-
Parkinson Disease 6, Autosomal Recessive Early-Onset
Omim
Bonifati et al. (2005) identified homozygous mutations in the PINK1 gene in 4 of 90 sporadic Italian patients with early-onset parkinsonism. Age at onset ranged from 28 to 35 years, and the disorder was characterized by tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, postural instability, response to L-DOPA, and L-DOPA-induced dyskinesias.
-
Horseshoe Kidney
Wikipedia
. ^ Suwannakhan A, Meemon K (2019-05-28). "Horseshoe kidney with extrarenal calyces and malformed renal vessels" .SON, MYRF, CHD7, ADAMTS3, SEMA3E, RBM8A, CD96, LEMD3, DSTYK, TCTN3, DYNC2LI1, FANCI, PACS1, HMGA2, SALL4, SMOC1, STRA6, PORCN, THOC6, FAT4, GREB1L, CCNQ, CCBE1, ESCO2, RBM10, WT1, DKC1, HRAS, FANCA, FANCC, FANCD2, FANCE, FGFR2, GJB2, MNX1, HNF4A, HNRNPU, KRAS, NRAS, PBX1, POR, RARB, SC5D, SNRPB, SRY, SSR4, HNF1B, C8orf37, TSC2, SMUG1, EGFR
-
Situs Inversus
Wikipedia
"A Rare Glimpse of Leonardo da Vinci's Anatomical Drawings" . ^ Silver, Katie (28 April 2015). "Here's why some people are left-handed, according to science" . sciencealert.com .CFAP53, NODAL, PKD1L1, DNAH9, CITED2, ACVR2B, NME7, MMP21, ANKS3, CFAP52, ANKS6, ZIC3, NPHP3, CFC1, ACTG2, LETM1, NSD2, NPHP3-ACAD11, NELFA, DNAH7, TNF, CCR5, ITIH4, HLA-C, IFNA1, PTPN11, IFNA13, IVNS1ABP, INVS, DNAH11, IL7, IL15, CXCR6, MNS1, CXCL10, TBX1, IFNB1, CCDC151, WAS, TRBV20OR9-2, IL10, CXCR4, HLA-B, IFITM3, DNM1L, CCL4L2, TNFSF13B, CH25H, PDLIM7, SIRT1, LRRC6, SH3BP4, ARTN, SDS, ACTB, DNAI1, IL37, CD24, CALHM6, EIF2AK4, MIR212, MIR206, MIR150, MIR130A, CCL4L1, DNAAF3, RSPH9, ENKUR, PIFO, MUC16, TRIM5, HAVCR2, MAVS, ACSS2, ARMC4, LZTFL1, CDON, IL21R, CD274, SESN1, RIPK1, SPP1, KMO, MADCAM1, IFN1@, HNF4A, GZMB, GDF1, GCK, FOXJ1, FCGR3B, FCGR3A, F3, DPP4, CDO1, CD58, CD80, CD28, CD4, CD247, CASP1, CXCR5, BCL6, BCL2, ATF4, APP, ANXA5, NR0B1, AGRP, IFNAR2, IL1B, IL2, PKD2, ZFP36, TLR4, SP1, SIGLEC1, SHH, CCL5, CCL4, CCL3, PRKCSH, PPARA, PMP22, OPRM1, IL6, NPR2, MRC1, MPZ, MPL, LTB, KLRC2, KLRC1, KIR2DL4, IRAK1, IL18, IL17A, LINC02605
-
Miller–dieker Syndrome
Wikipedia
"Miller–Dieker syndrome, type 1 lissencephaly" . Journal of Perinatology . 28 (4): 313–315. doi : 10.1038/sj.jp.7211920 .PAFAH1B1, YWHAE, HIC1, MNT, FANCB, DCX, FANCF, FANCD2, UBE2T, SBDS, PALB2, ERCC4, CTC1, FANCA, FANCC, FANCM, BRIP1, MAD2L2, BLM, SLX4, FANCE, FANCL, FANCG, XRCC2, RAD51, RAD51C, BRCA2, BRCA1, FANCI, DPH1, TP53, SGCE, RUNX1, EPO, FLT3, SF3B1, CD34, KMT2A, BCR, RPS14, RN7SL263P, MECP2, JAK2, CSF3, BCL2L10, PLCB1, DDX41, GFI1, NPM1, U2AF1, PIGA, DAPK1, ASXL1, CDKN1C, CCR7, CDKN2B, DERL1, LINC01194, MECOM, CSF2, IKBKG, CCL28, MSC, CDR3, ABCG2, ESPL1, SGCZ, PDIK1L, YY1, CTAG1A, COL6A4P1, MIR21, WT1, WNT1, UBE3A, PSC, U2AF1L5, H3P9, TLR2, TK2, THBS1, STUB1, MRPL28, CIB1, ATG7, QRSL1, SYT1, LSM2, TET2, PRDM16, PLCE1, GORASP1, NXT1, WNK1, DLL1, DNAI1, INTS1, SETBP1, PIGN, PRAME, BAALC, TBC1D9, PARK7, CHEK2, NDEL1, SUB1, SEPTIN9, SLC12A9, TCF4, ABL1, STAT3, HLTF, DCK, TOR1A, EZH2, FGF1, FLT1, GATA2, GEM, GSTM1, GSTT1, GZMB, HFE, HIF1A, HOXD13, HRAS, HSPA9, CYP2B6, CUX1, CTNNB1, CD14, APAF1, ATM, CCND1, BCL2, CAMP, CBL, CD33, CTAG1B, CD38, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2A, CD52, CRK, HTC2, IL2, IL2RA, PTEN, ABCB1, ABR, PLCG1, PLK1, MAPK8, PSMB6, RAP1GAP, NRAS, RARA, RELA, ROBO2, SCN4A, SCT, SRSF2, NUP98, NCAM1, CXCL8, MCL1, CXCR2, IRF1, ISG20, ITGB4, KIR3DL1, KRAS, MLF1, NBN, MMP1, MMP9, CD200, MPV17, MT1E, MVD, H3P10
- Spinocerebellar Ataxia, Autosomal Recessive, With Axonal Neuropathy 2 Omim
-
Osteogenesis Imperfecta, Type Iv
Omim
Astrom and Soderhall (2002) performed a prospective observational study using disodium pamidronate (APD) in 28 children and adolescents (aged 0.6 to 18 years) with severe OI or a milder form of the disease, but with spinal compression fractures.
-
Prolidase Deficiency
Gene_reviews
Summary of Molecular Genetic Testing Used in Prolidase Deficiency View in own window Gene 1 Test Method Pathogenic Variants Detected Proportion of Probands with Pathogenic Variants 2 Detectable by This Method PEPD Sequence analysis 3 Sequence variants 28/30 4 Gene-targeted deletion/duplication analysis 5 Exon or whole-gene deletions 2/30 4 Targeted analysis for pathogenic variants p.Arg265Ter 4/4 6 p.Ser202Phe 17/20 7 1. ... Glycylproline has been found in the urine of: A child with severe bone disease and hyperphosphatasia [Seakins 1963]; Two sisters with multiple fractures and striking bone deformities of unknown etiology [Alderman et al 1969]; A woman age 28 years with osteomalacia and severe hyperparathyroidism who excreted large amounts of glycylproline, equivalent to ~1 g/day [Cahill et al 1970]; Three individuals with rickets [Scriver 1964] who excreted decreasing amounts of glycylproline concomitant with clinical improvement, until the imidodipeptiduria disappeared with recovery from the disease.
-
Monoclonal B-Cell Lymphocytosis
Wikipedia
International Journal of Hematology . 101 (3): 219–28. doi : 10.1007/s12185-015-1733-0 . ... Best Practice & Research. Clinical Haematology . 28 (4): 200–7. doi : 10.1016/j.beha.2015.10.019 .NOTCH2, KRT20, MS4A1, LOC102724971, IGH, MBL2, LOC102723407, IGHV3OR16-7, IGHV3-69-1, CD19, LEF1, ITGA4, NOTCH1, IGF2BP1, IL22, MBL3P, CD274, IL21, AICDA, XPO1, HM13, CLEC12A, IMMP1L, MIR155, MIR15A, MIR21, LINC01672, COLEC10, BCL2, VIM, TP53, CXCR5, CD22, CD38, CD79B, CDK6, CCR6, IL2, IMPA1, JAK2, LAIR1, MME, NTF3, PIK3C2B, SELL, SIM1, BCL6, TNF, SPN
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Omim
For future genetic analyses, Lynn et al. (1995) suggested that families with an excess of affected males having a young age at onset might be most informative in identifying the putative recessive gene and its modifiers. Hasstedt et al. (1994) studied 28 pedigrees ascertained through pairs of first-degree relatives with RA. ... Kurreeman et al. (2011) extended their approach to other ethnic groups and identified a large overlap in the genetic risk score among individuals of European, African, East Asian, and Hispanic ancestry and demonstrated that the distribution of a genetic risk score based on 28 non-HLA risk alleles in ACPA+ cases partially overlaps with the ACPA- subgroup of RA cases. ... They showed that the risk allele, which is present in approximately 17% of white individuals from the general population and in approximately 28% of white individuals with RA, disrupts the P1 proline-rich motif that is important for interaction with CSK (124095), potentially altering these proteins' normal function as negative regulators of T cell activation.TNF, PTPN22, SLC22A4, CRP, IL6ST, CCR6, TRAF6, TRAF1, PADI4, IRF5, TNFAIP3, CD40, IL10, IL6R, IL2RA, FCGR2A, HLA-DRB1, HLA-DPB1, CIITA, STAT4, CD28, PTPN2, TYK2, RUNX1, PTPRC, AGER, NFKBIL1, IL2RB, REL, AFF3, BLK, CDK6, CD244, MMEL1, ANKRD55, GATA3, NFKBIE, DNASE1L3, PLD4, ARID5B, KIF5A, CXCR4, RASGRP1, IL18, IL6, TLR2, STAT1, CXCL8, PTGS2, IL1RN, MPO, ACAN, RCAN1, IL1B, MMP2, PON1, NCF2, FOXP3, MIF, MTHFR, VEGFA, ABCB1, ANXA3, IL23A, CTLA4, CCL21, HLA-DQA2, TNFRSF11B, ADIPOQ, AHR, CSF2, SPRED2, CAT, CCN1, ENO1, SLC11A1, IFNG, TNFSF14, CCN2, TNFRSF14, DHFR, TAGAP, IRAK1, ALOX5, GC, HOXD13, NCF1, TXNDC5, COL2A1, GGH, ATIC, IGFBP3, PTGS1, CCL8, FPGS, FASLG, PRKCQ, SOD2, GRK2, MMP12, PLB1, PRDM1, B3GNT2, CP, ACKR3, CD83, MMP10, STS, RBPJ, HSD11B1, BMP4, CXCL2, FKBP5, BGN, CLEC12A, ADORA2A, SMS, IKZF3, HCLS1, ABCC4, HOXD10, BMP6, ABCC5, CAV2, PXK, DDX6, GPRC5A, NR4A3, CTSD, GDF5, ABCC3, GRK6, BCL2A1, LHX2, CD2, RUNX2, PLEK, CD3E, TFPI2, B3GNT9, POU3F1, CALD1, ABCC2, ZFP36, MAB21L2, NDUFA4L2, LY96, DDIT4, GART, NR3C1, ABCG2, GIN1, F2, HOXD11, CXCL6, IRF8, TLE3, RGMB, MGARP, TNFAIP2, ITGA6, TMPO, CD5, GSDME, ST6GALNAC5, TXNIP, RAP2A, RAB8A, LCN2, BAIAP2L1, PTK2, BDKRB2, MARCKS, PSG5, HAPLN1, SLC25A12, MMP14, ZAP70, DNASE2, HNRNPA2B1, HLA-C, HLA-B, HLA-A, FCRL3, HLA-DQA1, PADI2, ISG20, CD226, HLA-DQB1, TAP2, DPP4, AIRE, MICA, HLA-DMB, ATG5, C5, AIF1, MECP2, NOTCH4, TNIP1, CFB, HLA-DOA, PTPN11, CCR3, HLA-DPA1, SFTPD, DDX39B, TSBP1, LST1, PRRC2A, APOM, BACH2, RAD51B, PSORS1C1, MICB, CCL27, ICOSLG, MACIR, BTNL2, PRKCH, SYNGR1, PHF19, RPP14, C2, GSDMB, UBE2L3, CDSN, KIAA1109, UBASH3A, NELFE, COG6, CASP10, CD247, COL11A2, SUPT20H, ELMO1, EMCN, WDFY4, COL4A1, ICAM3, PSMB9, TNXB, TMEM187, IL12RB2, PSMB8, SH3PXD2A, GPSM3, MYO18B, HSPA1L, RTKN2, FADS1, ETFA, CARD9, NTN1, MPIG6B, SMTNL2, DAXX, TPD52, RARB, ATP6V1G2, MBP, IL13, HSPD1, CCL5, HCG22, CCL2, GALNT18, CXCL12, LY6G5C, KIF26B, IL15, HSPA4, EGFL8, SOCS3, IL17A, LY6G6C, IL32, PRRT1, CCL20, IL9, SLC44A4, VPS52, TLR3, IL4, IFNA13, TLR4, IFNA1, ACOXL, RABEP1, IL1A, S100A8, TIMP1, IL2, SAA1, ZNRD1ASP, TCP11L1, IL7, IGF1, VWA7, ICAM1, PIK3CB, ENOX1, SOAT1, STAT3, WNK1, TCF19, RNASEH2B, GSTM1, GSTT1, FADS2, GUCY1B2, GRAP2, MTCO3P1, TRIM26BP, PPT2, SPP1, TRBV20OR9-2, GORASP1, PCDH15, DDA1, MIR146A, MIR155, PRORP, N4BP1, MDC1, RSBN1, GNL1, CLOCK, FTO, CXCR3, GPI, TAPBP, RBFOX1, GABBR2, SYT1, SUOX, MCCD1, LINC00243, SELE, LINC01185, PRDM16, LINC02649, HLA-DRB4, COL11A2P1, HLA-DRB9, HLA-G, HMGB1, SFTA2, RPS18, NAT2, TMEM179, VPS37C, SPSB1, ALPK1, ZKSCAN4, SKIV2L, HLA-DRA, HLA-DQB3, RPP21, HIF1A, TEC, GATA3-AS1, LINC02656, AGBL2, SLC19A1, HLA-DOB, HLA-DQB2, SLC6A11, HLA-DPB2, ATAT1, TGFB1, NOD2, CLSTN2, RPS19, MAGI3, ILF3, VARS2, NCOA5, CDR3, SGCZ, MUCL3, ANO8, TRIM40, CUL5, MMP13, FLACC1, RBM45, VARS1, NFKB1, NAV2, TRIM15, ASB15, MTX1, GEM, POU5F1, PPIL4, MTF1, COX2, MSI1, PPIAP9, C6orf47, MSH5, DRAIC, IL34, PPP1R10, IL23R, LINC01104, CEP89, RAVER1, DENND1A, AIMP2, CSMD3, PIK3CA, SERPINA1, PIK3CD, IL17F, PDE2A, PDCD1, PIK3CG, NLRP3, PBX2, VIM, TRIM26, ZNF175, VDR, ZSCAN26, PLCL1, NM, PHACTR3, RPL3P2, IL33, VCAM1, IP6K3, PLG, NUP88, BAG6, GPANK1, HSD17B8, OR2H2, PRR12, NOS3, ZPBP2, AIFM2, MMP9, CXCL10, LY6G6F, TP53, VIP, RELA, KDR, SYNGAP1, KIR3DL1, TNFRSF11A, HAVCR2, ZNF302, WDR27, RARA, HCG27, IL27, NKAPL, OR12D3, JAK3, RIT2, JAK2, JAK1, ITPR3, HLA-S, CDK5RAP2, LINC00294, HECTD4, OR5V1, TNFRSF1B, RNF5, TMEM235, STK19, TNFRSF1A, RPL37A, JAZF1, IL21, TRPS1, RETN, MMP3, MAPK1, MMP1, ZNF595, PRDM10, MAPK8, DHX16, ERICH1, PRL, MAP3K4, MEFV, MDGA2, PRTN3, PSMA4, MBL2, LEP, TNFSF11, ZNF679, LY6G5B, PGBD1, TRIM39, CLYBL, LTA, TYMS, UQCC2, C3orf67, TRIM39-RPP21, LMNA, LGALS3, LY6G6D, GFRA1, IL37, CCR5, LINC00452, CSNK2B, C2-AS1, CSTF3, CASTOR1, TNFSF13B, IL17D, HLA-DPA2, MIR499A, PHTF1, HTD2, CELF2, AR, HCG9, CYP21A2, ESR1, HPGDS, C3orf67-AS1, CPA4, IL17B, FCGR3B, EHMT2, PAPOLA, FGF2, TSPAN5, TRIM10, HCP5, EGFR, FCGR3A, TSBP1-AS1, LINC00824, ATF6B, CRH, CRK, CRYGD, MAPK14, SNORA38, FBXW8, FAS, LINC02196, LRRC18, BCL2L15, AGPAT1, NEBL, ASB15-AS1, LOC102724971, WNT16, LINC01748, POLDIP2, MTCO2P12, LINC02356, LINC02357, LINC02571, ETV7-AS1, RAB14, MYL8P, CYRIB, HCG17, RCHY1, LOC102723407, HCG18, SDF2L1, MDC1-AS1, DGKQ, CDC42EP3, STAG1, AHSA1, AKT1, EHMT2-AS1, EPHB2, ALB, ASF1A, CXCL13, RNF19A, DDR1-DT, DLG2, LINC01934, LNCPRESS1, FAM107A, FN1, CD40LG, ZDHHC20P2, ATP6V1G2-DDX39B, NECAB2, CD44, MUC22, CHI3L1, NRM, MSH5-SAPCD1, SNHG32, CD68, BSG, TNFSF15, AP4B1-AS1, UBDP1, IL22, TMPOP1, ACR, SMG7, WAKMAR2, HNRNPA1P2, BTK, CCHCR1, IL20, CDH11, BTF3P11, GABBR1, KRT20, PPT2-EGFL8, GCH1, DKK1, GPC5, SMIM40, OS9, MIR223, CCNG2, TNPO3, SIRT1, DCDC2C, RIPOR2, CYP4F23P, CNTFR, DKK3, GDAP1, NONOP2, CTIF, PDS5A, PLCL2, CD14, ACTB, CASP3, MS4A1, BCL2, ABCF1, DDR1, PSMB8-AS1, TRIM31, CLIC1, ACE, CX3CL1, JUN, THBS1, HLA-DMA, IL3, CX3CR1, CNTRL, CCR2, CDKN2A, EBI3, PARP1, FOXO3, HAVCR1, CDC42EP1, FOS, FCGR2B, COMP, IL7R, WG, PTX3, SOST, IL4R, TPO, CSF1, IL18R1, RFC1, TIMELESS, SYVN1, PRKN, MYDGF, MAPK3, TNFRSF6B, FSTL1, C3, ARHGEF5, MMP8, CXCR5, CARD8, LRPPRC, PTGES, ADAM17, LINC02605, TREM1, TRIM21, OSM, ANGPT2, CD69, CCL3, NOS2, KIR2DS1, NFE2L2, SAA2, ANP32B, MUL1, S100A9, TLR5, P2RX7, CDAN1, CFH, IFNL1, CBLL2, F2RL1, LPA, CTSK, TNFSF13, ETS1, MIR21, MBL3P, TAC1, CD34, ICOS, PPARG, C4B, CASP1, CD274, CD19, SEMA3A, PML, CALR, SERPINE1, IL12B, TEK, ESR2, TLR9, KLRK1, GDE1, CAST, GLP1R, ADAM15, LGALS9, LIF, MDK, ADM, BANK1, LAIR1, CASP8, BEST1, HP, TNFRSF25, C4A, BDNF, FLT1, WNT5A, GCG, C4B_2, MAP2K7, GABPA, NOTCH1, ZBTB16, IL21R, CD86, TBC1D9, SUMO1, BRAF, XRCC1, KLRC4-KLRK1, FOLR2, HAMP, GZMB, MYD88, HT, CLEC4A, TLR7, KIR3DL2, ITGAV, IRF4, DMD, IL16, NR1I2, IL17RA, AGBL3, IGHV3-69-1, CCL7, ANGPT1, TNFRSF17, MIR221, CNR2, PTH, MIR22, TNC, RAC1, TRB, PTEN, DHX40, CISH, ITGAM, CCR7, SP1, DNMT1, ADA, BTG3, RARRES2, S100A4, CXCL9, ITGB1, LILRB1, CREB1, FCGR1A, CFLAR, MDM2, S100A12, NFATC1, SLCO6A1, GSTP1, PLAU, MAP3K7, NLRP1, PLA2G1B, VEGFC, TSLP, IGHG3, CD80, VPS51, CD38, IL12A, TNFRSF13C, CXCL16, TSPO, SQSTM1, NR4A2, GDF15, ADAMTS4, KIR2DS2, CDKN1A, B3GAT1, MTOR, MIR126, FOSB, IGF1R, GSTM2, MCL1, LINC01193, EGR1, RPSA, TNFSF10, APOE, GSTK1, NFAT5, SOCS1, CYP1A2, TNFRSF10A, KLRB1, MIR34A, LGALS1, ADRB2, TM7SF2, JUNB, CTSL, JUND, DHODH, ROS1, ACAD8, OLIG3, HSPA14, KHDRBS1, C5AR1, FPR2, SELP, EHMT1, DECR1, ZGLP1, ARHGEF2, APC, MAP2K4, HOTAIR, TRBC1, NXF1, S1PR1, H3P13, S100B, MIR10A, PSMD7, PECAM1, LPAR1, ITGA1, PAEP, IGHV3OR16-7, SHBG, CLU, ARMH1, RMC1, TBX5, IGHV3-52, IGFBP5, CDKN2D, IL10RA, CCL3L1, BBC3, H3P28, ATN1, LOC105379528, MIR145, TRBV16, CXCR6, LRG1, MSC, CD27, CXCL5, GPT, ACACA, SUMO4, KIR2DL2, IL1F10, PGF, GRN, SELL, LBP, ANXA1, PRKCA, CXCR2, CYBB, MIR451A, SFRP1, USO1, FOXC1, RABEPK, STEAP4, SEC14L2, MMRN1, FSCN1, ANGPTL4, IL18BP, F3, MALT1, MIP, F9, TP63, CR2, CRABP2, CD1C, HTR2A, NAMPT, S100A1, HLA-DRB3, REG1A, SLC22A5, TIMD4, REN, LOC390714, CSF1R, TPMT, CD46, LCE3B, EGF, SOX5, EBNA1BP2, FLNB, CTNNB1, KLRC1, CCR4, IFNB1, IKBKB, VWF, LOX, EDNRA, IL5, HOXD9, TXN, IL26, CCND1, LANCL1, TAP1, TRBV7-9, SERPINA3, MMP19, IL19, CD276, LCE3C, GLB1, PYCARD, CAMP, RPS6KA3, ABCC8, PRKCB, TIMP3, CCL13, PPIA, PDCD1LG2, ALOX15, TIMP2, ABCC11, CXCL11, TACR1, SH3BP4, CCK, ST6GAL1, CCL18, SLPI, ORAI1, BGLAP, ADAMTS12, PTHLH, BCR, TXNRD1, VTCN1, CLEC16A, ACTG1, ACTG2, PRAM1, TLR10, ARNTL, TNFSF4, DICER1, RHO, SIGIRR, HRH4, CRISP2, ADAM10, SMUG1, TPI1, IFIH1, ACSBG1, PTCH1, TIE1, TRA, SULT2A1, AOC1, SDC1, FCRLA, AQP1, SCD5, SGSM3, STAT5B, PROC, SPZ1, ACP5, SST, ABCC6, HTRA1, NUP62, SLC22A1, SIK1B, RAPH1, TFF3, PSMD12, BMP2, APOB, GDNF, ITGB2, HDAC3, ITGA4, IRS1, DNMT3B, IRF1, DPEP1, APLN, PER2, TNFRSF9, NCKIPSD, SIRT6, E2F2, TYMP, CXCR1, MIR338, MIR323A, MEG3, IL1R1, NOD1, KLF2, ELAVL2, CCRL2, TLR8, ITGAL, HPSE, VIL1, DCTN4, PIK3R3, TRAF3IP2, SMAD3, LTB, BECN1, LRP5, PRSS55, POTEM, GP6, PDPN, FADD, CD55, KLRD1, KLRC2, DBP, KIR2DL1, GADD45A, CD84, COPD, H4C15, ACTBL2, PADI3, IGF2, POTEKP, FHL1, CD163, HFE, FLG, KL, FLT3LG, SCO2, ASPN, GZMA, GUSB, GTF2I, GTF2H1, FHL5, FRZB, CXCL1, MIR140, MIR143, MIR20A, GLS, BMS1, MSTN, MIR23B, MIR27A, FCN1, XPR1, H3P44, FCGR2C, IDDM8, EPHB1, MIR17HG, ERBB2, LPAR2, HSP90AA1, ERG, SPRY2, FCGR1B, NPSR1, SLC52A1, EZH2, HOXC6, HMOX1, DDX39A, ASIC3, SLCO1C1, HLA-DRB5, MAP3K5, ADI1, H4-16, H4C9, ACOT7, PDE3A, H4C11, H4C12, ADRM1, H4C6, MSRA, H4C4, H4C1, PFKFB3, PF4, OSCAR, SERPINF1, YY1, PRRT2, MTR, MTRR, CCR1, NFKBIA, SLC7A9, MUC1, SEMA6A, MYC, GADD45B, SLC7A5, ADAMTS5, NCAM1, CD160, MPP1, H4C3, MPG, FOXO4, CD6, H4C13, P4HB, PCSK6, OGG1, H4C8, OLR1, PIK3R2, POLG2, DDR2, ENTPD1, H4C14, MUC5B, H4C5, PAK3, CTHRC1, LILRA3, VTN, CDC42, SIK1, H4C2, PDLIM3, KLF12, CLEC7A, ATG16L1, KDM6B, IL1R2, TREM2, YWHAZ, CASC3, PRG4, TINAGL1, SEMA4A, CALCRL, HPLH1, MIB1, AGXT2, KLF4, ADGRE2, A1CF, FAM53B, SDC3, PIEZO1, SLC40A1, IKBKE, ARL15, KEAP1, SPATA2, CNTN2, TBCA, CCL4L2, TBPL1, ADAMTS3, CIP2A, VPREB1, LAMP3, GCFC2, AHI1, COG2, UQCRFS1, WARS1, TG, PHRF1, WNT3, SENP1, WNT10B, SH2B3, G0S2, SEMA7A, SPRY1, IVNS1ABP, WDR11, DLL1, HDAC9, TMEM158, KAT5, TNFRSF12A, CCN6, TNFRSF4, NRP1, IL18RAP, TTR, TNFRSF10B, BRD4, UBL5, SPHK1, ASCC1, IGAN1, TNFSF12, ADIPOR1, EBP, TRAV29DV5, TRAC, CCL28, LOH19CR1, TRAJ60, SLC12A9, PLEKHO1, CCR9, ATRNL1, TRPV2, TGFA, PSIP1, ADA2, HSPB8, NOX4, RAMP2, KIDINS220, PDCD5, SETD2, TGM2, NAT10, IRAK3, THBD, CUL1, THOP1, TYROBP, TLR1, CCL26, PSTPIP1, THY1, TIA1, WARS2, AICDA, CEMIP, PGLYRP1, TAM, CHD7, MBD2, MBD4, SEMA4D, TBX21, NT5E, MOG, KIR2DS5, KNG1, KPNA1, CPB1, COX8A, LDLR, LGALS2, LGALS3BP, LGALS8, LIG4, LRPAP1, POTEF, CNR1, SH2D1A, NLRP6, LTB4R, KLK1, ASPM, SMAD7, KIR2DL3, CST3, INHBA, CSK, CSF3, INSR, INSRR, VSTM1, ITGA2, CRHR1, ITGAE, CREBBP, ITGAX, ATF2, CR1, KCNMA1, DNAJB1P1, MCAM, IL11, CD70, CD48, MYO9B, PPARGC1B, TNFRSF8, CD22, NGF, NHS, CD8A, CD1D, NME1, NOS1, NOTCH3, NPPA, LINC01672, ODC1, MUTYH, ADGRE5, MET, CDK2, CHUK, MFAP1, MFAP4, CHAT, MKI67, BTLA, CFTR, CTSC, FCER2, MRC1, MRE11, CEBPD, MST1, COX1, MIR760, IDO1, IL10RB, OXA1L, EPAS1, ELK3, CBLIF, MIR192, ELF3, ELAVL1, ZFAS1, EIF4EBP1, MIR17, MIR152, CCR10, EFNB1, EDN1, MIR346, GPR15, GPR42, GH1, MIR98, GRP, FBL, FGB, FGF1, MIR29A, MIR30A, FGF13, PTK2B, MIR222, FOXO1, F2R, FLT4, MIR214, ETS2, MIR210, GAPDH, GAS6, GPX1, MIR132, IL9R, MALAT1, HSPA8, CYP26A1, CYP19A1, DNAJB1, CYP17A1, CYP3A5, ICA1, ID1, CYP2D6, IFNGR1, IGFBP1, CTSB, IGHA1, IL1RAP, IL5RA, MIR410, HSD11B2, GSK3B, HRAS, DUSP1, MSH6, TSC22D3, DRD2, DR1, HDAC1, DNTT, HDGF, HGF, HIP1, IRX1, DNASE1, NR4A1, CCL4L1, DHCR7, TADA1, FCN2, SERPINH1, ADRA2B, RB1, PLAAT4, JAM3, LINC-ROR, ROPN1L, LINC02210-CRHR1, ALPP, RAF1, MOK, RAC2, PTN, SUMO3, SUMO2, NLRC5, MINDY4, ALDH1A1, BAK1, CCL22, MAP2K1, IL17RC, SNCA, PRELP, JAG1, SOD1, BCHE, UBASH3B, SOD3, ANPEP, SLC6A2, SLC2A3, AQP9, CCL19, CCL17, CCL4, SAT1, SDC2, SAA3P, APP, APRT, KLK3, RPL17, RORC, BIRC5, AREG, RBP2, RNF2, ASRGL1, RNASE2, FCRL4, ANXA6, ARG1, C1QTNF6, RDX, ASIP, ASPA, ATHS, ATM, AFP, CCL25, PCNA, SSTR4, INTS4, CAV1, CA1, PITX2, STAT5A, ADRA1A, STAT6, RHBDF2, SAAL1, DNER, ENPP2, ADIPOR2, SSRP1, CAPG, CASP7, PDE4A, PGR, PLA2G4A, PDC, RPL17-C18orf32, BRS3, C1QTNF3, PDGFRA, BCL6, POU2AF1, PDE7A, ADAM8, MIR155HG, CASP5, ABO, TIRAP, PAK1, SPARC, PAM, PAX5, SIGLEC9, LOC102725035, H3P8, CCDC88C, H3P23, MIR382, HOOK1, ZBTB7A, IL20RB, LOC102724334, THRIL, TRBV28, TRBV27, TRBV20-1, MIR6785, MIR301A, KIR2DL5B, H3P19, MIR448, MIR320A, NELFCD, IL20RA, CERNA3, RABGEF1, GHRL, MIR99B, BMP10, MIR7-3, MIR7-2, CALHM6, APOBEC3C, SPA17, LOC107987462, ATP6V1H, MIR135B, LOC106007493, MIR148B, MIR7-1, ISYNA1, UPK3B, IGHV5-78, ERVK-32, SCLY, ZC3HC1, MIR34C, TARP, PLF, MIR34B, C5-OT1, MIR33A, TNFSF12-TNFSF13, CDR1-AS, IGHV1-69, SF3B6, MIR6089, RASL12, PSS, STXBP6, MIR708, TEC, CDKN2B-AS1, PARD6A, HIPK2, P2RX5-TAX1BP3, TSL, IBD5, TRBV14, MIR766, RGCC, MIR671, MIR4701, MIR4764, SFTPA2, LAMTOR2, MIR663A, MIR887, H3P43, CASP12, DEF6, EFEMP2, LOC100505909, GAPLINC, KCNIP3, LOC100506023, AAA1, MIR762, CD209, TAX1BP3, TMED7-TICAM2, MIR1908, MIR1246, TRAP, C20orf181, CNNM3-DT, OCLN, UHRF1, EXOSC1, TMED7, MIR650, IGKV3D-15, TRAV5, ZDHHC2, TRBC2, TRBV2, UCA1, LINC00273, MIR486-1, TRBV3-1, MIR506, MIR522, TRBV6-7, MIR498, MIR181D, CLEC1B, MIR6716, MIR432, MIR363, SPAG11A, MIR539, REM1, PPAN-P2RY11, PSC, IGKV2-29, NDUFA13, MIR642A, RMDN1, MIR633, MIR613, MIR590, IGKV3-20, IRAK4, DBR1, MIR573, MIR5571, IGKV1D-8, MIR551B, MIR5100, MIR421, ASPSCR1, BANP, MIR29B2, UCN3, GLCCI1, SLC46A1, CDCA5, BMS1P20, EPB41L5, ORMDL3, CLEC6A, MAGEE1, NAF1, MTDH, MFSD4B, GADD45GIP1, UCN2, LMLN, DCLK3, DNAJC14, TMEM60, GRHL3, MUC3B, RBPJP4, JAM2, ZNF469, MAP1LC3A, DOT1L, ZNF644, DBA2, SRGAP1, IL22RA1, PRAP1, PTPRVP, B3GNTL1, PWAR1, ADAMTS9, OR2AG1, PIWIL4, SIRPA, NRSN1, PCBP4, PCNP, PNPLA2, MUC17, CD248, SLURP1, CD109, ZFP42, KIR2DL5A, ADAD1, OSCP1, GGT6, ABHD6, REXO1, TPH2, IL36B, CYP2R1, TMPRSS13, HIVEP3, MIR29B1, ERVK-6, NAA25, TNIP3, CCDC134, CAMKMT, SHCBP1, ERAP2, STRA6, ROBO3, MMP25, LRRC31, DCLRE1C, CIAO3, ENGASE, P2RY12, IL25, CDCP1, NLRX1, TNFAIP8L2, SPAG16, CHID1, SLC52A2, NKAP, BHLHE41, GGCT, AHNAK, TRPM3, ZC3H12A, ITCH, WDR26, TRPV4, PBOV1, EXOC4, SESN2, PARP9, SLC5A7, FAM167A, BCL2L12, ARHGAP24, PPCDC, GAS5, MAP1LC3B, FIP1L1, LBH, GDPD5, SLC38A1, APOL6, COL18A1, MRPL17, CEP70, PPP1R2C, TET1, PDGFD, FER1L4, EFHC2, COMMD1, GPBAR1, RMDN2, MIR18A, UGT1A1, MIR16-1, MIR150, IL17RD, MIR147A, MIR142, MIR141, MIR137, SAMD9, QPCTL, MIR125A, MIR106A, MIRLET7B, ZCCHC2, LERFS, UHRF1BP1, CRIP3, SAPCD1, CDKAL1, RPS12P4, MARCHF1, TTC38, RTL1, THEMIS, PICSAR, UGT1A4, MIR182, CREBRF, MIR183, MIR27B, H2BS1, CYCS, MIR26B, MIR23A, TERF2IP, SIAE, MIR219A2, SMOX, MIR212, MIR204, MIR203A, MIR200C, MIR19B1, MIR19A, MIR199A2, UGT1A10, UGT1A8, MIR199A1, MIR196A2, UGT1A7, MIR193A, UGT1A6, EGLN1, MIR188, ENHO, AKIRIN2, MIA3, PIWIL2, PCSK9, TAC4, EBF3, ZBTB38, SPESP1, DLEU7, UNC5B, LVRN, C9orf72, ANKH, TIGIT, NLRC3, METTL3, PPAN, LTB4R2, CYP26B1, IDO2, KANK4, SAR1A, IFNLR1, SPHK2, ARNTL2, DUSP22, AMOT, PRDM8, NCR3, CENPJ, IL4I1, RSPO2, RMDN3, NADSYN1, CYCSP52, TICAM2, PADI6, THNSL2, HLA-P, NMNAT3, ZNF391, CYCSP51, IMPACT, SYBU, SELENOS, CYP4V2, NLRP2, ZNF334, MIF-AS1, ATF7IP, NEAT1, DHX32, H19, PAG1, IFNL2, PYDC1, A2M, TGIF1, DKK2, ITGA5, ISL1, IRF3, IRAK2, INPP5D, INS, IL15RA, IL12RB1, IL11RA, IL2RG, IGKC, IGH, IGFBP7, IGFBP6, IGFBP4, IFNGR2, IFIT1, IFIT2, IFI35, IFI27, IFI16, IDDM13, ITGA2B, ITGA9, PLD1, ITIH1, LCAT, LBR, LAMA3, LAIR2, LAG3, KRT16, KRT13, KRT8, KRT7, KRT5, KRTAP5-9, KPNA2, KIT, KIR3DS1, KIR2DS4, KIR2DS3, KCNQ1, KCNA4, CD82, ITPR2, ITIH4, IDDM7, IAPP, NDST1, HSPB2, HARS1, HAGH, GZMM, GYS1, GTS, GSN, GRPR, PDIA3, CXCL3, GRIK4, GRIA1, GRB2, GRK5, GPR39, GPER1, UTS2R, GPR3, GPLD1, GPC1, GNS, GNB3, HAS1, HAS3, HCRTR1, HOXB2, HSPB1, HSPA5, HSPA1B, HSPA1A, HES1, PRMT1, HRG, HPRT1, HOXD4, HNRNPC, HDC, HMMR, HMGCR, HLA-E, HLA-DRB6, HLA-DRB2, HK2, HK1, HEXB, HEXA, LCK, LECT2, LIFR, NEDD9, P2RX5, P2RX4, P2RX3, P2RX1, OPRK1, ODF1, OAZ1, OAP, NUCB2, NTRK1, NPPB, NPAS2, NONO, NMT1, NNAT, NFYA, NFKBIB, NFIL3, NFIA, NFATC2, NEU1, P2RY1, P2RY2, P2RY11, PGM1, PLAUR, PLAT, PLA2G2A, PKD1, PIN1, PIM1, PIGR, PI3, PHEX, PGK1, PEBP1, PDPK1, ENPP1, PDK1, PDE4D, PCYT1A, PCSK1, PCBP1, SERPINB2, FURIN, NELL1, NDUFS3, LNPEP, NDUFA7, MAP3K11, MITF, KITLG, MGAT5, MAP3K3, MDM4, ADAM11, MBNL1, MARK1, MAPT, MAL, SMAD1, MAA, CAPRIN1, LYZ, LTBR, LSP1, LRP6, LRP2, LRP1, LOXL2, KMT2A, AFF1, MMP7, ND1, NCF4, NBN, MYCN, MX1, MUC5AC, MUC4, MUC3A, MUC2, MTNR1B, MSMB, MMP15, MSH3, MSH2, MSD, MS, MOS, MOBP, MNAT1, MMP17, MMP16, GNAQ, GNA12, GLI1, BCL3, CD58, CD47, CD36, CD9, CD4, CCT, CCNB1, KRIT1, CASR, CALM3, CALM2, CALM1, CACNA1S, CA3, CA2, C3AR1, BTN1A1, BPI, DST, BMX, BMP5, CD59, CD63, CD74, CEACAM8, PLK3, CMKLR1, CLTA, TPP1, CIRBP, CHRNA7, CHRM3, CHN2, CHGA, CENPE, CD79A, CECR, CEBPB, CDKN3, CDKN2C, CDKN1B, CDK7, CDK4, CDK1, CDA, BCS1L, BCL2L1, COL1A1, BAX, AMD1, ALOX5AP, ALOX12, ALDH1A3, ALDH2, ALCAM, AKT2, AHSG, AGTR2, AGTR1, AGT, ADRB3, ADORA3, ADCYAP1R1, ADAR, ACTN1, ACTA2, ACP1, ASIC1, ABCA4, AAVS1, AMD1P2, AMH, AMPD1, ARG2, AZGP1, ATR, ATP1A1, ATOH1, ATF3, SERPINC1, ASAH1, ARRB2, ARRB1, APOA2, ANG, APOA1, XIAP, BIRC3, BIRC2, APCS, APAF1, ANXA5, ANXA4, ANXA2, CNN2, COL1A2, GCLC, EMD, FGF7, FGF4, FGD1, FCGRT, EFEMP1, FAT1, FAP, FABP5, F10, EXT1, MECOM, ESRRB, ERV3-1, EREG, ERCC2, ERBB3, EPO, CLN8, EPHA3, EPHA1, ENG, FGF9, FGFR1, FGFR3, GATA2, GJA1, GHSR, B4GALT1, GDF2, GCY, KAT2A, GCK, GCHFR, GATA4, GATA1, FHL2, GARS1, FUT4, FTL, FPR1, FOLR1, FLT3, FLNA, FOXJ1, VEGFD, MARK2, ELN, COL4A5, ELANE, CYLD, CYBA, CYB5A, CUX1, CTSS, CTRB1, CTH, CSNK1E, CSF3R, CSF2RA, CSE1L, CRKL, CRHR2, CRABP1, CPOX, CLDN7, CPB2, CPA1, KLF6, COL12A1, COL9A2, CYP1A1, CYP2B6, CYP2C19, DUSP2, EIF4G1, EIF4E, EGR2, EFNB2, EDNRB, S1PR3, DYRK1A, DVL2, DUSP8, DSPP, CYP2E1, DOCK2, DNAH8, SARDH, NQO1, DEFA3, DEFA1, DCK, DCC, CYP3A4, PLCG2, SERPINF2, PELP1, HDAC6, NR1I3, GAB2, TESPA1, GIT2, PCLAF, HDAC4, RIMS2, MARF1, LPIN2, ISG15, NCOR1, AKAP12, PRDX6, GTF2IRD1, ATP6V1G1, CHST3, IL27RA, AIM2, CYP7B1, CIAO1, COX5A, HNRNPDL, HDAC5, PLK1, BCL2L11, CFDP1, PRMT5, YAP1, SPAG11B, CPQ, CRISP3, DNAJA2, LILRB2, FSTL3, IRX5, CDK2AP2, SLC17A2, RASGRP2, GDF11, CHST4, G3BP1, PTPRU, DNM1L, SLC17A4, DNAJB6, PARP2, ZFYVE9, LONP1, PPIG, MMP20, PER3, ALDH1A2, CDK5R1, PROM1, CCN4, CCN5, SOCS2, HESX1, CREG1, TNFRSF18, TNFSF9, RIPK1, URI1, HYAL2, MARCO, NUMB, NCOA1, UNC5C, HSD17B6, PSMG1, STC2, IER3, ARHGEF7, MTMR3, OSMR, SRSF11, S1PR2, ADGRG1, PIWIL1, PDLIM7, AIMP1, RPS6KA5, LRAT, DEDD, EBAG9, KYNU, SLC28A2, P2RX6, SLC16A3, SLC16A4, MTA1, CLDN1, PKD2L1, HSPB3, RPS6KA4, TMEM147, MERTK, CLEC10A, CD93, AMACR, FAM215A, DDAH1, LPAR3, DDAH2, SNAPIN, CABIN1, HARS2, COTL1, SYNM, SATB2, ARC, PHLDB1, CIC, TAB2, ZNF423, SMG1, MON2, ZNF292, MAST3, P2RX2, CLEC5A, CD2AP, HSPBP1, KIFBP, LAT, SIGLEC7, SMR3A, RNU1-1, GREM1, SLC17A5, FGF21, CLEC4E, FBXO2, LRIT1, PPP1R15A, LRIG1, IBTK, POT1, PART1, PRDX5, QPCT, CIZ1, BRD1, PLD3, SNW1, SACM1L, FST, FOXJ3, SUB1, JTB, LYVE1, NEU3, CYSLTR1, MASP2, MAP3K2, YME1L1, DCTN6, POSTN, TRIM3, NPC2, IFI44, ARPC1A, BATF, ZNRD2, CIB1, MYBBP1A, SEMA3C, SEMA6B, CREB3, TMED2, IFI44L, RAB40B, TREH, PUF60, NR1I4, IKZF2, VSIG4, B4GALT7, TREX1, CHP1, CHEK2, WIF1, ADAMTS7, IL24, KAT7, IL1RAPL1, RCAN3, DNAJB4, TPPP, PIM2, LILRA2, LILRB3, LILRA1, KHSRP, PIR, PPM1D, RNASE3, SFRP2, SETMAR, SDC4, XCL1, CCL24, CCL23, CCL14, CCL11, CCL1, SRL, SCD, SAA4, S100A11, S100A10, RYR1, RXRA, RRM2, RRAS, RPS4X, RORA, ROBO1, SFRP4, SFRP5, SGCA, SLIT3, AKR1D1, SRC, SPR, SOX4, SNAI1, SIGLEC1, SMPD1, SMO, SNAI2, SLC22A2, SGCG, SLC8A3, SLC7A4, SLC5A5, SLC3A2, SLC2A1, SLAMF1, SHH, ITSN1, SH3BP2, BRD2, RNASE1, SRP54, RMRP, MASP1, PRSS2, PROP1, EIF2AK2, MAPK13, MAPK10, MAPK9, PRKCZ, PKN1, PRF1, PRCP, PPP1R1A, PPM1A, PPBP, PPARA, POU2F2, POU2F1, PON2, POMC, POLD1, PLTP, PSEN1, PSMB5, PSMB6, RAP1A, GRK1, RHCE, RGS12, RGS1, REV3L, RET, OPN1LW, RBP4, RARG, RAG2, PSMD9, RAG1, PTPRK, PTPRJ, PTPN14, PTMAP4, PTMA, PTGER4, PTGER2, PTBP1, SRF, SRY, MAP4K3, TRAF5, XBP1, WNT1, TRPV1, VIPR1, VDAC1, VAV1, KDM6A, UTRN, UNG, UGCG, UCP2, UCN, UBTF, UBE2N, TYRP1, TYRO3, TTN, TRPM2, TRPC5, TRPC1, CCT3, XBP1P1, XRCC4, SCG2, SLC14A2, CILP, GPR65, CAVIN2, RECK, PLA2G10, EOMES, COLQ, NCOA3, MIA, HMGA2, MANF, AAAS, FGF23, FOSL1, CSRP3, BRD3, NTT, TFEB, OPLL, DEK, HSP90B2P, TRAF3, RO60, HSP90B1, PPP1R11, TRGC1, TRG, TRD, TRAV6, TCN2, TCF7L2, TCF3, TBX3, TCEA1, TBX1, TAT, TAL1, TAGLN, TACR3, TACR2, AURKA, STIM1, STATH, ST2, SSB, TDGF1, TDGF1P3, PRDX2, TGFBI, NR2C2, TPT1, TPSAB1, TP73, TNNI3, TNNC1, NKX2-1, THAS, TGFBR1, TGFB3, TEF, TGFB2, TFF2, TFF1, TFDP1, NR2F1, TF, TERT, TERF2, TEP1, H3P40
-
Graft-Versus-Host Disease
Wikipedia
It can be seen as a multiple-organ autoimmunity in xenotransplantation experiments of the thymus between different species. [27] Autoimmune disease is a frequent complication after human allogeneic thymus transplantation, found in 42% of subjects over 1 year post transplantation. [28] However, this is partially explained by the fact that the indication itself, that is, complete DiGeorge syndrome , increases the risk of autoimmune disease. [29] Thymoma-associated multiorgan autoimmunity (TAMA) [ edit ] A GvHD-like disease called thymoma-associated multiorgan autoimmunity (TAMA) can occur in patients with thymoma. ... "Intraoral psoralen ultraviolet A irradiation (PUVA) treatment of refractory oral chronic graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic stem cell transplantation" . Bone Marrow Transplantation . 28 (8): 807–8. doi : 10.1038/sj.bmt.1703231 .
-
Salt Water Aspiration Syndrome
Wikipedia
South Pacific Underwater Medicine Society Journal . 28 (1). ISSN 0813-1988 . OCLC 16986801 . Archived from the original on 2011-01-28 . Retrieved 2008-07-04 . External links [ edit ] Diving Medicine Online — Salt Water Aspiration Syndrome v t e Underwater diving Diving modes Atmospheric pressure diving Freediving Saturation diving Scuba diving Snorkeling Surface oriented diving Surface-supplied diving Unmanned diving Diving equipment Cleaning and disinfection of personal diving equipment Human factors in diving equipment design Basic equipment Diving mask Snorkel Swimfin Breathing gas Bailout gas Bottom gas Breathing air Decompression gas Emergency gas supply Heliox Nitrox Oxygen Travel gas Trimix Buoyancy and trim equipment Buoyancy compensator Power inflator Dump valve Diving weighting system Ankle weights Integrated weights Trim weights Weight belt Decompression equipment Decompression buoy Decompression cylinder Decompression trapeze Dive computer Diving shot Jersey upline Jonline Diving suit Atmospheric diving suit Dry suit Sladen suit Standard diving suit Rash vest Wetsuit Dive skins Hot-water suit Helmets and masks Anti-fog Diving helmet Free-flow helmet Lightweight demand helmet Orinasal mask Reclaim helmet Shallow water helmet Standard diving helmet Diving mask Band mask Full-face mask Half mask Instrumentation Bottom timer Depth gauge Dive computer Dive timer Diving watch Helium release valve Pneumofathometer Submersible pressure gauge Mobility equipment Diving bell Closed bell Wet bell Diving stage Swimfin Monofin PowerSwim Towboard Diver propulsion vehicle Advanced SEAL Delivery System Cosmos CE2F series Dry Combat Submersible Human torpedo Motorised Submersible Canoe Necker Nymph R-2 Mala-class swimmer delivery vehicle SEAL Delivery Vehicle Shallow Water Combat Submersible Siluro San Bartolomeo Wet Nellie Wet sub Safety equipment Alternative air source Octopus regulator Pony bottle Bolt snap Buddy line Dive light Diver's cutting tool Diver's knife Diver's telephone Through-water communications Diving bell Diving safety harness Emergency gas supply Bailout block Bailout bottle Lifeline Screw gate carabiner Emergency locator beacon Rescue tether Safety helmet Shark-proof cage Snoopy loop Navigation equipment Distance line Diving compass Dive reel Line marker Surface marker buoy Silt screw Underwater breathing apparatus Atmospheric diving suit Diving cylinder Burst disc Diving cylinder valve Diving helmet Reclaim helmet Diving regulator Mechanism of diving regulators Regulator malfunction Regulator freeze Single-hose regulator Twin-hose regulator Full face diving mask Open-circuit scuba Scuba set Bailout bottle Decompression cylinder Independent doubles Manifolded twin set Scuba manifold Pony bottle Scuba configuration Sidemount Sling cylinder Diving rebreathers Carbon dioxide scrubber Carleton CDBA CDLSE Cryogenic rebreather CUMA DSEA Dolphin Electro-galvanic oxygen sensor FROGS Halcyon PVR-BASC Halcyon RB80 IDA71 Interspiro DCSC KISS LAR-5 LAR-6 LAR-V LARU Porpoise Ray Siebe Gorman CDBA Siva Viper Surface-supplied diving equipment Air line Diver's umbilical Diving air compressor Gas panel Hookah Scuba replacement Sea Trek Snuba Standard diving dress Escape set Davis Submerged Escape Apparatus Momsen lung Steinke hood Submarine Escape Immersion Equipment Diving equipment manufacturers AP Diving Apeks Aqua Lung America Aqua Lung/La Spirotechnique Beuchat René Cavalero Cis-Lunar Cressi-Sub Dacor DESCO Dive Xtras Divex Diving Unlimited International Drägerwerk Fenzy Maurice Fernez Technisub Oscar Gugen Heinke HeinrichsWeikamp Johnson Outdoors Mares Morse Diving Nemrod Oceanic Worldwide Porpoise Sub Sea Systems Shearwater Research Siebe Gorman Submarine Products Suunto Diving support equipment Access equipment Boarding stirrup Diver lift Diving bell Diving ladder Diving platform (scuba) Diving stage Downline Jackstay Launch and recovery system Messenger line Moon pool Breathing gas handling Air filtration Activated carbon Hopcalite Molecular sieve Silica gel Booster pump Carbon dioxide scrubber Cascade filling system Diver's pump Diving air compressor Diving air filter Water separator High pressure breathing air compressor Low pressure breathing air compressor Gas blending Gas blending for scuba diving Gas panel Gas reclaim system Gas storage bank Gas storage quad Gas storage tube Helium analyzer Nitrox production Membrane gas separation Pressure swing adsorption Oxygen analyser Oxygen compatibility Decompression equipment Built-in breathing system Decompression tables Diving bell Bell cursor Closed bell Clump weight Launch and recovery system Wet bell Diving chamber Diving stage Recreational Dive Planner Saturation system Platforms Dive boat Canoe and kayak diving Combat Rubber Raiding Craft Liveaboard Subskimmer Diving support vessel HMS Challenger (K07) Underwater habitat Aquarius Reef Base Continental Shelf Station Two Helgoland Habitat Jules' Undersea Lodge Scott Carpenter Space Analog Station SEALAB Tektite habitat Remotely operated underwater vehicles 8A4-class ROUV ABISMO Atlantis ROV Team CURV Deep Drone Épaulard Global Explorer ROV Goldfish-class ROUV Kaikō ROV Kaşif ROUV Long-Term Mine Reconnaissance System Mini Rover ROV OpenROV ROV KIEL 6000 ROV PHOCA Scorpio ROV Sea Dragon-class ROV Seabed tractor Seafox drone Seahorse ROUV SeaPerch SJT-class ROUV T1200 Trenching Unit VideoRay UROVs Safety equipment Diver down flag Diving shot Hyperbaric lifeboat Hyperbaric stretcher Jackstay Jonline Reserve gas supply General Diving spread Air spread Saturation spread Hot water system Sonar Underwater acoustic positioning system Underwater acoustic communication Freediving Activities Aquathlon Apnoea finswimming Freediving Haenyeo Pearl hunting Ama Snorkeling Spearfishing Underwater football Underwater hockey Underwater ice hockey Underwater rugby Underwater target shooting Competitions Nordic Deep Vertical Blue Disciplines Constant weight (CWT) Constant weight without fins (CNF) Dynamic apnea (DYN) Dynamic apnea without fins (DNF) Free immersion (FIM) No-limits apnea (NLT) Static apnea (STA) Skandalopetra diving Variable weight apnea (VWT) Variable weight apnea without fins Equipment Diving mask Diving suit Hawaiian sling Polespear Snorkel (swimming) Speargun Swimfins Monofin Water polo cap Freedivers Deborah Andollo Peppo Biscarini Sara Campbell Derya Can Göçen Goran Čolak Carlos Coste Robert Croft Mandy-Rae Cruickshank Yasemin Dalkılıç Leonardo D'Imporzano Flavia Eberhard Şahika Ercümen Emma Farrell Francisco Ferreras Pierre Frolla Flavia Eberhard Mehgan Heaney-Grier Elisabeth Kristoffersen Loïc Leferme Enzo Maiorca Jacques Mayol Audrey Mestre Karol Meyer Stéphane Mifsud Alexey Molchanov Natalia Molchanova Dave Mullins Patrick Musimu Guillaume Néry Herbert Nitsch Umberto Pelizzari Annelie Pompe Michal Risian Stig Severinsen Tom Sietas Aharon Solomons Martin Štěpánek Walter Steyn Tanya Streeter William Trubridge Devrim Cenk Ulusoy Danai Varveri Alessia Zecchini Nataliia Zharkova Hazards Barotrauma Drowning Freediving blackout Deep-water blackout Shallow-water blackout Hypercapnia Hypothermia Historical Ama Octopus wrestling Swimming at the 1900 Summer Olympics – Men's underwater swimming Organisations AIDA International Scuba Schools International Australian Underwater Federation British Freediving Association Confédération Mondiale des Activités Subaquatiques Fédération Française d'Études et de Sports Sous-Marins Performance Freediving International Professional diving Occupations Ama Commercial diver Commercial offshore diver Hazmat diver Divemaster Diving instructor Diving safety officer Diving superintendent Diving supervisor Haenyeo Media diver Police diver Public safety diver Scientific diver Underwater archaeologist Military diving Army engineer diver Clearance diver Frogman List of military diving units Royal Navy ships diver Special Boat Service United States military divers U.S. ... Barnette Victor Berge Philippe Diolé Gary Gentile Bret Gilliam Bob Halstead Trevor Jackson Steve Lewis John Mattera Rescuers Craig Challen Richard Harris Rick Stanton John Volanthen Frogmen Lionel Crabb Commercial salvors Keith Jessop Science of underwater diving Diving physics Breathing performance of regulators Buoyancy Archimedes' principle Neutral buoyancy Concentration Diffusion Molecular diffusion Force Oxygen fraction Permeation Psychrometric constant Solubility Henry's law Saturation Solution Supersaturation Surface tension Hydrophobe Surfactant Temperature Torricellian chamber Underwater acoustics Modulated ultrasound Underwater vision Snell's law Underwater computer vision Weight Apparent weight Gas laws Amontons's law Boyle's law Charles's law Combined gas law Dalton's law Gay-Lussac's law Ideal gas law Pressure Absolute pressure Ambient pressure Atmospheric pressure Gauge pressure Hydrostatic pressure Metre sea water Partial pressure Diving physiology Artificial gills Cold shock response Diving reflex Equivalent narcotic depth Lipid Maximum operating depth Metabolism Physiological response to water immersion Tissue Underwater vision Circulatory system Blood shift Patent foramen ovale Perfusion Pulmonary circulation Systemic circulation Decompression theory Decompression models: Bühlmann decompression algorithm Haldane's decompression model Reduced gradient bubble model Thalmann algorithm Thermodynamic model of decompression Varying Permeability Model Equivalent air depth Equivalent narcotic depth Oxygen window in diving decompression Physiology of decompression Respiration Blood–air barrier Breathing CO₂ retention Dead space Gas exchange Hypocapnia Respiratory exchange ratio Respiratory quotient Respiratory system Work of breathing Diving environment Classification List of diving environments by type Altitude diving Benign water diving Confined water diving Deep diving Inland diving Inshore diving Muck diving Night diving Open-water diving Black-water diving Blue-water diving Penetration diving Cave diving Ice diving Wreck diving Recreational dive sites Underwater environment Impact Environmental impact of recreational diving Low impact diving Environmental factors Algal bloom Currents: Current Longshore drift Ocean current Rip current Tidal race Undertow Upwelling Ekman transport Halocline Reef Coral reef Stratification Thermocline Tides Turbidity Wind wave Breaking wave Surf Surge Wave shoaling Other Bathysphere Defense against swimmer incursions Diver detection sonar Offshore survey Underwater domain awareness Awards and events Hans Hass Award International Scuba Diving Hall of Fame London Diving Chamber Dive Lectures NOGI Awards Deep-submergence vehicle Aluminaut DSV Alvin American submarine NR-1 Bathyscaphe Archimède FNRS-2 FNRS-3 FNRS-4 Harmony class bathyscaphe Sea Pole -class bathyscaphe Trieste II Deepsea Challenger Ictineu 3 JAGO Jiaolong Konsul -class submersible DSV Limiting Factor Russian submarine Losharik Mir Nautile Pisces -class deep submergence vehicle DSV Sea Cliff DSV Shinkai DSV Shinkai 2000 DSV Shinkai 6500 DSV Turtle DSV-5 Nemo Deep-submergence rescue vehicle LR5 LR7 MSM-1 Mystic -class deep-submergence rescue vehicle DSRV-1 Mystic DSRV-2 Avalon NATO Submarine Rescue System Priz -class deep-submergence rescue vehicle Russian deep submergence rescue vehicle AS-28 Russian submarine AS-34 ASRV Remora SRV-300 Submarine Rescue Diving Recompression System Type 7103 DSRV URF (Swedish Navy) Special interest groups Artificial Reef Society of British Columbia CMAS Europe Coral Reef Alliance Diving Equipment and Marketing Association Divers Alert Network Green Fins Historical Diving Society Karst Underwater Research Nautical Archaeology Program Nautical Archaeology Society Naval Air Command Sub Aqua Club Project AWARE Reef Check Reef Life Survey Rubicon Foundation Save Ontario Shipwrecks SeaKeys Sea Research Society Society for Underwater Historical Research Society for Underwater Technology Underwater Archaeology Branch, Naval History & Heritage Command Submarine escape and rescue Escape trunk International Submarine Escape and Rescue Liaison Office McCann Rescue Chamber Submarine Escape and Rescue system (Royal Swedish Navy) Submarine escape training facility Submarine Escape Training Facility (Australia) Submarine rescue ship Neutral buoyancy facilities for Astronaut training Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory Neutral buoyancy pool Neutral buoyancy simulation as a training aid Neutral Buoyancy Simulator Space Systems Laboratory Yuri Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center Other Nautilus Productions Category Commons Glossary Indexes: dive sites divers diving Outline Portal
-
High-Pressure Nervous Syndrome
Wikipedia
"Seeking man's depth level". Ocean Industry . London. 3 : 28–33. ^ Brauer, R. W.; S. Dimov; X. ... "The causes, mechanisms and prevention of the high pressure nervous syndrome" . Undersea Biomed. Res . 1 (1): 1–28. ISSN 0093-5387 . OCLC 2068005 . PMID 4619860 . ... Barnette Victor Berge Philippe Diolé Gary Gentile Bret Gilliam Bob Halstead Trevor Jackson Steve Lewis John Mattera Rescuers Craig Challen Richard Harris Rick Stanton John Volanthen Frogmen Lionel Crabb Commercial salvors Keith Jessop Science of underwater diving Diving physics Breathing performance of regulators Buoyancy Archimedes' principle Neutral buoyancy Concentration Diffusion Molecular diffusion Force Oxygen fraction Permeation Psychrometric constant Solubility Henry's law Saturation Solution Supersaturation Surface tension Hydrophobe Surfactant Temperature Torricellian chamber Underwater acoustics Modulated ultrasound Underwater vision Snell's law Underwater computer vision Weight Apparent weight Gas laws Amontons's law Boyle's law Charles's law Combined gas law Dalton's law Gay-Lussac's law Ideal gas law Pressure Absolute pressure Ambient pressure Atmospheric pressure Gauge pressure Hydrostatic pressure Metre sea water Partial pressure Diving physiology Artificial gills Cold shock response Diving reflex Equivalent narcotic depth Lipid Maximum operating depth Metabolism Physiological response to water immersion Tissue Underwater vision Circulatory system Blood shift Patent foramen ovale Perfusion Pulmonary circulation Systemic circulation Decompression theory Decompression models: Bühlmann decompression algorithm Haldane's decompression model Reduced gradient bubble model Thalmann algorithm Thermodynamic model of decompression Varying Permeability Model Equivalent air depth Equivalent narcotic depth Oxygen window in diving decompression Physiology of decompression Respiration Blood–air barrier Breathing CO₂ retention Dead space Gas exchange Hypocapnia Respiratory exchange ratio Respiratory quotient Respiratory system Work of breathing Diving environment Classification List of diving environments by type Altitude diving Benign water diving Confined water diving Deep diving Inland diving Inshore diving Muck diving Night diving Open-water diving Black-water diving Blue-water diving Penetration diving Cave diving Ice diving Wreck diving Recreational dive sites Underwater environment Impact Environmental impact of recreational diving Low impact diving Environmental factors Algal bloom Currents: Current Longshore drift Ocean current Rip current Tidal race Undertow Upwelling Ekman transport Halocline Reef Coral reef Stratification Thermocline Tides Turbidity Wind wave Breaking wave Surf Surge Wave shoaling Other Bathysphere Defense against swimmer incursions Diver detection sonar Offshore survey Underwater domain awareness Awards and events Hans Hass Award International Scuba Diving Hall of Fame London Diving Chamber Dive Lectures NOGI Awards Deep-submergence vehicle Aluminaut DSV Alvin American submarine NR-1 Bathyscaphe Archimède FNRS-2 FNRS-3 FNRS-4 Harmony class bathyscaphe Sea Pole -class bathyscaphe Trieste II Deepsea Challenger Ictineu 3 JAGO Jiaolong Konsul -class submersible DSV Limiting Factor Russian submarine Losharik Mir Nautile Pisces -class deep submergence vehicle DSV Sea Cliff DSV Shinkai DSV Shinkai 2000 DSV Shinkai 6500 DSV Turtle DSV-5 Nemo Deep-submergence rescue vehicle LR5 LR7 MSM-1 Mystic -class deep-submergence rescue vehicle DSRV-1 Mystic DSRV-2 Avalon NATO Submarine Rescue System Priz -class deep-submergence rescue vehicle Russian deep submergence rescue vehicle AS-28 Russian submarine AS-34 ASRV Remora SRV-300 Submarine Rescue Diving Recompression System Type 7103 DSRV URF (Swedish Navy) Special interest groups Artificial Reef Society of British Columbia CMAS Europe Coral Reef Alliance Diving Equipment and Marketing Association Divers Alert Network Green Fins Historical Diving Society Karst Underwater Research Nautical Archaeology Program Nautical Archaeology Society Naval Air Command Sub Aqua Club Project AWARE Reef Check Reef Life Survey Rubicon Foundation Save Ontario Shipwrecks SeaKeys Sea Research Society Society for Underwater Historical Research Society for Underwater Technology Underwater Archaeology Branch, Naval History & Heritage Command Submarine escape and rescue Escape trunk International Submarine Escape and Rescue Liaison Office McCann Rescue Chamber Submarine Escape and Rescue system (Royal Swedish Navy) Submarine escape training facility Submarine Escape Training Facility (Australia) Submarine rescue ship Neutral buoyancy facilities for Astronaut training Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory Neutral buoyancy pool Neutral buoyancy simulation as a training aid Neutral Buoyancy Simulator Space Systems Laboratory Yuri Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center Other Nautilus Productions Category Commons Glossary Indexes: dive sites divers diving Outline Portal
-
Complete Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome
Wikipedia
In some extreme cases, the vagina has been reported to be aplastic (resembling a "dimple"), though the exact incidence of this is unknown. [25] The gonads in these women are not ovaries , but instead, are testes ; during the embryonic stage of development , testes form in an androgen-independent process that occurs due to the influence of the SRY gene on the Y chromosome . [26] [27] They may be located intra-abdominally, at the internal inguinal ring , or may herniate into the labia majora , often leading to the discovery of the condition. [1] [28] [29] [30] Testes in affected women have been found to be atrophic upon gonadectomy . [31] Testosterone produced by the testes cannot be directly used due to the mutant androgen receptor that characterizes CAIS; instead, it is aromatized into estrogen , which effectively feminizes the body and accounts for the normal female phenotype observed in CAIS. [1] Immature sperm cells in the testes do not mature past an early stage, as sensitivity to androgens is required in order for spermatogenesis to complete. [32] [33] Germ cell malignancy risk, once thought to be relatively high, is now thought to be approximately 2%. [34] Wolffian structures (the epididymides , vasa deferentia , and seminal vesicles ) are typically absent, but will develop at least partially in approximately 30% of cases, depending on which mutation is causing the CAIS. [35] The prostate , like the external male genitalia , cannot masculinize in the absence of androgen receptor function, and thus remains in the female form . [18] [36] [37] [38] The Müllerian system (the fallopian tubes , uterus , and upper portion of the vagina) typically regresses due to the presence of anti-Müllerian hormone originating from the Sertoli cells of the testes. [19] These women are thus born without fallopian tubes, a cervix , or a uterus, [19] and the vagina ends "blindly" in a pouch. [1] Müllerian regression does not fully complete in approximately one third of all cases, resulting in Müllerian "remnants". [19] Although rare, a few cases of women with CAIS and fully developed Müllerian structures have been reported. In one exceptional case, a 22-year-old with CAIS was found to have a normal cervix, uterus, and fallopian tubes. [39] In an unrelated case, a fully developed uterus was found in a 22-year-old adult with CAIS. [38] Other subtle differences that have been reported include slightly longer limbs and larger hands and feet due to a proportionally greater stature than unaffected women, [40] [41] [42] larger teeth, [43] [44] minimal or no acne, [45] well developed breasts , [46] and a greater incidence of meibomian gland dysfunction (i.e. dry eye syndromes and light sensitivity ). [47] Endocrine [ edit ] Hormone levels have been reported in gonadally intact CAIS women in a number of studies. [48] [49] Hormone levels are similar to those of males, including high testosterone levels and relatively low estradiol levels. [48] [49] However, luteinizing hormone (LH) levels are elevated while sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) levels are more consistent with those of females. [48] [49] [50] Women with CAIS have low levels of progesterone similarly to males. [51] [52] [53] The production rates of testosterone, estradiol, and estrone have been reported to be higher in gonadally intact CAIS women than in men. [54] [55] v t e Hormone levels in gonadally intact adolescent and adult females with complete androgen insensitivity syndrome Schindler (1975) Blumenthal (1982) Melo (2003) Audi (2010) Doehnert (2015) King (2017) Reference ranges Male Female Location Tübingen, DE Johannesburg, ZA Sao Paulo, BR Barcelona, ES Lübeck, DE/Pisa, IT London, UK – – Sample size (n) 4 4 8 11 42 31 – – Age (years) ? (17–22) 19 (18–28) 16.5 (14–34) 20 (13.5–40) 17.3 (14–50) 19.7 (13.4–52.3) Adult Adult LH (IU/L) ? ... "Disorders of androgen action". Semin. Reprod. Med . 20 (3): 217–28. doi : 10.1055/s-2002-35386 . PMID 12428202 . ^ Zachmann M, Prader A , Sobel EH, Crigler JF, Ritzén EM, Atarés M, Ferrandez A (May 1986). ... "Androgen insensitivity syndrome" (PDF) . Lancet . 380 (9851): 1419–28. doi : 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60071-3 . ... "Invasive Ductal Carcinoma in a 46,XY Partial Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome Patient on Hormone Therapy". J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol . 28 (4): e95–7. doi : 10.1016/j.jpag.2014.08.005 .AR, FKBP4, SMS, PLAT, RSS, MTNR1B, LBX1, ESR1, LEP, MATN1, IL6, EGFR, ESR2, ADGRG6, PAICS, GART, MTHFR, C20orf181, IGF1, CALM1, F5, TPH1, MT2A, AMH, MTNR1A, MMP3, TSPAN33, TP53, TMPRSS6, BNC2, TNFRSF11B, SIRT1, NTF3, SLC39A8, NCOA2, FBN1, FBN2, LEPR, PYCARD, PAX1, PDXP, GPER1, GPX3, SERPINE1, TIMP2, SHBG, BRD2, TGFB1, SULT1E1, MIR494, VDR, SRY, STS, VEGFA, BDNF, MIR15A, EOS, TP63, ADIPOQ, CST3, IS1, PITX1, SOCS3, POC5, PON1, CTNNB1, PROM1, KAT7, GPR50, PDAP1, SIRT5, TUSC2, PAPOLA, NDRG1, TXN, ADAMTS13, MSC, MRPS30, AKR1C3, CHL1, BEST1, VWF, MYBBP1A, USP8, SMUG1, UXT, TNFSF11, ASAP2, GDF15, AANAT, TMEFF2, MIR145, DPP9, NLRP3, OCIAD2, HJV, NEAT1, C17orf67, SPATA21, MIRLET7I, MIR126, MIR130A, MIR134, MIR183, HECTD1, MIR185, MIR191, MIR192, MIR222, MIR93, PALM2AKAP2, MT1IP, MIR675, CDKN2B-AS1, MIR4300, OCLN, ADGRG7, IL17RC, DOT1L, SPRY4, SETBP1, CNTNAP2, PELP1, CD274, TBX21, ASAP1, ADIPOR1, APH1A, CLEC1B, TNF, MTPAP, LAPTM4B, SOX6, MIB1, PCDH10, MIER1, MID1IP1, SOX17, NUCKS1, AHNAK, IRX1, FUZ, VANGL1, HSD17B7, PSMD4, TIMP1, DLST, CLTC, COL4A2, COL11A1, COL11A2, COMP, MAP3K8, CREBBP, CRP, CYP2C19, DBP, DMD, CHI3L1, DPP4, DUSP2, EPO, F2, F3, FGFR3, FGR, FN1, NR5A1, GAD1, CLU, CDKN2A, THRSP, ASL, ACP3, ACTB, ADRA1D, ALB, APC, APOD, APOE, ARF6, ARG1, ARSF, ATP2A2, CDH13, ATP2B4, BGLAP, BMP4, BTF3P11, CALCA, CALM2, CALM3, CASP3, RUNX2, CD38, GC, GHSR, MSH6, ABO, MT1L, MT1X, NRGN, REG3A, PAX3, PBX1, PLG, PMCH, MAPK7, PSD, RARB, HDAC2, PRPH2, S100A12, SFPQ, SRSF1, ITSN1, SLC4A1, SOX9, SRD5A2, STAT4, TGM2, MT1M, MT1JP, MT1H, MT1G, HGF, HOXA10, HSPG2, IGFBP7, IL1A, IL1B, IL5, IL10, ITGA2B, KLK1, KRAS, LCN2, LGALS1, LGALS3, LRPAP1, KITLG, MKI67, MT1A, MT1B, MT1E, MT1F, H3P10
-
Down Syndrome
Wikipedia
Genetic disorder, also known as "trisomy 21" Down syndrome Other names Down's syndrome, Down's, trisomy 21 Illustration of the facial features of Down syndrome Specialty Medical genetics , pediatrics Symptoms Delayed physical growth , characteristic facial features , mild to moderate intellectual disability [1] Causes Third copy of chromosome 21 [2] Risk factors Older age of mother , prior affected child [3] [4] Diagnostic method Prenatal screening , genetic testing [5] Treatment Educational support, sheltered work environment [6] [7] Prognosis Life expectancy 50 to 60 years (developed world) [8] [9] Frequency 5.4 million (0.1%) [1] [10] Deaths 26,500 (2015) [11] Down syndrome or Down's syndrome , also known as trisomy 21 , is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21 . [2] It is usually associated with physical growth delays, mild to moderate intellectual disability , and characteristic facial features . [1] The average IQ of a young adult with Down syndrome is 50, equivalent to the mental ability of an 8- or 9-year-old child, but this can vary widely. [8] The parents of the affected individual are usually genetically normal. [12] The probability increases from less than 0.1% in 20-year-old mothers to 3% in those of age 45. [3] The extra chromosome is believed to occur by chance, with no known behavioral activity or environmental factor that changes the probability. [13] Down syndrome can be identified during pregnancy by prenatal screening followed by diagnostic testing or after birth by direct observation and genetic testing . [5] Since the introduction of screening, Down syndrome pregnancies are often aborted . [14] [15] Regular screening for health problems common in Down syndrome is recommended throughout the person's life. [8] There is no cure for Down syndrome. [16] Education and proper care have been shown to improve quality of life . [6] Some children with Down syndrome are educated in typical school classes, while others require more specialized education. [7] Some individuals with Down syndrome graduate from high school , and a few attend post-secondary education . [17] In adulthood, about 20% in the United States do paid work in some capacity, [18] with many requiring a sheltered work environment. [7] Support in financial and legal matters is often needed. [9] Life expectancy is around 50 to 60 years in the developed world with proper health care. [8] [9] Down syndrome is one of the most common chromosome abnormalities in humans. [8] It occurs in about 1 in 1,000 babies born each year. [1] In 2015, Down syndrome was present in 5.4 million individuals globally and resulted in 27,000 deaths, down from 43,000 deaths in 1990. [10] [11] [19] It is named after British doctor John Langdon Down , who fully described the syndrome in 1866. [20] Some aspects of the condition were described earlier by French psychiatrist Jean-Étienne Dominique Esquirol in 1838 and French physician Édouard Séguin in 1844. [21] The genetic cause of Down syndrome was discovered in 1959. [20] Contents 1 Signs and symptoms 1.1 Physical 1.2 Neurological 1.3 Senses 1.4 Heart 1.5 Cancer 1.5.1 Blood cancers 1.5.2 Non-blood cancers 1.6 Endocrine 1.7 Gastrointestinal 1.8 Teeth 1.9 Fertility 2 Cause 2.1 Trisomy 21 2.2 Translocation 3 Mechanism 3.1 Epigenetics 4 Diagnosis 4.1 Before birth 4.2 Abortion rates 4.3 After birth 4.4 Screening 4.4.1 Ultrasound 4.4.2 Blood tests 5 Management 5.1 Health screening 5.2 Cognitive development 5.3 Other 6 Prognosis 7 Epidemiology 8 History 9 Society and culture 9.1 Name 9.2 Ethics 9.3 Advocacy groups 10 Research 11 Other hominids 12 References 13 External links Signs and symptoms A boy with Down syndrome using cordless drill to assemble a book case An eight-year-old boy with Down syndrome Those with Down syndrome nearly always have physical and intellectual disabilities. [22] As adults, their mental abilities are typically similar to those of an 8- or 9-year-old. [8] They also typically have poor immune function [12] and generally reach developmental milestones at a later age. [9] They have an increased risk of a number of other health problems, including congenital heart defect , epilepsy , leukemia , thyroid diseases , and mental disorders . [20] Characteristics Percentage Characteristics Percentage Mental impairment 99% [23] Abnormal teeth 60% [24] Stunted growth 90% [25] Slanted eyes 60% [12] Umbilical hernia 90% [26] Shortened hands 60% [24] Increased skin on back of neck 80% [20] Short neck 60% [24] Low muscle tone 80% [27] Obstructive sleep apnea 60% [20] Narrow roof of mouth 76% [24] Bent fifth finger tip 57% [12] Flat head 75% [12] Brushfield spots in the iris 56% [12] Flexible ligaments 75% [12] Single transverse palmar crease 53% [12] Proportionally large tongue [28] 75% [27] Protruding tongue 47% [24] Abnormal outer ears 70% [20] Congenital heart disease 40% [24] Flattened nose 68% [12] Strabismus ~35% [1] Separation of first and second toes 68% [24] Undescended testicles 20% [29] Physical Feet of a boy with Down syndrome, showing the deviated first toes People with Down syndrome may have some or all of these physical characteristics: a small chin , slanted eyes , poor muscle tone , a flat nasal bridge , a single crease of the palm , and a protruding tongue due to a small mouth and relatively large tongue . [27] [28] These airway changes lead to obstructive sleep apnea in around half of those with Down syndrome. [20] Other common features include: a flat and wide face, [27] a short neck, excessive joint flexibility, extra space between big toe and second toe, abnormal patterns on the fingertips and short fingers. [24] [27] Instability of the atlantoaxial joint occurs in about 20% and may lead to spinal cord injury in 1–2%. [8] [9] Hip dislocations may occur without trauma in up to a third of people with Down syndrome. [20] Growth in height is slower, resulting in adults who tend to have short stature —the average height for men is 154 cm (5 ft 1 in) and for women is 142 cm (4 ft 8 in). [30] Individuals with Down syndrome are at increased risk for obesity as they age. [20] Growth charts have been developed specifically for children with Down syndrome. [20] Neurological This syndrome causes about a third of cases of intellectual disability. [12] Many developmental milestones are delayed with the ability to crawl typically occurring around 8 months rather than 5 months and the ability to walk independently typically occurring around 21 months rather than 14 months. [31] Most individuals with Down syndrome have mild (IQ: 50–69) or moderate (IQ: 35–50) intellectual disability with some cases having severe (IQ: 20–35) difficulties. [1] [32] Those with mosaic Down syndrome typically have IQ scores 10–30 points higher. [33] As they age, people with Down syndrome typically perform worse than their same-age peers. [32] [34] Commonly, individuals with Down syndrome have better language understanding than ability to speak. [20] [32] Between 10 and 45% have either a stutter or rapid and irregular speech , making it difficult to understand them. [35] After reaching 30 years of age, some may lose their ability to speak. [8] They typically do fairly well with social skills. [20] Behavior problems are not generally as great an issue as in other syndromes associated with intellectual disability. [32] In children with Down syndrome, mental illness occurs in nearly 30% with autism occurring in 5–10%. [9] People with Down syndrome experience a wide range of emotions. [36] While people with Down syndrome are generally happy, [37] symptoms of depression and anxiety may develop in early adulthood. [8] Children and adults with Down syndrome are at increased risk of epileptic seizures , which occur in 5–10% of children and up to 50% of adults. [8] This includes an increased risk of a specific type of seizure called infantile spasms . [20] Many (15%) who live 40 years or longer develop Alzheimer’s disease . [38] In those who reach 60 years of age, 50–70% have the disease. [8] Senses Brushfield spots , visible in the irises of a baby with Down syndrome Hearing and vision disorders occur in more than half of people with Down syndrome. [20] Vision problems occur in 38 to 80%. [1] Between 20 and 50% have strabismus , in which the two eyes do not move together. [1] Cataracts (cloudiness of the lens of the eye) occur in 15%, [9] and may be present at birth. [1] Keratoconus (a thin, cone-shaped cornea ) [8] and glaucoma (increased eye pressure ) are also more common, [1] as are refractive errors requiring glasses or contacts . [8] Brushfield spots (small white or grayish/brown spots on the outer part of the iris ) are present in 38 to 85% of individuals. [1] Hearing problems are found in 50–90% of children with Down syndrome. [39] This is often the result of otitis media with effusion which occurs in 50–70% [9] and chronic ear infections which occur in 40 to 60%. [40] Ear infections often begin in the first year of life and are partly due to poor eustachian tube function. [41] [42] Excessive ear wax can also cause hearing loss due to obstruction of the outer ear canal . [8] Even a mild degree of hearing loss can have negative consequences for speech, language understanding, and academics. [1] [42] Additionally, it is important to rule out hearing loss as a factor in social and cognitive deterioration. [43] Age-related hearing loss of the sensorineural type occurs at a much earlier age and affects 10–70% of people with Down syndrome. [8] Heart The rate of congenital heart disease in newborns with Down syndrome is around 40%. [24] Of those with heart disease, about 80% have an atrioventricular septal defect or ventricular septal defect with the former being more common. [8] Mitral valve problems become common as people age, even in those without heart problems at birth. [8] Other problems that may occur include tetralogy of Fallot and patent ductus arteriosus . [41] People with Down syndrome have a lower risk of hardening of the arteries . [8] Cancer Although the overall risk of cancer in Down syndrome is not changed, [44] the risk of testicular cancer and certain blood cancers, including acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL) is increased while the risk of other non-blood cancers is decreased. [8] People with Down syndrome are believed to have an increased risk of developing cancers derived from germ cells whether these cancers are blood- or non-blood-related. [45] Blood cancers Leukemia is 10 to 15 times more common in children with Down syndrome. [20] In particular, acute lymphoblastic leukemia is 20 times more common and the megakaryoblastic form of acute myeloid leukemia ( acute megakaryoblastic leukemia ), is 500 times more common. [46] Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL) is a leukemia of megakaryoblasts , the precursors cells to megakaryocytes which form blood platelets . [46] Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Down syndrome accounts for 1–3% of all childhood cases of ALL.S100B, SLC19A1, MTHFR, GATA1, RCAN1, SOD1, MIR155, DCR, MIR802, PRDX2, MIR125B2, MIR99A, VIP, PRDX6, CXCL8, CALCA, MIRLET7C, NTF3, GSTM2, DYRK1A, RPLP0, CBS, ETS2, ERG, JAK2, DSCAM, MAPT, CRLF2, MTR, MTRR, RUNX1, TP53, PAPPA, ACTB, APP, CBSL, APOE, AFP, SIM2, RFC1, PSEN1, COL6A1, TTC3, HTC2, CGB3, TNF, S100A1, CGA, POTEF, BACE1, BDNF, SOAT1, KCNJ6, CCL4L1, CCL4, CCL4L2, PLAC4, CGB5, CGB8, COL6A2, IL1B, IL6, CRELD1, DNMT3B, MECP2, SOD2, OLIG2, BACE2, ETV6, PGF, CASP3, RET, HLCS, GET1, EDNRB, PCNT, HMGN1, NEFL, IFNA1, SERPINA1, IFNG, IL1A, DOP1B, SYNJ1, IFNA13, MCIDAS, CAT, AIRE, ABL1, XPNPEP1, SH3BGR, CD6, SQSTM1, CHDH, ITSN1, ENO2, PRNP, SLC25A1, ADAM12, BHMT, IL10, CD19, POLB, CD34, MIR1246, DICER1, ITGB2, EZH2, FABP7, PTCH1, VEGFA, PIGP, GFAP, DNMT3L, CBR1, GART, GAPDH, RAB5A, ALB, HLA-A, PABPC4, TNFRSF10C, CHAF1B, AKT1, SUCLA2, CCL2, SET, FANCB, JAK3, REST, PCP4, BACH1, BCL2, CSF2, MTHFD1, BCHE, LEP, NOS3, CDKN2A, COL18A1, UBB, LAMC2, SNX27, HT, KIT, NFATC1, NGF, USP25, OXA1L, RENBP, NFIC, ABCG1, USP16, PRDX1, NFIB, CCND1, PTGS2, HMOX1, HMGB1, MX1, CALB2, NOP53, NCAM2, NFIA, MMP9, TRIB1, IKZF1, DSCR4, MPL, PIK3CD, KMT2A, APOA1, OPN1SW, BCR, ABCB1, ITGAM, ITGA2B, TARDBP, PKNOX1, INHA, ADIPOQ, RASSF1, PML, PFKL, IL10RB, IL2RA, IL2, IL1RN, IMMT, IGFBP7, STIP1, PRDX3, IFNAR2, RELN, TP73, IFIT3, CFAP410, NAE1, BCAR1, GRIK1, NFIX, GJB2, DHFR, U2AF1, CTNNB1, CTNND1, SYP, DBN1, DCK, DLX4, XRCC1, CD63, DPYSL2, SORL1, CD59, TMX2-CTNND1, MYL7, CSTB, TCN2, CSF3, CSE1L, TYMS, H3P7, TWIST1, ERVH48-1, TTN, P2RY8, COMT, TSHR, TGFB1, TGM2, ESCO1, TNFRSF1A, TPO, SLC12A5, CDA, FLT3, RHD, FAM3B, GATA4, FN1, TREM2, MTOR, PICALM, ARHGEF5, TRRAP, MATR3, USP9X, TXN, VAMP8, PSG10P, POU5F1P4, TNFSF10, TP63, TYRP1, GATD3A, APOBEC3B, MIR590, CCR2, GDF15, TTR, MIR3197, AKR7A2, RCAN2, LOH19CR1, DENR, H3P9, TPTE, HSP90B1, TRH, TRPM2, TSC2, MIR486-1, FXR2, ACTR2, PDXK, DNM1L, POU5F1P3, MAGI2, TMEM72, ZEB2, SCRN1, PHYHIP, ADAMTS1, YWHAG, DSCAM-AS1, GATD3B, EIF2B4, ZMYM2, IL1RL1, EIF2B2, RNF103-CHMP3, AVSD1, LPAR2, UBA3, FAS-AS1, MAP3K14, WT1, XIST, ZFY, HAP1, BCL10, EIF2S2, MTRNR2L12, COX5A, RECQL4, ZNF587B, NTN1, EIF2AK3, MIR3196, NRIP1, ABCG2, UBE3A, USP5, SOD2-OT1, UTRN, UVRAG, USP7, LINC02605, VIPR1, BEST1, MIR1973, MCM3AP, PAX8, VPREB1, TET3, SDS, DCAF7, ACKR3, ENOSF1, KIF21A, SEPTIN11, PARD3, NPDC1, SLC12A9, PLSCR4, STRBP, ACTR3B, AICDA, LRRC47, NUFIP2, MRTFA, RNF213, MIA3, RTL1, DCTN4, RBM11, NT5C3A, PRRX2, TDP2, CHMP3, RIPPLY3, BRWD1, SETD4, PACC1, RIPK4, C21orf91, RBFOX1, TET2, PGPEP1, STX17, LSM2, PRM3, HPSE2, TAF8, AP5B1, UBXN11, SLC13A5, MYL12B, PRRT2, DSCR9, AHSA2P, PRDM16, VENTXP1, LYPD4, STRC, TMPRSS6, ARX, HEPACAM, BAGE2, TMEM241, GLIS2, COL25A1, FGFBP2, ARHGAP24, MED25, LPAL2, TET1, DERL1, TAS2R62P, NANOS3, WNK1, GORASP1, CPEB1, NOD2, SAMSN1, HSPA14, COPS4, EFS, CKAP4, NES, ARPP19, PPARGC1A, PSG8, SUB1, PRSS21, DHFR2, CXCR6, STMN2, MMRN1, MCF2L, ICOSLG, SYNM, ANGPTL2, CHL1, KHDRBS1, APH1A, SLC9A6, TUBB3, RACK1, PEMT, OLFM1, MCRS1, MAD2L2, PLF, MYL12A, CIB1, DPYSL4, MRPL28, GNLY, AHSA1, SPAG5, HEY2, TMEM131, MORC3, REM1, CRCP, APEX2, HPGDS, MIR145, SGSM3, IGHV1-12, NXT1, FAM215A, LGALS13, CNOT7, GMPPA, ZBTB21, IL22, GMNN, GPR162, B3GAT1, CKAP2, PLA2G2D, APPL1, MIR146A, CHD5, MIR17, MTHFD1L, MIR183, MIR191, POC1A, MIR199B, MIR30C1, NUP62, MIR30C2, DAPK2, A1BG, PTH, TNNT2, EDNRA, EEF1A2, EGFR, EGR2, EGR3, EIF2B1, ELANE, ELK1, ENG, ENSA, EPAS1, ERBB2, ERCC2, ERCC3, ERF, ESR1, EEF1A1, E2F1, HP, DSG1, NKX2-5, CYP2B6, CYP17A1, CYP19A1, DBH, DBP, DGCR, DMD, DNAH8, DNASE1, DNMT1, DNMT3A, DPYSL3, DRD4, ATN1, ESR2, FABP3, FABP5, FBN2, GPT, GPX1, GPX3, GSN, GTF2H1, GYPA, GYPB, GYPE, HSD17B10, HAS2, CFH, HINT1, HLA-B, HLA-DQA1, HNMT, GPR42, GPI, GJA1, FLT1, FCGR3A, FCGR3B, FEB1, FGFR1, FGFR3, FLNA, FMR1, GHR, FYN, GABPA, GAD1, GAP43, GDI2, GH1, CST3, CRP, CRMP1, BTG1, ARNT, ARSA, STS, ARSD, ASPA, SERPINC1, AZGP1, BAX, BCL2L1, BCL6, BDKRB1, BGN, BLVRA, BMI1, BRS3, AQP4, APOC2, APOA2, ADRA1A, SERPINA3, ACO1, ACVR1, ADAR, PARP1, PARP4, ADRA2B, APEX1, ADRB2, AGA, AGTR1, AHSG, AMPH, ANK1, BST2, C9, CREB1, CA2, CHRNA7, CHRNB2, CLU, CCR5, CNR1, COL4A3, COL6A3, COL7A1, COX8A, CP, CPE, CPOX, CPS1, CPT1B, CR2, CHRNA4, CHRNA3, CHAT, CDK1, CAMP, CASP1, RUNX1T1, CD247, CD14, CD38, CDK6, CENPB, CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN1C, CDKN2B, CEBPE, CECR, HNRNPA2B1, PRMT2, TLR4, PSMA5, PTPN4, PTPN11, PTPRF, PWP2, RAB4A, RARA, RBM4, RBP4, RCN1, RELA, BRD2, RPE65, RPL17, RPS19, RYR2, A2M, PSG5, HSPA4, PSEN2, PDYN, PGD, PIP4K2A, PLG, PLEK, PLTP, PRRX1, POLD1, PON1, POU5F1, PPP2CA, MAPK10, PRL, TMPRSS15, PSD, SETMAR, SFPQ, SRSF6, SH3BGRL, CDKL5, SYT1, TBX1, TCP1, TRBV20OR9-2, TEAD4, TERC, TFAM, TFCP2, TFF1, TG, THBS1, TIAM1, TIMP3, TLR2, HSPA13, STATH, STAT3, SLC6A4, SHBG, SHMT1, SHMT2, SHOX, SIM1, SLC5A3, SNAP25, STAT1, SNCA, FSCN1, SNRNP70, SOX11, SRY, SSTR4, PDGFB, PDE9A, PDE4C, MDM4, KCNE1, KCNJ15, KISS1, KNG1, KRT8, STMN1, LBP, LBR, LHCGR, LRP2, LTA4H, MAOA, MARK1, MBP, CD46, KCNA3, ITGAL, ISL1, IL7, HSPD1, ICAM1, IDE, IFNAR1, IGH, IL4, IL15, ISG20, IL16, IL17A, IDO1, INPP5D, INSL4, IRF1, MDM2, MME, PDE4B, MOS, NFKB1, NHS, NME1, NME2, NOS2, NPM1, NT5E, NTRK1, NR4A2, OCA2, PAH, PAK1, PAK3, PAX5, PCYT1A, NFE2L2, NFATC2, NEFH, RNR2, MPO, MRC1, MT2A, ATP6, ND3, MTNR1B, MYD88, NDUFV3, MYO9B, NACA, NAIP, NCAM1, NDUFA2, NDUFS3, H3P10
-
Doping At The 2007 Tour De France
Wikipedia
A blood transfusion is meant to increase the number of red blood cells in the body, improving oxygen flow from the lungs to the muscles. [25] Vinokourov rejected the failed test, blaming the anomaly on excessive blood flow in his thighs following a heavy collision earlier in the Tour. [25] Accordingly, he asked for his B sample to be tested; however, the lab test for locating blood cells from another donor in "old fashioned" homologous transfusions is considered fool-proof. [26] It was later revealed that he had also failed tests on his win of stage 15, and that his B sample had since returned "non-negative". [27] Astana responded by sacking Vinokourov. [28] Cristian Moreni [ edit ] Cristian Moreni Cofidis rider Moreni was placed 54th at the time he was withdrawn from the Tour and had participated in the rider protest prior to Stage 16. ... The move meant that neither Contador, the 2007 winner, nor third-place Levi Leipheimer , both of whom signed with the revamped Astana setup, were able to compete in the 2008 tour. [57] See also [ edit ] Wikinews has News related to this article: Tour de France: Alexander Vinokourov fails blood test Tour de France: Yellow jersey Rasmussen withdrawn Doping at the Tour de France Doping (sport) Blood doping List of doping cases in cycling References [ edit ] ^ "Doping incidents ahead of and during 2007 Tour de France" . The Associated Press. 2007-07-28 . Retrieved 2008-10-17 . ^ "Rasmussen Under Rabobank Investigation As Doping Scandal Rages On" . eFluxMedia. 30 July 2007. ... BBC News . 2007-11-27 . Retrieved 2007-11-28 . ^ "Cycling boss calls for life bans" .
-
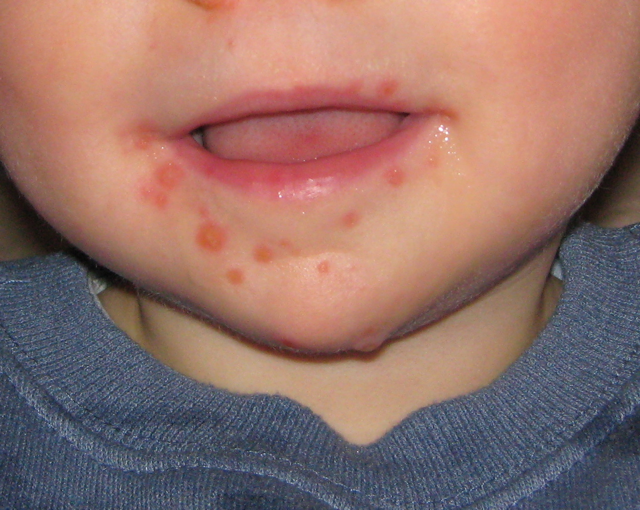
Hand, Foot, And Mouth Disease
Wikipedia
Other serious complications of HFMD include encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), or flaccid paralysis in rare circumstances. [17] [18] Fingernail and toenail loss have been reported in children 4–8 weeks after having HFMD. [4] The relationship between HFMD and the reported nail loss is unclear; however, it is temporary and nail growth resumes without treatment. [4] [25] Minor complications due to symptoms can occur such as dehydration, due to mouth sores causing discomfort with intake of foods and fluid. [26] Epidemiology [ edit ] Hand, foot and mouth disease most commonly occurs in children under the age of 10. [4] [18] It tends to occur in outbreaks during the spring, summer, and autumn seasons. [6] This is believed to be due to heat and humidity improving spread. [21] HFMD is more common in rural areas than urban areas; however, socioeconomic status and hygiene levels need to be considered. [27] Poor hygiene is a risk factor for HFMD. [28] [ better source needed ] Outbreaks have occurred in China , Japan , Hong Kong , the Republic of Korea , Malaysia , Singapore , Thailand , Taiwan , and Vietnam . [21] HFMD most commonly affects young children under the age of 10 and more often under the age of 5, but can also affect adults with varying symptoms. [19] Since 1997 there have been 71 large enterovirus outbreaks reported, mostly in East and South East Asia, primarily affecting children. [21] From the years 2008 to 2014, more than 1 million HFMD cases have been reported in China each year. [29] Outbreaks [ edit ] In 1997, an outbreak occurred in Sarawak of Malaysia with 600 cases and over 30 children died. [30] [31] [32] [33] In 1998, there was an outbreak in Taiwan , affecting mainly children. [34] There were 405 severe complications, and 78 children died. [35] The total number of cases in that epidemic is estimated to have been 1.5 million. [6] In 2008 an outbreak in China, beginning in March in Fuyang, Anhui , led to 25,000 infections, and 42 deaths, by May 13. [6] Similar outbreaks were reported in Singapore (more than 2,600 cases as of April 20, 2008), [36] Vietnam (2,300 cases, 11 deaths), [37] Mongolia (1,600 cases), [38] and Brunei (1053 cases from June–August 2008) [39] In 2009 17 children died in an outbreak during March and April 2009 in China's eastern Shandong Province , and 18 children died in the neighboring Henan Province . [40] Out of 115,000 reported cases in China from January to April, 773 were severe and 50 were fatal. [41] In 2010 in China, an outbreak occurred in southern China's Guangxi Autonomous Region as well as Guangdong, Henan, Hebei and Shandong provinces. ... PMID 27273688 . ^ "Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease" . WebMD . Retrieved November 28, 2017 . ^ Lei, Xiaobo; Cui, Sheng; Zhao, Zhendong; Wang, Jianwei (September 1, 2015).CA10, CXCL8, IL10, IL6, TNF, VDR, AQP4, IL18, IFNG, TLR3, OAS1, SCARB2, CCL2, IL22, VIP, CCL4L2, CERS1, ATG4B, TLR4, DDX58, IL37, ACTB, DLL1, SLC6A1, TLR7, TLR8, SCARA3, GDE1, DLL4, ROBO3, IL17F, MIR155HG, CCL4L1, MIR221, POTEF, TGFB1, REN, SELPLG, CCL4, ATP1A3, CASP3, CRP, FN1, GDF1, GZMB, HMGB1, IFNA1, IFNA13, IFNAR1, IFNAR2, IL4, IL13, IL17A, INSRR, MMP8, NM, NOTCH1, NOTCH2, PLXNA2, PLAAT4, ADRB1, S100B, PERCC1
-
Chronic Prostatitis/chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
Wikipedia
Recent studies have questioned the distinction between categories Ⅲa and Ⅲb, since both categories show evidence of inflammation if pus cells are ignored and other more subtle signs of inflammation, like cytokines , are measured. [25] In 2006, Chinese researchers found that men with categories Ⅲa and Ⅲb both had significantly and similarly raised levels of anti-inflammatory cytokine TGFβ1 and pro-inflammatory cytokine IFN-γ in their EPS when compared with controls; therefore measurement of these cytokines could be used to diagnose category Ⅲ prostatitis. [26] A 2010 study found that nerve growth factor could also be used as a biomarker of the condition. [27] For CP/CPPS patients, analysis of urine and expressed prostatic secretions for leukocytes is debatable, especially due to the fact that the differentiation between patients with inflammatory and non-inflammatory subgroups of CP/CPPS is not useful. [28] Serum PSA tests, routine imaging of the prostate, and tests for Chlamydia trachomatis and Ureaplasma provide no benefit for the patient. [28] Extraprostatic abdominal/pelvic tenderness is present in >50% of patients with chronic pelvic pain syndrome but only 7% of controls. [29] Healthy men have slightly more bacteria in their semen than men with CPPS. [30] The high prevalence of WBCs and positive bacterial cultures in the asymptomatic control population raises questions about the clinical usefulness of the standard Meares-Stamey four-glass test as a diagnostic tool in men with CP/CPPS. [30] By 2000, the use of the four-glass test by American urologists was rare, with only 4% using it regularly. [31] Men with CP/CPPS are more likely than the general population to suffer from chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), [32] and Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). ... Archived from the original on 2009-07-28 . Retrieved 2009-07-28 . The star of Monty Python and "A Fish Called Wanda" has been diagnosed with prostatitis, the inflammation of the prostate gland and is undergoing treatment. ^ Roger Ebert.
-
Shift Work Sleep Disorder
Wikipedia
To promote a healthy lifestyle, the American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommended that an adult have 7 or more hours of sleep per day. [8] Each year there are almost 100,000 deaths estimated in the U.S. because of medical errors . [8] Sleep deprivation and sleep disorders are factors that contribute significantly to these errors. [8] In the same article, the authors affirm that there is a high prevalence of sleepiness and symptoms of sleep disorders related to the circadian system in medical center nurses. [8] In a study done with around 1100 nurses, almost half of them (49%) reported sleeping less than 7 hours per day, a significant increase compared to national figures, in which 28% of people claimed to sleep less than 7 hours per night. [9] Having a lack of sleep can impact cognitive performance. [1] For example, it might become difficult to stay focused and concentrate, and reaction times might also be slowed down. [10] [1] SWSD might interfere with making decisions quickly, driving, or flying safely. [1] Sleep loss seen in shift workers greatly impairs cognitive performance, being awake for 24 hrs. straight results in a cognitive performance that is equal to a blood-alcohol of 0.10, which is over the legal limit in most states. [5] All of these factors can affect work efficiency and cause accidents. ... There is an inevitable degree of sleep deprivation associated with sudden transitions in sleep schedule. [26] The prevalence of SWSD is unclear because it is not often formally diagnosed but it is estimated to affect 5–10% of night and rotating workers. [27] [28] [3] There are various risk factors, including age.
-
Yaws
Wikipedia
Yaws eradication remained a priority in south-east Asia. [20] [26] Prior to the 2012-onwards WHO campaign, India launched its own national yaws elimination campaign which appears to have been successful. [26] [28] Certification for disease-free status requires an absence of the disease for at least five years. ... S2CID 1699547 . ^ Mitjà, O; Hays, R; Ipai, A; Penias, M; Paru, R; Fagaho, D; de Lazzari, E; Bassat, Q (Jan 28, 2012). "Single-dose azithromycin versus benzathine benzylpenicillin for treatment of yaws in children in Papua New Guinea: an open-label, non-inferiority, randomised trial".
-
Obesity In The United States
Wikipedia
In 1977, 18% of an average person's food was consumed outside the home; in 1996, this had risen to 32%. [28] Contributing factors [ edit ] Obesity rates of adult females, 1960–2015 Numerous studies have attempted to identify contributing factors for obesity in the United States. ... "This suggests that people from the South come closer to telling the truth than people from other regions, perhaps because there's not the social stigma of being obese in the South as there is in other regions." [76] The area of the United States with the highest obesity rate is American Samoa (75% obese and 95% overweight). [77] States , district , & territories Obesity rank Obese adults (mid- 2000s ) Obese adults (2020) [78] [73] [79] Overweight (incl. obese) adults (mid- 2000s ) Obese children and adolescents (mid- 2000s ) [80] Alabama 5 30.1% 36.3% 65.4% 16.7% Alaska 9 27.3% 34.2% 64.5% 11.1% American Samoa — — 75% [77] 95% [81] 35% [77] [82] Arizona 30 23.3% 29.5% 59.5% 12.2% Arkansas 7 28.1% 35.0% 64.7% 16.4% California 48 23.1% 25.1% 59.4% 13.2% Colorado 51 21.0% 22.6% 55.0% 9.9% Connecticut 42 20.8% 26.9% 58.7% 12.3% Delaware 23 25.9% 31.8% 63.9% 22.8% District of Columbia 50 22.1% 23.0% 55.0% 14.8% Florida 35 23.3% 28.4% 60.8% 14.4% Georgia 24 27.5% 31.6% 63.3% 16.4% Guam — — 28.3% — 22% [83] Hawaii 49 20.7% 23.8% 55.3% 13.3% Idaho 32 24.6% 29.3% 61.4% 10.1% Illinois 27 25.3% 31.1% 61.8% 15.8% Indiana 12 27.5% 33.6% 62.8% 15.6% Iowa 4 26.3% 36.4% 63.4% 12.5% Kansas 18 25.8% 32.4% 62.3% 14.0% Kentucky 8 28.4% 34.3% 66.8% 20.6% Louisiana 6 29.5% 36.2% 64.2% 17.2% Maine 33 23.7% 29.1% 60.8% 12.7% Maryland 26 25.2% 31.3% 61.5% 13.3% Massachusetts 44 20.9% 25.9% 56.8% 13.6% Michigan 19 27.7% 32.3% 63.9% 14.5% Minnesota 35 24.8% 28.4% 61.9% 10.1% Mississippi 2 34.4% 37.3% 67.4% 17.8% Missouri 17 27.4% 32.5% 63.3% 15.6% Montana 46 21.7% 25.3% 59.6% 11.1% Nebraska 15 26.5% 32.8% 63.9% 11.9% Nevada 43 23.6% 26.7% 61.8% 12.4% New Hampshire 38 23.6% 28.1% 60.8% 12.9% New Jersey 41 22.9% 27.3% 60.5% 13.7% New Mexico 35 23.3% 28.4% 60.3% 16.8% New York 45 23.5% 25.7% 60.0% 15.3% North Carolina 20 27.1% 32.1% 63.4% 19.3% North Dakota 13 25.9% 33.2% 64.5% 12.1% Northern Mariana Islands — — — — 16% [84] Ohio 11 26.9% 33.8% 63.3% 14.2% Oklahoma 3 28.1% 36.5% 64.2% 15.4% Oregon 31 25.0% 29.4% 60.8% 14.1% Pennsylvania 24 25.7% 31.6% 61.9% 13.3% Puerto Rico — — 30.7% — 26% [85] [86] Rhode Island 29 21.4% 30.0% 60.4% 11.9% South Carolina 10 29.2% 34.1% 65.1% 18.9% South Dakota 22 26.1% 31.9% 64.2% 12.1% Tennessee 15 29.0% 32.8% 65.0% 20.0% Texas 14 27.2% 33.0% 64.1% 19.1% Utah 46 21.8% 25.3% 56.4% 8.5% Vermont 40 21.1% 27.6% 56.9% 11.3% Virgin Islands (U.S.) — — 32.5% — — Virginia 28 25.2% 30.1% 61.6% 13.8% Washington 39 24.5% 27.7% 60.7% 10.8% West Virginia 1 30.6% 38.1% 66.8% 20.9% Wisconsin 21 25.5% 32.0% 62.4% 13.5% Wyoming 34 24.0% 28.8% 61.7% 8.7% ^ Except territories, whose data is from the late 2000s to 2010s Total costs to the US [ edit ] There has been an increase in obesity-related medical problems, including type II diabetes , hypertension , cardiovascular disease , and disability. [87] [17] In particular, diabetes has become the seventh leading cause of death in the United States, [88] with the U.S. ... NHANES Table" (PDF) . stateofobesity.org . p. 16 . Retrieved February 28, 2019 . ^ a b c "StateofObesity 2016. ... NHANES Table" (PDF) . stateofobesity.org . p. 17 . Retrieved February 28, 2019 . ^ "Summary Health Statistics: National Health Interview Survey, 2015" (PDF) .