-
Necrotizing Fasciitis
Wikipedia
Hanneman and his family had apparently been unaware of the extent of the condition until shortly before his death. [28] 2011 Peter Watts , Canadian science-fiction author, contracted the disease. ... Archived from the original on 14 December 2013 . Retrieved 28 May 2013 . ^ " Moorad's life changed by rare disease Archived 2009-09-08 at the Wayback Machine ^ "Don Rickles was politically incorrect before it was incorrect.
-
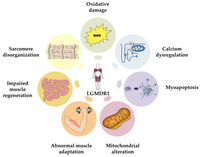
Muscular Dystrophy, Limb-Girdle, Autosomal Recessive 1
Omim
The results of peripheral blood mRNA analysis confirmed the known mutations. In addition, 7 (25%) of 28 mutations identified by analyzing white blood cell mRNA were splice site mutations that modified the CAPN3 transcript, but would not have been detected by direct DNA sequencing of coding regions. ... Disease onset was between ages 8 and 15 years, occurring in the pelvic girdle in most cases, and patients became wheelchair-bound between 11 and 28 years after onset. No pseudohypertrophy of calves or contractures were observed.
-
Episodic Ataxia
Wikipedia
Yes [24] A1593_Y1594delinsD D4S2 ? Yes [24] R1661H D4S4 ? Yes [28] R1664Q * D4S4 ? Yes [29] E1756K D4-pore ? ... Yes [24] Splicing Intron 26 ? Yes [24] Splicing Intron 28 ? Yes [25] * Also diagnosed as Spinocerebellar ataxia type-6 EA3: 1q42 [ edit ] Episodic ataxia type-3 (EA3) is similar to EA1 but often also presents with tinnitus and vertigo .
-
Lichen Sclerosus
Wikipedia
Scratching has been theorized to increase cancer risks. [27] Furthermore, the patient should wear comfortable clothes and avoid tight clothing, as it is a major factor in the severity of symptoms in some cases. [27] [28] Topically applied corticosteroids to the LS-affected skin are the first-line treatment for lichen sclerosus in women and men, with strong evidence showing that they are "safe and effective" when appropriately applied, even over long courses of treatment, rarely causing serious adverse effects. [29] [30] [31] [32] [33] They improve or suppress all symptoms for some time, which highly varies across patients, until it is required to use them again. [34] Methylprednisolone aceponate has been used as a safe and effective corticosteroid for mild and moderate cases. [35] For severe cases, it has been theorized that mometasone furoate might be safer and more effective than clobetasol. [35] Recent studies have shown that topical calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus can have an effect similar to corticosteroids, but its effects on cancer risks in LS are not conclusively known. [36] [37] Based on limited evidence, a 2011 Cochrane review concluded that clobetasol propionate , mometasone furoate, and pimecrolimus (calcineurin inhibitor) all are effective therapies in treating genital lichen sclerosus. [38] However, randomized-controlled trials are needed to further identify the optimal potency and regimen of topical corticosteroids and assess the duration of remission and/or the prevention of flares patients experience with these topical therapies. [38] Continuous usage of appropriate doses of topical corticosteroids is required to ensure symptoms stay relieved over the patient's life time. ... "High prevalence of thyroid disease in patients with lichen sclerosus". J Reprod Med . 52 (1): 28–30. PMID 17286064 . ^ Meyrick Thomas, RH; Kennedy, CT (Mar 1986).TP53, CDKN2A, ECM1, H3P10, TNF, IL1B, CAT, RBP2, S100A7, CCL4, CCL4L2, SOD1, TRBV20OR9-2, THBS1, RARB, PTGS1, CRISP2, ARHGEF1, FSCN1, RASSF2, SERPINA1, MMRN1, CADM1, KRT20, MIB1, SPZ1, MIR155HG, PRSS55, CXCL17, CCL4L1, MIR155, LINC01191, DEFB4B, PTCH1, AFM, PCNA, IL1A, CCND1, CALCA, MS4A1, CRABP2, CCN2, DEFB4A, FLG, GATA3, CXCR3, GZMB, HLA-B, HSPA4, IL1RN, AR, IL13, CXCL10, IRF6, KRAS, KRT1, KRT17, SMAD3, MAL, MGMT, MKI67, MMP9, COX1, MUC2
-
Air Embolism
Wikipedia
Sayers made use of direct injection air embolism as a murder method in her 1927 Lord Peter Wimsey mystery novel Unnatural Death (published in the USA in 1928 as The Dawson Pedigree ), although her description was subsequently criticised as implausible on account of the injection site and volume. [28] Air embolism was the method used by an insane nurse to euthanize seven terminally ill patients in the episode "Amazing Grace" of the TV series Shadow Chasers . [29] Other organisms [ edit ] Air embolisms generally occur in the xylem of vascular plants because a fall in hydraulic pressure results in cavitation . ... Episode 1/4, "Amazing Grace," Shadow Chasers . First aired November 28, 1985. External links [ edit ] Arterial Gas Embolism Classification D ICD - 10 : O88.0 , T79.0 ICD - 9-CM : 673.0 , 999.1 MeSH : D004618 DiseasesDB : 313 SNOMED CT : 271376002 External resources eMedicine : emerg/787 v t e Pathology of pregnancy , childbirth and the puerperium Pregnancy Pregnancy with abortive outcome Abortion Ectopic pregnancy Abdominal Cervical Interstitial Ovarian Heterotopic Embryo loss Fetal resorption Molar pregnancy Miscarriage Stillbirth Oedema , proteinuria and hypertensive disorders Gestational hypertension Pre-eclampsia HELLP syndrome Eclampsia Other, predominantly related to pregnancy Digestive system Acute fatty liver of pregnancy Gestational diabetes Hepatitis E Hyperemesis gravidarum Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy Integumentary system / dermatoses of pregnancy Gestational pemphigoid Impetigo herpetiformis Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy Linea nigra Prurigo gestationis Pruritic folliculitis of pregnancy Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP) Striae gravidarum Nervous system Chorea gravidarum Blood Gestational thrombocytopenia Pregnancy-induced hypercoagulability Maternal care related to the fetus and amniotic cavity amniotic fluid Oligohydramnios Polyhydramnios Braxton Hicks contractions chorion / amnion Amniotic band syndrome Chorioamnionitis Chorionic hematoma Monoamniotic twins Premature rupture of membranes Obstetrical bleeding Antepartum placenta Circumvallate placenta Monochorionic twins Placenta accreta Placenta praevia Placental abruption Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome Labor Amniotic fluid embolism Cephalopelvic disproportion Dystocia Shoulder dystocia Fetal distress Locked twins Nuchal cord Obstetrical bleeding Postpartum Pain management during childbirth placenta Placenta accreta Preterm birth Postmature birth Umbilical cord prolapse Uterine inversion Uterine rupture Vasa praevia Puerperal Breastfeeding difficulties Low milk supply Cracked nipples Breast engorgement Childbirth-related posttraumatic stress disorder Diastasis symphysis pubis Postpartum bleeding Peripartum cardiomyopathy Postpartum depression Postpartum psychosis Postpartum thyroiditis Puerperal fever Puerperal mastitis Other Concomitant conditions Diabetes mellitus Systemic lupus erythematosus Thyroid disorders Maternal death Sexual activity during pregnancy Category v t e Trauma Principles Polytrauma Major trauma Traumatology Triage Resuscitation Trauma triad of death Assessment Clinical prediction rules Revised Trauma Score Injury Severity Score Abbreviated Injury Scale NACA score Investigations Diagnostic peritoneal lavage Focused assessment with sonography for trauma Management Principles Advanced trauma life support Trauma surgery Trauma center Trauma team Damage control surgery Early appropriate care Procedures Resuscitative thoracotomy Pathophysiology Injury MSK Bone fracture Joint dislocation Degloving Soft tissue injury Resp Flail chest Pneumothorax Hemothorax Diaphragmatic rupture Pulmonary contusion Cardio Internal bleeding Thoracic aorta injury Cardiac tamponade GI Blunt kidney trauma Ruptured spleen Neuro Penetrating head injury Traumatic brain injury Intracranial hemorrhage Mechanism Blast injury Blunt trauma Burn Penetrating trauma Crush injury Stab wound Ballistic trauma Electrocution Region Abdominal trauma Chest trauma Facial trauma Head injury Spinal cord injury Demographic Geriatric trauma Pediatric trauma Complications Posttraumatic stress disorder Wound healing Acute lung injury Crush syndrome Rhabdomyolysis Compartment syndrome Contracture Volkmann's contracture Embolism air fat Chronic traumatic encephalopathy Subcutaneous emphysema v t e Underwater diving Diving modes Atmospheric pressure diving Freediving Saturation diving Scuba diving Snorkeling Surface oriented diving Surface-supplied diving Unmanned diving Diving equipment Cleaning and disinfection of personal diving equipment Human factors in diving equipment design Basic equipment Diving mask Snorkel Swimfin Breathing gas Bailout gas Bottom gas Breathing air Decompression gas Emergency gas supply Heliox Nitrox Oxygen Travel gas Trimix Buoyancy and trim equipment Buoyancy compensator Power inflator Dump valve Diving weighting system Ankle weights Integrated weights Trim weights Weight belt Decompression equipment Decompression buoy Decompression cylinder Decompression trapeze Dive computer Diving shot Jersey upline Jonline Diving suit Atmospheric diving suit Dry suit Sladen suit Standard diving suit Rash vest Wetsuit Dive skins Hot-water suit Helmets and masks Anti-fog Diving helmet Free-flow helmet Lightweight demand helmet Orinasal mask Reclaim helmet Shallow water helmet Standard diving helmet Diving mask Band mask Full-face mask Half mask Instrumentation Bottom timer Depth gauge Dive computer Dive timer Diving watch Helium release valve Pneumofathometer Submersible pressure gauge Mobility equipment Diving bell Closed bell Wet bell Diving stage Swimfin Monofin PowerSwim Towboard Diver propulsion vehicle Advanced SEAL Delivery System Cosmos CE2F series Dry Combat Submersible Human torpedo Motorised Submersible Canoe Necker Nymph R-2 Mala-class swimmer delivery vehicle SEAL Delivery Vehicle Shallow Water Combat Submersible Siluro San Bartolomeo Wet Nellie Wet sub Safety equipment Alternative air source Octopus regulator Pony bottle Bolt snap Buddy line Dive light Diver's cutting tool Diver's knife Diver's telephone Through-water communications Diving bell Diving safety harness Emergency gas supply Bailout block Bailout bottle Lifeline Screw gate carabiner Emergency locator beacon Rescue tether Safety helmet Shark-proof cage Snoopy loop Navigation equipment Distance line Diving compass Dive reel Line marker Surface marker buoy Silt screw Underwater breathing apparatus Atmospheric diving suit Diving cylinder Burst disc Diving cylinder valve Diving helmet Reclaim helmet Diving regulator Mechanism of diving regulators Regulator malfunction Regulator freeze Single-hose regulator Twin-hose regulator Full face diving mask Open-circuit scuba Scuba set Bailout bottle Decompression cylinder Independent doubles Manifolded twin set Scuba manifold Pony bottle Scuba configuration Sidemount Sling cylinder Diving rebreathers Carbon dioxide scrubber Carleton CDBA CDLSE Cryogenic rebreather CUMA DSEA Dolphin Electro-galvanic oxygen sensor FROGS Halcyon PVR-BASC Halcyon RB80 IDA71 Interspiro DCSC KISS LAR-5 LAR-6 LAR-V LARU Porpoise Ray Siebe Gorman CDBA Siva Viper Surface-supplied diving equipment Air line Diver's umbilical Diving air compressor Gas panel Hookah Scuba replacement Sea Trek Snuba Standard diving dress Escape set Davis Submerged Escape Apparatus Momsen lung Steinke hood Submarine Escape Immersion Equipment Diving equipment manufacturers AP Diving Apeks Aqua Lung America Aqua Lung/La Spirotechnique Beuchat René Cavalero Cis-Lunar Cressi-Sub Dacor DESCO Dive Xtras Divex Diving Unlimited International Drägerwerk Fenzy Maurice Fernez Technisub Oscar Gugen Heinke HeinrichsWeikamp Johnson Outdoors Mares Morse Diving Nemrod Oceanic Worldwide Porpoise Sub Sea Systems Shearwater Research Siebe Gorman Submarine Products Suunto Diving support equipment Access equipment Boarding stirrup Diver lift Diving bell Diving ladder Diving platform (scuba) Diving stage Downline Jackstay Launch and recovery system Messenger line Moon pool Breathing gas handling Air filtration Activated carbon Hopcalite Molecular sieve Silica gel Booster pump Carbon dioxide scrubber Cascade filling system Diver's pump Diving air compressor Diving air filter Water separator High pressure breathing air compressor Low pressure breathing air compressor Gas blending Gas blending for scuba diving Gas panel Gas reclaim system Gas storage bank Gas storage quad Gas storage tube Helium analyzer Nitrox production Membrane gas separation Pressure swing adsorption Oxygen analyser Oxygen compatibility Decompression equipment Built-in breathing system Decompression tables Diving bell Bell cursor Closed bell Clump weight Launch and recovery system Wet bell Diving chamber Diving stage Recreational Dive Planner Saturation system Platforms Dive boat Canoe and kayak diving Combat Rubber Raiding Craft Liveaboard Subskimmer Diving support vessel HMS Challenger (K07) Underwater habitat Aquarius Reef Base Continental Shelf Station Two Helgoland Habitat Jules' Undersea Lodge Scott Carpenter Space Analog Station SEALAB Tektite habitat Remotely operated underwater vehicles 8A4-class ROUV ABISMO Atlantis ROV Team CURV Deep Drone Épaulard Global Explorer ROV Goldfish-class ROUV Kaikō ROV Kaşif ROUV Long-Term Mine Reconnaissance System Mini Rover ROV OpenROV ROV KIEL 6000 ROV PHOCA Scorpio ROV Sea Dragon-class ROV Seabed tractor Seafox drone Seahorse ROUV SeaPerch SJT-class ROUV T1200 Trenching Unit VideoRay UROVs Safety equipment Diver down flag Diving shot Hyperbaric lifeboat Hyperbaric stretcher Jackstay Jonline Reserve gas supply General Diving spread Air spread Saturation spread Hot water system Sonar Underwater acoustic positioning system Underwater acoustic communication Freediving Activities Aquathlon Apnoea finswimming Freediving Haenyeo Pearl hunting Ama Snorkeling Spearfishing Underwater football Underwater hockey Underwater ice hockey Underwater rugby Underwater target shooting Competitions Nordic Deep Vertical Blue Disciplines Constant weight (CWT) Constant weight without fins (CNF) Dynamic apnea (DYN) Dynamic apnea without fins (DNF) Free immersion (FIM) No-limits apnea (NLT) Static apnea (STA) Skandalopetra diving Variable weight apnea (VWT) Variable weight apnea without fins Equipment Diving mask Diving suit Hawaiian sling Polespear Snorkel (swimming) Speargun Swimfins Monofin Water polo cap Freedivers Deborah Andollo Peppo Biscarini Sara Campbell Derya Can Göçen Goran Čolak Carlos Coste Robert Croft Mandy-Rae Cruickshank Yasemin Dalkılıç Leonardo D'Imporzano Flavia Eberhard Şahika Ercümen Emma Farrell Francisco Ferreras Pierre Frolla Flavia Eberhard Mehgan Heaney-Grier Elisabeth Kristoffersen Loïc Leferme Enzo Maiorca Jacques Mayol Audrey Mestre Karol Meyer Stéphane Mifsud Alexey Molchanov Natalia Molchanova Dave Mullins Patrick Musimu Guillaume Néry Herbert Nitsch Umberto Pelizzari Annelie Pompe Michal Risian Stig Severinsen Tom Sietas Aharon Solomons Martin Štěpánek Walter Steyn Tanya Streeter William Trubridge Devrim Cenk Ulusoy Danai Varveri Alessia Zecchini Nataliia Zharkova Hazards Barotrauma Drowning Freediving blackout Deep-water blackout Shallow-water blackout Hypercapnia Hypothermia Historical Ama Octopus wrestling Swimming at the 1900 Summer Olympics – Men's underwater swimming Organisations AIDA International Scuba Schools International Australian Underwater Federation British Freediving Association Confédération Mondiale des Activités Subaquatiques Fédération Française d'Études et de Sports Sous-Marins Performance Freediving International Professional diving Occupations Ama Commercial diver Commercial offshore diver Hazmat diver Divemaster Diving instructor Diving safety officer Diving superintendent Diving supervisor Haenyeo Media diver Police diver Public safety diver Scientific diver Underwater archaeologist Military diving Army engineer diver Clearance diver Frogman List of military diving units Royal Navy ships diver Special Boat Service United States military divers U.S.
-
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, Vascular Type
Omim
Mild myopathic features were seen on muscle biopsy of 5 (28%) of 18 patients. Patients with the hypermobility type EDS caused by TNXB haploinsufficiency were least affected. ... Families were ascertained after a complication in a single individual, but only 28% of relatives, some of whom had reached their seventies or eighties without incident, had a complication and only 30% had minor clinical features of vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV.
-
Retinal Detachment
Wikipedia
A retrospective Indian study of more than 500 cases of rhegmatogenous detachments found that 11% were due to trauma, and that gradual onset was the norm, with over 50% presenting more than one month after the inciting injury. [28] Treatment [ edit ] There are several methods of treating a detached retina, each of which depends on finding and closing the breaks that have formed in the retina. ... October 2009. Archived from the original on 28 July 2016 . Retrieved 26 July 2016 . ^ a b c d e f Gelston, CD (15 October 2013).PRKCQ, AIFM1, COL2A1, COL18A1, FAS, IFNA2, CPAMD8, CASP3, CASP9, APAF1, HP, CRB1, TNF, BNIP3, CASP8, NTRK1, JAK2, FGFR1, MAP1LC3A, EPOR, EPO, KIF11, PAX6, FBN1, FZD4, CAPN5, COL1A1, NDP, IKBKG, YAP1, RHO, TEK, POMT1, DEAF1, VHL, LARGE1, BEST1, XRCC4, B4GAT1, RXYLT1, BAP1, RAI1, PTEN, PRSS23, PRDM5, NSMCE2, ARL6IP6, B3GALNT2, CHST14, ADAMTSL1, TUBGCP6, POMGNT2, LOXL3, ZNF469, POMK, ZNF408, FKRP, ALG12, XYLT2, CYSLTR2, TENM3, POMGNT1, BCOR, PLOD1, GMPPB, PTPN22, SF3B1, IQSEC2, POMT2, CRPPA, LTBP2, COL9A1, COL5A1, MYOC, COL9A2, COL4A1, COL9A3, COL11A1, LRP5, NHS, CYP1B1, LRP2, CBS, DAG1, HLA-A, GNAQ, GNA11, FKTN, FLII, COL5A2, VEGFA, GFAP, ALOX5AP, FN1, TP53, TGFB2, PVR, MIR148A, MYP2, TRPV4, POU5F1P4, POU5F1P3, MYP10, FBLN2, XIAP, EDN1, MTOR, SRR, P2RY12, C9, CD34, CHM, CCN2, IL33, MAP1LC3B, CFD, PLXNA2, SLCO4A1, MDM2, SERPINF1, MAP2K7, NPY1R, OPN1LW, NM, RPE, RS1, CCL2, CXCL12, NGF, TYR, MMP2, NR3C2, BECN1, GCH1, TNFSF10, PKD2L1, LTA, LRPPRC, EIF1, IL6ST, IL6, IL1B, HMGB1, NES, HLA-C, POU5F1, GH1, CXCL1
-
Marfan Syndrome
Wikipedia
The importance of the TGF-β pathway was confirmed with the discovery of the similar Loeys–Dietz syndrome involving the TGFβR2 gene on chromosome 3 , a receptor protein of TGF-β. [24] Marfan syndrome has often been confused with Loeys–Dietz syndrome, because of the considerable clinical overlap between the two pathologies. [25] Marfanoid–progeroid–lipodystrophy syndrome [ edit ] Main article: Marfanoid–progeroid–lipodystrophy syndrome Marfanoid–progeroid–lipodystrophy syndrome (MPL), also referred to as Marfan lipodystrophy syndrome (MFLS), is a variant of MFS in which Marfan symptoms are accompanied by features usually associated with neonatal progeroid syndrome (also referred to as Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch syndrome) in which the levels of white adipose tissue are reduced. [26] Since 2010, evidence has been accumulating that MPL is caused by mutations near the 3'-terminus of the FBN1 gene . [27] [28] It has been shown that these people are also deficient in asprosin , a gluco-regulatory protein hormone which is the C-terminal cleavage product of profibrillin. ... Archived from the original on 2010-06-17 . Retrieved 2009-08-28 . ^ "What is Marfan Syndrome?" . Marfan Trust. ... Archived from the original on 2009-08-29 . Retrieved 2009-08-28 . ^ Kohlmeier L, Gasner C, Bachrach LK, Marcus R (1995). ... Archived from the original on 2009-08-20 . Retrieved 2009-08-28 . ^ "Living with Marfan Syndrome: Dental issues" . ... Archived from the original on 2009-09-06 . Retrieved 2009-08-28 . ^ "2010 Revised Ghent Nosology" .FBN1, TGFBR2, LTBP2, MMP2, CBS, NOS2, MMP9, SOD2, LAMC1, CAT, SOD1, TGFBR1, MUS81, FBN2, KCNQ1, EGF, ELN, TGFB1, AGTR1, COL1A2, AGT, TGFB2, DCN, SMAD2, COL3A1, COX2, PKD1, MMP14, PPARG, MAPK1, LRP1, TAGLN, TNF, ADAMTS1, SMAD3, MMRN1, ADAMTSL4, CD109, ACTA2, MAPK3, LOX, BGLAP, SLC35A1, FBLN5, RBM8A, GAL3ST1, BRAF, GRAP2, KLF4, SLC33A1, CLDN6, AXIN2, HBHR, AIMP2, VWF, TRPV1, VEGFA, TP53, VPS51, TIMP3, TIMP2, AHSA1, SIRT1, FADS3, PART1, CST12P, CBSL, PGR-AS1, SPESP1, PTPRVP, ALOX5, DCBLD2, FBN3, SPRTN, ANGPT2, P3H2, CASZ1, ATM, NOX4, GPR162, SIGLEC7, POLDIP2, RNF19A, SUMF2, THBS1, TGFBR3, CD34, CD44, NOTCH3, NOTCH1, NOS3, CSF2, NF1, MYBPC3, MTHFR, VCAN, DECR1, MMP13, MMP12, EPHB2, MMP3, FXN, MFAP4, MFAP1, MET, CCN1, LAMC2, MAPK14, PLXNA2, CRP, SLN, TGFBI, TGFB3, CDH5, CNN1, COL1A1, SULT1E1, COL2A1, COX8A, SLC12A3, CRK, SLC3A1, SCD, ACSM3, ROS1, REN, PTGS2, MAP2K7, ACTB, MTCO2P12
-
Measles
Wikipedia
Viral disease affecting humans Measles Other names Morbilli, rubeola, red measles, English measles [1] [2] A child showing a day-four measles rash Specialty Infectious disease Symptoms Fever, cough, runny nose, inflamed eyes, rash [3] [4] Complications Pneumonia , seizures , encephalitis , subacute sclerosing panencephalitis , immunosuppression , hearing loss, blindness [5] [6] Usual onset 10–12 days after exposure [7] [8] Duration 7–10 days [7] [8] Causes Measles virus [3] Prevention Measles vaccine [7] Treatment Supportive care [7] Frequency 20 million per year [3] Deaths 140,000+ (2018) [9] [10] Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus . [3] [11] Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. [7] [8] Initial symptoms typically include fever , often greater than 40 °C (104 °F), cough, runny nose , and inflamed eyes . [3] [4] Small white spots known as Koplik's spots may form inside the mouth two or three days after the start of symptoms. [4] A red, flat rash which usually starts on the face and then spreads to the rest of the body typically begins three to five days after the start of symptoms. [4] Common complications include diarrhea (in 8% of cases), middle ear infection (7%), and pneumonia (6%). [5] These occur in part due to measles-induced immunosuppression . [6] Less commonly seizures , blindness , or inflammation of the brain may occur. [5] [7] Other names include morbilli , rubeola , red measles , and English measles . [1] [2] Both rubella , also known as German measles , and roseola are different diseases caused by unrelated viruses. [12] Measles is an airborne disease which spreads easily from one person to the next through the coughs and sneezes of infected people. [7] It may also be spread through direct contact with mouth or nasal secretions . [13] It is extremely contagious–nine out of ten people who are not immune and share living space with an infected person will be infected. [5] Furthermore, measles's reproductive number estimates vary beyond the frequently cited range of 12 to 18. [14] People are infectious to others from four days before to four days after the start of the rash. [5] While often regarded as a childhood illness, it can affect people of any age. [15] Most people do not get the disease more than once. [7] Testing for the measles virus in suspected cases is important for public health efforts. [5] Measles is not known to occur in other animals. [13] Once a person has become infected, no specific treatment is available, [13] although supportive care may improve outcomes. [7] Such care may include oral rehydration solution (slightly sweet and salty fluids), healthy food, and medications to control the fever. [7] [8] Antibiotics should be prescribed if secondary bacterial infections such as ear infections or pneumonia occur. [7] [13] Vitamin A supplementation is also recommended for children. [13] Among cases reported in USA between 1985 and 1992 the death was the outcome in just 0.2% of cases, [5] but may be up to 10% in people with malnutrition . [7] Most of those who die from the infection are less than five years old. [13] The measles vaccine is effective at preventing the disease, is exceptionally safe, and is often delivered in combination with other vaccines. [7] [16] Vaccination resulted in an 80% decrease in deaths from measles between 2000 and 2017, with about 85% of children worldwide having received their first dose as of 2017. [13] Measles affects about 20 million people a year, [3] primarily in the developing areas of Africa and Asia. [7] It is one of the leading vaccine-preventable disease causes of death. [17] [18] In 1980, 2.6 million people died of it, [7] and in 1990, 545,000 died; by 2014, global vaccination programs had reduced the number of deaths from measles to 73,000. [19] [20] Despite these trends, rates of disease and deaths increased from 2017 to 2019 due to a decrease in immunization. [21] [22] [23] Play media Video summary ( script ) Contents 1 Signs and symptoms 1.1 Complications 2 Cause 3 Pathophysiology 4 Diagnosis 4.1 Laboratory testing 5 Prevention 6 Treatment 6.1 Medications 7 Prognosis 8 Epidemiology 8.1 Europe 8.2 Americas 8.2.1 United States 8.2.2 Brazil 8.3 Southeast Asia 8.4 South Pacific 8.4.1 Samoa 8.5 Africa 8.5.1 Madagascar 8.5.2 Democratic Republic of Congo 9 History 10 Society and culture 10.1 Alternative names 11 Research 12 References 13 External links Signs and symptoms Maculopapular rash on the abdomen after 3 days of measles infection Symptoms typically begin 10–14 days after exposure. [24] [25] The classic symptoms include a four-day fever (the 4 D's) and the three C's— cough , coryza (head cold, fever, sneezing), and conjunctivitis (red eyes)—along with a maculopapular rash . [26] Fever is common and typically lasts for about one week; the fever seen with measles is often as high as 40 °C (104 °F). [27] Koplik's spots seen inside the mouth are diagnostic for measles, but are temporary and therefore rarely seen. [26] Koplik spots are small white spots that are commonly seen on the inside of the cheeks opposite the molars. [25] They appear as "grains of salt on a reddish background." [28] Recognizing these spots before a person reaches their maximum infectiousness can help reduce the spread of the disease. [29] The characteristic measles rash is classically described as a generalized red maculopapular rash that begins several days after the fever starts. ... Complications Complications of measles are relatively common, ranging from mild ones such as diarrhea to serious ones such as pneumonia (either direct viral pneumonia or secondary bacterial pneumonia ), laryngotracheobronchitis (croup) (either direct viral laryngotracheobronchitis or secondary bacterial bronchitis), otitis media , [32] acute brain inflammation [33] (and very rarely subacute sclerosing panencephalitis ), [34] and corneal ulceration (leading to corneal scarring ). [35] In addition, measles can suppress the immune system for weeks to months, and this can contribute to bacterial superinfections such as otitis media and bacterial pneumonia. [6] [36] [37] [38] [39] Two months after recovery there is a 11–73% decrease in the number of antibodies against other bacteria and viruses. [40] The death rate in the 1920s was around 30% for measles pneumonia. [41] People who are at high risk for complications are infants and children aged less than 5 years; [15] adults aged over 20 years; [15] pregnant women; [15] people with compromised immune systems, such as from leukemia , HIV infection or innate immunodeficiency; [15] [42] and those who are malnourished [15] or have vitamin A deficiency . [15] [43] Complications are usually more severe in adults. [44] Between 1987 and 2000, the case fatality rate across the United States was three deaths per 1,000 cases attributable to measles, or 0.3%. [45] In underdeveloped nations with high rates of malnutrition and poor healthcare , fatality rates have been as high as 28%. [45] In immunocompromised persons (e.g., people with AIDS ) the fatality rate is approximately 30%. [46] Even in previously healthy children, measles can cause serious illness requiring hospitalization. [42] One out of every 1,000 measles cases progresses to acute encephalitis, which often results in permanent brain damage. [42] One to three out of every 1,000 children who become infected with measles will die from respiratory and neurological complications. [42] Cause An electron micrograph of the measles virus Measles is caused by the measles virus , a single-stranded, negative-sense , enveloped RNA virus of the genus Morbillivirus within the family Paramyxoviridae . [47] The virus is highly contagious and is spread by coughing and sneezing via close personal contact or direct contact with secretions. [48] Measles is the most contagious transmissible virus known. [16] It remains infective for up to two hours in that airspace or nearby surfaces. [24] [48] Measles is so contagious that if one person has it, 90% of nearby non-immune people will also become infected. [24] Humans are the only natural hosts of the virus, and no other animal reservoirs are known to exist. [24] Risk factors for measles virus infection include immunodeficiency caused by HIV or AIDS, [49] immunosuppression following receipt of an organ or a stem cell transplant , [50] alkylating agents , or corticosteroid therapy , regardless of immunization status; [15] travel to areas where measles commonly occurs or contact with travelers from such an area; [15] and the loss of passive, inherited antibodies before the age of routine immunization. [51] Pathophysiology Drawing of the measles virus attaching to the lining of the trachea Once the measles virus gets onto the mucosa , it infects the epithelial cells in the trachea or bronchi. [52] [53] Measles virus uses a protein on its surface called hemagglutinin (H protein), to bind to a target receptor on the host cell, which could be CD46 , which is expressed on all nucleated human cells, CD150 , aka signaling lymphocyte activation molecule or SLAM, which is found on immune cells like B or T cells, and antigen-presenting cells, or nectin-4 , a cellular adhesion molecule. [52] [54] Once bound, the fusion, or F protein helps the virus fuse with the membrane and ultimately get inside the cell. [52] As the virus is a single-stranded negative-sense RNA virus , it includes the enzyme RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) which is used to transcribe its genome into a positive-sense mRNA strand. [52] After that it is ready to be translated into viral proteins, wrapped in the cell's lipid envelope, and sent out of the cell as a newly made virus. [55] Within days, the measles virus spreads through local tissue and is picked up by dendritic cells and alveolar macrophages , and carried from that local tissue in the lungs to the local lymph nodes. [52] [53] From there it continues to spread, eventually getting into the blood and spreading to more lung tissue, as well as other organs like the intestines and the brain. [24] [52] Functional impairment of the infected dendritic cells by the measles virus is thought to contribute to measles-induced immunosuppression. [6] Diagnosis Typically, clinical diagnosis begins with the onset of fever and malaise about 10 days after exposure to the measles virus, followed by the emergence of cough , coryza , and conjunctivitis that worsen in severity over 4 days of appearing. [56] Observation of Koplik's spots is also diagnostic. [29] Other possible condition that can result in these symptoms include parvovirus , dengue fever , Kawasaki disease , and scarlet fever . [57] Laboratory confirmation is however strongly recommended. [58] Laboratory testing Laboratory diagnosis of measles can be done with confirmation of positive measles IgM antibodies or detection of measles virus RNA from throat, nasal or urine specimen by using the reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assay. [57] [59] This method is particularly useful to confirm cases when the IgM antibodies results are inconclusive. [57] For people unable to have their blood drawn , saliva can be collected for salivary measles-specific IgA testing. [59] Salivary tests used to diagnose measles involve collecting a saliva sample and testing for the presence of measles antibodies. [60] [61] This method is not ideal, as saliva contains many other fluids and proteins which may make it difficult to collect samples and detect measles antibodies. [60] [61] Saliva also contains 800 times fewer antibodies than blood samples do, which makes salivary testing additionally difficult.CD46, SLAMF1, MRC1, NECTIN4, PLAAT4, IFNG, DDX58, TLR4, CEACAM5, IL2, ROBO3, MYBPH, PDR, MYOM2, IFI44L, IFNAR2, ADAR, STAT1, IL18R1, IL6, RBPMS, SLC5A5, PYCR1, MX1, HLA-DRB1, EBI3, IFIH1, KDELR2, SARS1, APOBEC3G, ERVK-6, CCL20, CCL1, SRL, CAMKMT, TFPI, AGBL2, CCDC115, TRIM5, RBM45, MIR31, PVR, STAT2, TLR2, WDR5, LAMP3, AGTPBP1, NXF1, SEC14L2, ATP2C1, NR1I2, PROM1, ERVW-1, TLR3, CD207, TLR8, USO1, TRIM25, MFSD6, SARS2, EIF2AK2, MS, PRDX1, CHEK1, GLB1, CBLIF, FOLR2, FOLR1, FLNB, ERBB2, EGFR, DPT, SARDH, CSF2, TNFRSF8, HLA-DQA1, MS4A1, CD19, KRIT1, CANX, CALM3, CALM2, CALM1, ASAH1, APRT, ALB, HLA-A, HPRT1, OCA2, IL13, MYD88, AKT1, MFAP1, LSAMP, LBR, LAMC2, KPNB1, IRF3, IDO1, IL17A, IL12B, HSPA5, IL10, CXCL8, IL7R, IL4R, IL4, IFNR, IFNAR1, IFNA13, IFNA1, IFN1@, ERVK-20
-
Bronchiectasis
Wikipedia
Historically, about half of all case of non-CF bronchiectasis were found to be idiopathic , or without a known cause. [23] However, more recent studies with a more thorough diagnostic work-up have found an etiology in 60 to 90% of patients. [22] [24] [25] Cystic fibrosis [ edit ] Cystic fibrosis is the most common life-threatening autosomal recessive disease in the United States and Europe. [26] It is a genetic disorder that affects the lungs , but also the pancreas , liver , kidneys , and intestine . [27] It is caused by mutations in the CFTR protein , a chloride channel expressed in epithelial cells. [26] Lung disease results from clogging of the airways due to mucus build-up, decreased mucociliary clearance , and resulting inflammation . [28] In later stages, changes to the structure of the lung, such as bronchiectasis, occur. ... June 2, 2014. Archived from the original on 28 July 2016 . Retrieved 10 August 2016 . ^ a b Corris, PA (Jun 2013). ... Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology . 28 (5): 647–653. ISSN 0392-856X . PMID 20883638 . ^ Chatzidionisyou, Aikaterini; Catrina, Anca I. ... "The lung in rheumatoid arthritis, cause or consequence?". Current Opinion in Rheumatology . 28 (1): 76–82. doi : 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000238 .CFTR, SERPINA1, SCNN1B, SCNN1G, DNAH11, DNAI1, DNAH5, DNAAF1, PIK3R1, PIK3CD, NFKB2, NME8, CCDC40, SCNN1A, DNAI2, DNAL1, DNAAF2, RSPH9, RSPH4A, CCDC39, TNF, ICAM1, STAT1, TAP2, TAP1, TGFB1, TNFRSF13B, MUC5B, DNAAF3, ARHGEF1, TNFSF12, CCNO, FAM13A, ATP11A, LRRC6, DNAH1, RIPK1, CXCR4, DNAJB13, OFD1, USP11, BLNK, TERT, TERC, CCDC103, SFTPA1, TCF3, TAPBP, SPAG1, SFTPC, SFTPA2, STK36, PIH1D3, ICOS, STN1, CCDC151, TNFRSF13C, LRRC56, CCDC114, DNAAF4, DRC1, DPP9, RSPH1, CCDC65, CFAP300, ZNF341, RSPH3, TTC25, GAS2L2, CARMIL2, BACH2, CFAP298, LRRC8A, BTNL2, DNAH7, SLC29A3, COPD, ARMC4, DNAAF5, HYDIN, RTEL1, ZMYND10, MCIDAS, IL21R, ABCA3, RPGR, PRKCD, NFKB1, IGLL1, IGHM, IRF8, HLA-DRB1, PARN, GAS8, FCGR2A, ENG, PGM3, DSP, DNMT3B, CR2, LRBA, CD81, CD79B, CD79A, MS4A1, CD19, CD8A, BLM, B2M, ATM, NBN, MBL2, ELANE, CXCL8, MPO, IL17A, CALR, PLF, CRP, IL6, NTM, HLA-C, ELN, FOLH1, USO1, SEC14L2, ALB, MMP8, MMP9, NXF1, FLNB, MMP1, CTSB, SLC26A9, DIAPH1, G6PC3, PREP, PCBD1, PPARG, PDCD1, PRTN3, MUC2, PZP, CEL, STAT3, ADRB2, TRIM21, FCGRT, TNFRSF8, SGCA, SFTPD, RASA1, CAMP, CXCL12, CCL20, AVP, CCL17, TIMP3, RGMA, PARP9, RMRP, TRAF3IP2, SLC27A5, JMJD6, MUC5AC, LGALS9, PTPN22, LCN1, IL18, FLVCR1, IL13, IL10, MBL3P, FOXP3, ISYNA1, FCN2, IL23A, IL1B, IL1A, NHS, IFNG, CFI, NOS2, HOXB@, PAEP, HLA-B, RGS6, TLR2, FOXJ1, MICA
-
Diffuse Panbronchiolitis
Wikipedia
A genetic predisposition among East Asians is suggested. [9] The disease is more common in males, [25] with the male to female ratio at 1.4–2:1 (or about 5 men to 3 women). [4] The average onset of the disease is around age 40, and two-thirds of those affected are non-smokers, although smoking is not believed to be a cause. [7] The presence of HLA-Bw54 increases the risk of diffuse panbronchiolitis 13.3-fold. [26] In Europe and the Americas, a relatively small number of DPB cases have been reported in Asian immigrants and residents, as well as in individuals of non-Asian ancestry. [27] [28] [29] Misdiagnosis has occurred in the West owing to less recognition of the disease than in Asian countries. ... The European Respiratory Journal . 28 (4): 862–71. doi : 10.1183/09031936.06.00131805 .
-
Alopecia Areata
Wikipedia
In 2014, preliminary findings showing that oral ruxolitinib , a drug approved by the US Food and Drug Administration ( FDA ) for bone marrow disorder myelofibrosis , restored hair growth in three individuals with long-standing and severe disease. [28] The medicine costs almost US$10,000 a month. [29] History [ edit ] Alopecia areata and alopecia barbae have been identified by some as the biblical nethek condition that is part of the greater tzaraath family of skin disorders; the said disorders are purported to being discussed in the Book of Leviticus , chapter 13. [30] Notable people with alopecia areata include actor Anthony Carrigan , [31] and congresswoman Ayanna Pressley . [32] See also [ edit ] Noncicatricial alopecia Trichotillomania References [ edit ] ^ a b c d e f g h "Alopecia Areata - NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders)" . ... American Journal of Human Genetics . 80 (2): 316–28. doi : 10.1086/511442 . PMC 1785354 .IL2RA, CTLA4, IKZF4, STX17, CXCL10, CXCL9, RAET1L, CXCR3, PRDX5, ULBP3, PTPN22, CLEC16A, IL13, LPP, TRPS1, HR, ATXN2, KDM5C, PADI3, TGM3, ACOXL, TSBP1-AS1, TSBP1, RAET1M, PTCSC2, TH2LCRR, MAGI3, MALRD1, LINC01254, IFNG-AS1, ERBB3, MIR924HG, SLC16A12, AIRE, IFNG, IL1A, IL1B, TNF, HLA-DRB1, IL1RN, IL17A, FAS, VDR, NOTCH4, MIF, CRP, IL4, KLRC4-KLRK1, IL18, ICAM1, FLG, HT, VAMAS6, KLRK1, ICOSLG, DKK1, IL23R, IL36RN, FCRL3, CD274, FOXP3, TLR7, TLR9, PSIP1, MIR30B, ATOD1, SPATA5, PDCD1LG2, MED25, MCHR2, LINC01193, IL23A, ABO, STAMBP, CD200, JAK1, IL16, HSPA1B, HLA-G, HLA-DQB1, HLA-C, GZMB, CXCL2, CXCL1, GATA3, FCGR1B, FCGR1A, ACE, CRH, CP, CD40, FASLG, MC2R, MTHFR, MCRS1, MX1, SOCS3, TRAF1, TNNI3, TLR1, TH, TGFB1, ALB, TAP1, STAT1, SPP1, SOAT1, CCL2, RBP1, PRL, PDC, NOS3, NFE2L2, TRBV20OR9-2
-
Herpes Simplex
Wikipedia
The virus interacts with the components and receptors of lipoproteins , which may lead to its development. [28] [29] Pathophysiology Herpes shedding [30] HSV-2 genital 15–25% of days HSV-1 oral 6–33% of days HSV-1 genital 5% of days HSV-2 oral 1% of days Herpes is contracted through direct contact with an active lesion or body fluid of an infected person. [31] Herpes transmission occurs between discordant partners; a person with a history of infection (HSV seropositive) can pass the virus to an HSV seronegative person. ... As many as one in seven Canadians aged 14 to 59 may be infected with herpes simplex type 2 virus [85] and more than 90 per cent of them may be unaware of their status, a new study suggests. [86] In the United States, it is estimated that about 1,640,000 HSV-2 seroconversions occur yearly (730,000 men and 910,000 women, or 8.4 per 1,000 persons). [87] In British Columbia in 1999, the seroprevalence of HSV-2 antibody in leftover serum submitted for antenatal testing revealed a prevalence of 17%, ranging from 7% in women 15–19 years old to 28% in those 40–44 years. [88] In Norway, a study published in 2000 found that up to 70–90% of genital initial infections were due to HSV-1. [89] In Nova Scotia, 58% of 1,790 HSV isolates from genital lesion cultures in women were HSV-1; in men, 37% of 468 isolates were HSV-1. [90] History Herpes has been known for at least 2,000 years. ... The Good News about the Bad News: Herpes: Everything You Need to Know . New Harbinger Publications. p. 28. ISBN 978-1-57224-618-8 . Archived from the original on 2016-05-27. ^ "AHMF: Preventing Sexual Transmission of Genital herpes" . ... J. Infect. Dis . 186 (Suppl 1): S3–28. doi : 10.1086/343739 . PMID 12353183 . ^ Xu, Fujie; Fujie Xu; Maya R.NECTIN1, NECTIN2, ACKR1, UBE3B, TP53, ZNF35, IFNA13, IFNG, ERVK-6, APOE, LAT, ERBB2, TLR3, IL2, TNFRSF14, AFP, THBS1, GLB1, TNF, IFNA1, IFNB1, TNFSF14, PENK, ERVK-20, IL6, ERVW-1, CEACAM5, PML, CSF2, VEGFA, IFI16, IL4, ERVK-32, MUL1, PRKN, TLR9, IRF3, CBLL2, TG, NGF, BCL2, MDK, NXF1, EGR1, SEC14L2, FLNB, ACTB, TERT, EGFR, IL10, USO1, TLR2, KLK3, COL18A1, UBE2B, CASP3, IL13, HCFC1, FLT3LG, ITIH4, SLPI, AKT1, CASP8, CTCF, STAT3, ATRX, DUT, TH, STAT1, APP, HSPA8, HSPA4, CTNNB1, ESR1, PTGS2, FXN, LOC110013312, MAP2K7, GJA1, SST, TRAF3, RPL41, CRP, SLC5A5, CXCL8, CDK1, PPP1R15A, UNG, LTA, CD40, MAPK14, CAT, CGAS, TBC1D9, LGALS4, GEMIN4, CYTIP, MYBL2, HLA-DRB1, HLA-C, HLA-A, LAG3, ITGAL, DDX58, HBB, GZMB, KDR, MX1, IRF7, POLD1, HDAC5, ITGB2, NR3C1, ITPR1, TLR7, CFDP1, NFKB1, NHS, IL18, HDAC4, POLDIP2, IGHG3, DCAF1, IL11, GFAP, NFE2L2, MBL2, GRAP2, IL17A, HSP90AA1, IDO1, SH3KBP1, RNF19A, ABCB1, TBK1, INSM1, TREH, CD274, AHSA1, SENP1, AGFG1, HPRT1, SERPINA1, PILRA, FGF2, RIPK1, CDK9, CISH, SLC3A2, SLC2A1, VCP, CCL2, CRK, CSF1, TRPV1, GAD1, CX3CR1, CYP2B6, CYP4B1, DCK, RPAIN, CTTNBP2, BTLA, CD44, UNC93B1, CD40LG, ALB, TAP1, ARRB2, CCR2, ATM, MIR155, MIR145, BMP2, TLR4, SPARC, SP1, TRE-TTC3-1, IFNL1, CD80, CD34, DTYMK, EIF4H, SOCS1, BECN1, EPO, PRKRA, ROBO3, MTOR, PLAAT4, TNFSF11, F3, EIF4G2, EIF2AK2, NANOG, PSMD2, AIMP2, MAPK1, IL21, KDM4A, ABCC5, TOP2A, TRAF6, TNKS, NPEPPS, TMPO, CES2, KIF23, PROM1, SCLC1, HDAC9, TIMP2, THBD, AKT3, TIA1, HNRNPDL, TNFSF13, TNFSF15, TIMP3, SUCLA2, HS3ST1, TK2, MARCO, TRIM14, EIF2AK3, TNFRSF6B, BCLAF1, TYMS, AIM2, HIRA, CH25H, MTMR4, SLC6A5, USP7, ZAP70, MLRL, EEA1, XRCC5, NOLC1, MSC, PDLIM7, XPA, SMARCA5, PARG, VWF, SOCS3, IKBKG, VIM, HSPB3, KDM6A, MTMR3, TMPRSS11D, TYRO3, TYR, PSMG1, ARHGEF7, PAX8, MED23, FCGBP, SMC4, AAVS1, ABCB6, MED25, TRIM69, UPRT, RAET1E, HSPB6, PDZD8, ANTXR2, RAB39B, GPR146, TRS-TGA2-1, TRIM41, ZCCHC3, HAVCR2, PUS3, TRIM56, SENP7, TMX1, HM13, KCNIP4, TET1, AGBL2, SUGCT, GDPD3, HS3ST6, DCLRE1C, PJA1, XYLT2, LSM2, LRRC7, TICAM1, PYHIN1, GPBAR1, DDX53, MTCO2P12, ERVK-19, MYMX, IFNL4, RNA5SP141, ERVK-11, ERVK-18, ERVK-9, COMMD3-BMI1, KLRC4-KLRK1, POTEF, MIR21, MIR146A, MIR132, LINC01194, VHLL, NUPR2, STING1, BPIFA4P, STON1-GTF2A1L, CLEC9A, NEAT1, H19, IL27, TRIML2, NLRC3, RHOV, KIAA1210, PSMG2, TSPAN1, CD160, PHGDH, TOR1AIP1, SAMHD1, POU2F3, TRIM29, RCOR1, SMC5, KDM1A, RAB3GAP1, ATF6, KLRK1, MON1B, CHP1, ADRM1, IL36G, STON1, GTF2A1L, SPIN1, GADD45G, NES, POLQ, TNFSF13B, MCRS1, RACK1, NET1, ABCC4, CD96, G3BP1, PABPC1, RPUSD2, INTU, IGKV2D-10, ERBIN, ZNF415, NBPF1, LGR4, PRPF38B, AHI1, CPVL, IL17D, CHMP3, CXXC5, NCKIPSD, SLC25A37, SLC15A3, NT5C3A, HSPA14, LEF1, AADAT, DBR1, IRAK4, SIDT2, ASCC1, TRAT1, IL22, NOP53, PSAT1, PHPT1, HIPK2, ANKRD1, PTGER2, TGFB1, EIF2S1, GAD2, GABPA, XRCC6, FUT6, FUT3, FUS, FOS, FLT3, FGF1, FDXR, FCGR3B, FCGR3A, FASN, FANCD2, EZH2, ETV5, ETFA, ERCC6, EPHB4, EPHA3, EP300, SLC29A1, ENPEP, EMD, ELAVL3, EIF4G1, EIF4EBP1, EIF4E, EIF4A2, GH1, GJB1, CXCR3, HNRNPC, CCN1, IGF2, IGF1, IFNGR1, ICAM1, DNAJB1, HSPD1, HSPB2, HSPB1, HSPA9, HES1, HRG, TLX2, HMOX1, GRIN1, HMGA1, HMGB2, HMGB1, HLA-G, HLA-DQB1, HBZ, H2AX, GZMA, GUSB, GTF2H1, GRP, GRIN2D, GRIN2A, EPHA2, EGF, TRBV20OR9-2, EDN1, CCK, CASP9, CASP1, CAMP, CALR, CALCR, C3, BTK, BRCA2, BPHL, BMI1, BGLAP, BDNF, ADGRB1, ATR, ATF3, ASS1, ASNS, ASAH1, AR, FAS, APC, ANPEP, AKR1B1, AFM, ADSS2, GRK2, ADCYAP1R1, ACY1, CD19, CD28, CD86, CSH1, TOR1A, DUSP2, ATN1, DPP6, TIMM8A, DEFA5, DDX3X, DAXX, CYP2D6, CYP1A1, CTSB, CTLA4, CSH2, CRH, CD38, CPS1, COX8A, KLF6, COMT, CCR5, CCR1, ERCC8, CDX2, CDKN2A, CDKN1A, CDC34, CD68, CD47, IL1B, IL3, IL15, CXCL10, RPL22, RPL21, RPL11, RNASE1, REST, RBL2, RBBP6, RAG1, RAD51, PVR, PTPRC, PTGER4, PSMD13, PSMB8, PSEN1, PRTN3, PROS1, PRKD1, PRKCE, PPIB, CTSA, POU2F1, POMC, POLH, PLAU, PLAG1, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, RPL26, RPL29, RPS11, SOAT1, TCF4, TBCE, TAF2, SUPT5H, SULT2A1, STAT6, STAT4, SRPK1, SPRR2A, SPR, SOX3, SOD2, SOD1, SNCA, RPS19, SMPD1, SLC22A1, SLC18A2, SLC6A8, SLC6A2, SFTPC, SELPLG, CXCL11, CCL5, CCL3, SCT, SALL1, RPS23, PIK3CA, SERPINF1, PECAM1, LMNA, MIP, CXCL9, MICE, MICB, MDM2, MAPT, MAL, SMAD4, SMAD3, EPCAM, LTF, LTBR, LMNB1, LIF, NR3C2, LHCGR, LGALS9, LGALS1, LBR, KNG1, KIR2DL2, JAK2, STT3A, ITGAV, ITGAM, IRS1, IRF2, INS, AFDN, MME, PDYN, NFKBIA, ENPP1, PDCD1, PCNA, PAX6, PAEP, CLDN11, ODC1, NUMA1, NTSR1, NTS, PNP, NOS2, NFYA, NFIX, MMP9, NFIC, NFIB, NFIA, NEDD4, NCL, MUC4, MUC1, COX2, MSI1, MSH2, MS, MRC1, MOG, H3P40
-
Visceral Leishmaniasis
Wikipedia
The CD4+ clones had little effect on IL-10 secretion but decreased IFN-γ secretion when mixed with self PBMC collected after successful treatment. [ citation needed ] Regulatory B cells are known to favor development of regulatory T cells and suppress development of Type 1 T helper cells by producing IL-10 and other down-regulatory cytokines. [19] IL-10 levels are elevated in B cells from VL PBMC. [25] A study of dogs with naturally acquired VL showed that the percentage of regulatory B cells increased three-fold during VL. [28] Depletion of B cells increased CD4+ T cell proliferation and IFN-γ secretion but decreased IL-10 secretion. ... Main side effects are gastrointestinal disturbance in the first or second day of treatment (a course of treatment is 28 days) which does not affect the efficacy.TNF, IL10, IFNG, SLC11A1, IL1B, HLA-DRB1, IL6, HMOX1, CSF2, HLA-DQA1, CXCL8, IL10RA, CRP, IL4, HSPA4, TLR4, MBL2, FOXP3, HIF1A, SLC6A3, TLR2, LEP, IL17A, IL9, IL2, TLR9, P4HB, CYTB, IL15, LMLN, IL12RB1, DDX56, IGF1, CCR7, CD69, MAPK1, ODC1, DLL1, RAB6A, MPL, NOS2, IL4R, CD58, IFNGR1, RCE1, NUP93, NPEPPS, PDCD1LG2, RABEPK, IL32, UNC13D, CPQ, ZNRD2, CXCL13, DCTN6, TICAM2, LANCL1, SOCS1, ARHGEF2, TGFB1, SMPD2, SPAG1, ST2, STAT3, TARS1, TBP, TGFBI, PKD2L1, H3P23, TP53, TNFSF4, TP63, POP1, HSPB3, TNFSF13B, SMUG1, EBNA1BP2, MON2, MIR155, CDK12, TREM1, ZNF469, FBLIM1, GOPC, HAMP, MIR122, CXCL16, AGMO, ASPG, NOD2, FAM120B, POPDC3, MLST8, PDIA2, TARS2, TMED7-TICAM2, IL33, IL23A, CLEC4D, DICER1, SIRT1, PIGZ, SLC17A5, CD274, RBM45, PADI1, PYDC5, NELFCD, PSAT1, TARS3, NLRP3, SMARCB1, MTCO2P12, TMED7, PRRT2, ARMH1, ACTB, SLAMF1, SGTA, F5, FCN2, FH, FOXO1, G6PD, GABPA, HLA-C, HLA-G, HSPA1A, HSPA1B, HSPA2, HSP90AA1, IFI27, IFNA1, IFNA13, IL2RA, IL2RB, ELF2, EEF1B2, DUSP4, CD14, AHCY, APOA1, KLK3, AQP1, BCS1L, CASP3, CD1A, CD34, DPP4, CD40, CD40LG, CPB1, CTLA4, CTSB, CYP51A1, DDT, IL5, CXCR1, CXCR2, PPARA, NCAM1, NFE2L2, NOTCH3, NRAS, ADA, PHB, PLAG1, PRKCA, COX2, PRKCB, MAPK10, PROS1, PSMD7, PSMD9, RNASE2, CCL2, MYD88, MMP9, IL13, RPSA, IL18, CXCL10, INPP5D, IRF1, IRF5, ISG20, ITGB2, LCK, MMP2, LECT2, LGALS1, LPL, LTA, MATK, MIF, CXCL9, H3P28
-
Spinal Muscular Atrophy
Wikipedia
Symptoms are critical (including respiratory distress and poor feeding) which usually result in death within weeks, in contrast to the mildest phenotype of SMA (adult-onset), where muscle weakness may present after decades and progress to the use of a wheelchair but life expectancy is unchanged. [28] The more common clinical manifestations of the SMA spectrum that prompt diagnostic genetic testing: Progressive bilateral muscle weakness (Usually upper arms & legs more so than hands and feet) preceded by an asymptomatic period (all but most severe type 0) [28] Flattening of the chest wall when taking a breath and belly protrusion when taking a breath in. hypotonia associated with absent reflexes .SMN1, SMN2, TRPV4, ASCC1, ATAD3A, DYNC1H1, BICD2, VRK1, UBA1, ASAH1, IGHMBP2, TRIP4, VAPB, EXOSC8, SIGMAR1, TK2, CHCHD10, DNAJB2, SNURF, NAIP, FBXO38, KCNK9, DYSF, PLS3, SNRPN, TBCE, PLEKHG5, LSM2, MAP1B, STMN1, ATP7A, CNTNAP1, GEMIN2, SOD1, IGFALS, ACTB, FUS, TP53, BCL2, SERF1A, ZPR1, IGF1, NCALD, KHDRBS1, SLC9A3R2, GUSBP1, GUSBP3, GTF2H2, MSTN, SCAF11, SYNCRIP, DDX20, ZEB2, SCO2, GUSBP14, DMD, IFI44, H3P33, SERF1B, CARM1, TMEM41B, NEFL, AR, WDR77, HDAC9, TARDBP, COPA, EXOSC3, DCPS, VIM, RPL3, CORO1C, LMNA, PART1, MUC1, HTRA2, LIX1, PTEN, DROSHA, RNPC3, SLCO2A1, CHODL, CARD16, SNCA, SLC25A21, NRXN2, TIA1, CHP1, PLA1A, SLC7A10, AAVS1, ALB, CDK5, DES, CTNNB1, MAPK14, AKT1, GJB1, ETFA, GTF2H1, GARS1, ACVR2B, MORC2, ITGA11, COMP, SETX, KIF1B, NCDN, CREM, CRK, CREB1, IGF2, CD2AP, NUP62, CNTN1, RNF19A, POLDIP2, EIF3K, SGSM3, CHML, KLF15, CD47, GEMIN4, HAPLN1, CSF2, STRAP, HNRNPR, CLOCK, MAD2L1BP, NCOR2, EEF1D, HDAC4, TYMP, SLC23A2, DPP4, ABCB6, RBM7, POP7, GUSBP15, DNM1, SMNDC1, PRMT5, FST, CCN2, AHSA1, CTF1, CELF2, PPARGC1A, CD36, CD40, LEF1, DCTN4, GRAP2, ANXA1, FBXO32, ANG, ALPP, C9orf72, CYP4V2, HCN1, ALPI, GTF2H5, MIR146A, MIR206, MIR223, MIR23A, MIR335, MIR375, MIR431, OCLNP1, HNRNPA1P10, POTEF, AGRP, ADRB2, RNU4ATAC, RNU6ATAC, OCLN, UPK3B, CDCA5, SLC25A46, STARD13, KIDINS220, CAT, CASP8, POP5, VPS54, ARID4B, GEMIN8, WRAP53, CASP3, CANX, CALR, BMP4, CIP2A, APOE, BICD1, ARHGAP22, HCN2, GORASP1, WNK1, BCL2L1, GEMIN6, ATP6V1B2, CCDC8, ARSF, MAGT1, NR1D1, EPHA4, ELAVL4, EMX1, NOS2, OXA1L, PAX3, PAX7, PFN1, PGK1, HTT, PML, PPARG, MAPK1, MAPK10, PSMD4, GTF2H4, PTGS2, PVALB, RAB1A, RELA, RNASE4, BRD2, GTF2H3, RPL9, RPS6KB2, RYR1, S100A1, S100A10, NOS1, NFKB1, HDAC2, MBP, IAPP, IL1B, IL6, IL12A, KIT, LAMC2, HSPG2, LBR, LGALS3, HOXA5, HNRNPA1, MDM2, NEFH, MDM4, MECP2, RAB8A, MAP3K10, MNAT1, NRG1, MYH7, MYOG, HEXA, NCL, NEDD8, S100B, ATXN2, CCL2, KHSRP, BEST1, GAPDH, ZAP70, AIMP2, SPPM, CDK2AP1, COIL, KDSR, FUT1, FOXO1, FCN2, BECN1, UCHL1, SOCS2, CDK5R1, ARHGEF7, SQSTM1, BCL10, ERCC3, ARTN, ERCC2, ERBB4, KLF4, IGF1R, VDAC2, GART, CCL18, STAT5A, CCL21, XCL1, SRSF1, TRA2B, SLC1A3, GSK3B, GRIN2A, GM2A, ACHE, SPP1, SRF, STAT5B, TTN, STATH, SYT1, TBCD, GFAP, PPP1R11, TFRC, GCHFR, GCG, TNF, GATA6, TRH, H3P40
-
Thrombosis
Wikipedia
Also, atrial fibrillation , causes stagnant blood in the left atrium (LA), or left atrial appendage (LAA), and can lead to a thromboembolism. [22] Cancers or malignancies such as leukemia may cause increased risk of thrombosis by possible activation of the coagulation system by cancer cells or secretion of procoagulant substances ( paraneoplastic syndrome ), by external compression on a blood vessel when a solid tumor is present, or (more rarely) extension into the vasculature (for example, renal cell cancers extending into the renal veins). [22] Also, treatments for cancer (radiation, chemotherapy) often cause additional hypercoagulability. [22] There are scores that correlate different aspects of patient data (comorbidities, vital signs, and others) to risk of thrombosis, such as the POMPE-C, which stratifies risk of mortality due to pulmonary embolism in patients with cancer, who typically have higher rates of thrombosis. [26] Also, there are several predictive scores for thromboembolic events, such as Padua, [27] Khorana, [28] [29] and ThroLy score. [30] Pathophysiology [ edit ] Natural history [ edit ] Fibrinolysis is the physiological breakdown of blood clots by enzymes such as plasmin . ... Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol . 28 (3): 398–9. doi : 10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.162586 .F2, SERPINC1, P2RY12, PLAU, FGA, F5, F3, PROC, VWF, SERPINE1, PROCR, SELP, PLAT, ADAMTS13, PROS1, TNF, PF4, FCGR2A, PTGS2, THBD, VHL, CRP, MERTK, GAS6, GP1BA, PDE3A, P2RY1, AGT, PTGER3, PODXL, HMOX1, TYRO3, KLF4, SIRT1, VKORC1, KLKB1, MAS1, HGF, FUT4, BDKRB2, CD2, CYP2C19, CYP3A5, EPO, F9, F10, FLT3, BCRP3, GUCY1A1, APOH, CD40LG, TBXAS1, C5AR1, PIK3CB, ACE2, JAK2, MTHFR, NOS3, ITGA2, ITGB3, CPB2, VASP, TFPI, F8, P2RX1, MPL, TNFSF14, SCUBE2, CD177, GP6, C1QBP, C4B, IL1B, SCUBE1, TUBB1, IL6, KLF2, MRVI1, CANT1, LPA, DCN, PLA2G6, F11, LEPR, LEP, FGG, PECAM1, FGB, F13A1, PTGS1, ITGA2B, ICAM4, EGR1, SLC19A1, TBXA2R, ANXA5, CD55, ENG
-
Venous Ulcer
Wikipedia
Compression therapy is used for venous leg ulcers and can decrease blood vessel diameter and pressure, which increases their effectiveness, preventing blood from flowing backwards. [9] Compression is also used [9] [24] to decrease release of inflammatory cytokines , lower the amount of fluid leaking from capillaries and therefore prevent swelling , and prevent clotting by decreasing activation of thrombin and increasing that of plasmin . [2] Compression is applied using elastic bandages or boots specifically designed for the purpose. [9] Regarding effectiveness, compression dressings improve healing. [25] It is not clear whether non-elastic systems are better than a multilayer elastic system. [25] Patients should wear as much compression as is comfortable. [26] In treatening an existing ulcer, the type of dressing applied beneath the compression does not seem to matter, and hydrocolloid is not better than simple low adherent dressings. [27] [28] Good outcomes in ulcer treatment were shown after the application of double compression stockings, e.g. ulcer stockings. ... "Healing rates following venous surgery for chronic venous leg ulcers in an independent specialist vein unit". Phlebology . 28 (3): 132–9. doi : 10.1258/phleb.2012.011097 .
-
Varicose Veins
Wikipedia
Newer methods including endovenous laser treatment , radiofrequency ablation and foam sclerotherapy appear to work as well as surgery for varices of the greater saphenous vein . [27] Conservative [ edit ] The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) produced clinical guidelines in July 2013 recommending that all people with symptomatic varicose veins (C2S) and worse should be referred to a vascular service for treatment. [28] Conservative treatments such as support stockings should not be used unless treatment was not possible. ... "Experiences of living with varicose veins: A systematic review of qualitative research" (PDF) . Journal of Clinical Nursing . 28 (7–8): 1085–1099. doi : 10.1111/jocn.14720 .VHL, MGP, TIMP1, TNC, DPT, KCNN3, FOXC2, CASZ1, GLG1, GJC2, GP1BB, KIF5A, HLA-A, LBH, FLT4, CNGB3, HIRA, SLC29A3, RREB1, SMAD3, NFATC2, NOTCH3, PIK3CA, PRKAR1B, PIEZO1, SEC24C, RASA1, FIBP, SLC12A2, SLC12A3, TBX1, VEGFC, G6PC3, HDAC7, UFD1, ARVCF, COL3A1, EBF1, CLCNKB, JMJD1C, EPHB4, COMT, LINC02549, LINC01152, ROCR, MMP9, VEGFA, SNCA, BLOC1S2, SYP, SLC17A6, NLRP3, ELN, MMP3, MMP2, MMP1, MTHFR, HIF1A, SLC18A3, TGFB1, STS, CALCA, NPY, GFAP, MCF2L2, TAC1, CALB1, KDR, TIMP2, DBH, ROCK2, CYP4F2, CHST3, CLOCK, HOMER1, RBM14-RBM4, TNFSF11, GNG13, TRPV4, MFAP5, PORCN, VIM, EHMT1, EGLN3, DCLK3, PAPLN, FOXC2-AS1, USH2A, ZGLP1, PPARGC1A, MIR202, AKR1B10, TRPV2, DLL4, SLC17A8, PRLH, EXOSC3, PACSIN1, PYCARD, CBLN4, SLC32A1, TSACC, ADI1, CACYBP, RBM14, KANK2, TP53INP1, BACE2, SLC17A7, HEY2, SYNM, EXOC7, PRRT2, ERC1, PGP, MMRN1, MYOCD, ACHE, TRH, GJA1, F13B, FLT1, FN1, FOS, FOSB, GCG, GJA8, ESR1, GLP1R, GRM1, HCCS, HCRT, HTT, HFE, F2, EPAS1, TIMP3, CALR, ADM, JAG1, AKT1, RHOA, AVP, CALB2, CASP1, DSP, CAV2, CYP4A11, CYP19A1, DES, DLD, DOCK3, ICAM1, ITGB2, ITGB3, CCL2, PRKCA, PRKCB, PTGS2, ACP3, S100A10, S100A12, SELE, JUN, SLC6A3, SLC18A2, SPP1, SST, TH, THBD, PPARG, POU2F1, PLG, PEPD, OPRM1, NOS1, NGFR, NGF, MTR, COX2, MMP13, SMAD2, LIF, LGALS3BP, LAD1, JUND, JUNB, MTCO2P12
-
Vertigo
Wikipedia
Naturally, the nerve conduction slows with aging and a decreased vibratory sensation is common. [26] Additionally, there is a degeneration of the ampulla and otolith organs with an increase in age. [27] Persistent onset is commonly paired with central vertigo signs and symptoms. [25] The characteristics of an episodic onset vertigo are indicated by symptoms lasting for a smaller, more memorable amount of time, typically lasting for only seconds to minutes. [25] Pathophysiology [ edit ] The neurochemistry of vertigo includes six primary neurotransmitters that have been identified between the three-neuron arc [28] that drives the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). ... "New developments in aminoglycoside therapy and ototoxicity" . Hearing Research . 281 (1–2): 28–37. doi : 10.1016/j.heares.2011.05.008 .CACNA1A, COCH, SLC26A4, STRC, SCN5A, PRKAR1A, RARA, RYR2, SCN1B, SCN2A, NAGA, SLC1A3, SLC12A3, SPG7, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5B, PML, NUMA1, PDGFB, TLR4, NPM1, NF2, MYO7A, MYL2, MYD88, MVK, MPL, MEN1, MEFV, KCNJ10, KCNA1, JUP, JAK2, THPO, TNFRSF1A, IL10, VHL, IRF2BP2, UBAC2, TECRL, IL23R, TUBB6, FIP1L1, TBL1XR1, FKRP, NABP1, CDH23, BCOR, CNNM2, TRPM4, TET2, ADA2, ERAP1, STRN4, TPK1, PTPN22, DKK1, AFG3L2, NOP56, TRDN, SH2B3, TMEM94, AIP, CACNA1G, KLRC4, ZBTB16, IL12A, IL12A-AS1, CALM1, DBH, CACNB4, C4A, FLI1, GATA2, BRAF, EPOR, GCDH, CCND1, B2M, CASQ2, ATP1A2, CTNNB1, NKX2-5, FAS, FOXI1, EGF, GLA, SLC25A4, COL3A1, CALM2, GYG1, CCR1, HFE, CLCNKB, HLA-B, CLCN1, CALM3, CKMT1B, S100B, CYP2D6, ABCB1, CHRNA4, CCT, CHRNA3, CHRNA7, CHRNB2, CHRNB3, ASIC3, LGI1, TES, IL1B, CASP9, PRIMA1, ZGLP1, GRXCR1, ADCY5, ADRA1A, COPD, ADRB1, ADRB2, APOE, CCHCR1, SPRTN, PANK2, EHMT1, AVP, HRH4, SPAG9, CAD, CHRNB4, CRY1, SELENBP1, OPRM1, NT5E, NPPA, GCG, NPY, GFAP, ACR, GFER, GJA1, GJB2, GLP1R, MME, GRM5, KCNJ13, HINT1, IFNA1, ITGB3, IFNA13, NTRK1, PAEP, CHRNA6, PFN2, PER2, TPM3, COMT, IGF1, TAC1, CUX1, SRY, CYP3A5, SHBG, SGSH, CCL2, DPP4, DSPP, S100A1, ERF, FES, PGR, ACHE
-
Hangover
Wikipedia
This may explain the temporary postponement of symptoms reported in the common remedy of drinking more alcohol to relieve hangover symptoms. [11] [28] Since methanol metabolism is effectively inhibited by consumption of alcohol, methanol accumulates during drinking and only begins to be metabolized once ethanol has been cleared. ... Social drinkers and alcoholics claim that drinking more alcohol gives relief from hangover symptoms, but research shows that the use of alcohol as a hangover cure seems to predict current or future problem drinking and alcohol use disorder, through negative reinforcement and the development of physical dependence . [28] [35] While the practice is popular in tradition [46] and promoted by many sellers of alcoholic beverages, [47] medical opinion holds that the practice merely postpones the symptoms, and courts addiction. [48] Favored choices include a Corpse Reviver , Fernet Branca [49] and Bloody Mary . [50] Kudzu (葛, Pueraria montana var. lobata ): The main ingredient in remedies such as kakkonto .