-
Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis
Wikipedia
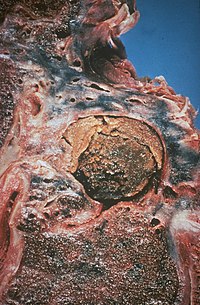
Most commonly, pre-existing pulmonary cavities from other diseases such as tuberculosis become colonised with Aspergillus conidia which have been inhaled—humans inhale between 1,000 and 10 billion spores per day, of which A. fumigatus is the most common. [27] Aspergillomas themselves usually form in existing cavities but the cavities may form directly from chronic pulmonary aspergillosis. [8] People with pulmonary tuberculosis with a cavity larger than 2 cm appear to have a 20% increased risk of developing chronic pulmonary aspergillosis. [28] It is postulated that conidia , once inhaled, are attacked by the host immune defences—specifically phagocytes and alveolar macrophage resident in the small airways.
- Gastric Antral Vascular Ectasia Wikipedia
-
Cavernous Hemangioma
Wikipedia
The statistics for this are very broad, ranging from 4–23% a year. [25] Additional studies suggest that women and patients under the age of 40 are at higher risk of bleeding, but similar conducted studies did not reach the same conclusion. [25] However, when cavernous hemangiomas are completely excised, there is very little risk of growth or rebleeding. [27] In terms of life expectancy, not enough data has been collected on patients with this malformation in order to provide a representative statistical analysis. [15] Epidemiology [ edit ] The true incidence of cavernous hemangiomas is difficult to estimate because they are frequently misdiagnosed as other venous malformations. [28] Cavernous hemangiomas of the brain and spinal cord (cerebral cavernous hemangiomas (malformations) (CCM)), can appear at all ages but usually occur in the third to fourth decade of a person's life with no sexual preference.
-
Indigestion
Wikipedia
In a recent multicenter U.S. trial that randomized 240 patients to treatment or placebo, and followed patients for 12 months, 28% of treated patients versus 23% of those receiving placebo reported relief of symptoms at the 12-month follow-up.IFNG, CRH, GNB3, SLC6A4, TRPV1, S100A8, GAST, IL1B, ATP12A, CYP2C19, SSTR3, MIF, ATP4A, IL1RN, TNF, TPH1, TGFB1, SYMPK, SEMA4D, TP53, AGA, CELA3B, KCNIP3, SCN10A, UGT1A9, CHD7, CYSLTR2, IL17F, SLCO6A1, VMA21, GSTK1, MIR325, GGTLC5P, GGTLC3, GGT2, FOXP3, SLC26A4, PTGS2, PTGS1, CD14, CHGA, COMT, CTBP1, CYBA, DECR1, FAP, FHIT, GABPA, GGT1, PRLHR, HLA-DQB1, HP, HTR3A, IL17A, MCM5, NFE2L2, SERPINE1, SERPINB2, PPY, PTGDS, GGTLC4P
-
Transcortical Motor Aphasia
Wikipedia
Since the lesion that results in TMoA usually occurs in the watershed area and does not directly involve the areas of the brain responsible for general language abilities, prognosis for these patients is good overall. [1] Other factors that determine a patient's prognosis include age, education prior to the stroke, gender, motivation, and support. [28] See also [ edit ] Transcortical sensory aphasia References [ edit ] ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x Brookshire, R.
-
Schizotypal Personality Disorder
Wikipedia
The study did not address homeless people who do not show up at drop-in centres. [28] See also [ edit ] Psychology portal Boundaries of the mind DSM-5 codes (personality disorders) ICD-10 codes (personality disorders) Paranoid personality disorder Schizoid personality disorder Schizotypy References [ edit ] ^ Schacter, Daniel L., Daniel T.
-
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
Wikipedia
"The Utility of a Diagnostic Scoring System for Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation". Critical Care Clinics . 28 (3): 378–88. doi : 10.1016/j.ccc.2012.04.004 .F3, F2, THBD, PROC, SERPINC1, OXT, F7, SERPINE1, IL6, TFPI, PLAT, FGA, PROS1, SERPIND1, NUMA1, NPM1, CFI, BCOR, NLRC4, CFH, NABP1, CD46, STAT5B, PML, TBL1XR1, ZBTB16, STAT3, FIP1L1, PRKAR1A, HELLPAR, RARA, IRF2BP2, HMGB1, PC, TNF, F10, MBL2, MPO, COX8A, BTBD8, OTOR, SLC25A10, ALB, TLR4, ZFP36, NCAM1, PLG, ADAMTS13, F5, ANGPT2, CD34, COLEC11, EGF, IL10, SH3BP4, SLC17A5, FCRL6, RN7SL263P, TEK, CABIN1, PGR-AS1, C20orf181, MIR122, ASPG, VEGFA, VTN, TAT, VWF, IL4I1, PROCR, RNF34, CLDN10, ARTN, DNAI2, RHOF, MBL3P, AGRP, TAL1, STIL, HGF, GPT, F13A1, F2R, EPHB2, EGFR, MAPK14, CRP, CPB2, COL4A2, CEACAM8, CD14, VPS51, BRAF, APOH, ANXA5, ALK, HLA-DOA, HMOX1, IFNG, PRH2, PMEL, SELL, SDC1, PTAFR, MASP1, MAPK8, MAPK1, PRH1, IL1B, PLD1, NRAS, MUC1, MMP10, ATXN3, MB, IL7, LINC02605
-
Health Effects Of Tattoos
Wikipedia
"Red tattoo reactions". Clin Exp Dermatol . 28 (5): 508–10. doi : 10.1046/j.1365-2230.2003.01358.x .
-
Ventricular Tachycardia
Wikipedia
Critical Care Nursing Clinics of North America . 28 (3): 317–29. doi : 10.1016/j.cnc.2016.04.004 .RYR2, CASQ2, ABCC9, SCN5A, LMNA, KCNJ2, TNNT2, KCNJ8, NOS3, EPO, NPPB, FKBP1B, PKP2, TMEM43, DSG2, DSP, HCN4, TPM1, MYL2, JUP, TECRL, BTNL2, NDUFB11, MYH7, TRDN, CTNNA3, TTN, RYR1, NAA10, GYG1, CSRP3, HLA-DRB1, ACADVL, CALM3, CALM2, CALM1, CACNA1S, SLC25A20, GJA1, KCNH2, CALR, SLC6A8, CALCR, ACE, SCD, KCNQ1, EDN1, SCN4A, MTMR11, NOS1AP, CAD, PART1, FXR1, TRPV1, POU2F3, GNAS, CACNA1C, KCNIP2, ARVD3, ANK2, CHPT1, GOLPH3, FKRP, FSD1, AGT, IRX3, DHDDS, FSD1L, ADRB1, MIR145, SEC1P, LUC7L3, ELOB, TJP1, ACTN2, KCNE1, FUT1, FLNC, KCNK2, FGF12, LRP5, MECP2, MSR1, COX2, PTK2B, FABP4, F5, PDE4B, PLN, TGFB3, POR, PTGS2, PTPN11, REN, RLN2, CYBB, SCN4B, CTNNB1, SKP1, ELOC, GNAQ, ELOA, TCF7L2, MTCO2P12
-
Hypospadias
Wikipedia
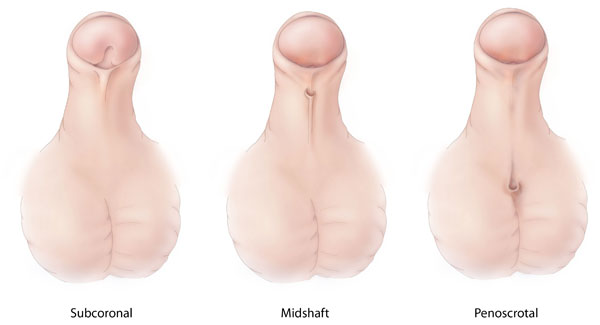
This procedure can be used for all distal hypospadias repairs, with complications afterwards expected in less than 10% of cases. [25] [26] Less consensus exists regarding proximal hypospadias repair. [27] TIP repair can be used when the penis is straight or has mild downward curvature, with success in 85%. [25] Alternatively, the urinary channel can be reconstructed using the foreskin, with reported success in from 55% to 75%. [28] Most distal and many proximal hypospadias are corrected in a single operation.DGKK, HSD3B2, MAMLD1, ATF3, HOXA13, HOXD13, GLI3, HHIP, FGF10, FGFR2, FGF8, AR, NR5A1, SRY, CYP17A1, MID1, WT1, SOX9, MAP3K1, TMEM70, HAAO, HUWE1, MED12, ABL1, WASHC5, FIG4, ZMPSTE24, CUL7, PTDSS1, KIAA0586, TMEM94, PQBP1, KDM5B, APC2, KLHL41, MAD2L2, DLL3, SEC24C, CPLX1, MAPRE2, POLR3A, EXOC3, CILK1, OBSL1, SPECC1L, ZFPM2, GRIP1, PIGN, PHACTR2, TAX1BP1, PEX16, COG1, KDM6A, UFD1, UBE2A, UBA1, HIRA, NKX2-1, TFAP2A, HNF1B, TBX1, VAMP7, STAR, ACTA1, SSR4, SRD5A2, SOX2, SMS, SKI, WHCR, NSD2, NELFA, OGT, SMC3, NIPBL, PEX11B, DCHS1, TP63, KCNAB2, PEX3, CUL4B, WNT5A, CDC45, NAA10, SMC1A, MKKS, KMT2D, XRCC2, WNT7A, ORC6, FBXL4, RTTN, MED25, TTC8, ATPAF2, HES7, SLX4, BRIP1, CCDC8, CDCA7, CDT1, KLHL40, B9D2, FRAS1, CSPP1, EHMT1, PALB2, FAT4, ALG12, DNAJC19, EVC2, PRDM16, HYLS1, KIF7, FREM2, FLG-AS1, HOXA-AS2, RSPO1, H19, JMJD1C, TUBB, RIPPLY2, TAPT1, UBR1, ARX, ESCO2, MESP2, B3GLCT, CCDC26, NSD1, PIEZO2, SIN3A, TBX22, FGFRL1, WWOX, SUFU, DYNC2LI1, DACT1, RLIM, GMNN, UBE2T, NDUFB11, CCDC59, SETD2, CCDC22, GREM1, RREB1, KIFBP, SETBP1, WNT4, SAMD9, EEFSEC, MCTP2, DMRT3, FANCM, WDR35, ARID1B, GATAD2B, LMOD3, HDAC8, ERMARD, BCOR, VAC14, PEX26, FANCI, SETD5, RFWD3, FANCL, NSUN2, SALL1, DENND2B, RPL35A, GPC3, FANCD2, FANCE, FANCB, FANCF, FANCG, GPC4, FGFR1, FOXC1, FLG, FLNA, MTOR, FZD2, GABRD, GATA4, GLI1, FANCA, GP1BB, RPL10, HBA1, HBA2, HCCS, MNX1, HNF4A, HOXA3, HOXA4, IGF2, KCNMA1, KRAS, LETM1, LFNG, FANCC, EVC, LMNA, CDKN1C, ADK, NR0B1, ARCN1, ARVCF, ZFHX3, RERE, ATR, ATRX, BRCA1, BRAF, BRCA2, BUB1B, CDC6, CDC42, CHRNG, ERCC4, COL3A1, COMT, COX7B, CREBBP, CTBP1, CYB5A, CYP21A2, DHCR7, DKC1, DNAH6, DVL1, DVL3, EFNB1, EP300, LIG4, KCNMA1-AS1, PSPH, PEX10, PEX6, PEX1, NEB, RAF1, PEX5, RAD51C, RAD51, NOTCH2, SIX6, ORC1, RAD21, ORC4, PAX6, RAC1, PCNT, RAP1A, RAP1B, PTPN11, POLE, SMAD4, PRKAR1A, MECP2, POR, PEX14, KMT2A, RBBP8, PEX19, PDE4D, PITX2, PEX13, PEX2, PEX12, ESR1, ESR2, CYP19A1, BMP7, HSD17B3, CYP1A1, FKBP4, TGFB1, WTIP, GSTM1, ARNT2, GSTT1, SRD5A1, INSL3, MMP11, ZEB2, TGFBR2, MAPK9, DHDDS, CYP1B1, CYP2B6, CYP11A1, RNF128, IRX6, FLAD1, SCARB1, TGFBR1, KLF6, MIR145, SHH, HSD17B13, AFP, AGRP, RMRP, AHR, AKT1, AMH, ARSD, SOD1, PRSS3P2, DOCK11, CD44, STAT3, DHRS11, MAFB, MAPK8, CYP27B1, ARTN, NHS, ZMYM3, NFE2L2, PLA2G15, EIF2AK3, WTAP, MYH11, MYBPH, MTHFR, HOXB6, DKK1, MSD, TPPP, IRF6, JUN, JUNB, JUND, LAMA5, EDIL3, LHCGR, GABPA, CD207, FOSB, CHD7, DMD, PROK2, UROD, PIP, EFNB2, CHPT1, ELN, EMX2, PIK3CG, PIK3CB, FOS, EYA1, PIK3CA, SF1, ZFY, PTK2B, BNC2, PDGFRA, HSD17B7, WT1-AS, PIK3CD
-
Hyperparathyroidism
Wikipedia
Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology . 28 (2): 257–9. doi : 10.1111/jdv.12187 .CASR, CDC73, MEN1, CCND1, PTH1R, VDR, RET, CDKN1B, CDKN2C, ACTG2, FOXI1, SLC26A4, OCRL, KCNJ10, GNAS, PTH, CDKN1A, CDKN2B, FGF23, HPT, LEP, CTNNB1, TNFRSF11B, CALCA, KL, GCM2, IL6, PHEX, EGFR, GAST, AP2S1, WT1, GNA11, DCTN6, VHL, WNT10B, ZNRD2, SPAG11B, TRIM13, RGS5, ZNF197, NR1I3, MAFK, TBX4, SEPHS1, USP6, TNFSF11, EEF1E1, TMED7, PDSS1, HPGDS, H3P12, PPR1, TMED7-TICAM2, SPAG11A, CXADRP1, MIR25, TICAM2, SEMA3D, HT, PTRH1, TPPP2, CORO7, APC, LAMTOR1, ATRAID, UBE2I, SOST, ARR3, SLC12A1, TNF, BTF3P11, MTHFR, MSH3, ABCC1, MDM4, SMAD4, LEPR, IL17A, IL6R, IFI27, HTC2, HRAS, CFL1, G6PD, FECH, EZH2, DMP1, ACE, PCNA, ABCB1, TCF21, PLCB3, HNF1B, SST, SPG7, SMS, CXADR, SDHD, SDHB, CCL2, BMPR1A, BRCA2, PTHLH, PTGS2, AMELX, PTGER2, PSMD9, PRKAR1A, PPY, H3P23
-
Ullrich Congenital Muscular Dystrophy 1
Omim
The most commonly observed mutation was G284R in the COL6A1 gene (120220.0012), found in 28 cases with variable phenotypes. Glycine substitutions in the TH domain were dominantly acting in 96% of cases, and recessive mutations tended to occur in the C-terminal end of the TH domain.
-
Rolandic Epilepsy
Wikipedia
The traumatizing, sometimes long-lasting effect on parents is significant. [27] It is unclear if there are any benefits to clobazam over other seizure medications. [28] Prognosis [ edit ] The prognosis for Rolandic seizures is invariably excellent, with probably less than 2% risk of developing absence seizures and less often GTCS in adult life. [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] Remission usually occurs within 2–4 years from onset and before the age of 16 years.GRIN2A, SRPX2, GABRG2, KCNQ3, SCN1A, RBFOX3, RBFOX1, SCN9A, CNTNAP2, IER3IP1, CPA6, TBC1D24, ASAH1, PCDH19, PLCB1, KCNT1, SNIP1, STRADA, PRICKLE2, SCN1A-AS1, SZT2, SIK1B, SCN1B, CHD2, GRIN1, RELN, SCN2A, SLC2A1, SLC6A1, SPTAN1, EPM2A, SCARB2, DEPDC5, CSTB, ELP4, KCNQ2, FMR1, ECT, MDGA2, SLC12A6, SHANK3, ATP1A2, DISC1, RBFOX2, ELP1, SEMA3C
-
Lordosis
Wikipedia
"Arthrogenic neuromusculature inhibition: A foundational investigation of existence in the hip joint". Clinical Biomechanics . 28 (5): 171–77. doi : 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2012.11.014 .SGCA, CAPN3, ACP5, SPEG, HERC1, BAZ1B, HACD1, TRIP11, EIF2AK3, GTF2IRD1, CUL7, KLHL41, PPM1D, AGPAT2, COLEC10, POP1, RAB3GAP1, SYNE2, EXOC6B, SYNGAP1, COLQ, SYNE1, TPM2, ACTA1, SCN9A, SGCG, TBX6, TFAP2A, TGFB1, TPM3, DYSF, TRPS1, TTN, TWIST1, VCP, CLIP2, NAA10, BICD2, SMCHD1, RMRP, PLEKHG5, TRAPPC11, MTMR14, WNK1, COLEC11, FKRP, TMEM43, CCDC8, SLC10A7, GNPTG, KLC4, CANT1, B3GALT6, AMER1, CAVIN1, KY, TRPV4, SELENON, OBSL1, LMOD3, RAB3GAP2, BSCL2, TBL2, POMT2, SMARCAL1, NSDHL, INPP5K, MAP3K20, RETREG1, DYM, BCOR, SETD5, POMGNT1, IARS2, ZC4H2, RYR1, SCN4A, RFC2, GLB1, FRG1, FN1, FLNB, FHL1, FGFR2, FGFR3, FKTN, EMD, ELN, TOR1A, DNM2, DYNC1H1, DNA2, DMD, DES, CTSK, CRKL, COMP, COL11A2, COL5A2, COL5A1, COL2A1, COL1A2, COL1A1, CFL2, CAV1, BCR, KIF1A, BIN1, GALNS, FOS, DUX4, IHH, MYL2, MYH7, MMP13, LMNA, LIMK1, LAMA2, L1CAM, NPR2, PCYT1A, ITGA7, IGHMBP2, NOTCH3, PPARG, HSPG2, HNRNPH2, MAPK1, HNRNPA2B1, MASP1, HNRNPA1, NECTIN1, GTF2I, RET, NEB, GPER1, ESR1, ESR2, FTH1, ROM1, CHPT1, ADAMTS1, CRPPA, AMH, LIAS, ARSD, GH1, KISS1R, CD6, POMC, GNRH1, DHDDS, PNOC, PGR, PDE4A, OPRL1, OPRK1, PROK2, CRP, CYP19A1
-
Musculoskeletal Disorder
Wikipedia
The target of MSD prevention efforts is often the workplace in order to identify incidence rates of both disorders and exposure to unsafe conditions. [21] Workplace controls [ edit ] Groups who are at particular risk can be identified, and modifications to the physical and psychosocial environment can be made. [21] Approaches to prevention in workplace settings include matching the person's physical abilities to the tasks, increasing the person's capabilities, changing how tasks are performed, or changing the tasks. [22] Employers can also utilize engineering controls and administrative controls to prevent injury happening on the job. [4] Implementation of engineering controls is the process of designing or redesigning the workplace to account for strengths, weaknesses, and needs of the working population- examples would be workstation layout changes to be more efficient or reducing bending over, or moving necessary tools within shorter reach of the worker's station. [4] Employers may also utilize administrative controls like reducing number of hours in a certain position, limiting overtime, or including more breaks during shifts in order to reduce amount of time at risk for each worker. [4] Ergonomics [ edit ] Encouraging the use of proper ergonomics not only includes matching the physical ability of the worker with the correct job, but it deals with designing equipment that is correct for the task. [23] Limiting heavy lifting, training, and reporting early signs of injury are examples that can prevent MSD. [24] Employers can provide support for employees in order to prevent MSD in the workplace by involving the employees in planning, assessing, and developing standards of procedures that will support proper ergonomics and prevent injury. [24] One focus of ergonomic principles is maintaining neutral postures, which are postures in which muscles are at their normal length and able to generate the most force, while reducing stress and possible injury to muscles, tendons, nerves, and bones- therefore, in the workplace or in everyday life, it is ideal for muscles and joints to maintain neutral positions. [25] Additionally, to prevent hand, wrist, and finger injuries, understanding when to use pinch grips (best for fine motor control and precise movements with low force) and power grips (best for high-force movements done repeatedly) is important for employees and general tasks outside the workplace. [25] The choice of tools should match that of the proper grip and be conducive to neutral postures, which is important for employers to consider when purchasing equipment. [25] In order to reduce injuries to the low back and spine, it is recommended to reduce weight and frequency of lifting cycles as well as decreasing the distance between the body and the load to reduce the torque force on the back for workers and individuals doing repeated lifting to avoid fatigue failure of the spine. [25] The shape of objects being lifted should also be considered, especially by employers, because objects which are easier to grip, lift, and access present less stress on the spine and back muscles than objects which are awkwardly shaped and difficult to access. [25] The National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has published ergonomic recommendations for several industries, including construction, mining, agriculture, healthcare, and retail, among others. [26] Epidemiology [ edit ] Deaths from musculoskeletal diseases per million persons in 2012 0-7 8-11 12-15 16-20 21-24 25-30 31-36 37-46 47-54 55-104 General population [ edit ] MSDs are an increasing healthcare issue globally, being the second leading cause of disability. [8] For example, in the U.S. there were more than 16 million strains and sprains treated in 2004, and the total cost for treating MSDs is estimated to be more than $125 billion per year. [27] In 2006 approximately 14.3% of the Canadian population was living with a disability, with nearly half due to MSDs. [28] Neck pain is one of the most common complaints, with about one fifth of adults worldwide reporting pain annually. [29] Workplace [ edit ] Most workplace MSD episodes involve multiple parts of the body. [30] MSDs are the most frequent health complaint by European, United States and Asian Pacific workers. [31] and the third leading reason for disability and early retirement in the U.S. [13] The incidence rate for MSDs among the working population in 2014 was 31.9 newly diagnosed MSDs per 10,000 full-time workers. [32] In 2014, the median days away from work due to MSDs was 13, and there were 10.4 cases per 10,000 full-time workers in which an MSD caused a worker to be away from work for 31 or more days. [32] MSDs are widespread in many occupations, including those with heavy biomechanical load like construction and factory work, and those with lighter loads like office work. [13] The transportation and warehousing industries have the highest incidence rate of musculoskeletal disorders, with an incidence rate of 89.9 cases per 10,000 full-time workers. [32] Healthcare , manufacturing , agriculture , wholesale trade, retail , and recreation industries all have incidence rates above 35 per 10,000 full-time workers. [32] For example, a national survey of U.S. nurses found that 38% reported an MSD in the prior year, mainly lower back injury. [33] The neck and back are the most common sites of MSDs in workers, followed by the upper limbs and lower limbs. [32] The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that 31.8 new cases of MSDs per 10,000 full-time workers per year are due to overexertion, bodily reaction, or repetitive motions. [32] In 2013, members of the United States Army Medical Command Band (now the 323rd Army Band ) were the center of a study which concluded that musicians have a high rate of MSDs and that it exceeds percentages in the general population. [34] See also [ edit ] Carpal Tunnel Human factors and ergonomics Human musculoskeletal system Low back pain Sprain Repetitive strain injury Ischemia-repurfusion injuries of the appendicular musculoskeletal system References [ edit ] ^ "CDC - NIOSH Program Portfolio : Musculoskeletal Disorders : Program Description" . www.cdc.gov .
-
Status Epilepticus
Wikipedia
. ^ Zhao, ZY; Wang, HY; Wen, B; Yang, ZB; Feng, K; Fan, JC (28 March 2016). "A Comparison of Midazolam, Lorazepam, and Diazepam for the Treatment of Status Epilepticus in Children: A Network Meta-analysis".GRIA2, TNF, CASP3, BDNF, PTGS2, CNR1, CCL2, DMD, HMOX1, AQP4, SLC8A3, SLC8A1, ANK3, BECN1, SRC, SSTR4, PTK2B, MEF2C, SNTA1, CCL3, CASP8, ABCC2, SLC12A5, SCN8A, PNPO, NTRK2, POLG, VEGFA, HSPB1, CCR2, NOS1, EPO, GRM5, NOS2, GAP43, IL1RN, CAT, CCR3, NGF, CCR7, CCR10, CCR8, FOS, GRM1, KCNMA1, HCN1, EIF2S1, IL1B, CRH, CCR9, JUN, LAMP2, EIF2AK3, JUNB, NTF3, JUND, GDNF, PDXK, SSTR5, RRM2B, RET, ATP2A2, SSTR1, SSTR2, SSTR3, CASP1, EIF2AK2, KCNK5, CD40, CDH2, NTRK3, ABCB1, GRIA1, BCL2, MTOR, GRIN2A, DPYSL2, AIF1, HRH3, RELA, GSK3B, GRIN1, GRN, ADAM10, CFL1, ABCG2, MMP9, ABCC8, SOD2, PLAUR, NR3C1, NPY, RGS4, PGF, PCP4, GRIK1, MFN1, NT5E, CXCL12, OGG1, CCL4, NLGN1, PPP1R1B, GHSR, TFAM, QDPR, PRKCB, PROX1, KCNC4, IL18, HTRA2, NLGN2, PLAU, KCNJ11, IL6ST, KCNK3, CXCL1, IDH2, SLC8A2, HSD11B1, SLC6A8, PTPRZ1, H2AX, PLAT, RELN, CX3CL1, AQP1, ACAN, ATM, ELAVL4, ASCL1, XRN2, CASP6, APOD, APEX1, CX3CR1, ALAD, CASP2, CKMT1B, CYP11A1, BAX, GJB6, CCR5, CCND1, SOCS3, BCL2L1, NQO1, ADAM9, CRP, ABAT, DAB1, DNM1L, SCN1A, SLC1A2, ALDH5A1, KCNA2, PCDH19, SZT2, EHMT1, SLC2A1, CACNA1B, ATXN10, CACNA1E, CACNB4, COX7B, STXBP1, CLTC, JRK, CAD, CLCN2, CHD2, PARS2, NECAP1, CACNA1A, TIMM50, SMARCA2, GPAA1, ACTL6B, SCN9A, FIG4, SCN3A, SCN2A, ST3GAL5, YARS2, SLC6A1, AARS1, SYNJ1, QARS1, RNU4ATAC, PRODH, BSCL2, ATP1A1, TRAPPC2L, ATP1A3, ALDH7A1, PPP3CA, WWOX, DEAF1, ATP6V1A, NDUFB11, CYFIP2, SYNGAP1, CNKSR2, AMACR, CARS2, RHOBTB2, ECE1, CCDC88A, EEF1A2, EPM2A, TRAK1, NARS2, ARX, HCCS, YWHAG, DIS3L2, GRIN2D, FGF12, FH, NUS1, EFHC1, GABRA1, UBA5, DHDDS, CILK1, SLC19A3, GABRB2, TRIM8, GABRD, COG8, LMNB2, GABRG2, GALC, SLC13A5, GRIA3, TWNK, NEXMIF, KCNQ3, CTSD, NHLRC1, TBC1D24, ARV1, ATP6V0A2, PLPBP, KCNB1, KIF11, DHCR24, PDSS2, AP3B2, DNM1, ITPA, KCNT1, P2RX7, MIR134, HMGB1, NFE2L2, MIR146A, GFAP, GRIN2B, MAPK3, PVALB, GABPA, F2R, IL1A, S100B, MIR21, MIR155, MAPK8, ACHE, KEAP1, CABIN1, DAPK2, SP1, DENR, SPAG11B, UTRN, RIPK3, SLC30A3, PEA15, SRF, TSC2, MGLL, TRPC6, TRPC3, NR1I2, GJD2, DLG4, ADK, DCX, CSF1R, CRMP1, GABRA4, GCG, SPAG11A, COX2, DDIT3, PAG1, SLC52A2, PCBP4, MIR23A, MIR22, CDK5, IL10, CREBBP, P2RY1, MTCO2P12, PDGFRB, OPN1LW, PWAR1, PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PIK3CD, PIK3CG, PAM, EIF4E, MAPK1, MLKL, PTGER2, ADAMTS5, KLK8, RPP14, TPPP, CXCL13, AHSA1, SUB1, ATG7, KCNIP1, MIR187, P2RX5-TAX1BP3, ADAMTS4, EEF1E1, PTGES, PPP6R2, H3P8, SV2A, H3P12, FTX, MIR203A, C20orf181, ZNF197, ZGLP1, DCAF7, MIR451A, MIR96, CDK2AP2, H4C15, H4-16, BTBD8, UGT1A6, RHOT1, ATG16L1, LAMTOR1, TRPM7, TRPM4, TMED9, UGT1A1, POLDIP2, NPAS4, UGT1A7, KCNK10, SGSM3, SF3B6, ATRAID, NDUFA13, LAMTOR2, RNF19A, CCDC91, SAGE1, FAM20C, OPN5, SYNPO, RSS, TPPP2, NOX4, ATF5, NDEL1, RTL10, P2RX2, LRFN4, WNK1, MPRIP, GORASP1, TRPV4, SIRT3, A2M, RASGRF1, GRAP2, FMR1, IL4, IFNB1, IFIT1, HSPA4, HRES1, HDAC1, GRK5, FFAR1, GOT1, GLP1R, GCLC, GJB1, GJA1, GIP, GAPDH, IL6, IL13, IL17A, LCN2, MPO, MMP13, MMP3, MAP2, LIMK1, LEP, KNG1, IRAK1, KCNQ2, KCNK2, KCNJ10, KCNJ6, KCNJ3, ITGAM, GABBR1, FLT4, MTF1, FGF2, CD44, CD86, CALCA, CALB2, C5AR1, SERPING1, TSPO, CXCR5, ANXA1, ALB, AKT1, PARP1, ADORA2A, ACTB, ASIC2, CDK4, CDKN2A, CDKN2C, S1PR1, ERBB4, EPOR, MARK2, EGR3, EGR1, EFNB3, DRD4, CNR2, DRD2, DIO2, CYP19A1, CYBA, MAPK14, CRK, MST1, MYD88, ZFYVE9, TP53, H4C12, H4C6, H4C4, H4C1, H4C9, MAFK, AIMP2, VIP, VEGFC, UROD, UGCG, UCHL1, UBE2I, TYRO3, TSC1, H4C11, H4C3, H4C8, CDK5R1, LONP1, PPIG, MSC, ZBED1, P2RX6, CDKL2, GALR2, H4C2, SOCS1, TP63, DYRK2, H4C14, H4C13, H4C5, TRAF6, TLR4, NEUROD1, TLR3, PTPN11, PTH1R, PTEN, PSMC1, MAPK10, PPP2CA, POMC, PLA2G4A, SERPINI1, P2RY2, P2RX5, P2RX4, P2RX3, P2RX1, OGDH, UPF1, RPS6, RYR1, STAT3, THBS1, TGFBR2, TAT, TACR1, SYT1, SYP, STAT2, S100A9, SST, SPAST, SMS, SLC18A3, SLC12A2, SLC6A3, H3P45
-
Disorders Of Consciousness
Wikipedia
The decrease of cerebral metabolism occurs also when patients are treated with anesthetics to the point of unresponsiveness. Lowest value (28% of normal range) have been reported during propofol anesthesia.
-
Intrahepatic Cholestasis Of Pregnancy
Wikipedia
Whilst Ovadia's research [21] suggests differently, it is important to note that in the United States bile acid tests can take up to seven days to be processed, and this means that it may be more prudent to base delivery on the US research. [28] See also [ edit ] ICP Support ICP Care Cholestasis Cholestatic pruritus List of cutaneous conditions Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP) an itchy condition of pregnancy that is associated with a rash.ABCB4, ATP8B1, ABCB11, ABCC2, NR1H4, TNF, VCAM1, ABCG8, LOC102724197, GGTLC1, GPT, NR1I2, TERC, MMP2, MMP9, F2R, ABCG2, GPBAR1, FGF19, PPARG, ERP29, XPR1, ABCC3, PRDX6, PUM1, NR1I3, ABCB6, TJP2, SLCO1B1, CXCR6, PTGES3, LPAR2, ACTG2, TMED10, PNPLA3, LINC02527, LINC02210-CRHR1, MIR1182, SYCE1L, MIR148A, IL31, TMED10P1, KLB, RBM45, KLHL1, RASSF1, ACKR3, ANGPTL8, WDR11, ISYNA1, FETUB, SLC17A5, POU2F3, FAM215A, CDK5R1, SIRT1, UCN, HDAC3, EDNRA, HPRT1, HLA-DRB1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-C, HLA-B, HLA-A, GPR42, GABRA2, ACE, IL1B, CRHR1, CHI3L1, CD59, BRS3, AVP, APOE, ALB, ADRA2B, IFNG, IL4, PLA2G6, PLA2G2A, YWHAZ, ADRA1A, TPT1, TNNI3, SSTR4, SLCO1A2, SLC10A1, RRAS, PLA2G1B, IL6, PAPPA, OXTR, NPY, NOS2, NFE2L2, KIFC3, IL18, IL17A, H3P17
-
Hypogonadism
Wikipedia
"Gonadotropin therapy for infertile men with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism". Journal of Andrology . 28 (5): 644–6. doi : 10.2164/jandrol.107.003400 .TACR3, GNRHR, GNRH1, TAC3, NR0B1, LHB, FSHB, KISS1R, LEP, LEPR, NR5A1, KISS1, PRL, CYP19A1, SLC29A3, POLD1, CYP17A1, CGB3, CSHL1, FGFR1, GHRH, SOX2, ANOS1, POLR3A, PROKR2, FGF8, PROP1, CHD7, PROK2, POLR3B, PNPLA6, NSMF, NDN, SEMA3A, RNF216, HS6ST1, FGF17, SRY, GJB2, AXL, CCDC141, TYMP, WDR11, UBA6-AS1, TFR2, SRA1, PWAR1, SEMA3E, GTF2IRD1, NTN1, HJV, SNORD116-1, SNORD115-1, CTDP1, PWRN1, AIP, BAZ1B, HERC2, MKRN3-AS1, HESX1, PTCH2, TP63, LZTR1, MKRN3, WT1, CLIP2, FEZF1, DNAL4, ZMPSTE24, A2ML1, RBM28, IL17RD, MAGEL2, HDAC8, CDH23, DCAF17, SUFU, SOX10, SPRY4, LAS1L, DHH, RRM2B, TBL2, GPR101, RAB3GAP2, FLRT3, NPAP1, KAT6B, PLXND1, RAB3GAP1, MRAS, CBX2, LHX4, SOS1, RNU4ATAC, SOX9, OTX2, POU1F1, ELN, POLG, PMM2, PDGFB, PCSK1, GLI2, GTF2I, SIX6, PTPN11, HFE, NRAS, HSD17B3, NF2, IPW, MEN1, MAP3K1, KRAS, LMNA, PTCH1, RAD51, RAF1, SOX3, SOS2, SNRPN, ANK1, SMARCB1, BMP2, BRAF, RRAS, BRD2, RIT1, CTNNB1, DCC, RFC2, REV3L, DMRT1, DUSP6, RASA2, LIMK1, AR, GH1, ESRRB, GK, MPZ, SERPINA4, VDR, SHBG, PMP22, GGN, NRP2, BECN1, DAZ1, PDE5A, CTLA4, CBLL2, NEUROG3, S1PR1, CPE, IGSF10, S100A4, TYRO3, AMH, NRP1, POMC, CD274, SCO2, FGF2, FGF3, MUL1, FGF9, FGF10, MSTN, TUBB3, PRKN, NT5E, NGF, IGF1, STAR, MC4R, ADH5
- Radiculopathy Wikipedia