- Gallbladder Disease 1 Omim
- 15q13.3 Microdeletion Gene_reviews
-
Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser Syndrome
Omim
Shokeir (1978) described 18 unrelated females, aged 15 to 28, with aplasia of the mullerian duct derivatives.
-
Hyper-Igd Syndrome
Omim
Exclusion Studies Drenth et al. (1994) did linkage studies in 10 families with 19 members affected by hyper-IgD syndrome and 28 unaffected members. They used highly polymorphic markers surrounding the familial Mediterranean fever locus on 16p to test for a possible allelic relationship.
- Distributive Shock Wikipedia
- Occult Macular Dystrophy Omim
- Branchiooculofacial Syndrome Omim
-
Aneurysm, Intracranial Berry, 1
Omim
In the parental generation, 11 men and 37 women were affected (including both SIA and PIA); in the consecutive generation, 28 men and 32 women were affected. There was a significant difference in sex ratio of affected family members when the generations were compared (P less than 0.02).
- Allergies In Children Wikipedia
-
Geleophysic Dysplasia 1
Omim
Serial ultrasound scans, performed on 2 of the cases during pregnancy, failed to demonstrate short limbs until after 28 weeks of gestation. The facies and small hands with limitation of movement of interphalangeal joints were pictured.
-
Mitochondrial Dna Depletion Syndrome 2 (Myopathic Type)
Omim
The pathogenicity of these mutations was confirmed by reduced TK2 activity in muscle (28 to 37% of controls). In a family originally described by Tritschler et al. (1992) in which 3 sibs had myopathic mtDNA depletion syndrome, Mancuso et al. (2003) identified homozygosity for the T150M mutation.
-
Ichthyosis Hystrix
Wikipedia
The Open Dermatology Journal . 5 : 28–30. doi : 10.2174/1874372201105010028 .
-
Spastic Paraplegia 7
Gene_reviews
., Krabbe disease, arylsulfatase A deficiency [metachromatic leukodystrophy]) ABCD1 GALC ARSA XL AR Paraplegia neuropathy Dementia On MRI: leukodystrophy, adrenal dysfunction, long-chain fatty acid accumulation Spinocerebellar ataxia type 28 AFG3L2 AD Paraplegia Ataxia Rare dystonia or parkinsonism Dopa-responsive dystonia GCH1 AD Brisk reflexes Spasticity Extensor plantar responses Young-onset dystonia parkinsonism responsive to levodopa Diurnal variation Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis See footnote 1 AD AR XL Spasticity Muscle atrophy, weakness & fasciculations Primary lateral sclerosis 2 Unknown N/A Spasticity Survival 15-20 years Arginase deficiency ARG1 AR Spasticity Epileptic seizures Severe mental retardation Elevated plasma arginine Hyperammonemia Structural abnormalities of the brain or spinal cord N/A N/A Gait difficulties On MRI: spine abnormalities Vitamin B 12 deficiency N/A N/A Unsteady gait Subacute combined degeneration Improvement after vitamin B 12 supplementation Primary progressive multiple sclerosis N/A N/A Spasticity MRI white matter changes Oligoclonal IgG bands Elevated IgG index Progressive external ophthalmoplegia Various AR AD Eyelid ptosis External ophthalmoplegia Proximal myopathy No pyramidal signs Tropical spastic paraplegia (caused by HTLV1 infection) N/A N/A Paraplegia HTLV-1 serology Optic neuropathy KLC2 3 MFN2 4 AR AD Pale optic disks No pyramidal signs AD = autosomal dominant; AR = autosomal recessive; DiffDx = differential diagnosis; MOI = mode of inheritance; N/A = not applicable; XL = X-linked 1.
-
Isodicentric 15
Wikipedia
Incidence at birth appears to be 1 in 30,000 [13] with a sex ratio of almost 1:1; however, since dysmorphic features are absent or subtle and major malformations are rare, chromosome analysis may not be thought to be indicated, and some individuals, particularly in the older age groups, probably remain undiagnosed. [13] There are organizations for families with idic(15) children that offer extensive information and support. [3] Research [ edit ] Spontaneous EEG recordings (right) from a 28-month-old child with idic(15) show diffuse beta frequency oscillations that represent an EEG signature of idic(15) and Dup15q. [14] Patients with idic(15) and int dup(15) often feature a distinctive electroencephalography (EEG) signature or biomarker in the form of high amplitude spontaneous beta frequency (12–30 Hz) oscillations.
-
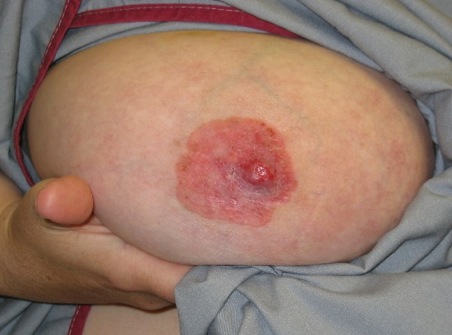
Paget's Disease Of The Breast
Wikipedia
If there is a palpable mass, it is 32% and 31% respectively, with adjuvant chemotherapy (40% and 35%). [18] Positive lymph-nodes have been positively associated with a palpable mass and affect the prognosis to be now just 28% survival after 10 years (vs 79% without palpable mass and without affected lymph-nodes). [18] Involvement of the lymph nodes does not directly cause any harm, but is merely an indicator of systemic spread. [19] Furthermore, patients with an identifiable associated underlying breast tumor have a survival rate of 38-40% at five years and a survival rate of 22-33% at 10 years.OPTN, NUP205, DPYS, PML, SQSTM1, SLC25A43, DCSTAMP, PIGN, IL6, VCP, TNFRSF11A, ERBB2, KHDRBS1, VDR, GTF2H1, KRT7, NUP62, DCTN4, ESR1, AR, CEACAM5, RIN3, LPAR2, TNFSF11, FSIP2, NEURL1, BEST1, BIRC6, CASP8AP2, ARID2, ACKR3, CXCR6, ATF7, DKK1, TRIP6, KMT2C, ADRA1A, PTH, TP53, TAF12, BCL2, BGLAP, BRCA2, BRS3, CALCA, CASR, CEBPB, CSF2, DMD, EDNRA, EGF, FOS, GJA1, GPR42, FOXA1, IL3, IL6ST, KRT8, MUC1, NEU1, TNFRSF11B, PDB1, ADRA2B, SSTR4, TAF2, KRT8P3
-
Pervasive Developmental Disorder
Wikipedia
"Autism spectrum disorders". Neuron . 28 (2): 355–63. doi : 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)00115-X .MECP2, DRD4, MRTFB, ARSD, PTEN, OXTR, SHANK3, CNTNAP2, FMR1, SLC6A4, NRXN1, SHANK1, SHANK2, BDNF, CHD8, MET, SCN2A, MAOA, NLGN3, RBFOX1, RELN, CD38, VDR, HTR2A, ADNP, PRKN, FOXP1, FOXP2, PVALB, IMMP2L, IL1RAPL1, EN2, AVPR1A, CADPS2, PAFAH1B1, APOE, NLGN4X, HTC2, PAX6, GRIN2B, LRP1, OPRM1, NOS2, NOS1, MTHFR, S100B, MAPT, ACTB, ST8SIA2, SCN1A, SCN3A, NEXMIF, PTCHD1, ZNF804A, EBPL, KIRREL3, CMIP, ARID1B, MAGEL2, PHF21A, AUTS2, NCS1, ARHGEF9, TBR1, GPR37, YWHAE, UBE3A, TCF4, TBX1, SYN1, STX1A, SLC6A3, GRIK2, SLC19A1, ELK3, COMT, DRD3, DPYD, AVP, CACNA1C, CACNA1D, AKT1, CHD2, CYP2D6, GABRB3, NCOR1, CS, RAB11FIP5, NRXN3, IL37, ARHGEF3, BUB1, KMT5B, RMDN1, BST1, WWOX, OPN1SW, UGT1A1, CADM1, TAOK2, KIF1A, CC2D1A, SLC33A1, RPP25, FAM120C, RMDN3, SETD5, ELMOD1, SYBU, MBD5, CALB2, TSPAN12, NUAK1, CHRNA7, ABCB6, GPHN, SLU7, CLOCK, PTGES3, PPARGC1A, CHRNB2, KLF12, PARK7, FNDC3A, NLGN1, ZNF292, SLC35A3, POGZ, TBC1D9, AIM2, ADGRL3, DMXL2, NRXN2, CUX2, RERE, CHAT, SIRT1, CDH13, ATP10A, GLO1, AR, PRICKLE2, RAB39B, MACROD2, RPS10P2, RSS, PRICKLE1, LRFN5, RBFOX3, CBLN2, RMDN2, CNTN4, JAKMIP1, ABCA13, CBLL2, KCTD13, SYTL4, MIF-AS1, SH2D6, ADORA2A, SERINC2, ZNF713, LINC-PINT, MIR137, MIR140, PTLS, HOTAIR, FMR1-AS1, DEL11P13, IFNG-AS1, CDCA5, ALB, HERC2, TBL1XR1, APP, PCDH19, NUFIP2, NLGN2, PCDH10, TSHZ3, APC, ZNF462, KMT2C, LRRC4, LIN7B, TFB2M, MUL1, EHMT1, ALDH1A1, NAA15, APBA2, TTC25, ANK3, ELMOD3, SRRM4, TMEM185A, AMY1C, AMY1B, CAPS2, AMY1A, CNTNAP4, ALDH1A3, SEMA5A, PLA2G4C, CACNA1G, ESR1, FKBP5, FH, NR3C2, FGF2, NCAM1, NDUFS1, FGA, FABP3, NPY, NTS, NR4A2, EZH2, OTX1, P2RX7, MPDZ, ERCC2, CLN8, EPHA5, PEX7, ABCB1, PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PIK3CD, PIK3CG, SEPTIN5, PPARG, PPP2R5D, MAPK7, MDK, AFF2, FOLR1, FOLR2, GDNF, GRIN2A, GRM7, GRM8, GRP, H1-4, HTT, NRG1, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HP, HRAS, AGFG1, GABRA4, FRA7A, HTR2C, HTR7, IFNG, CXCL8, IL10, IL17A, IRS1, ITGB3, JAK2, JARID2, LAMB1, LAMC2, PRL, PRODH, PSD, CYP11A1, CYP1A2, TCF20, TGFB1, TGM2, TNF, TRIO, TRPM2, TSC1, TSNAX, CUX1, UCP3, CTNND2, WT1, XPO1, XRCC4, CTNNB1, ZIC2, USP7, CSF2, GAN, MIA, KDM5C, TMEM187, MKNK1, CASK, SLC25A12, GFAP, CYP2C19, SPAST, EIF4E, SNCA, EEF1A2, RAC1, RFC1, RHCE, RHD, RIT2, RPS6, RPS6KA3, SCD, DRD2, DHCR7, SCN8A, SCT, CXCL12, SLC1A1, SLC2A3, SLC6A1, SLC6A2, DBI, CYP11B1, SLC6A8, ADCYAP1R1, SMARCA2, SMARCA4, SMARCB1, SMS, SNCB, LOC110806262
-
Membranous Glomerulonephritis
Wikipedia
Pediatric Nephrology . 25 (8): 1419–28. doi : 10.1007/s00467-009-1324-5 .C3, HLA-DQA1, ALB, HLA-DRB1, APOA1, GAA, NPHS1, LRP2, NQO1, CDKN1B, NPHS2, CFH, APOE, PTPRU, IL1B, MAP3K5, PLG, ABCA1, PTGER3, LRPAP1, SPARC, TBXAS1, MMP9, A2M, CD40, RHOA, C7, TSBP1, TSBP1-AS1, PPT2-EGFL8, SFTA2, THSD7A, PSORS1C1, PLB1, MUCL3, PLA2G1B, EGFL8, POU5F1, PRKCD, PPT2, IGAN1, RNF5, BTNL2, FOXP3, TCF19, PLA2R1, YWHAZ, EHMT2, PRRC2A, GPANK1, STK19, HLA-DQA2, SLC7A7, EHMT2-AS1, HLA-DMB, CYP21A2, HLA-B, ACTN4, MS4A1, KRT20, RBM45, MBL2, TRPC6, TNF, TGFB1, HLA-A, PLA2G2A, SERPINE1, XIST, F5, TNFRSF12A, MTHFR, HPSE, VEGFA, PLA2G6, SYNPO, POMC, IFNG, ACTB, AGT, MIR217, IL6, CST3, CNTN1, MIR130A, NES, TNFSF13B, CP, P3H4, MIR186, ANP32B, CIB1, C5AR1, MIR193A, CCR6, DNM1L, KEAP1, CCN2, PTER, USP2, POTEF, CTH, SNURF, PER2, CTLA4, HELT, MLYCD, CIC, CLCN5, CXCR5, KLHDC8B, NLRP3, CHRDL1, BRSK1, APOH, RABEP2, PDLIM2, CD69, NPNT, ACE2, PDGFC, CD5L, NEAT1, LINC01193, TNFSF11, CDC42BPG, TLR9, FIS1, CLU, MBL3P, KLF15, DIANPH, CABIN1, TNFSF13, HLA-DQB1, APOL1, MIF, FN1, PITX1, PECAM1, GABPA, NOTCH1, NOS3, NFE2L2, NEFH, MYC, MUC1, MTNR1A, MPO, GLS, GNAO1, UBL4A, SMAD7, STMN1, JAK3, CXCL10, IL4, IL2, HLA-DMA, IKBKB, IGHA1, IFI27, HSPG2, HRAS, HLA-DRB3, EXT2, PPBP, PRKCA, EXT1, FOSL1, CTSL, CYP3A5, ACE, HLA-DQB2, VCL, UCHL1, UBE2V1, TLR4, THY1, TGFB2, DNMT1, EGFR, TAP1, STAT4, EIF4A2, SNRPN, SMN2, SMN1, CXCL12, SDC2, CCL2, EIF4E, REN, EIF4G1, PSMB8, ENO1, PRKCB
- Fecal Impaction Wikipedia
-
Canine Influenza
Wikipedia
The virus is an H3N2 variant that adapted from its avian influenza origins. [22] An outbreak in the US was first reported in the Chicago area during 2015. [23] Outbreaks were reported in several US states during the spring and summer of 2015 [23] and had been reported in 25 states by late 2015. [24] As of April 2015, the question of whether vaccination against the earlier strain offered protection had not been resolved. [25] The US Department of Agriculture granted conditional approval for a canine H3N2-protective vaccine in December 2015. [24] [21] [26] [27] In March 2016, researchers reported that this strain had infected cats and suggested that it may be transmitted between them. [28] No human risk [ edit ] The H3N2 virus as a stand-alone virus is deemed harmless to humans.
- Diplegia Wikipedia