCN2, FCER1G, F12, F10, F2, ERN1, ERBB2, EPO, EPHX2, ELF1, EIF4EBP1, EGR2, EGFR, EFNA2, DUSP4, TSC22D3, ATN1, ARID3A, DNMT3B, DNMT3A, DNASE1, IFI6, GFI1, GPI, HLA-H, IFNR, IFNB1, IFNAR2, IFI27, HSPG2, HSPA5, HSPA4, HNRNPC, HMGN2, HLA-DQA1, CXCR3, HLA-C, HIF1A, HGF, CFHR1, CFH, H1-0, GRIN2A, GRN, GPER1, DLAT, CTBP2, EZR, CSF3R, CASP9, CASP8, CASP6, CAST, C4B, C1QC, TSPO, BST2, BGN, ATF3, SERPINC1, FAS, KLK3, APOE, ANXA2, ABCD1, AKT1, AGER, PARP1, ADD2, ACP5, CAT, RUNX1T1, CBL, CD52, CSF1, MAPK14, CRK, CRH, CREBBP, COX8A, CCR5, CHRM3, AKR1C4, CDKN1A, CD1D, CDH13, CDK1, CD48, ENTPD1, CD36, CD80, CD8B, CD247, CD2, IL1RN, IL15, IL16, TNFRSF9, SLC4A1, SH3BP2, SRSF1, SELP, SDC2, CX3CL1, CCL14, CCL3L1, SERPINB3, S100B, RPS6, RPL17, TRIM27, RELB, RELA, ACR, PTX3, PTPRC, PTPN11, PTPN6, PTGS2, SIGLEC1, SNCA, SNRNP70, TNFAIP3, VDR, UMOD, TYK2, TRPC6, TRAF6, TRAF2, HSP90B1, TPO, TNFRSF1B, TIMP3, SNRPA, THAS, TG, ZEB1, ADAM17, SYT1, SYK, SUV39H1, SRI, SNRPB, PTGS1, PSMD9, MASP1, LY6E, MNAT1, MMP11, MMP2, AFF1, CIITA, MFGE8, CD46, MCL1, CD180, LDLR, MPO, LCT, LCN2, LBR, LAG3, KIR2DL4, KIF5A, ITGAX, ITGAE, IRF6, MPL, MRC1, MAP2K1, PC, PRKCD, PRKCA, PPARG, PON1, SERPINA1, PGK1, PF4, PDE7A, PCNA, OCA2, MSH5, NT5E, PNP, NOTCH1, NHS, NFKB1, NF1, NEDD9, NCL, COX1, H3P23
- Myoglobinuria Wikipedia
-
Drug Diversion
Wikipedia
In some jurisdictions, drug diversion programs are available to first time offenders of diversion drug laws, which "divert" offenders from the criminal justice system to a program of education and rehabilitation. [ citation needed ] Contents 1 Commonly diverted drugs 2 Registration of drug suppliers 2.1 Examples 3 DEA investigation into oxycodone diversion 4 See also 5 References 6 External links Commonly diverted drugs [ edit ] Z-drug example Controlled prescription drug classes which are commonly diverted include: [3] Benzodiazepines – including diazepam , temazepam , clonazepam , and alprazolam – prescription anxiolytics and sedatives Opioids – including morphine , hydrocodone , oxycodone and codeine – prescription pain medications Stimulants – amphetamine , methylphenidate , and modafinil – prescribed to treat ADHD and narcolepsy Z-drugs – including zolpidem (Ambien), Eszopiclone (Lunesta) – prescription sleep medications According to the United States Department of Justice , "Most pharmaceuticals abused in the United States are diverted by doctor shopping, forged prescriptions, theft and, increasingly, via the Internet." [4] To reduce the occurrence of pharmaceutical diversion by doctor shopping and prescription fraud, almost all states have established prescription monitoring programs (PMPs) that facilitate the collection, analysis, and reporting of information regarding pharmaceutical drug prescriptions. [5] Registration of drug suppliers [ edit ] 21 U.S.C. § 823 of the Controlled Substances Act provides for registration of manufacturers and distributors of controlled substances.
-
Vaginal Trauma
Wikipedia
Risk factors [ edit ] Risk factors include: first episode of consensual intercourse, [6] breastfeeding , [ citation needed ] menopause , [ citation needed ] and medication side effects . [13] Prevention [ edit ] A safe environment can be created for young children in addition to keeping small objects out of reach . [7] [14] Treatment [ edit ] Treatment begins with a thorough assessment.
-
Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm
Wikipedia
Contents 1 Pathophysiology 2 Diagnosis 2.1 Differential diagnosis 3 References 4 External links Pathophysiology [ edit ] In the human heart the sinoatrial node is located at the top of the right atrium. The sinoatrial node is the first area of the heart to depolarize and to generate the action potential that leads to depolarization of the rest of the myocardium.
-
Schmorl's Nodes
Wikipedia
When surgical treatment is indicated, eradication of the intervertebral disc including Schmorl's node and segmental fusion are preferable. [6] Eponym [ edit ] Schmorl's nodes are named after German pathologist Christian Georg Schmorl (1861–1932). [7] References [ edit ] ^ Can an Incidental Schmorl’s Node Be a Cause for Low Backache? – Enigma Resolved By a First Ever Prospective Case Control Study in A South Indian Town Population Authors Saraswathi S1, Adaikkapan M2, Senthilnathan A3, Sivakolunthu M4 1Post graduate, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Rajah Muthiah Medical College and Hospital, Chidambaram – 608002, Tamilnadu, India 2Professor and Head, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Rajah Muthiah Medical College and Hospital, Chidambaram – 608002, Tamilnadu, India 3Professor and Head, Department of Orthopaedics, Rajah Muthiah Medical College and Hospital, Chidambaram – 608002, Tamilnadu, India 4Lecturer, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Rajah Muthiah Medical College and Hospital, Chidambaram – 608002, Tamilnadu, India CONCLUSIONS The prevalence of Schmorl’s nodes in subjects with low backache in our present study representing a South Indian town population is 84%, majority of whom were males (65.4%) with male: female ratio of 1.8:1. the occurrence of Schmorl’s node was highest in superior end plates of upper lumbar vertebrae.
-
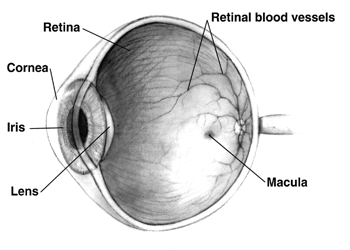
Purtscher's Retinopathy
Wikipedia
Prognosis [ edit ] Purtscher's retinopathy can lead to loss of vision, [4] and recovery of vision may occur very little. [2] However, vision recovery does occur in some cases, and reports have varied on the long-term prognosis. [5] History [ edit ] Purtscher's retinopathy was first characterized in 1910 and 1912 as a syndrome of sudden blindness after head trauma , [6] with patches of hemorrhage and whitening of the retina in both eyes. [2] Later, it was discovered to occur after other types of trauma , such as chest trauma, and is associated with several non-traumatic systemic diseases. [2] Purtscher's retinopathy may also be associated with acute pancreatitis , vasculitis , embolization of such materials as fat and amniotic fluid , [7] systemic lupus erythematosus, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, and chronic kidney failure. [2] Purtscher's retinopathy may be caused by extensive fractures of the long bones. [8] References [ edit ] ^ Buckley, Sally A.; James, B (July 1996).
-
Liver Failure
Wikipedia
Several important measures are immediately necessary when the patient presents for medical attention. [5] The diagnosis of acute liver failure is based on physical exam, laboratory findings, patient history, and past medical history to establish mental status changes, coagulopathy, rapidity of onset, and absence of known prior liver disease respectively. [3] :1557 The exact definition of "rapid" is somewhat questionable, and different sub-divisions exist which are based on the time from onset of first hepatic symptoms to onset of encephalopathy.AKR1D1, MPV17, F2, OTC, VEGFA, ACADM, ORM1, FAH, IL18, ARG1, RPS10, RPS9, RPS6, ASL, ASS1, CPS1, DGUOK, POLG, FECH, ATP7B, POLG2, SERPINA1, HLA-DRB1, SCYL1, CYP7B1, TFAM, LIPA, ND4, ND5, PEX6, PEX1, PCK2, PCK1, PARN, TNPO3, AMACR, NDUFS4, TRNW, TRNV, TRNL1, TRNK, ND6, ND3, CAVIN1, ND2, ND1, ATP6, SLC25A20, IFT172, MPI, PTPN22, SMAD4, TINF2, BSCL2, COQ2, OSTM1, ACAD9, PEX10, PEX12, PEX13, PEX14, MOGS, PEX3, PEX11B, SLC7A7, TERT, TERC, SPIB, SMPD1, PEX16, TJP2, SC5D, ALB, PEX5, PEX2, ABCD3, PEX19, TTC37, TNFSF15, NR1H4, PPARG, POU2AF1, NHLRC1, SLC25A15, ACVRL1, WARS2, AGPAT2, ATRX, IRF5, EPM2A, FH, GBE1, PEX26, ALG8, GPT, ALG1, DKC1, HSD3B7, DLD, CTC1, GDF2, GBA, CAV1, GALT, BTNL2, FOS, ALG9, ENG, USB1, IL12RB1, MMEL1, F13A1, NHP2, IFT122, NOP10, MRPS7, IL12A, CPT1A, CPT2, ALG6, DAXX, IL21R, F13B, WRAP53, RTEL1, TNF, FBL, IL6, NUP210, MARS1, HPGDS, SLA2, GLUL, CCL4, NBAS, SST, ABCB11, TGFB1, PNPLA3, NLRP3, TALDO1, CCL4L2, SQSTM1, EIF2AK3, SCO1, SOCS1, AFP, TP53, CCL4L1, IL17A, ATP8B1, ARNTL2, GSTP1, SLCO6A1, GSTK1, IL1B, MET, GFER, IL1RN, TRMU, PLAU, CXCL8, HAVCR1, SETD2, NR4A3, IL33, EVL, FOXP3, PARP9, TIMELESS, SLC17A5, KMT2D, EPX, MIR223, USP8, ARHGEF5, RBM45, IL17F, TNFAIP8, MIR146A, TANK, OPRPN, AKR1A1, TNFAIP8L2, PRDX4, GPBAR1, NPC2, SLC27A5, MALAT1, RETN, MIR122, RIPK3, ASPG, BTBD8, CD163, NT5C2, MSC, GFM1, PLA2G4A, CXCR4, NR3C1, EZH2, F3, PTK2B, FGFR4, FOXO3, FLT1, GAST, GABPA, GPLD1, GSTM3, EGFR, GSTT1, GSTZ1, HLA-DRB4, HMGB1, HNF4A, HSPA1L, HSPA5, IDH2, IFNAR1, ESR1, EDN1, PTP4A1, CASP8, PARP1, JAG1, AHCY, AKT1, FAS, FASLG, AVP, BCHE, BDNF, CCK, DLAT, CEL, CHN1, CHUK, CISH, COL11A2, CP, CRP, CYP2E1, DECR1, IFNG, IL2RA, IL10, SLC12A2, PRKAA1, PRKAA2, PRKAB1, PTPN1, RORA, ROS1, SCN1A, CCL2, SLC6A12, SOD1, ISG20, ADAM17, THPO, TK2, TLR1, TLR4, UCP2, UQCRC2, WARS1, WNT5A, PLRG1, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, ITGA4, KCNQ1, KRT8, LECT2, LGALS3, LGALS3BP, EPCAM, MLN, MPO, NEDD4, NFE2L2, NOS1, NOS2, NPC1, SERPINE1, REG3A, ABCB1, ABCB4, PIK3CA, MIR375
- Coccidiosis Wikipedia
-
Abortion In Bangladesh
Wikipedia
For example, in 1972, the law allowed for abortion for those women who has been raped during the war. [2] In 1976, the Bangladesh National Population Policy unsuccessfully attempted to legalize abortion in the first trimester . [3] Since 1979, menstrual regulation has been the favored alternative to induced abortion, and it is legally permitted because pregnancy cannot be established. [3] [2] In 2012, the Drug Administration for Bangladesh legalised the combination of mifepristone and misoprotol for medical abortion. [4] Contents 1 Menstrual regulation 2 Abortion 3 Statistics 4 References Menstrual regulation [ edit ] Part of the family planning program in Bangladesh since 1979, menstrual regulation is a procedure that uses manual vacuum aspiration to make it impossible to be pregnant after missing a period . [1] It is simple and can be done with inexpensive equipment.
-
Tietze Syndrome
Wikipedia
Specialty Rheumatology Tietze syndrome (also called costochondral junction syndrome ) is a benign inflammation of one or more of the costal cartilages . [1] It was first described in 1921 by the German surgeon Alexander Tietze (1864–1927). [2] [3] Tietze syndrome is not the same as costochondritis . [4] Tietze syndrome is differentiated from costochondritis by swelling of the costal cartilages, which does not appear in costochondritis.