- Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Wikipedia
- Atypical Trigeminal Neuralgia Wikipedia
-
Cramp
Wikipedia
PMID 7431559 . Archived from the original on 28 December 2010 . Retrieved 26 October 2011 . ^ Schwellnus MP, Nicol J, Laubscher R, Noakes TD (2004).
-
Mirror-Touch Synesthesia
Wikipedia
"Somatosensory Activations During the Observation of Touch and a Case of Vision-Touch Synaesthesia" . Brain . 128 (28): 1571–1583. doi : 10.1093/brain/awh500 .
-
Opisthorchiasis
Wikipedia
The Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health . 28 Suppl 1: 65–72. PMID 9656352 . . ^ "Opisthorchiasis - Treatment Information" .
-
Female Genital Mutilation In Sierra Leone
Wikipedia
Female genital mutilation in Sierra Leone (also known as female genital cutting) is the common practice of removing all or part of the female's genitalia for cultural and religious initiation purposes, or as a custom to prepare them for marriage. Sierra Leone is one of 28 countries in Africa where female genital mutilation (FGM) is known to be practiced. [1] Contents 1 Cultural reasons 2 Prevalence 3 Health effects 4 Community response 5 See also 6 References Cultural reasons [ edit ] FGM is regularly performed in Sierra Leone. [2] The reason that FGM is common in Sierra Leone is because FGM is practiced in a ‘secret society’ called the bondo secret society.
- Angiostrongyliasis Wikipedia
-
Coronary Vasospasm
Wikipedia
"Ischaemia with no obstructive coronary arteries" . Netherlands Heart Journal . 28 (Suppl 1): 66–72. doi : 10.1007/s12471-020-01451-9 .
-
Hyperacusis
Wikipedia
His story was told in BuzzFeed . [27] Musician Stephin Merritt has monaural hyperacusis in his left ear, which influences the instrumentation of his band, The Magnetic Fields , leads him to wear earplugs during performances and to cover his affected ear during audience applause. [ citation needed ] Musician Laura Ballance of Superchunk has hyperacusis and no longer tours with the band. [ citation needed ] American politician, activist, and film producer Michael Huffington has mild hyperacusis and underwent sound therapy after finding that running tap water caused ear pain. [28] Russian communist revolutionary, politician, and political theorist Vladimir Lenin was reported seriously ill by the latter half of 1921, having hyperacusis and symptoms such as regular headache and insomnia. [29] Musician Chris Singleton had hyperacusis, but made a full recovery. [30] His story was told in The Independent . [31] Musician Peter Silberman of The Antlers had hyperacusis and tinnitus which put his musical career on hold, but was quoted saying it died down to a 'manageable level' [32] He has now resumed his musical career.
-
Chronic Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia
Wikipedia
"Mutation of POLG is associated with progressive external ophthalmoplegia characterized by mtDNA deletions". Nature Genetics . 28 (3): 211–212. doi : 10.1038/90034 .POLG, TRNL1, TRNS1, TRNN, TRNL2, SOD2, SOD1, IL1A, IL1B, TWNK, SLC25A4, POLG2, RRM2B, TK2, TYMP, TOP3A, C1QBP, DGUOK, APTX, RNASEH1, TRNK, ATP8, ATXN3, MGME1, TRNT, DNA2, PRPF6, CHMP1B, OPA1, TRNI, AFG3L2, RPTOR, FGF21, MAPKAP1, PRIMPOL, COX2, SPG7, SCO2, TYR, TFAM, CYTB, PTGS2, POLRMT, NPTX2, GJB1, TNPO1, TRNM, TRNE, RNR2, MTCO2P12
-
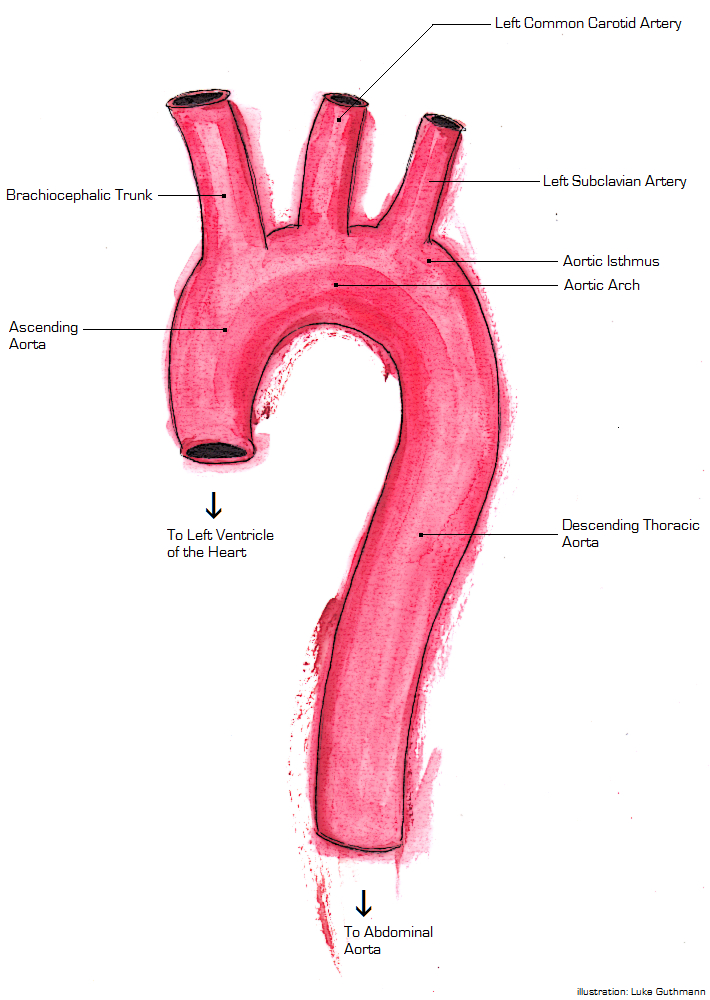
Thoracic Aorta Injury
Wikipedia
If the patient does develop a more severe injury including a full thickness injury through the media layer then the patient should be treated with surgery. [8] Outcomes [ edit ] Thoracic aortic injury is the 2nd leading cause of death involving both blunt trauma. 80% of patients that have a thoracic aortic injury will die immediately. [4] Of the patients that do make it to be evaluated only 50% will survive 24 hours. [1] Of the patients that do survive the first 24 hours 14% develop paraplegia. [6] Epidemiology [ edit ] Thoracic aortic injury is most commonly caused by a penetrating trauma in up to 90% of cases. [10] Of these cases around 28% are confined to the thoracic portion of the aorta including the ascending aorta, aorta arch, and the descending aorta. [10] Of the thoracic aortic injuries the ligament arteriosum is the most common location followed by the portion of the aorta after the origin of the left subclavian artery. [10] The most common mechanism leading to thoracic aortic injury is a motor vehicle collision.
-
Periapical Cyst
Wikipedia
Journal of Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry . 28 (3): 203–8. doi : 10.4103/0970-4388.73795 .TNF, TGFB1, MMP9, TP53, FN1, IL6, TIMP1, CXCL8, IFNG, HSPB2, HSPB1, HSPB3, BCL2, PTGS2, MMP1, CD68, MMP2, PTCH1, IL1B, SPP1, SMO, TIMP2, VEGFA, VDR, NME1, TP63, TNFRSF11A, CD83, CD163, PDPN, B3GAT1, HSPA14, IL17D, MYDGF, IL27, LGALS7B, TNFRSF11B, MME, COX2, HSPD1, CASP3, CD8A, CD14, CDH1, EDA, FGF2, FHIT, GLI1, HIF1A, HSPA4, HSPG2, MMP13, ICAM1, IL1A, IL10, IL17A, KRT13, LGALS1, LGALS3, LGALS7, MDM2, BTF3P11, MTCO2P12
- Neurasthenia Wikipedia
- Bacteriuria Wikipedia
-
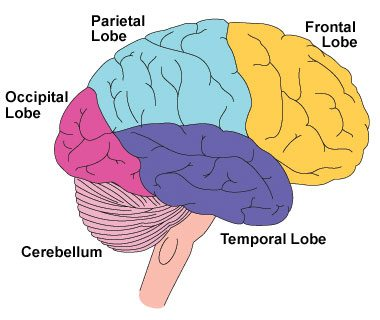
Frontal Lobe Disorder
Wikipedia
External links [ edit ] Classification D ICD - 10 : F07 External resources eMedicine : article/1135866 Scholia has a topic profile for Frontal lobe disorder . v t e Anatomy of the cerebral cortex of the human brain Frontal lobe Superolateral Prefrontal Superior frontal gyrus 4 6 8 Middle frontal gyrus 9 10 46 Inferior frontal gyrus : 11 47 - Pars orbitalis Broca's area 44 - Pars opercularis 45 - Pars triangularis Superior frontal sulcus Inferior frontal sulcus Precentral Precentral gyrus Precentral sulcus Medial/inferior Prefrontal Superior frontal gyrus 4 6 Medial frontal gyrus 8 9 Paraterminal gyrus / Paraolfactory area 12 Straight gyrus 11 Orbital gyri / Orbitofrontal cortex 10 11 12 Ventromedial prefrontal cortex 10 Subcallosal area 25 Olfactory sulcus Orbital sulcus Precentral Paracentral lobule 4 Paracentral sulcus Both Primary motor cortex 4 Premotor cortex 6 Supplementary motor area 6 Supplementary eye field 6 Frontal eye fields 8 Parietal lobe Superolateral Superior parietal lobule 5 7 Inferior parietal lobule 40 - Supramarginal gyrus 39 - Angular gyrus Parietal operculum 43 Intraparietal sulcus Medial/inferior Paracentral lobule 1 2 3 5 Precuneus 7 Marginal sulcus Both Postcentral gyrus / Primary somatosensory cortex 3, 1 and 2 Secondary somatosensory cortex 5 Posterior parietal cortex 7 Occipital lobe Superolateral Occipital pole of cerebrum Lateral occipital gyrus 18 19 Lunate sulcus Transverse occipital sulcus Medial/inferior Visual cortex 17 Cuneus Lingual gyrus Calcarine sulcus Temporal lobe Superolateral Transverse temporal gyrus / Auditory cortex 41 and 42 Superior temporal gyrus 38 22 / Wernicke's area Middle temporal gyrus 21 Superior temporal sulcus Medial/inferior Fusiform gyrus 37 Medial temporal lobe 27 28 34 35 36 Inferior temporal gyrus 20 Inferior temporal sulcus Interlobar sulci/fissures Superolateral Central (frontal+parietal) Lateral (frontal+parietal+temporal) Parieto-occipital Preoccipital notch Medial/inferior Longitudinal fissure Cingulate (frontal+cingulate) Collateral (temporal+occipital) Callosal sulcus Limbic lobe Parahippocampal gyrus anterior Entorhinal cortex Perirhinal cortex Postrhinal cortex Posterior parahippocampal gyrus Prepyriform area Cingulate cortex / gyrus Subgenual area 25 Anterior cingulate 24 32 33 Posterior cingulate 23 31 Isthmus of cingulate gyrus : Retrosplenial cortex 26 29 30 Hippocampal formation Hippocampal sulcus Fimbria of hippocampus Dentate gyrus Rhinal sulcus Other Indusium griseum Uncus Amygdala Insular cortex Insular cortex General Operculum Poles of cerebral hemispheres Some categorizations are approximations, and some Brodmann areas span gyri. v t e Medicine Specialties and subspecialties Surgery Cardiac surgery Cardiothoracic surgery Colorectal surgery Eye surgery General surgery Neurosurgery Oral and maxillofacial surgery Orthopedic surgery Hand surgery Otolaryngology ENT Pediatric surgery Plastic surgery Reproductive surgery Surgical oncology Transplant surgery Trauma surgery Urology Andrology Vascular surgery Internal medicine Allergy / Immunology Angiology Cardiology Endocrinology Gastroenterology Hepatology Geriatrics Hematology Hospital medicine Infectious disease Nephrology Oncology Pulmonology Rheumatology Obstetrics and gynaecology Gynaecology Gynecologic oncology Maternal–fetal medicine Obstetrics Reproductive endocrinology and infertility Urogynecology Diagnostic Radiology Interventional radiology Nuclear medicine Pathology Anatomical Clinical pathology Clinical chemistry Cytopathology Medical microbiology Transfusion medicine Other Addiction medicine Adolescent medicine Anesthesiology Dermatology Disaster medicine Diving medicine Emergency medicine Mass gathering medicine Family medicine General practice Hospital medicine Intensive care medicine Medical genetics Narcology Neurology Clinical neurophysiology Occupational medicine Ophthalmology Oral medicine Pain management Palliative care Pediatrics Neonatology Physical medicine and rehabilitation PM&R Preventive medicine Psychiatry Addiction psychiatry Radiation oncology Reproductive medicine Sexual medicine Sleep medicine Sports medicine Transplantation medicine Tropical medicine Travel medicine Venereology Medical education Medical school Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery Bachelor of Medical Sciences Master of Medicine Master of Surgery Doctor of Medicine Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine MD–PhD Related topics Alternative medicine Allied health Dentistry Podiatry Pharmacy Physiotherapy Molecular oncology Nanomedicine Personalized medicine Public health Rural health Therapy Traditional medicine Veterinary medicine Physician Chief physician History of medicine Book Category Commons Wikiproject Portal Outline
- Technophobia Wikipedia
-
Noonan Syndrome With Multiple Lentigines
Wikipedia
"Acute myelomonocytic leukemia in a boy with LEOPARD syndrome (PTPN11 gene mutation positive)". J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol . 28 (3): 123–5. doi : 10.1097/01.mph.0000199590.21797.0b .PTPN11, RAF1, BRAF, MAP2K1, SOS1, PTEN, KRAS, HRAS, SHOC2, EPHA2, SOS2, RRAS, RIT1, LZTR1, RASA2, RASA1, NRAS, PPP1R13L, MRAS, MAP2K2, PPP1CB, A2ML1, AKT1, MAPK3, MTOR, NF1, PIK3CG, TSC1, CDC73, TESC, SASH1, ZHX2, DSP, EGF, EPHB2, FBN1, MAPK1, FXN, SLC12A3, GAB1, IRS1, NFATC4, PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PIK3CD, MAP2K7, ACP1
-
Muscular Dystrophy, Limb-Girdle, Autosomal Recessive 5
Omim
Of the 93 cases, 75 came from 17 families with affected persons of both sexes and the other 18 came from 11 families with only girls affected. The 28 kindreds included 45 pairs of parents with myopathic children.
-
Gastrointestinal Defects And Immunodeficiency Syndrome
Omim
Of 13 affected individuals, 8 were alive at the time of the report, with the 3 oldest being 14, 28, and 50 years of age. Lemoine et al. (2014) also studied a 2-year-old boy from an unrelated family who had a similar but milder phenotype, with protracted neonatal bloody diarrhea and recurrent anal abscesses.
-
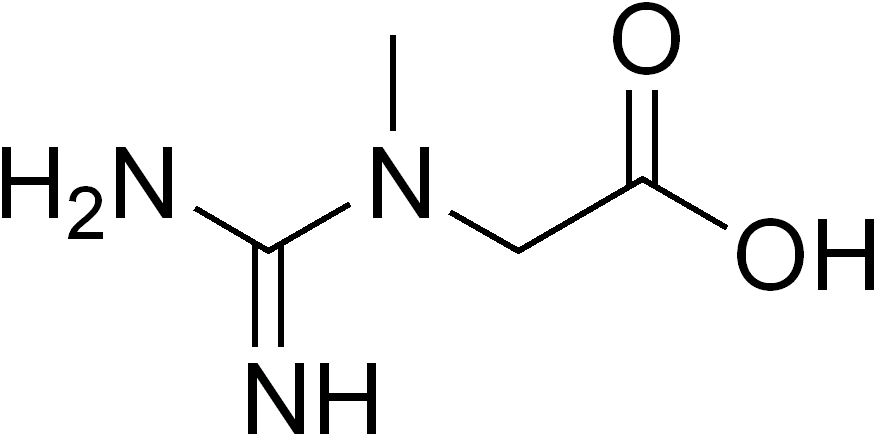
Cerebral Creatine Deficiency Syndrome 1
Omim
A total of 10 patients (36%) demonstrated response to treatment, manifested by either an increase in cerebral creatine or improved clinical parameters. Seven of the 28 patients had quantified pre- and posttreatment creatine, and it was significantly increased posttreatment.