-
Amnesia
Wikipedia
Recent memories are less likely to be recovered, but older memories will be easier to recall due to strengthening over time. [28] [ better source needed ] Retrograde amnesia is usually temporary and can be treated by exposing them to memories from the loss. [29] [ better source needed ] Another type of consolidation (process by which memories become stable in the brain) occurs over much longer periods of time/days, weeks, months and years and likely involves transfer of information from the hippocampus to more permanent storage site in the cortex. ... ISBN 978-1-61705-100-5 . ^ Pavlopoulos, Elias; Jones, Sidonie; Kosmidis, Stylianos; Close, Maggie; Kim, Carla; Kovalerchik, Olga; Small, Scott A.; Kandel, Eric R. (28 August 2013). "Molecular mechanism for age-related memory loss: the histone-binding protein RbAp48" . ... PMID 26302472 . ^ Kopelman, Michael; Morton, John (28 January 2005), "Psychogenic Amnesias: Functional Memory Loss", Recovered Memories: Seeking the Middle Ground , John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, pp. 219–243, doi : 10.1002/0470013486.ch11 , ISBN 978-0-470-01348-9 ^ Zola-Morgan, S; Squire, LR ; Amaral, DG (1986).HRH3, APP, SIGMAR1, IL6, CSF2, NGF, POMC, PREP, GNAI1, AVP, IL2, PDYN, GNAI3, TAC1, GRP, TRH, IL1A, BCHE, DRD3, HTR7, GJA1, FUT10, BDNF, APOE, ACHE, MAPT, PSEN1, TARDBP, RBBP4, PVALB, CREB1, NFE2L2, LGI1, FUS, GSK3B, GABPA, SIRT1, PSEN2, SST, CNR1, ADM, STAT3, MTHFR, SUCLA2, S100A9, TRPV1, PTPN1, GRAP2, NRXN2, PTS, KL, RAC1, SNCA, NR1I2, SOD1, AIMP2, TNF, ANP32A, SULT1A3, NTN1, TFF1, SLBP, ABAT, LILRB2, NLRP3, DPYSL5, ACKR3, ELOVL6, FSD1, SLC52A2, FSD1L, PTPN5, PWAR1, ATF7IP, TAS2R64P, MIR142, SULT1A4, MIR423, ECT, BACE1-AS, SLX1A-SULT1A3, CENPJ, TREM2, AHSA1, WWC1, NEU3, NMU, PTGER1, BTG3, TUSC2, FASTKD2, NLGN1, CRTC1, ADAM22, TNFRSF13B, BACE1, RNF19A, SIN3A, POLDIP2, WWOX, CD244, GADD45G, NTF3, PRTN3, DLG4, MAPK14, CSF1R, CSN2, CTNNB1, CTSB, CX3CR1, EGFR, CRK, EPHB2, ERBB2, F2R, FANCE, FGF14, FMR1, CRYGD, CHRM1, MAPK8, BGLAP, ACTB, PARP1, AGER, JAG1, ALAD, ALDH2, CALB1, CHD3, CASP1, CASP2, CASP3, CD38, CDK5, CETP, FOLH1, MTOR, GABRA5, NTRK2, LAMC2, LEP, LNPEP, MBP, RNR2, NQO2, PDE4A, GAD1, PDGFB, PNOC, PRKAA1, PRKAA2, PRKAB1, MAPK1, KCNMA1, ITGB2, ITGAM, IRS1, IL7, IGF1R, IGF1, HSP90AA1, HSF1, HSD11B1, HMGB1, GRM3, GRM2, GRIN2B, GRIA2, GATA3, GAD2, LINC02605
-
Carcinoma
Wikipedia
Less than 1% of carcinoma diagnoses are in children. [27] The two biggest risk factors for ovarian carcinoma are age and family history. [28] References [ edit ] ^ Lemoine, Nigel Kirkham, Nicholas R. (2001).PTEN, SCD, FN1, ESR1, HRAS, BCL2, CCND1, CDK4, FHIT, STAT3, MYC, KRAS, ABCB1, PGR, TGFB1, HIF1A, GATA3, EPCAM, TP53, CDH1, TP63, VHL, MET, PTGS2, BRCA1, EGFR, ACTB, GSTP1, RB1, CSF2, TYMP, TSHR, TGFBR2, SOX9, EZR, RBP1, PTGS1, KRT5, ESR2, CDC42, TPM3, STMN1, LGALS7, COX1, PKM, DNMT1, ANXA1, BCL2L1, PPARA, MGP, AQP1, LPL, ALCAM, DES, ACTN4, PIK3R1, ATP7B, TLR4, PEBP1, EEF1A1, RHOA, RASA1, FURIN, SGK1, BLM, PTBP1, STAT5A, PLAUR, TRPS1, SNCG, CASK, KITLG, SPINT2, ENO1, ACKR3, ANGPTL4, YWHAZ, GSTT1, CORO1A, PLK2, GGT1, TP53I3, IL6ST, NDN, ACSL1, PSMA4, SCARB1, PSME1, FABP4, EPHX1, MIF, EIF5A, S1PR1, DUSP6, COL5A1, PTN, RAN, DNMT3B, CSF3, CSN2, RASGRF2, CSN3, DBI, PRLR, RCN1, CDS1, CAPZB, OXT, ID4, ID3, KYAT1, PDGFA, HNRNPA1, INSIG1, HBA1, PGAM1, MDH2, PHB, GSS, GNAI2, CCNH, GATM, CNN3, EFEMP1, RBP4, SLC25A10, URI1, NSMF, TMEM37, TF, KRT71, THRSP, TKT, TLE4, UBE2I, LSR, G0S2, UCP2, LY96, PRDX2, PADI4, XDH, VAMP8, LIN7A, TSC22D1, MPZL1, ANXA4, GDA, MRC2, MERTK, TUBB2B, BASP1, SOD2, S100A6, RPL3, RPL6, SELENOP, GLYCAM1, ADCY5, SNRPD3, ACTG1, SLC12A2, RPS14, SRSF2, HPGD, SMARCA4, MSH2, STK11, MLH1, H3-3B, CDKN1B, ATP5IF1, APC, FGFR3, KIT, POLE, BCL10, POLD1, HGF, MSH6, CKAP4, RASSF1, TICAM2, HPSE, HMGA1, DCTN6, NLRP1, H3P23, HTC2, ZNRD2, IFI27, LOC110806263, MTCO2P12, TBC1D9, SIRT1, RSPO1, EGF, NUTM1, MALAT1, EPHB2, MIR21, ERBB2, ERBB3, DKC1, ERG, CDC73, MIB1, EZH2, IGF1, KRT20, FASN, TMED7, TMED7-TICAM2, FGF3, CD274, FOXM1, DCC, SEC14L2, INTS2, RPE65, IGF1R, PIK3CG, TP73, NME1, NRAS, TNF, NKX2-1, PCNA, TGFA, TFF1, TFE3, PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PIK3CD, TERT, MUTYH, PLAG1, SPP1, PPARG, SOX2, MAPK1, PSMD9, SMARCB1, CTNNB1, SLC2A1, CXCL12, SDC1, S100A4, TYMS, MUC5AC, IGF2, VIM, IL6, CXCL8, PDLIM7, L1CAM, LGALS3, RET, SMAD4, ARID1A, HMGA2, MDM2, PAX8, MGMT, VEGFA, MUC4, MMP1, MMP2, MMP7, MMP9, MMP11, MRC1, ABCC1, UVRAG, MSH3, COX2, MUC1, MUC2, PTCH1, H3P10, CDKN1A, CEACAM3, AR, BRCA2, RUNX3, CDK2, BRAF, CEACAM5, CDX2, CA9, ALK, CD44, AKT1, CASP3, BMI1, CDKN2B, CEACAM7, ATM, CDKN2A, CD40, MMP14, ARHGAP24, PSG2, CTTN, THBS1, TACSTD2, IL2, FGF2, ETV6, PROM1, AKT2, ETS1, AMACR, SAI1, FAS, MDK, CCDC6, FOLH1, FGFR1, SLCO6A1, CD24, TAS2R38, SKP2, MTOR, MKI67, CAV1, CXCR4, ALB, PARP1, F9, NEURL1, BAX, CBX7, CLDN4, NOTCH1, MTA1, SLC12A9, NEU1, GAST, TIMP2, TIMP1, GSTK1, SATB2, BUB1, CLU, NAPSA, EWSR1, SERPINE1, MUC6, CHEK2, CCNE1, RAD51, CD34, IFNG, PIP, TMPRSS2, COMMD3-BMI1, MDM4, ADGRE2, PPP2R1A, PRL, PLK1, E2F1, PDZK1IP1, TWIST1, MMP13, SCO2, FOXP3, TTF1, NACC1, RPSA, BMP2, ZEB1, KRT18, IL4, IL10, MUC16, TIMP3, IDH2, FGF4, AURKA, MEN1, KLK3, ADGRE5, GNAS, KLF4, CEACAM1, SNAI1, SCN1A, SMAD2, CHGA, SGSM3, FGFR2, MCL1, MC2R, SRC, ROS1, BECN1, CYP19A1, CYP1A1, DAP, SUB1, NTRK1, MARCKSL1, HOTAIR, PLAU, RARB, RAF1, CIB1, ANXA10, VDR, CASR, TAP1, VEGFC, ABCC3, CDC25A, CDH13, TNFSF10, LGALS1, MIR155, MSLN, TXN, TNC, LINC01194, MIR145, DYNLL1, MAP2K4, MMP26, HPGDS, MIR210, SMARCA1, GRP, CDK1, FSCN1, GLI1, GPC3, MME, FBXW7, PTP4A3, CD40LG, GAPDH, ASPSCR1, SST, MIR34A, FOXA1, AREG, SYP, EPHA2, ANO1, POMC, WLS, RELA, MTDH, PDPN, EBAG9, IDO1, VTCN1, CTSK, AGR2, BRD4, TFF3, FAP, CUX1, BAAT, SCGB3A1, KRT14, ERBB4, KRT19, MIR375, S100A9, TERC, NCAM1, NEAT1, WNK1, SPARC, SOX10, CTCF, TAS2R64P, COPS5, LAMTOR2, AQP3, GADD45A, ILK, ANXA2, NOTCH3, EML4, NR3C1, IL24, DMBT1, PMS2, MIR205, GSK3B, KHDRBS1, CDK2AP2, PSEN2, FOSL1, NQO1, IL15, WWOX, MAGEA1, CDH3, TSC2, PRCC, NXF1, HNF1B, MIR100, HSP90AA1, HNF1A, MAGED4B, ADM, IGFBP5, LGALS9, IGFBP7, SF3B6, KDR, DDX53, SYT1, CD82, PLG, STAT1, XRCC1, H3P8, TSC1, TG, HLA-A, TGFBR1, MAP2K7, DLC1, ALDH1A1, SALL4, DICER1, DLEC1, GORASP1, F2R, MYCN, MYB, MSMB, PAX2, USO1, EIF4E, MAGED4, CCKBR, MST1, COL11A2, MVP, NTRK3, PRKN, LAPTM4B, BNIP3, EIF3A, BSG, FOSB, BCAR1, FOS, PTHLH, ZEB2, WIF1, NFE2L2, CCL2, PTPRJ, FLNB, XIAP, CALCA, SQSTM1, CCN6, ABCG2, PEG10, SMARCA2, EPHB4, NDRG2, BAP1, PDCD4, AGO2, SNAI2, AURKB, RPP14, NOX1, CKS1BP7, DCLK1, CADM1, EIF4EBP1, IMP3, ANKRD30A, CKS1B, MYOD1, CCND3, CCND2, LOXL4, NPEPPS, SLC5A5, MMP3, GHRH, PDXP, KLF5, PCDH10, KRT7, NEDD4, LMLN, TERF2, MCPH1, TUG1, S100A1, NFATC1, CDKN1C, RBL2, NR0B1, AKR1B10, IL33, AGER, JUND, JUNB, JUN, CASP1, ITGAV, BUB1B, H19, S100B, TBX1, CXCL16, PROS1, OTUD4, CD36, CALB2, SMAD7, MMP15, MAGEA3, MAL, PSMD7, PDGFRB, MCC, CBLL2, CD68, MCM2, BCHE, MCM7, PDK1, PECAM1, SMYD3, CALR, TMPRSS13, MSI1, MAPK3, RIOX2, LEP, MUL1, PLA2G1B, PRKACA, MYD88, CASP8, CCK, LCN2, ANIB1, TLR9, MUC3A, ABO, AFP, TARBP2, LGALS8, PIM1, MTHFR, LOX, BAG1, PAWR, BAGE, IRS1, NANOG, HNF4A, XRCC3, SCLC1, ZNF217, CEACAM4, AKT3, DUSP1, HDAC2, MIR182, ABCB6, FRA16D, POTEF, XRCC5, HLA-C, PTGES, ACE, CSE1L, BAG3, XPO1, CSF1, HMGB1, WT1, WNT2, RABEPK, DHCR24, TBPL1, ADAM9, FLI1, H2AX, TMSB10, MIR200B, SOCS1, MIR29B2, CISH, SPARCL1, NUPR1, GHRHR, GATA4, APEX1, MIR29B1, GJB2, GLB1, AXIN2, AXIN1, MIR221, CYTIP, NCOA3, GPX3, GRB7, MIR214, TINF2, APBA2, GABPA, GSN, LGR5, UNC5C, TFPI2, HOXA9, RECK, PSAT1, CASP14, EPS8, LGALS7B, IDH1, LIN28B, CRTAP, HSP90B1, CPOX, CDX1, FANCF, IGFBP3, TPBG, ABCC2, SPHK1, ERCC1, MBD2, TP53BP1, CXADR, ARHGEF2, TOP2A, SOCS3, COX8A, IL9, MALT1, CXCR2, ARMH1, TUBB3, DAXX, EBNA1BP2, H3P28, STAG2, MIR126, HSPA1A, TLE1, HSPA1B, UCHL1, CTLA4, CFLAR, LANCL1, LEF1, C17orf97, ING1, CYP24A1, ASCL1, ALOX15, TIAM1, RAD51C, ANKRD36B, RARA, ZBED1, RAD52, TRAF4, CCAR2, PTTG1, LPIN1, RNASE3, REST, REG1A, KLK4, COX5A, KDM4C, SLC9A3R2, SCYL1, C3, RARRES1, HACE1, BIRC2, RBBP8, CLOCK, ATG5, ZHX2, KLHL1, THBS2, PTGDS, RAD21, ISG15, SPRY2, RAMP3, FRTS1, RACK1, RALBP1, YAP1, CFDP1, LYVE1, PKN1, PRKAR1A, SMR3B, SLC52A2, SEMA4D, ADAM28, ANXA5, ANGPT1, PTPA, ANGPT2, MRPL28, NES, RBBP9, SIX2, LIN28A, POU5F1, CAMKMT, PINK1, CDCP1, UBE2C, NR1I3, RRAS2, RAB1A, ZNF350, ESPL1, GALNT6, LGR6, MTSS1, KEAP1, PTPRA, PTMA, LZTS1, STRAP, TRIM13, DDR1, PSIP1, PTGER4, ABI1, CALM1, CALM2, CALM3, TSPAN1, RAD50, PSMD2, NAMPT, SCAF11, SFRP1, SIRT3, VRK2, TERF2IP, DELEC1, VCL, VCP, VDAC1, TACR1, UGT1A7, RHOC, CERS2, ARG1, SYK, SULT2A1, NXT1, TRAM1, ST14, EGLN1, SSTR2, YY1, NOB1, XAF1, MCTS1, ZNF146, BAK1, SPN, SPINK1, SPG7, GEMIN4, F11R, TCF4, ARR3, THBD, SIRT6, TGM2, ATR, ATP2A3, TGFBI, ATRX, MED15, ZBTB7A, TM7SF2, TMSB4X, ATF1, AXL, ASPH, TFAP2C, TFAP2A, TPD52, TPO, TERF1, CLDN18, TEP1, TMBIM6, TCF21, DCTN4, LINC00328, ZMYM2, USP7, TFEB, BHLHE40, PDE5A, SIRT7, TNKS, SEL1L, EIF3H, TNFRSF25, PBK, TNFSF13, ADAM15, SCTR, PART1, TNFRSF6B, DLK1, SULT4A1, GKN1, INPP4B, CCN4, KSR1, NUP62, SMUG1, LPAR3, ALOX5, F2RL3, SMYD2, GPRC5A, SFTPC, EHF, BCL2A1, RAB20, PSCA, BDNF, NR4A3, MCAT, TESC, FASLG, ANP32A, HLTF, DKK3, BBC3, PBRM1, SLC16A1, SLC12A3, GREM1, SLC6A2, PLA2G6, ZNF654, INTS6, CUL4A, SLC2A2, GEMIN2, STIL, PMEL, ST3GAL4, PPM1D, NAT2, CD226, MIR183, IL13, ENO2, EP300, INHA, EPHA1, MYCL, FUT4, MXI1, EPHA5, INHBB, CD9, CAGE1, MIR93, INSR, EPHB1, IRF1, EPHB3, EPHB6, CPT1A, ITGA5, CD38, MRE11, STEAP2, CLDN7, FSHR, FRA7G, ARL11, MIR34B, CMTM3, XRCC6, GH1, SYCE1L, GFAP, PLIN2, NPM1, CRABP2, CGB5, NOTCH4, JAG1, CCN1, GCNT1, NOS2, IL1A, IL1B, IL1RN, GATA6, NFKB1, EIF4G2, CRABP1, PWAR4, ELF5, NEUROD1, CXCR1, NEDD9, MACC1, EIF6, MPO, YBX1, ALKBH3, MIR135B, MIR324, MIR497, CMA1, FOXJ1, FBN2, SMAD3, MAD2L1, MXD1, FOXC1, MIR451A, LEPR, CDH17, MIR424, FGF7, LRATD2, FGF8, LHCGR, ADAMTS18, CCR5, LRPAP1, LRP1, CDH11, LOXL2, VEGFD, MED19, CDH2, FOSL2, KRT17, CASC2, CD200, MOS, ETS2, KIF2A, RBM45, CD63, CXADRP1, CD109, KMT2A, MAP3K11, KISS1, FOLR1, CD74, MUC17, CDC6, CDC20, GATA5, CTCFL, KLF6, KRT8, MELTF, MFGE8, KRT15, FABP5, CEBPA, CGB8, GHR, GPX2, PDCD1, ING5, CYP1B1, GRN, MIR125A, MAP1LC3A, CYP1A2, DDIT3, REG3A, PKP2, GOT2, PLA2G2A, PAK1, CYLD, HPN, HLA-G, MIR20A, MIR17, CSF1R, DMP1, TCHP, GHSR, VCAN, PPP1R1B, CHD1, HMOX1, CHEK1, PIGR, SERPINB5, SESN2, CYP27B1, GSTA4, MIR200C, FOXA2, CD55, CGA, CASP9, SERPINH1, CGB3, REG4, SLC26A4, CXCL1, DAPK1, SERPINB2, MIR124-2, OTX2, GLS, GLO1, KRIT1, HLA-DRB1, HTN3, CTSB, H3P9, DUSP4, CRYZ, OPCML, HK2, ICAM1, HAS2, PPP1R2C, HIC1, PML, ID1, HHEX, KLLN, NRG1, EDNRB, ROR2, HAS1, GTF2H1, PLCD1, HSPA4, DPT, CTSD, GLUL, CTSL, CHUK, MIR223, PAEP, P2RX5, KDM2B, MIR222, HLA-B, DPP4, DLL1, FLVCR1, VN1R17P, KLK5, TMEM158, SLCO1B3, PRDX5, GCA, RASGRP3, MIR199B, CIZ1, RCHY1, SPDEF, ABI3BP, ZFAS1, MIR192, GPR166P, MIR133B, XRCC6P5, BAMBI, RABGEF1, MIR200A, B3GAT1, SRPX2, IL17C, MIR31, SIGLEC9, MIR30E, LHX6, SLC39A1, MIR30C2, MIR23A, EML2, POLM, PELP1, MIR30C1, MIR23B, MIR29C, HBP1, AGO1, RNU1-1, HAVCR1, AATF, DHDH, FBXO5, MIR34C, FBXO8, LINC01191, SOSTDC1, MIR203A, SNED1, ADARB1, ALDOA, POLL, CHD5, MIR211, RPS6KA6, LHX8, MIR215, MIR98, RBMS3, MIR96, KLK13, SPAG8, PHGDH, ADAMDEC1, TFIP11, ASRGL1, MIR325, ADAMTS8, KAT7, H3P41, MIR4284, ZWINT, PTPRT, FGFR1OP, OCLN, DNAJB4, KLF8, CCAT1, TOPBP1, TMEM115, SNHG16, C8orf17, MICA, TENT4A, AMHR2, HOTTIP, PCNA-AS1, FSTL1, DUSP10, MIR944, MIR760, GAEC1, TSTD1, PTENP1, PKP3, ALPP, MAP4K1, HEY, LIMS4, DEFB4B, MIR664A, MIR1301, ADAM8, TMX2-CTNND1, P2RX5-TAX1BP3, KCNQ1OT1, CBSL, ACVR1, SLC26A1, PPP1R13L, ACACB, NEU3, SEPTIN9, LOC111589215, KDM5B, MAP3K2, H3P17, ACACA, H3P30, H3P42, PTGES3, H3P47, LOC105373985, SIK1B, ERVW-4, CASC9, COPS6, TMED10, AMPD1, SPRY4-IT1, PCAT1, RAB40B, ERP29, TOMM34, HIF1A-AS2, CYP3A7-CYP3A51P, EHMT2, MAGED2, BLCAP, PGR-AS1, PANDAR, MIR885, MIR708, MIR370, POU5F1P4, ANP32D, SUZ12, MIR483, SNHG6, POU5F1P3, ADAR, CBX5, FABP9, PARK7, AHCYL2, MIR191, LINC00273, UCA1, ANXA8, ATP11A, PDS5A, ANP32C, SRRM2, ZNF281, PRAME, MIR372, MIR373, AKR1B1, MIR383, MIR429, ARL2BP, H4C15, MIR491, CDK20, PSD4, MIR202, PIK3R5, MIR493, MIR498, MIR505, GGTLC5P, SIK2, NME1-NME2, ANXA8L1, GGTLC3, GGT2, MMRN1, SBNO2, KRT8P3, HULC, DIS3, CCR2, ALPI, RHOBTB3, GGTLC4P, TDRG1, HPP1, PDAP1, GPR182, RAB3GAP1, SIRT2, MIR588, DKK1, RHOBTB2, MIR92B, ALOX15B, LRCH1, EPB41L3, MIG7, NCOA6, SMG1, PDS5B, KDM1A, SPEN, KDM2A, TPX2, MIR654, P2RX2, SYNE1, LINC00511, RGCC, LEMD1, TP73-AS1, CD248, CAMK1D, TWSG1, FOXQ1, LIMS3, CCNL1, AZIN2, ADAMTS9, MAL2, CHPT1, STK11IP, EMSY, LXN, C1GALT1, CBX8, ARID1B, UGGT1, MTA3, EP400, ZIC5, TRMT9B, CFAP97, NAV3, ZNF398, SIGLEC12, CTU1, AGTR2, STARD13, XPO5, ALKBH8, MTUS1, WDR20, AGXT, PNO1, RAD18, NKD1, TWIST2, CHFR, CCDC88A, MMP21, LIMS2, TMEM132D, NLRP2, H4-16, ALKBH2, FERMT1, ITLN1, SAGE1, DDX43, TDRD9, TRPV6, ZNF331, CACNA2D3, ADCY10, SPHK2, KDM3A, FBXO32, MUC13, DIABLO, CTHRC1, ACSM1, CCL28, NXF2, BAIAP2L1, SLC26A8, LRG1, MRGPRX3, ASH1L, USE1, MRGPRX4, SLC16A10, SLC45A3, CIP2A, B4GALNT2, NETO2, QTRT1, ATP13A3, FSD1, MMP28, MAPKAP1, ATG9A, SCRT1, SOX7, GGCT, BRD9, STK33, FSD1L, ATAD3B, MRO, FGFBP2, AGT, RNASEH2B, BRIP1, MAP1LC3B, TET1, HDAC11, EPHX3, CSPP1, CD276, ZNF750, ITIH5, COL18A1, TBL1XR1, EGFL8, NEIL1, SLC38A1, DLL3, TXNDC5, TNFAIP8L2, MRPL41, GINS3, MYLK2, LRRC4, CLSPN, AFAP1, LOXL3, HRH4, NTN4, OVOL2, FOXD2-AS1, TP53INP2, HAVCR2, RSPO3, ZNF382, MUC3B, SLC49A4, RBM17, SCUBE2, GOLPH3, CENPK, CREB3L2, FBRS, MAGT1, CCDC136, ANTXR1, SMURF2, SLC49A3, TMPRSS3, PROK1, LZTS2, MAK16, KISS1R, SPZ1, CSRNP1, CSMD1, HHIP, MMP25, LGR4, LARP6, SETD2, ARMCX1, NUP43, NCR3LG1, PAIP2, PHF20, ABI3, IGF2-AS, C12orf75, NIN, PLCE1, MUC21, FENDRR, HSPA14, DCXR, MUS81, KLHL31, TLR7, IGFBPL1, MIRLET7B, SLC22A17, MRGPRX1, MAGEA2B, LYPD5, AP2A1, LINC00319, SCLY, VGLL1, SCARA3, TMED10P1, TRIM59, POLK, ATRAID, UBR5, GADL1, TNFRSF12A, LINC00997, HSD17B12, AFM, MIR143, MIR150, MIR152, HILPDA, HOOK2, PSMC3IP, CNOT7, MIR15A, SENP1, UHRF1, ALDH3A1, CTNNA3, MIR15B, PYCARD, MIR181A2, DROSHA, MIR144, MIR142, MIRLET7E, MIR139, MIR106A, METTL9, SH3GLB1, KLHL5, NDUFA13, LAP3, MIR106B, MIR10A, MIR124-1, IL22, NOX4, DUOX2, ALDH2, MIR132, MIR134, IL23A, TCERG1L, PIGU, C1orf52, APTX, PHF13, IL23R, SIK1, TET2, SEPTIN10, LRATD1, LY6K, TAFA4, RBFOX1, GTPBP2, UGT1A3, CMTM8, UGT1A1, UGT1A4, PGPEP1, DACT3, CREBRF, NSD3, GPR151, QRSL1, UBA6, SBNO1, SLC25A36, RMDN3, PIWIL2, PRPF38B, HT, KRT72, GSC, ISM2, PINX1, TMEM70, PWAR1, UGT1A9, UGT1A5, CTAG1A, NAIF1, FXYD5, PTOV1, SLC25A43, SHC3, LRP1B, RSF1, TMEM8B, ARID4B, DLEU7, ACSL5, RSPH9, HOXA11-AS, SUFU, GPRC6A, MAPK15, CT83, PRSS55, RDH10, FLCN, GRASP, SLC5A8, UGT1A6, EML5, OXER1, DACT2, UGT1A8, UGT1A10, BHLHA15, DLL4, ING3, RETREG1, RLS1, WNT4, DCUN1D1, RHBDF2, CST6, ANPEP, MPST, CD247, CD14, MTR, NUDT1, MTF1, COX3, CD28, MTAP, MST1R, MPP3, CCNG1, MPG, MMP10, CD47, MMP8, CD70, FOXO4, MIP, CD99, SCGB2A2, CCNG2, NAP1L1, SCGB2A1, NOS3, NTHL1, NT5E, NRDC, CCNB1, NPTX2, NPPA, NPC1, PNP, NPY, NOS1, CEACAM6, NNMT, NME2, NGFR, NGF, NFKB2, NFIB, NF1, NCL, NBN, MGAT5, MFAP1, CXCR6, CDK5, LGALS4, LDLR, LDHB, LDHA, LASP1, LAMC2, LAMB1, LAMA4, LAG3, CDK6, LMNA, KLK2, KIF5B, KCNH2, KCNA5, JAK2, ITK, ITGB4, ITGAX, ITGAM, LMAN1, LPA, MEST, MAGEA2, MEF2A, CDC25B, MCM3, MBD1, MB, MAX, MAPT, MAN2C1, MAGEB2, SMAD6, LSAMP, MARCKS, CDH4, TM4SF1, LUM, BCAM, LTF, LTBP3, CYP4F3, LTB, ROR1, DDR2, NTS, POU2F1, SRGN, PRB1, PPP2R5C, PPP2R2A, PPP1R3A, PPL, PPIA, PPARD, CASP2, POU1F1, PRKAA2, POLR2F, POLH, POLD2, CASP5, POLB, SEPTIN4, PMP22, PMAIP1, PLXNB1, PRKAA1, PRKAB1, NTSR1, PROX1, PTAFR, PSMD8, PSMC6, PSMB6, PSMA5, KLK6, PRSS1, LGMN, PRPS1, PRNP, PRKCA, CAPN2, MAP2K1, MAPK8, MAPK7, MAPK6, CAPS, PRKDC, PRKD1, PRKCB, PLP2, FXYD3, PLD2, P2RY1, PCM1, PCDHGC3, PCBP2, PCBP1, PAX7, PAX6, PRDX1, P4HB, P2RY2, P2RX7, PLD1, P2RX4, P2RX3, P2RX1, OXTR, OTX1, ORM1, TNFRSF11B, OPA1, OGG1, CBS, PDCD2, CBR1, PDGFRA, PLCG1, CASP6, PLAT, CASP7, PKHD1, CASP10, CAT, PIK3C3, PI3, SLC25A3, RUNX2, RUNX1, PGK1, PGC, PFKM, PDZK1, ENPP1, PDHA1, PDGFRL, ITGAE, ITGA9, ITGA2, ENG, ETFA, CLDN3, EREG, ERCC2, CPT2, EPHA7, EPHA4, EPAS1, CR2, MARK2, ETV5, EMD, ELN, ELK3, ELAVL1, EIF4A2, EIF4A1, EIF2S1, EIF1AX, EGR1, ETV4, MAP3K8, FH, FBN1, FGF13, FGF6, PLK3, FGF1, FECH, FCGR3B, FCGR3A, FBP1, COL4A2, FBLN2, F3, COL11A1, FBLN1, PTK2B, FAH, FANCC, FABP7, FABP3, FABP1, F8, CREBBP, EFNB2, EFNA1, CYP2A6, DAG1, DACH1, DAB2, CYP26A1, CYP17A1, CYP4B1, CYP3A5, CYP2E1, CYP3A7, CTSZ, EEF1A2, CTSE, CTNND2, CTNND1, CST3, CTNNA2, CTNNA1, CTH, CCN2, CTBP1, BRINP1, DBN1, CSK, DCN, CREM, EDNRA, CRKL, CRP, E2F4, E2F3, DVL3, DVL2, DUT, DSG2, DSC2, DSC1, ATN1, DPYD, DNMT3A, TIMM8A, CSH1, DEFB4A, DEFB1, FGFR4, FKBP4, ITGA6, CFL1, HYAL1, CEBPD, HSPG2, DNAJB1, HSPA8, HSPA2, HSD3B1, HES1, CELP, HP, IARS1, HOXD10, HOXC8, HOXC@, HOXB5, HOXB1, HOXB@, HOXA10, HOXA7, HOXA4, IAPP, IBSP, FOXO3, IL6R, EIF3E, INSM1, INSL3, CXCL10, IL17A, IL13RA2, IL12RB2, IL11RA, CDKN2C, CDKN2D, IRF8, IGHG1, IGFBP4, IGFBP2, CDKN3, IFNB1, IFNA13, IFNA1, CEBPB, ID2, HOXA@, HMMR, HMGCS2, FUT1, GFI1, GDI2, GDF1, CKS2, GATA1, GALNT3, G6PC, FUT6, FUT3, FUS, HLA-E, NR5A1, NR5A2, FLT4, FLT1, FLOT2, FLNC, MLANA, FLII, FLG, GJB1, GCLC, GCLM, GNAQ, HLA-DPB1, HDGF, HDAC1, HAS3, HAGH, RCC1, GZMM, GUSB, GTF2H4, CHI3L1, GSPT1, GRPR, PDIA3, GRM1, GRIK2, GRIA2, GRB2, SFN, GNRHR, CAD, PTK2, PTK6, CD164, SOCS2, NRP1, NRP2, IQGAP1, APOBEC1, CDKL1, TNFRSF10A, TNFRSF10B, TNFRSF11A, RIPK1, HDAC3, ADAM19, APOD, HYAL2, APP, EIF3I, EIF3B, NCOA1, AKR1C3, RNASET2, GGH, ALKBH1, CCNB2, ANGPTL1, SMC3, SLC16A3, SLC16A4, LATS1, USP14, CLDN1, CLDN2, CLDN6, ASH2L, HAP1, APOB, P4HA2, MBD4, APOA1, CCNA1, PER3, APLN, NR1I2, ALDH1A2, CDK5R1, APRT, PLPP2, MMP23A, FZD5, MIA, CDK2AP1, USP5, PTP4A2, ADAM12, ST7, GHS, ST8SIA4, SEMA3B, BSND, MMP23B, PRDM2, ZBTB16, ZFP36, SF1, AQP5, YES1, XPC, XPA, WNT11, CHAF1B, TKTL1, H4C9, FZD4, PPFIA1, CUL2, CUL4B, RAD54L, LTBP4, MAD1L1, HYAL3, H4C14, H4C13, H4C5, H4C2, H4C8, H4C3, H4C11, H4C12, H4C6, H4C4, H4C1, FZD7, P2RX6, ATG12, WNT7B, GPA33, NDRG1, MICU1, TFG, CRISP3, KATNB1, NET1, RAMP1, RAMP2, GLYAT, EIF1, NDC80, CALCRL, RNF41, ADGRG2, OPTN, TRAP1, ARL4A, PTPRU, HUWE1, CHAF1A, ST3GAL6, WFDC2, DYRK1B, ARL6IP5, IGF2BP2, IGF2BP1, POSTN, TRIM16, ARID3B, SCGN, SLC34A2, CXCL13, OLFM4, PRDX4, APBA1, UBD, KAT5, CAP1, HOXB13, SLC30A9, APAF1, LYPLA1, PRMT5, RAPGEF3, BCL2L10, CASP8AP2, DMTF1, CNOT8, GSTO1, NTN1, TJP2, TMPRSS11D, LPXN, RECQL4, LONP1, LHX2, SLIT2, BIRC3, CD302, AIMP1, IL32, NOLC1, MTA2, DEDD, BUB3, OSMR, LPAR2, SLC6A5, AIM2, ITM2A, GDF15, CXCL14, AP5Z1, WASHC5, TOX4, SETDB1, ARMCX2, BMS1, PCLAF, TOX, STARD8, DOCK4, GREB1, KDM4A, MDC1, FEZ1, RNF14, AKAP12, PRDX6, APOBEC3B, MINPP1, WNT10B, WNT5A, PTMAP4, SAA4, SEA, SDHD, CXCL5, CCL21, CCL5, SATB1, SAT1, MAPK12, SALL1, SAA1, SEMA3F, S100A10, S100A7, BRS3, S100A5, S100A2, RXRA, RRM1, RRBP1, RRAS, SELE, BMP7, SMN2, SLC3A2, BID, SLC22A3, SLC22A1, SLCO1A2, SLC20A1, SLC19A1, PRDM1, SLC5A4, SLC5A2, CXCR5, SET, SKIL, SIX1, SIM2, ST6GAL1, SHH, SHC1, SHBG, SGTA, SFRP2, RRAD, RPS27A, BTC, PXN, PLAAT4, RAP2B, RAP1GAP, RAP1A, RANBP2, MOK, RAD17, RAC1, PYGM, ABCD3, RPS6, PTX3, PTPRM, PTPRF, PTPRC, PTPRB, PTPN13, PTPN12, CA11, PTMS, CA8, CA2, VPS51, RBBP4, RPL31, RPL29, RPL19, RPA1, RP9, RNPEP, RNH1, RNASEL, RIT2, RGS2, TRIM27, RFC1, REV3L, TSPO, UPF1, C1QBP, RBP2, C5AR1, RBBP6, SMN1, SMO, VTN, TPM1, TTR, STS, TSG101, TRPM2, HSP90B2P, TRAF1, CRISP2, TPT1, ASCL2, TNFAIP6, ARSA, ATF3, TMPO, TSPAN8, SEC62, TLN1, ALDH7A1, ATP5F1E, THY1, ATP6V1E1, TNFRSF4, UBE2B, SNAP25, NR1H2, VRK1, VLDLR, CTAG1B, VIL1, VEGFB, ARHGDIA, ARHGDIB, UQCRFS1, UPK2, USP4, UBE2E2, UMPS, UGT2B7, UGT1A, SCGB1A1, SLC35A2, UFD1, ARNTL, UCN, UPK1B, THOP1, THBS4, THAS, TRIM21, TBXT, STAT6, ST13, ST3, SS18, SSTR5, SSTR4, SSTR1, SSRP1, SRF, TGFB2, SPTA1, SPRR3, SPINT1, SP1, SOX11, SOX4, SOS1, SNX1, BGN, TACR2, ADAM17, TAGLN, MAP3K7, AVP, TFPI, AZGP1, B2M, TEK, BAD, TDO2, TDGF1, TCTE3, TRD, GCFC2, TCF7L2, TCF7, TBX3, ELOC, TAZ, TARBP2P1, TAPBP, TAL1, VIP
-
Decompression Sickness
Wikipedia
Symptoms of DCS in healthy individuals are subsequently very rare unless there is a loss of pressurization or the individual has been diving recently. [27] [28] Divers who drive up a mountain or fly shortly after diving are at particular risk even in a pressurized aircraft because the regulatory cabin altitude of 2,400 m (7,900 ft) represents only 73% of sea level pressure . [15] [21] [29] Generally, the higher the altitude the greater the risk of altitude DCS but there is no specific, maximum, safe altitude below which it never occurs. ... From 1998 to 2002, they recorded 50,150 dives, from which 28 recompressions were required — although these will almost certainly contain incidents of arterial gas embolism (AGE) — a rate of about 0.05%. [2] [102] Around 2013, Honduras had the highest number of decompression-related deaths and disabilities in the world, caused by unsafe practices in lobster diving among the indigenous Miskito people , who face great economic pressures. [103] At that time it was estimated that in the country over 2000 divers had been injured and 300 others had died since the 1970s. [103] History [ edit ] 1670: Robert Boyle demonstrated that a reduction in ambient pressure could lead to bubble formation in living tissue.EGR1, SELL, ACTB, VEGFA, PSS, FCGR2B, AFM, CHRD, LPAR3, ISYNA1, BFAR, VPS36, PDLIM3, SIT1, DKKL1, ATRNL1, FZD4, JMJD6, PIAS2, NAT10, OGFR, SLC27A4, IMMT, CCL27, NDC80, NR1H4, BCAR1, RIPPLY3, TWNK, ZNF143, OXER1, SMIM10L2B, GPR166P, VN1R17P, SMIM10L2A, SLC35B2, MRGPRX1, CACNA1G-AS1, GPRC6A, ENKUR, PTRH1, PSMG2, GPR151, MRGPRX4, MRGPRX3, PSMG3, MINDY4, ASRGL1, LGR6, HAMP, SLC12A5, ZBTB17, APEX1, AQP1, HMGB1, HIF1A, GYPA, FTH1, FN1, FGF1, FEN1, ALPP, DSC3, DNASE1, DNAH9, DMD, ACE, CRP, CHRM3, RUNX2, TSPO, BMP2, ATHS, AQP5, HMBS, ICAM1, BEST1, IFNG, ADRB2, VDR, TRPC3, TG, TFAM, TBCE, SPINK1, SOX9, SLPI, ROM1, RARB, PTH, POLG, SEPTIN4, SERPINF2, REG3A, MMP3, LTB, KDR, XPA
-
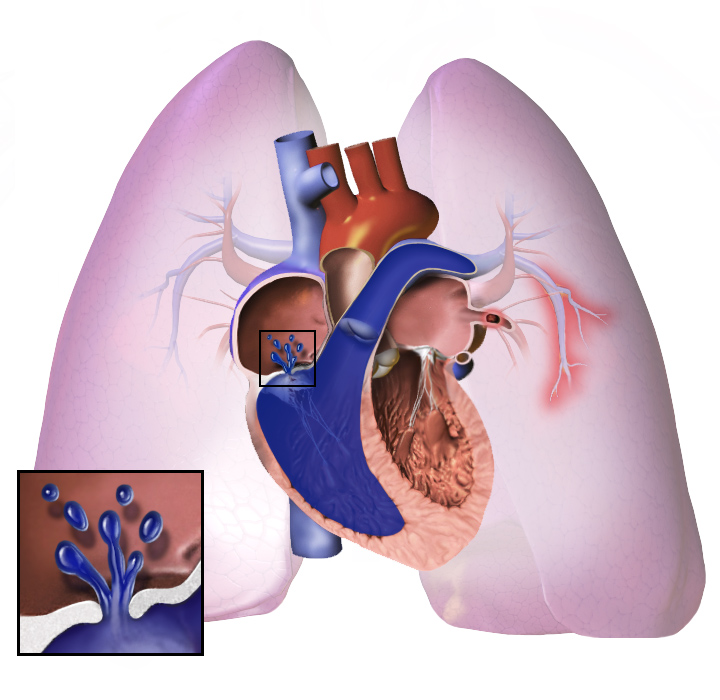
Pulmonary Hypertension
Wikipedia
January 2016. Archived from the original on 28 July 2017 . Retrieved 30 July 2017 . ^ a b "What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary Hypertension? ... NHLBI . 2 August 2011. Archived from the original on 28 July 2017 . Retrieved 30 July 2017 . ^ a b c d "What Is Pulmonary Hypertension? ... NHLBI . 2 August 2011. Archived from the original on 28 July 2017 . Retrieved 30 July 2017 . ^ "How Is Pulmonary Hypertension Diagnosed? ... "Pathology of pulmonary hypertension" . Clinics in Chest Medicine . 28 (1): 23–42, vii. doi : 10.1016/j.ccm.2006.11.010 . ... Retrieved 2015-12-30 . ^ "Pulmonary arterial hypertension" . Genetics Home Reference . 2015-12-28. Archived from the original on 2015-12-24 .NPPB, EDN1, SLC6A4, ACVRL1, NFATC2, EDNRB, CD40LG, ALOX5, HIF1A, KCNA5, NOS3, CCL2, BMPR2, ACE, TGFA, PRKG1, TPH1, MIR204, CBLN2, FOXO1, BRD4, GBA, GDF2, FBLN5, HTR2B, TNF, CCL1, CXCL8, KCNK3, KCNMA1, LEPR, LOX, SLC31A1, SOD2, ABCA3, EIF2AK4, CA9, ATP7A, CALCA, ARG2, NOS2, AGT, CCN2, UTS2, PTGS2, ANGPT1, TNC, MMP1, RHOA, RELA, PTGIS, ATP2A2, SERPINA1, PECAM1, MMP9, MYC, PDGFA, CX3CL1, PDE3A, SERPINE1, ATP5F1A, NPPA, ATP5PF, PDGFB, TAC1, SLC2A4, HDAC5, CAVIN1, HIF3A, MFN1, SMPD3, ALAS1, GPR182, CYSLTR1, ALOX5AP, RAMP2, NAMPT, HYAL2, SMAD7, PDE5A, VIP, VCAM1, ANGPT2, TGFBR2, TGFBR1, BIRC5, TERT, TACR1, TACR2, SMAD9, COL4A1, SMAD6, PDIA3, CAV1, CD40, GATA6, SMAD4, MTOR, CDKN1A, FGFR1, FGF2, ESR2, EPHX2, EPAS1, EGR1, CDKN1B, EDNRA, CLU, ECE1, COL1A1, CYP1A1, CYBB, CYBA, CX3CR1, GJA1, GATA4, IL6, SMAD1, HYAL1, HMOX1, HMGCR, IL13, BDKRB2, BCL2, HMGB1, BCL2L1, HK1, CASR, HDAC1, HAS3, HAS2, HAS1, ID1, PPARG, BMP2, UTS2B, BMPR1B, NOX4, GREM1, BMP7, JUN, ADM, ARG1, ARHGEF6, APOE, F3, PLA2G7, VWF, FGA, VEGFA, TRPC6, TRPC4, TRPC3, HLA-A, SELP, F2
-
Keratoconus
Wikipedia
At an ultrastructural level the weakening of the corneal tissue is associated with a disruption of the regular arrangement of the collagen layers and collagen fibril orientation. [22] While keratoconus is considered a noninflammatory disorder, one study shows wearing rigid contact lenses by people leads to overexpression of proinflammatory cytokines , such as IL-6 , TNF-alpha , ICAM-1 , and VCAM-1 in the tear fluid. [23] A genetic predisposition to keratoconus has been observed, [24] with the disease running in certain families, [25] and incidences reported of concordance in identical twins. [26] The frequency of occurrence in close family members is not clearly defined, though it is known to be considerably higher than that in the general population, [14] and studies have obtained estimates ranging between 6% and 19%. [27] Two studies involving isolated, largely homogenetic communities have contrarily mapped putative gene locations to chromosomes 16q and 20q. [27] Most genetic studies agree on an autosomal dominant model of inheritance. [9] A rare, autosomal dominant form of severe keratoconus with anterior polar cataract is caused by a mutation in the seed region of mir-184 , a microRNA that is highly expressed in the cornea and anterior lens. [28] Keratoconus is diagnosed more often in people with Down's syndrome , though the reasons for this link have not yet been determined. [29] Keratoconus has been associated with atopic diseases , [30] which include asthma , allergies , and eczema , and it is not uncommon for several or all of these diseases to affect one person. ... "Keratoconus and related noninflammatory corneal thinning disorders". Survey of Ophthalmology . 28 (4): 293–322. doi : 10.1016/0039-6257(84)90094-8 . ... PMID 27163622 . ^ Salmon, H A; Chalk, D; Stein, K; Frost, N A (28 August 2015). "Cost effectiveness of collagen crosslinking for progressive keratoconus in the UK NHS" .VSX1, MIR184, FOXO1, FNDC3B, ZNF469, AIPL1, CRB1, PRDM5, TOPORS, SAG, NMNAT1, LMX1B, RPE65, KCNJ13, LOX, SEMA4A, IFT172, ABCA4, IMPDH1, PRPF31, MAK, FSCN2, IDH3B, IDH3A, ZNF408, HRAS, DHDDS, MAP3K19, CEP290, PIEZO2, AGBL5, GUCY2D, SLC7A14, IMPG2, SCAPER, PLOD1, RGR, RHO, RLBP1, AHI1, ROM1, PDE6B, PDE6G, PDE6A, PCYT1A, RP9, NRL, POMGNT1, RP1, RP2, SPATA7, NEK2, KIZ, KLHL7, RPGRIP1, MERTK, KIAA1549, RPGR, PRPF6, ARL2BP, GUCA1B, CLRN1, CNGB1, RD3, EYS, BEST1, CERKL, IFT88, CA4, PCARE, BBS2, PRPF8, OFD1, GDF6, ARL3, PROM1, PRPF4, PRPF3, LRAT, IQCB1, AHR, PRCD, IFT140, DHX38, NR2E3, CNGA1, USH2A, RBP3, TTC8, SLC2A10, ARL6, FOXE3, FAM161A, ANTXR1, USP45, CDHR1, REEP6, COL3A1, ARHGEF18, CRX, ZNF513, UBXN4, SNRNP200, HGSNAT, RDH12, TUB, TULP1, C8orf37, LCA5, PRPH2, SOD1, TGFBI, TIMP1, MMP9, COL4A4, IL1B, HGF, IL6, RAB3GAP1, DOCK9, IL1A, COL4A3, COL5A1, TIMP3, MPDZ, PLK3, PLXNA2, PIP, RXRA, CAST, CAT, ACTB, COL8A2, PPRC1, KLF6, BANP, CTSB, PRL, TGFB1, TGFB2, TIMP2, ROBO3, PYCARD, SFTPA1, AQP5, SFRP1, NGF, MMP2, ATM, IL1RN, MIR17HG, ETDA, PROB1, KTCN8, ADAMTS17, SERINC3, HPSE, MIR568, POTEF, KERA, NOX4, ADAMTS8, MMRN1, GAL, PLLP, KIF26B, NAXD, ANAPC1, IL17B, GALNT14, NEIL1, HKDC1, WNT10A, ABCA6, SLC4A11, GGTLC1, TUBA3D, ARC, A2M, SLPI, STK24, LGALS3, CTSV, CYBB, DSG3, ELAVL1, EMP3, ENO1, PTK2B, FLG, GABPA, GCLC, GPX1, GSN, HLA-A, HMOX1, HMOX2, HTC2, IPO5, KRT3, KRT12, CTSG, CST4, CREB1, ATF4, ACP2, ADH1B, PARP1, AKT1, ALDH3A2, APEX1, FAS, FASLG, BAD, COL8A1, BDNF, CASP9, CCT, CLC, CNTF, COL4A1, COL4A2, COL6A1, LGALS1, LIG3, XRCC1, SMAD2, SLC7A2, SOD3, SP1, STATH, ZEB1, TF, TFAM, TLR2, TLR4, TNF, TNFRSF1A, TNFRSF1B, TSC1, TSC2, TWIST1, TYMS, UGCG, WNT3, WNT5A, CCL24, S100A6, S100A4, NGFR, SMAD7, MEFV, MMP1, MMP3, MSD, COX1, ND1, NFE2L2, NOTCH1, S100A2, NT5E, PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PIK3CD, PIK3CG, POLG, RAD51, REST, LOC102724197
-
Major Depressive Disorder
Wikipedia
The 1990–92 National Comorbidity Survey (US) reports that half of those with major depression also have lifetime anxiety and its associated disorders such as generalized anxiety disorder . [26] Anxiety symptoms can have a major impact on the course of a depressive illness, with delayed recovery, increased risk of relapse, greater disability and increased suicide attempts. [27] There are increased rates of alcohol and drug abuse and particularly dependence, [28] [29] and around a third of individuals diagnosed with ADHD develop comorbid depression. [30] Post-traumatic stress disorder and depression often co-occur. [15] Depression may also coexist with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), complicating the diagnosis and treatment of both. [31] Depression is also frequently comorbid with alcohol abuse and personality disorders . [32] Depression can also be exacerbated during particular months (usually winter) for those with seasonal affective disorder .
-
Melioidosis
Wikipedia
About 1 to 5% of those infected develop inflammation of the brain and brain covering or collection of pus in the brain ; 14 to 28% develop bacterial inflammation of the kidneys , kidney abscess or prostatic abscesses; 0 to 30% develop neck or salivary gland abscesses; 10 to 33% develop liver, spleen, or paraintestinal abscesses; 4 to 14% develop septic arthritis and osteomyelitis . [1] Rare manifestations include lymph node disease resembling tuberculosis, [7] mediastinal masses, collection of fluid in the heart covering , [3] abnormal dilatation of blood vessels due to infection , [1] and inflammation of the pancreas . [3] In Australia, up to 20% of infected males develop prostatic abscess characterized by pain during urination , difficulty in passing urine, and urinary retention requiring catheterisation . [1] Rectal examination shows inflammation of the prostate . [3] In Thailand, 30% of the infected children develop parotid abscesses. [1] Encephalomyelitis can occur in healthy people without risk factors. ... There were 24 African countries and three Middle Eastern countries predicted to be endemic with melioidosis, however not a single case was reported from them. [28] A total of 51 cases of melioidosis were reported in Bangladesh from 1961–2017. ... Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease . 3 (1): 28. doi : 10.3390/tropicalmed3010028 .TLR5, PRMT1, CYCSP51, PDE7A, TNF, SLC46A1, TLR4, IL1B, IL10, IL18, TLR1, IFNG, NLRC4, TLR2, CASP1, NLRP3, HSPD1, HSD17B6, TNFSF4, TXNRD1, VWF, ABCA4, ABCG2, SELL, IL24, ADAMTS13, PYCARD, IL23A, TREM1, RHOF, NOD2, NBEAL1, GSDMD, RNF34, RBM45, SLC11A1, KITLG, PTPN6, POMC, ARG1, STS, CALR, CASP6, CD14, CPOX, CRP, CSF2, CX3CR1, DECR1, EMP1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DRB1, HMGB1, HRC, IFNA1, IFNA13, IL1A, IL4, IL6, CXCL8, IL17A, LTA, AMBP, NM, BIRC6-AS1
-
Mesothelioma
Wikipedia
Indeed, the relationship between asbestos and mesothelioma is so strong that many consider mesothelioma a "signal" or "sentinel" tumor. [28] [29] [30] [31] A history of asbestos exposure exists in most cases.MSLN, BAP1, CDKN2A, NF2, EGFR, SPP1, RASSF1, MUC1, FGF2, MTOR, IFNG, SOD2, ITLN1, GPC3, MYO18B, PDGFA, PGR, CDKN1B, GSTM1, EGR1, FHIT, GDF10, ESR1, FGF1, APC, SLC6A20, CAT, PUF60, JMJD6, CDH1, PDGFC, PPP1R14A, TP53, NME2, ZNF667-AS1, EID1, XRCC1, SYK, GSN, XRCC3, TXNRD1, DIO2, CDKN2B, WT1, BCL10, CTNNB1, CD274, MDM2, H3P10, CALB2, MTAP, MET, CTLA4, VEGFA, CEACAM5, BCL2, HGF, TYMS, AKT1, LINC01194, MAPK1, CASP3, CD44, PIK3CD, VIM, PDPN, MAPK7, AQP1, GJA1, EPHB2, REN, PIK3CG, PTEN, PIK3CB, PIK3CA, TXN, HMGB1, STAT3, DPP4, MMP9, EIF4G1, EIF4A2, MARCKSL1, EGF, ETFA, DCTN6, CCL2, EIF4E, TMED7, KRT20, PSMD9, PSG2, IFI27, FOLR1, MAPK3, KRT5, GLI1, TNFSF10, IGF1R, IGF1, MFAP1, IFNB1, MMP2, ABCC1, ZNRD2, NKX2-1, CDK2, CYP19A1, CEACAM3, CDK4, CLDN4, BIRC5, APRT, TMED7-TICAM2, ASS1, H3P23, CEACAM7, BRCA1, TICAM2, C17orf97, MDK, XIAP, CD40, SLC46A1, WIF1, CUL4A, BMS1, HTRA1, CD74, PSMD8, PDGFB, PTGS2, HMOX1, NOTCH1, CDKN1A, RBL2, MUC16, PAX8, ANGPT1, TNFRSF8, TP63, METAP2, MMP14, CD46, MCL1, MIR182, ABCB1, CCND1, COPD, CTAG1A, MIR183, PIM1, AXL, ATP6V1E1, STMN1, YAP1, KRAS, KDR, GCLM, SUB1, IL6, CA9, HPSE, NFE2L2, GDE1, SLC5A5, FOLR2, NQO1, TM7SF2, CTAG1B, FGFR1, TERT, SP1, EPHB4, CSF1R, PARP1, SRC, SSAV1, ACACA, MINDY4, USE1, CCN2, TTF1, VHL, EZH2, GABPA, THY1, SFRP1, COL11A2, XRCC6, SFRP4, DVL3, ABCC2, WLS, TGFBI, SDC1, ALK, SLC2A1, MIR214, H3P8, TSC2, TSC1, TRIP6, TPBG, TLR3, NCR1, DCLK1, CD163, TNXB, TNFSF18, ABCG2, TNF, MIR126, SOCS3, CBFA2T2, EBAG9, LPAR2, SELENOF, WNT7A, TNFRSF18, SPHK1, MIR25, CXADRP1, WNT2, YY1, SCFV, SCLC1, MIRLET7B, SYCE1L, CSRP3, MIR31, MIR29C, VEGFC, FOSL1, TRAP, VCAM1, UVRAG, ARHGEF7, TYROBP, LIMS4, MIR215, USO1, AKR1C3, ABCC3, DDH2, PRB2, TNFRSF10B, H3P9, TNFRSF10A, FGF18, CFLAR, NR1I2, CAMKMT, PDZK1IP1, ROCK2, NAPSA, SF3B6, NSG2, SCARA3, CHRFAM7A, ARHGEF3, MTDH, EFEMP2, OBP2A, ZDHHC8, NXT1, DTD1, SETD2, MARS2, LAMTOR2, SGSM3, HPGDS, LSM1, ANKRD1, GREM1, WWTR1, TLE1, HAVCR2, KISS1R, PROK1, SLC7A14, FSD1, AHNAK, PDGFD, CD276, SETD7, FSD1L, NOD2, VSIR, GAS5, KLHL1, PCGF5, SALL4, AVEN, TWSG1, ACKR3, LIMS2, TRAF7, ASXL2, MARCHF1, PPP1R12C, CADM1, SMUG1, PSD4, GADL1, NOD1, ABCA8, CDK2AP2, ABCC4, TRIM13, MPHOSPH6, SLC52A2, IL4I1, ACTR1A, ABCC5, NXF1, GJC1, SCO2, ABCB5, NR1I3, SETDB1, ZEB2, MUC21, HDAC9, ABCG1, PIAS3, LRRN4, SEC14L2, AZIN2, PRAME, ABCA5, PPP1R13B, PPRC1, DKK1, LIMS3, GABARAP, TUSC2, PRRT2, NLRP3, PLB1, RPP14, KLK11, IL24, CKAP4, ESCO1, CXCR6, PWAR1, MRPL28, PROCR, POT1, ABCA1, TGM2, SLC29A2, F8, F3, F2R, EWSR1, ETS2, ESR2, ERCC1, ERBB4, ERBB3, ERBB2, EPOR, EPO, ELAVL1, EPHA2, EDNRA, S1PR1, TYMP, E2F1, SLC26A2, DLD, AKR1C2, AKR1C1, DCX, FANCD2, FAP, EFEMP1, GBP1, HDAC2, HDAC1, GRN, GPR42, GPER1, GPI, GPC1, GCLC, GLB1, GJA5, GATA3, FGF4, FYN, FUT4, FRZB, FOLR3, FLT4, FLT1, FLNB, MLANA, FOXO1, FGFR2, CXADR, CSPG4, VCAN, ANGPT2, BRCA2, BRAF, BMP6, BMP2, BAX, BAK1, ARR3, ARNTL, BIRC3, ANXA4, ALOX15, BST1, ALOX5, ALOX12, ALDH1A1, ALCAM, ADRA2B, ADRA1A, ADM, ADAM10, ADA, ACTB, BRS3, TSPO, CSF1, CD68, MAPK14, HAPLN1, CLDN3, COX8A, COPA, CHRM3, CHEK1, CDKN1C, CDK7, CD70, CD40LG, VPS51, CD14, CD247, KRIT1, CASR, CASP9, CALR, CALM3, CALM2, CALM1, DDR1, HIF1A, HOXA1, TGFA, HOXA7, PTK2, MAP2K5, MAP2K1, MAPK8, PKN1, PRKCD, PRKCB, PRKCA, PRKAR1A, POU1F1, POMC, PLXNA1, PLG, ABCA2, PLAT, PLA2G4A, PIK3R2, PIK3R1, PDGFRB, PCNA, PAX5, SERPINE1, PEBP1, RAN, RELA, REV3L, SPG7, TFPI, TEK, TCN2, ZEB1, TBXAS1, TAT, AURKA, STAT1, ST14, SSTR4, SMO, RFC1, SMARCB1, SNAI2, SLC20A2, SLC20A1, SLC19A1, SHH, SDC2, S100A9, S100A4, RPE65, NTSR1, NTS, NT5E, IGF2, KIT, KISS1, ITGB3, CXCL10, IL13RA2, CXCL8, IL4, IL1B, IL1A, IGFBP2, IFNA13, KIF22, IFNA1, ICAM1, TNC, HTC2, HSPA5, HSPA4, HOXB9, HOXB4, HOXA10, HOXA9, KIF25, KRT19, NOTCH2, MITF, NOS3, PPP1R12A, MYOG, MYOD1, MUC2, MSH3, MRC1, MPZ, MPST, MKI67, KITLG, L1CAM, MDM4, MCAM, MC1R, SMAD3, EPCAM, LYN, LTBP3, LTBP2, LGALS9, LGALS3, PLAU
-
Osteoporosis
Wikipedia
At least 30 genes are associated with the development of osteoporosis. [27] Those who have already had a fracture are at least twice as likely to have another fracture compared to someone of the same age and sex. [28] Build: A small stature is also a nonmodifiable risk factor associated with the development of osteoporosis. [29] Potentially modifiable [ edit ] Excessive alcohol: Although small amounts of alcohol are probably beneficial (bone density increases with increasing alcohol intake), chronic heavy drinking (alcohol intake greater than three units/day) probably increases fracture risk despite any beneficial effects on bone density. [30] [31] Vitamin D deficiency : [32] [33] Low circulating Vitamin D is common among the elderly worldwide. [4] Mild vitamin D insufficiency is associated with increased parathyroid hormone (PTH) production. [4] PTH increases bone resorption, leading to bone loss.PTH, TGFB1, TNF, IL6, IL1B, CAT, HIF1A, PTK2B, PTGER4, ACP5, COL1A1, COL1A2, ESR1, VDR, LRP5, TNFSF11, TNFRSF11B, BTF3P11, TNFRSF11A, IL17A, SOST, PTHLH, PIK3CD, PIK3CG, ESR2, BGLAP, PIK3CA, CTNNB1, PIK3CB, DMD, BEST1, CALCA, C4orf3, IL1RN, NPY, WNT3A, TRAF6, SQOR, DANCR, IL1A, REN, BRD2, RPS5, SPP1, TAC1, VEGFA, PTH1R, SMAD2, CYP19A1, ELAVL2, BMP2, CNR2, RUNX2, MIR214, CLCF1, SNHG1, DGCR5, IL36A, ADGRF5, REM1, ARHGEF3, MIR409, IL17D, MIR422A, MIR410, MIR503, GPR87, CRNDE, SIRT1, PPWD1, NCF1, SEMA4D, MIR542, MIR618, CPQ, MIR708, TUBA1B, SEMA3A, TRAP, MIR373, MEG3, FBXW7, IL27, ZBTB8OS, CCL4L1, TMPRSS6, MIRLET7C, CCL4L2, PTRH1, MIR146A, TRIM63, FNDC1, MIR155, MAP9, MIR203A, VKORC1, MIR21, MIR210, MIR27A, GAS5, MIR320A, HAMP, MIR98, MIR331, MIR338, RETN, ITLN1, DHTKD1, IL18BP, CCL4, ADIPOQ, LGALS8, ICAM1, IBSP, PRMT1, HP, HLA-B, HLA-A, GPX1, GNAI2, GLI2, GJA4, GAPDH, FLNA, EZH2, ETS1, EGR3, CTSK, CSF1, COL9A1, CDX2, CD38, CD34, CD14, CASP3, CACNG1, C3, BMP4, AR, IGF1, SMAD4, NRIP1, MT2A, FGF23, VIP, UMOD, TNFRSF1A, TLR4, SOX9, SOX5, SOD2, SLIT3, SFRP1, CCL11, ADRB1, CCL2, REL, RDX, RBP4, RBBP4, RAC2, RAC1, LGMN, MAP2K7, MAPK3, PLCG2, SERPINE1, NPPB, NEO1, MTNR1B, CASC11
-
Panic Disorder
Wikipedia
Archived from the original on 8 July 2013 . Retrieved 28 June 2013 . ^ "FASTSTATS — Illegal Drug Use" . ... Archived from the original on 5 July 2013 . Retrieved 28 June 2013 . ^ Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with panic disorder (PDF) . ... "Substance abuse and panic-related anxiety: a critical review". Behaviour Research and Therapy . 28 (5): 385–93. doi : 10.1016/0005-7967(90)90157-E . ... Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment . 8 (1–2): 19–28. doi : 10.1016/0740-5472(91)90023-4 . ... National Institute of Mental Health. Archived from the original on 28 April 2006 . Retrieved 12 May 2006 . ^ van Apeldoorn, F.COMT, CCKBR, ADORA2A, ADRA2A, HTR1A, INS, ANO2, HTR2A, PKP1, PEPD, NPSR1, CALCOCO1, CCK, SGCZ, BDNF, PRDM11, SDK2, NPS, MAOA, SLC6A4, SLC6A2, TMEM132D, CRHR1, ARSI, ACE, TPH2, PTK7, ASIC1, GAD1, TPH1, LOC110806262, RGS2, CRHR2, HCRT, OPN1SW, ELK3, CRP, EPHB1, IL10, TSPO, GLRB, GRPR, CRH, CCKAR, IKBKE, KRT7, APOE, CYP2C19, HP, MIR22, TAL1, SLC3A1, TNF, NPY5R, GRP, GRM2, IL6, LEP, CBLIF, CREM, SCLY, GABRA6, HBHR, DRD4, DRD1, TSHZ1, TACR1, OGA, DEAF1, PER2, TCF3, WASF1, SGCE, AKR1C3, KHSRP, THAS, GPR65, TMEM98, TNFRSF1B, PSIP1, EFHC2, SIGLEC7, FOXP3, LINC02210-CRHR1, C20orf181, MIR579, MIR491, MIR488, MIR339, MIR148A, CCL4L1, DAOA-AS1, DAOA, MPEG1, DGKH, DYNLL2, SLC43A2, TMEM132E, PLA2G4E, DTNBP1, NPL, SNRNP70, LRRC8E, MANEA, GFRA4, CFAP46, GHRL, HECA, NBAS, GAL, SRD5A1, ASIC2, SNAPC2, DRD2, HCRTR2, HCRTR1, HCLS1, GPX1, GPM6A, GLO1, GDNF, GANC, GAD2, GABRB3, GABRA5, GABBR1, ELN, AKR1C1, HLA-DRB1, CYP2B6, CUX1, CLU, CHRNA4, CDS1, VPS51, BDKRB2, BDKRB1, AVPR1B, ANGPT2, ALAD, AGTR1, AGT, HLA-B, HTR2C, SLC6A3, NTRK3, SET, SCN7A, RGS7, PSG5, PSAP, MAP2K7, PON1, PGR, PDE4B, SERPINE1, OXTR, OPRK1, OGG1, NPPA, HTR3A, NPY, NOS2, NOS1, NGFR, NAGLU, MECP2, MBL2, LSAMP, LDHB, LDHA, IL2RB, IL2, IL1R1, NTRK2
-
Skin Condition
Wikipedia
Diseases of the skin include skin infections and skin neoplasms (including skin cancer ). [28] History [ edit ] See also: History of dermatology In 1572, Geronimo Mercuriali of Forlì , Italy , completed De morbis cutaneis ('On the diseases of the skin').FYN, COL7A1, KRT10, DUH1, FLCN, ECM1, IKBKG, ATP2A2, KRT1, USB1, ADAR, KRT9, KRT5, PKP1, POMP, EBP, ADA, MBTPS2, SLC29A3, DSP, TRPV3, KRT14, FOXP3, SASH1, SPINK5, UBL5, FERMT1, SLURP1, CHST8, SUV39H2, HSDL1, GJB4, TMC8, FLG2, GJB6, TGM1, ABCB6, GJB2, BRAF, CDSN, CTSC, COL17A1, DSG1, EDA, ERCC2, GJA1, GJB3, HAND2, IGFBP3, ITGA6, ITGB4, KRT16, PTCH1, FZD6, CRLF1, SNAP29, GTF2H5
-
Thyroid Disease
Wikipedia
It is an imaging process that can often be done in a doctor's office, is painless, and does not expose the individual to any radiation. [27] The main characteristics that can help distinguish a benign vs. malignant (cancerous) thyroid nodule on ultrasound are as follows: [28] Possible thyroid cancer More likely benign irregular borders smooth borders hypoechoic (less echogenic than the surrounding tissue) hyperechoic incomplete "halo" spongiform appearance significant intranodular / central blood flow by power Doppler marked peripheral blood flow microcalcifications larger, broad calcifications (note: these can be seen in medullary thyroid cancer) nodule appears more tall than wide on transverse study "comet tail" artifact as sound waves bounce off intranodular colloid documented progressive increase in size of nodule on ultrasound Although ultrasonography is a very important diagnostic tool, this method is not always able to separate benign from malignant nodules with certainty.TSHR, CCL2, DIO2, KLF9, GULP1, DIO1, ITGB5, TGOLN2, TBX3, ID2, ZNF676, CNST, ID3, PTEN, TG, CTLA4, SLC5A5, TPO, HT, SLC16A2, BRAF, PTPN22, RET, TNF, FOXP3, CALCA, SLC26A4, IL17A, IL4, IL13, CD40, DICER1, TNFRSF1A, VDR, HLA-DRB1, GH1, VEGFA, PAX8, NCOA4, TNFSF10, SH2B3, NKX2-1, IL6, ZFAT, IGF1, IFNG, VAMAS6, MIR125A, ICAM1, HMGA1, STAT3, ABO, CD52, BCL2, GAD2, CAT, CTSB, GNB3, MED12, IL18RAP, IL18R1, INPP4B, NRP2, SQSTM1, SOCS3, CD83, VAV3, AQP4, RNASET2, SLC19A2, TXNRD2, FASLG, KHDRBS1, IKZF3, TBC1D9, ICOSLG, ATD, BAX, PDE8B, TNFSF4, TLR4, CD47, CD34, TNFRSF1B, TP53, CD14, TRH, UCP2, FOSL1, CAPZB, PTTG1IP, BEST1, XRCC3, XRCC5, TNDM, SMUG1, XIAP, NUP62, TGFB1, AIRE, FCRL3, CYP2R1, RBM45, ALB, CEP128, IL23R, SLC5A8, AHSG, AGA, GLIS3, PARP4, IL27, LINC01193, SERPINA13P, PARP1, MIR34A, MIR499A, MT1IP, PSS, FCRL1, MAGT1, SECISBP2, HSD17B7, HIPK2, DROSHA, CD274, TBX21, NOX4, APC, DCTN4, ALPP, GHRL, SMOC2, DUOX1, BANK1, UACA, CHDH, SELENOS, ZNF395, ALG1, ALPI, THRA, CISH, CXCR3, JUND, IL16, ERBB2, CXCL10, INSL3, IRAK1, DMD, JUN, JUNB, KIT, FOXE1, LGALS1, LGALS3, LRP2, LTA, EPCAM, MBL2, MECP2, CXCL9, IL15, FOXO3, MT1B, GAD1, GPX4, GSTM1, GSTT1, GTF2H1, HFE, HLA-A, LRRC32, IAPP, GABPA, FOLH1, FSHR, IFNA1, IFNA13, FOSB, FOS, IGFBP3, IL1B, IL2RA, MT1A, MT1E, TFPI, SNX2, S100A1, S100B, CTSL, CCL5, CXCL12, SEL1L, SLC2A1, CTAG1B, SPTAN1, CYP1A1, SSTR2, CCR6, STAT4, STATH, TBXT, CCR5, TRA, TERT, RXRB, REN, MT1F, MYO9B, MT1G, MT1H, MT1JP, MT1M, MT1L, MT1X, MTHFR, MTNR1A, NFE2L2, PTGS2, TNFRSF11B, SERPINE1, PDE4D, CYP1A2, ABCB1, PTCH1, ACR, PTGDS, THRA1/BTR
-
Urinary Incontinence
Wikipedia
Screening questions should inquire about what symptoms they have experienced, how severe the symptoms are, and if the symptoms affect their daily lives. [28] As of 2018, studies have not shown a change in outcomes with urinary incontinence screenings in women. [29] Management [ edit ] Treatment options range from conservative treatment, behavioral therapy, bladder retraining, [30] pelvic floor therapy , collecting devices (for men), fixer-occluder devices for incontinence (in men), medications and surgery. [31] A 2018 systematic review confirms that several nonsurgical treatments can improve or even stop UI in women. [32] The success of treatment depends on the correct diagnoses. [33] Behavioral therapy [ edit ] Behavioral therapy involves the use of both suppressive techniques (distraction, relaxation) and learning to avoid foods that may worsen urinary incontinence. ... Retrieved 2018-05-10 . ^ a b Saraswat, L; Rehman, H; Omar, MI; Cody, JD; Aluko, P; Glazener, CM (28 January 2020). "Traditional suburethral sling operations for urinary incontinence in women" .ADRA1A, MAPK1, IL1RAPL1, CNKSR2, DKK1, IQSEC2, ADNP, ATP13A2, ZFYVE26, FTSJ1, SUFU, ATXN10, CHMP2B, TOR1AIP1, SACS, COQ2, FLVCR1, ATL1, MID2, VCP, SLC9A6, COG5, ZNF41, USP7, USP9X, JRK, PEX11B, CACNA1H, CACNA1G, CYP7B1, ARHGEF6, FRMPD4, LRIG2, WASHC5, AP5Z1, MED12, STUB1, FARS2, RETREG1, BNC2, IFT57, ASXL3, VANGL1, C19orf12, SLC9A7, HS6ST2, TIMM50, RAB39B, NIPA1, CPT1C, HGSNAT, PTCHD1, ARX, NEXMIF, ZNF81, USP27X, SPG11, FUZ, PANK2, GBA2, PRDM8, GJC2, VANGL2, GATAD2B, HACE1, ALS2, TRPV4, ALG13, HPSE2, CXorf56, IRF2BPL, MTMR14, UPF3B, FA2H, ZNF711, ATXN8, MYF6, HEXB, NF2, NAGLU, BIN1, MECP2, KIF5A, KCND3, KCNC3, IGHMBP2, ARSA, HSPD1, HMBS, HLA-DRB1, HLA-DQB1, MNX1, HCFC1, CLCNKB, GRIN2B, GDI1, GBE1, GABRG2, GABRB3, GABRA1, FMR1, ACSL4, DNMT1, DNM2, DMD, DLG3, AUH, ADGRB2, ABCD1, NOTCH3, PAK3, PDCD1, TYROBP, TTR, TRIO, TSPAN7, AGTR2, TBP, TBCD, TBXT, SYP, SPG7, SPAST, SMARCB1, SLC20A2, SLC16A2, SLC12A3, SLC2A1, SGSH, CCL2, SCN9A, SCN8A, ATXN8OS, RYR1, RTN2, RPS6KA3, ALDH18A1, PSAP, HTRA1, PDGFRB, PDGFB, CLCN4, VIP, COL1A1, COL3A1, DCN, HTR2A, VIPR1, NPY, TGFB1, A2M
-
Cardiac Arrest
Wikipedia
Near-death experiences are reported by 10 to 20 percent of people who survived cardiac arrest. [17] Certain types of prompt intervention can often reverse a cardiac arrest, but without such intervention, death is all but certain. [18] In certain cases, cardiac arrest is an anticipated outcome of a serious illness where death is expected. [19] Causes [ edit ] Conduction system of heart Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) and sudden cardiac death (SCD) occur when the heart abruptly begins to beat in an abnormal or irregular rhythm ( arrhythmia ). [20] Without organized electrical activity in the heart muscle, there is no consistent contraction of the ventricles , which results in the heart's inability to generate an adequate cardiac output (forward pumping of blood from heart to rest of the body). [21] There are many different types of arrhythmias , but the ones most frequently recorded in SCA and SCD are ventricular tachycardia (VT) or ventricular fibrillation (VF). [22] Less common causes of dysrhythmias in cardiac arrest include pulseless electrical activity (PEA) or asystole . [20] Such rhythms are seen when there is prolonged cardiac arrest, progression of ventricular fibrillation, or due to efforts such as defibrillation to resuscitate the person. [20] Sudden cardiac arrest can result from cardiac and non-cardiac causes including the following: Coronary artery disease [ edit ] Coronary artery disease (CAD), also known as ischemic heart disease , is responsible for 62 to 70 percent of all SCDs. [23] [24] CAD is a much less frequent cause of SCD in people under the age of 40. [23] Cases have shown that the most common finding at postmortem examination of sudden cardiac death (SCD) is chronic high-grade stenosis of at least one segment of a major coronary artery, the arteries that supply the heart muscle with its blood supply. [25] Structural heart disease [ edit ] Structural heart diseases not related to CAD account for 10% of all SCDs. [21] [24] Examples of these include: cardiomyopathies ( hypertrophic , dilated , or arrythmogenic ), cardiac rhythm disturbances , congenital coronary artery anomalies , myocarditis , hypertensive heart disease , [26] and congestive heart failure . [27] Left ventricular hypertrophy is thought to be a leading cause of SCD in the adult population. [28] [20] This is most commonly the result of longstanding high blood pressure which has caused secondary damage to the wall of the main pumping chamber of the heart, the left ventricle . [29] A 1999 review of SCDs in the United States found that this accounted for over 30% of SCDs for those under 30 years. ... June 22, 2016. Archived from the original on 28 July 2016 . Retrieved 16 August 2016 . ^ a b c "How Can Death Due to Sudden Cardiac Arrest Be Prevented?" ... June 22, 2016. Archived from the original on 28 July 2016 . Retrieved 16 August 2016 . ^ a b c Schenone AL, Cohen A, Patarroyo G, Harper L, Wang X, Shishehbor MH, Menon V, Duggal A (November 2016). ... PMID 16314375 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Cydulka, Rita K., editor. (2017-08-28). Tintinalli's emergency medicine manual . ... PMID 22968891 . ^ American Heart Association (May 2006). "2005 American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and emergency cardiovascular care (ECC) of pediatric and neonatal patients: pediatric advanced life support". Pediatrics . 117 (5): e1005-28. doi : 10.1542/peds.2006-0346 . PMID 16651281 .CACNA1C, TMEM43, DSP, LMNA, MYBPC3, TNNT2, NKX2-5, PPP1R13L, SCN5A, KCNH2, KCNQ1, CACNA2D1, NOS1AP, KCNE1, TRDN, IKZF1, AKAP9, CRLF1, HCN4, KCNE2, ZNF365, GTF2IRD1, ACADL, BAZ1B, RAB3GAP1, CSRP3, CLIP2, WIPF1, WAS, TNNI3, TGFB3, SNTA1, SCN10A, SCN4B, RYR2, RFC2, AP1G2, ZFPM2, SYNE2, SYNE1, TPTE2P6, KCTD1, RBM20, PCSK9, TECRL, ARL5B, MARCHF10, UPP2, ZNF385B, ALG10B, DNAJC19, DEGS2, TANC1, MAML2, ZRANB3, ABCG8, ABCG5, TRPM4, PRKAG2, PLCE1, BAZ2B, ACAD9, TBL2, PTPN22, ABCA12, LDLRAP1, NGEF, CLCF1, PLN, PTEN, MYH7, PKP2, CPT1A, GRIA1, GNAI2, FHL1, FGFR3, ESR1, EYA4, EMD, ELN, DTNA, DSG2, DSC2, DES, CHRNB4, HLA-B, CAV3, CASQ2, CALM3, CALM2, CALM1, ATF1, ABCC6, APOB, ANK2, AKT1, PARP4, ACYP2, ENPP1, GTF2I, ND6, ND4, MYL3, ACADVL, MYH6, TRNW, TRNS2, TRNS1, TRNQ, TRNL1, TRNH, TRNF, JUP, ND5, CEP85L, ND1, COX3, KCNJ2, KCNJ5, LDLR, LIMK1, LRP6, COX1, COX2, CACNB2, LIPC, KCNJ11, ADRB2, ADRA2B, ROCK2, ROCK1, IL18
-
Conduct Disorder
Wikipedia
Co-variation between two variables can arise, for instance, if they represent age-specific expressions of similar underlying genetic factors. [28] For example, the tendency to smoke during pregnancy (SDP) is subject to substantial genetic influence (D'Onofrio et al., 2007), as is conduct disorder. ... Troy University at Montgomery . 33 (2) . Retrieved 28 September 2020 – via files.eric.ed.gov.
-
Migraine
Wikipedia
Disorder resulting in recurrent moderate-severe headaches Migraine Woman with migraine headache Specialty Neurology Symptoms Headaches , nausea , sensitivity to light , sensitivity to sound , sensitivity to smell [1] [2] Usual onset Around puberty [1] Duration Recurrent, long term [1] Causes Environmental and genetic [3] Risk factors Family history , female [4] [5] Differential diagnosis Subarachnoid hemorrhage , venous thrombosis , idiopathic intracranial hypertension , brain tumor , tension headache , sinusitis , [6] cluster headache [7] Prevention Metoprolol , valproate , topiramate [8] [9] Medication Ibuprofen , paracetamol (acetaminophen), triptans , ergotamines [5] [10] Frequency ~15% [11] Migraine ( UK : / ˈ m iː ɡ r eɪ n / , US : / ˈ m aɪ -/ ) [12] [13] is a primary headache disorder characterized by recurrent headaches that are moderate to severe. [1] Typically, episodes affect one half of the head, are pulsating in nature, and last from a few hours to 3 days. [1] Associated symptoms may include nausea , vomiting , and sensitivity to light , sound , or smell . [2] The pain is generally made worse by physical activity, [14] although regular exercise may have prophylactic effects. [15] Up to one-third of people affected have aura : typically a short period of visual disturbance that signals that the headache will soon occur. [14] Occasionally, aura can occur with little or no headache following it. [16] Migraine is believed to be due to a mixture of environmental and genetic factors. [3] About two-thirds of cases run in families. [5] Changing hormone levels may also play a role, as migraine affects slightly more boys than girls before puberty and two to three times more women than men. [4] [17] The risk of migraine usually decreases during pregnancy and after menopause . [4] [18] The underlying mechanisms are not fully known. [18] They are, however, believed to involve the nerves and blood vessels of the brain. [5] Initial recommended treatment is with simple pain medication such as ibuprofen and paracetamol (acetaminophen) for the headache, medication for the nausea , and the avoidance of triggers. [10] Specific medications such as triptans or ergotamines may be used in those for whom simple pain medications are not effective. [5] Caffeine may be added to the above. [19] A number of medications are useful to prevent attacks including metoprolol , valproate , and topiramate . [8] [9] Globally, approximately 15% of people are affected by migraine. [11] In the Global Burden of Disease Study of 2010, it was ranked as the third most prevalent disorder in the world. [20] It most often starts at puberty and is worst during middle age. [1] As of 2016, it is one of the most common causes of disability . [21] An early description consistent with migraines is contained in the Ebers papyrus , written around 1500 BC in ancient Egypt . [22] The word migraine is from the Greek ἡμικρᾱνίᾱ ( hēmikrāníā ), 'pain in half of the head', [23] from ἡμι- ( hēmi- ), 'half', and κρᾱνίον ( krāníon ), 'skull'. [24] Contents 1 Signs and symptoms 1.1 Prodrome phase 1.2 Aura phase 1.3 Pain phase 1.4 Postdrome 2 Cause 2.1 Genetics 2.2 Triggers 2.2.1 Physiological aspects 2.2.2 Dietary aspects 2.2.3 Environmental aspects 3 Pathophysiology 3.1 Aura 3.2 Pain 3.3 Neuromodulators 4 Diagnosis 4.1 Classification 4.2 Abdominal migraine 4.3 Differential diagnosis 5 Prevention 5.1 Medication 5.2 Alternative therapies 5.3 Devices and surgery 6 Management 6.1 Analgesics 6.2 Triptans 6.3 CGRP receptor antagonists 6.4 Ergotamines 6.5 Magnesium 6.6 Other 6.7 Children 6.8 Chronic migraine 7 Prognosis 8 Epidemiology 9 History 10 Society and culture 11 Research 12 References 12.1 Notes 13 Further reading 14 External links 15 See also Signs and symptoms [ edit ] Migraine typically presents with self-limited, recurrent severe headache associated with autonomic symptoms. [5] [25] About 15–30% of people living with migraine experience episodes with aura , [10] [26] and they also frequently experience episodes without aura. [27] The severity of the pain, duration of the headache, and frequency of attacks are variable. [5] A migraine lasting longer than 72 hours is termed status migrainosus. [28] There are four possible phases to a migraine, although not all the phases are necessarily experienced: [14] The prodrome , which occurs hours or days before the headache The aura, which immediately precedes the headache The pain phase, also known as headache phase The postdrome , the effects experienced following the end of a migraine attack Migraine is associated with major depression , bipolar disorder , anxiety disorders , and obsessive compulsive disorder . ... Children [ edit ] Ibuprofen helps decrease pain in children with migraines and is the initially recommended treatment. [163] [164] Paracetamol does not appear to be effective in providing pain relief. [163] Triptans are effective, though there is a risk of causing minor side effects like taste disturbance, nasal symptoms, dizziness, fatigue, low energy, nausea, or vomiting. [163] Ibuprofen should be used less than half the days in a month and triptans less than a third of the days in a month to decrease the risk of medication overuse headache. [164] Chronic migraine [ edit ] Topiramate and botulinum toxin (Botox) have evidence in treating chronic migraine. [116] [165] Botulinum toxin has been found to be useful in those with chronic migraine but not those with episodic ones. [166] [167] The anti-CGRP monoclonal antibody erenumab was found in one study to decrease chronic migraines by 2.4 days more than placebo. [168] Prognosis [ edit ] Long-term prognosis in people living with migraine is variable. [25] Most people with migraine have periods of lost productivity due to their disease; [5] however typically the condition is fairly benign [25] and is not associated with an increased risk of death. [169] There are four main patterns to the disease: symptoms can resolve completely, symptoms can continue but become gradually less with time, symptoms may continue at the same frequency and severity, or attacks may become worse and more frequent. [25] Migraine with aura appears to be a risk factor for ischemic stroke [170] doubling the risk. [171] Being a young adult, being female, using hormonal birth control , and smoking further increases this risk. [170] There also appears to be an association with cervical artery dissection . [172] Migraine without aura does not appear to be a factor. [173] The relationship with heart problems is inconclusive with a single study supporting an association. [170] Migraine does not appear to increase the risk of death from stroke or heart disease. [169] Preventative therapy of migraines in those with migraine with aura may prevent associated strokes. [174] People with migraine, particularly women, may develop higher than average numbers of white matter brain lesions of unclear significance. [175] Epidemiology [ edit ] Disability-adjusted life year for migraines per 100,000 inhabitants in 2004 no data <45 45–65 65–85 85–105 105–125 125–145 145–165 165–185 185–205 205–225 225–245 >245 Worldwide, migraine affects nearly 15% or approximately one billion people. [11] It is more common in women at 19% than men at 11%. [11] In the United States, about 6% of men and 18% of women experience a migraine attack in a given year, with a lifetime risk of about 18% and 43% respectively. [5] In Europe, migraines affect 12–28% of people at some point in their lives with about 6–15% of adult men and 14–35% of adult women getting at least one yearly. [17] Rates of migraine are slightly lower in Asia and Africa than in Western countries. [54] [176] Chronic migraine occurs in approximately 1.4 to 2.2% of the population. [177] These figures vary substantially with age: onset of migraine is most commonly between 15 and 24 years of age, and occur most frequently in those 35 to 45 years of age. [5] In children, about 1.7% of 7 year olds and 3.9% of those between 7 and 15 experience migraine, with the condition being slightly more common in boys before puberty . [178] Children as young as two years may be affected. [163] During adolescence, migraine becomes more common among women [178] and this persists for the rest of the lifespan, being twice as common among elderly females than males. [179] In women migraine without aura are more common than migraine with aura; however in men the two types occur with similar frequency. [54] During perimenopause symptoms often get worse before decreasing in severity. [179] While symptoms resolve in about two thirds of the elderly, in 3 to 10% they persist. [48] History [ edit ] The Head Ache , George Cruikshank (1819) An early description consistent with migraine is contained in the Ebers papyrus , written around 1500 BCE in ancient Egypt. [22] In 200 BCE, writings from the Hippocratic school of medicine described the visual aura that can precede the headache and a partial relief occurring through vomiting. [180] A second-century description by Aretaeus of Cappadocia divided headaches into three types: cephalalgia, cephalea, and heterocrania. [181] Galen of Pergamon used the term hemicrania (half-head), from which the word migraine was eventually derived. [181] He also proposed that the pain arose from the meninges and blood vessels of the head. [180] Migraine was first divided into the two now used types – migraine with aura ( migraine ophthalmique ) and migraine without aura ( migraine vulgaire ) in 1887 by Louis Hyacinthe Thomas, a French Librarian. [180] The mystical visions of Hildegard von Bingen , which she described as “reflections of the living light", are consistent with the visual aura experienced during migraines. [182] A trepanated skull, from the Neolithic .TRPM8, NOTCH3, PRDM16, LRP1, TGFBR2, SUGCT, FHL5, CALCA, ATP1A2, COL4A1, ESR1, HTR2A, GABRQ, HTR7, CACNA1A, MFN1, PRRT2, MEF2D, HTR1A, OPA1, COX2, SLC1A3, TGFB1, POLG, IL10, GABRG2, HPSE2, TREX1, PHACTR1, ASTN2, TWNK, CSNK1D, NRP1, PIK3CA, ADARB2, TRNS2, RPS27, RPS26, ZMYND8, RPS24, RPS20, RPS19, AMACR, RPS17, IL12A, RPS28, IL12B, INPP5A, KCNA1, RPS15A, RPS10, LEPROTL1, RRM2B, KCNQ2, KCNQ3, PRKG1, SRPX2, KRAS, HLA-B, MARCHF4, PMS1, MSH6, MYORG, FAN1, WAPL, MLH3, SLC24A3, SCN8A, PMS2, SCN2A, SCN1A, S100A12, PGK1, HTR1B, RPS29, PDGFB, NMUR2, WDR12, RELA, TRNS1, ND5, COX1, MYD88, COX3, CYTB, RPL5, MTHFR, MVK, ND1, ND4, ND6, NOS3, MRPL37, NEDD4L, TRNW, TRNF, TRNH, TRNV, TRNK, TRNL1, TRNQ, TRNC, NDP, MSH2, MMP17, RPS7, PLCE1, HJURP, RPL35A, NFIX, EPCAM, RPL27, SMAD4, RPL26, RPL18, NF2, MEFV, CNNM2, MLH1, GRIN2A, RPL15, ADA2, ERAP1, RPL11, SMAD3, SH2B1, RNF213, COL5A2, VHL, RNASEH1, ACSF3, VSTM4, CCR1, COL1A1, COL3A1, TWIST1, COL5A1, COMT, KCNK18, TNFRSF1A, CLVS1, IL23R, TNF, TLR4, YAP1, DBH, ACE, DRD2, UBAC2, SLC6A19, NOP56, PLCE1-AS1, ACVRL1, LINC02646, AIP, ADCYAP1, LINC02109, LINC01752, BAZ1B, IL12A-AS1, WASL, SLC25A4, MPPED2, PEX11B, APP, KCNK5, FAS, KLRC4, RABGAP1L, DNM1L, BMPR1A, C4A, CFDP1, MRVI1, GP1BB, GPR101, FBN2, SLC6A4, FGFR3, FGFR2, GDF2, GP1BA, RPL35, STIM1, CARF, SMARCB1, SUV39H2, POLG2, GATA2, SEMA4A, STAT4, GATA1, C11orf95, ADAMTSL1, ENG, NLRP3, GP9, MLX, NLRC4, HAUS1, DCLRE1C, SLC2A1, GCDH, TSR2, LTA, HCRT, BDNF, GOLPH3, TRPV1, APOE, TRPA1, MAOA, CRP, RAMP1, AVP, PSMG1, HTR1F, MZB1, LEP, DUSP2, VIP, IL6, ADCYAP1R1, KLF6, PGR, SLC6A3, PTGS2, GRIA1, ADIPOQ, GRIA3, CNR1, F5, NOS1, EDNRA, HTR2C, TAC1, MTDH, SPRTN, INSR, NOS2, PANX1, PTX3, STX1A, POMC, VEGFA, CALCRL, VWF, TSPAN2, STIN2-VNTR, DRD3, HTR1D, P2RX7, AGT, KCNN3, HLA-DRB1, OPRM1, FAAH, HCRTR1, DAO, GC, SOD2, FMR1, HCRTR2, GRIN2B, MGLL, HNMT, UTS2, PART1, EDN1, TPH2, ICAM1, CYP19A1, RLS1, TYRP1, TSPAN33, CACNA1C, MIR34A, HEPH, ALB, MTCO2P12, ASIC3, IAPP, GABRA3, TBPL1, REN, MTHFD1, PRL, KCNK2, PON1, AKR1A1, CD274, GABRR3, MMD, ADHD1, TRIM13, ANKK1, MGR6, PYCARD, PTCRA, CCL4L1, MIR30A, TRPV3, REM1, MIR375, NR1I3, PSAT1, CCL4L2, LOC110806262, LOC107987479, NBEA, ACAD8, IL37, OPN1MW3, LINC01672, CCR2, KLK4, BMS1, OPN1MW2, CXADRP1, MIR382, BACE1, OR2AG1, AJAP1, SYNE1, RETN, P2RY12, ACE2, PGPEP1, RPTOR, MOCOS, NPEPPS, OLAH, ZMIZ1, CHMP1B, IMPACT, VWA8, TBC1D9, PAG1, ZKSCAN7, ZC4H2, KCNK10, HRH3, MAPKAP1, ATP5MD, RBM45, GAL, TRAF3IP2, EFHC1, OPN4, DCLK3, NES, CA14, CSAD, CYSLTR1, HPSE, ISYNA1, ADRM1, ACSL5, AK3, AOC1, ROCK2, F9, GABRR2, GABRR1, FSHR, FOS, FLNA, FOXM1, F11, F2RL1, TNFSF10, F2, ETFA, ESR2, ESD, ERCC5, EPHB2, EDNRB, GAD1, GCH1, OPN1MW, GEM, IFNG, HTR5A, HLA-DQB2, HLA-DQB1, HFE, GUCY2D, GSTM2, GSTM1, GRIA4, GRIA2, UTS2R, GPI, GNB3, GNAS, GNAO1, DRD5, DRD4, CYP2D6, OPN1SW, STS, ARR3, AQP4, KLK3, APEX1, ANK3, AMELX, AKT1, AGTR1, ADRA2B, ADH1B, ADARB1, ADAR, ACHE, ASIC1, ATP1A3, BGN, CYP1A1, C3, CXADR, CX3CR1, CTLA4, COL4A2, CLTA, CES1, CD40LG, CD40, ENTPD1, CD14, CAV2, CAT, CASR, CALCR, CACNA1E, IGF1, IL1A, IL1B, SPTAN1, SPAST, SOD1, SLCO1A2, SLC20A2, SLC1A2, SELL, CCL4, CCL2, S100B, RYR2, RNASE2, RHAG, PTPRC, PTEN, PROS1, SPG7, SST, MAPK1, STATH, SLC4A4, NR4A3, XRCC3, XRCC1, WAS, VIPR2, VIPR1, VDR, TYMS, TPH1, TNFRSF1B, TIMP2, THAS, TH, TGFBI, PRNP, ACACA, IL1RN, MUC1, MTR, MMP16, MMP9, MMP3, MMP2, MEIS1, SMCP, MAOB, LPA, LGALS3, LDLR, LBR, TNPO1, IL9, CXCL8, MTRR, NGF, PNOC, NNMT, PLAG1, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, ABCB1, PRDX1, P2RX4, P2RX3, OPRK1, OGG1, NTSR1, NT5E, NRAS, NOTCH4, NPY, PRKAR1A
-
Crohn's Disease
Wikipedia
In severe Crohn's colitis, bleeding may be copious. [25] Flatulence , bloating , and abdominal distension are additional symptoms and may also add to the intestinal discomfort. [25] [28] [29] Symptoms caused by intestinal stenosis are also common in Crohn's disease. ... The Crohn's and Colitis Foundation of America cites this number as approx 149:100,000; NIH cites 28 to 199 per 100,000. [201] [202] Crohn's disease is more common in northern countries, and with higher rates still in the northern areas of these countries. [203] The incidence of Crohn's disease is thought to be similar in Europe but lower in Asia and Africa . [201] It also has a higher incidence in Ashkenazi Jews [1] [204] and smokers. [205] Crohn's disease begins most commonly in people in their teens and 20s, and people in their 50s through to their 70s. [1] [25] [18] It is rarely diagnosed in early childhood.TNF, IL10, NR1H4, NCF4, CRP, NOD2, FUT2, HLA-DRB1, MST1, PPARG, NLRP3, ERAP2, MTHFR, BACH2, PPARA, CCL2, PTPN2, ATG16L1, LEP, TLR9, SLC11A1, TCF7, TLR4, TYK2, VTN, ADIPOQ, SMAD3, PHOX2B, TAGAP, GPBAR1, IRGM, FAM92B, DNMT3A, FPR2, CCNY, DENND1B, NKX2-3, FN1, IL23R, IGF1, IL2RA, IL6, IFNG, IL12B, PTGS2, MADCAM1, TNFRSF1A, EFS, TNFRSF1B, PIKFYVE, DEFB4B, LYZ, DEFB4A, DEFB103A, XPR1, FGF19, DEFB103B, TRIM22, SOCS3, FFAR4, CCR9, ACAD8, IL22, PLB1, BRAF, STAT4, NR0B2, YWHAZ, CHUK, CCN2, DEFA5, DEFB1, FGF7, GH1, GUCA2A, GUCA2B, GUCY2C, HPS1, CXCL8, INPP5D, KRAS, MLH1, COX2, NFKBIA, NRAS, PLA2G1B, PTPN11, CCL25, STAT3, CEACAM4, MAP3K7, TGFB1, TGFB2, NR2C2, TTR, MTCO2P12
-
Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease, Demyelinating, Type 1b
Omim
Studying 109 persons from completed sibships at risk for dominant CMT in 15 unrelated families, Bird and Kraft (1978) concluded that penetrance (as indicated by physical examination and nerve conduction) was 28% complete in the first decade and essentially complete by the middle of the third decade.
-
Dehydrated Hereditary Stomatocytosis 1 With Or Without Pseudohyperkalemia And/or Perinatal Edema
Omim
Blood smears showed 5% stomatocytes, and she displayed a left shift of the osmotic gradient curve on ektacytometry, highly characteristic for DHS. Her 28-year-old son, who was asymptomatic except for jaundice, exhibited blood smears and ektacytometry similar to those of his mother.
-
Metastatic Breast Cancer
Wikipedia
Improvements in the treatment of brain metastases are clearly needed. [28] See also [ edit ] breast cancer metastasis neoplasm chemotherapy Mouse models of breast cancer metastasis Phyllodes tumour References [ edit ] ^ John’s Hopkins. ... Cancer.Net . 2017-05-19 . Retrieved 2019-10-28 . ^ Macedo F, Ladeira K, Pinho F, Saraiva N, Bonito N, Pinto L, Goncalves F (March 2017).EGFR, AKT1, VEGFA, ERBB2, MTOR, BRCA1, BRCA2, AR, ABCB1, MUC1, PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, CYP19A1, RUNX2, EPCAM, CDK4, KRT19, CXCR4, ESR1, TP53, CD274, PTEN, PGR, SMUG1, PARP1, TBC1D9, IL6, BCL2, COL11A2, CEACAM5, GATA3, ERBB3, CXCL8, PTGS2, CD44, MIR10B, CSF2, HIF1A, PSG2, MET, FGFR1, CST6, CEACAM3, MIR21, STAT3, CDH1, CYP2D6, CEACAM7, TGFB1, IL2, EGF, ALB, CCR7, KDR, MDM2, HPSE, FES, CRP, CSF3, EZH2, PIP, SCGB2A2, MMP9, IGF1, NBN, FOXA1, FN1, PLAU, SPP1, SELP, CDK6, TNF, MIR200C, ANGPT2, FCGR3A, FOLH1, ALDH1A1, UBL5, BRD4, PCNA, CCND1, RRM1, GJA1, FASN, FABP4, DHDDS, COL18A1, NECTIN4, IL13RA2, APC, HMGA2, S100A4, CHPT1, VCAM1, BMP2, CXCL12, SETD2, SDCBP, NEU1, COX2, MT1E, HMGB1, NEURL1, SCO2, NT5E, NTRK3, IL1A, P2RY2, SQSTM1, GPT, PAEP, PROM1, FOSL1, ESR2, SMG1, MAPT, CAV1, TOP1, PLAT, PTPRC, CTSB, CD80, KRAS, MTCO2P12, ACTB, TWIST1, LILRB1, LDHA, MIR200B, LIMS1, PRL, CDKN2A, DCN, MYC, SNAI2, TSLP, TYMP, NLRP12, MUC16, BSG, LOX, MIR374A, CAP1, BAG2, ADAMTS1, CITED2, NET1, ADAM17, FHL5, SRC, PSMD14, STK11, SSBP1, FST, BCAR1, KLK4, STAT6, SSTR2, GPNMB, PARP3, WASF2, PTPRU, PSME3, TAT, MAP3K7, PAK4, TUBB3, VDR, NTN1, TBX3, TLR1, LAP, RWS, TLR2, TLR4, TNFRSF1A, ST8SIA4, NR2C2, ZNF143, ZNF35, TRPC5, YY1, XRCC3, TYMS, XRCC1, VRK1, VIM, TYROBP, UBE2D3, ARHGEF5, NCOA4, TK1, NR1I2, CD163, PTTG1, PRDX2, HACD1, SLC16A3, SLC16A4, HSPB3, BUD31, HDAC3, TIMP3, NRP1, TFF3, TIE1, INPP4B, TNFSF10, HSD17B6, TIMP1, CAVIN2, CREB3, SERPINA3, SORBS1, MIR106B, MIR210, MIR206, MIR205, MIR203A, MIR200A, MIR19B1, MIR196A1, MIR195, MIR190A, MIR155, MIR143, MIR141, MIR126, MIR106A, HEXIM1, C17orf97, AGRN, GSTK1, ACTBL2, TRIM59, PGP, MOSPD2, CTCFL, SLCO6A1, KLF17, MUCL1, PRRT2, CAVIN3, MIR214, MIR224, MIR23B, MIR29A, DM1-AS, SNORD138, COMMD3-BMI1, MAGI2-AS3, FECD3, MIR1258, MIR1246, FECD2, MIR708, MIR216B, MIR298, HOTAIR, MIR454, MIR33B, LGALS7B, UCA1, POTEM, MIR494, MIR452, MIR429, MIR424, MIR381, MIR379, MIR361, MIR335, POTEKP, MIR33A, FOXQ1, MTDH, IGFN1, GIT1, SPARC, BBC3, FBXO4, NOC2L, LDLRAP1, BRMS1, SPDEF, SLC39A6, PANX1, NUP62, CBX5, SASH1, RHOBTB2, NT5C2, MMRN1, ACOT7, ECD, AKAP13, CHEK2, NISCH, RASSF1, DUSP14, ADRM1, STIP1, CBX1, NES, KHDRBS1, HPGDS, PADI1, CREB3L1, NOP53, BMF, LMLN, ANTXR1, TMPRSS13, ITCH, SCRT1, PALB2, LIN28A, NABP2, SOX17, STIM2, SLC39A10, SMARCAD1, PARVA, IMPACT, FBXW7, SLC52A1, LY6K, UGT1A1, PIMREG, KRT20, ERRFI1, ADA2, DCTN4, JPT1, FOXP3, ADGRE2, BMP10, PLD2, SPAM1, ENG, FGFR2, FCGR3B, FCGR2B, F5, F2RL1, MECOM, ETS1, ERCC4, ERBB4, EPHB1, EPAS1, SLC29A1, ELK3, IFIT3, EIF4G1, EIF4E, EDN1, LPAR1, E2F1, ATN1, DRD2, DPYD, DDX3X, CYP1A1, CTSL, CTSK, FOXC1, FOXM1, GCNT2, GDF2, ICAM1, IBSP, TNC, HTC2, HSPB2, HSPB1, HSPA1A, HSF1, HOXC10, HMGA1, HLA-DRB1, HGF, HDC, HDAC1, HCRT, GTF2H1, GSTT1, GSTP1, GSTM1, GRPR, CXCL1, NR3C1, CXCR3, GLI2, GLI1, CTLA4, CTBP1, CTAA1, VPS51, BRAF, BMP7, BMI1, CEACAM1, BCYRN1, BCHE, BAX, B2M, ATF3, ASPH, RHOC, RHOB, APEX1, ANXA13, ALK, ALDH1A3, AHR, ADRB2, ADORA2B, ADM, ACTG2, ACTG1, ACOX1, ACAT1, ABL1, BST2, CA9, CSPG4, CAMP, CSN2, CSF1R, CLDN3, COL17A1, CCR5, CHUK, CETN2, CEBPB, CEBPA, CDK9, CDK3, CDH11, CDH5, CDC25A, CDK1, CDA, ADGRE5, CD68, CD47, CD40LG, CD1D, CCNE1, CBR1, RUNX1, CASR, ID1, IFNG, SOX10, PIK3R1, PTGFR, KLK6, PROX1, PRLR, PRKCB, PRKCA, POLD1, PML, PLK1, PLIN1, PLG, ABCB7, SERPINB6, IGF1R, SLC25A3, PGF, PFN1, PFKFB4, PFKFB3, ENPP2, PDGFRB, PDCD1, PCDH7, PC, PAK2, PRDX1, PTH, PTHLH, PTH1R, PTK2, SOX4, FSCN1, SNAP25, SNAI1, SLC22A3, SLC9A1, SLC6A2, SLC3A2, SIPA1, CCL20, CCL2, SCD, RSU1, RRM2, RPL36A, RORC, RET, RELA, REG1A, RB1, RARB, RALA, RAC1, PTX3, PTPRF, PEBP1, P4HB, OSM, LIPE, LEP, LCN1, LBR, STMN1, KRT18, KRT16, KISS1, KCNMA1, CD82, JUNB, JAG2, ITK, ITGB1, ITGA6, INSR, IDO1, ILK, IL13, IL11, IL10, CXCR1, IL2RG, IL1B, IKBKB, CCN1, LGALS7, LNPEP, NRAS, LOXL2, NOTCH1, NOS3, NME1, NNAT, NFKB1, NFATC2, NF2, MTTP, MSX2, MST1, MSMB, MPO, CD200, MMP17, MMP13, MMP11, MMP2, MMP1, NR3C2, MDM4, MB, MAT1A, MAOB, SMAD3, SMAD2, H3P7