-
Spinal Disc Herniation
Wikipedia
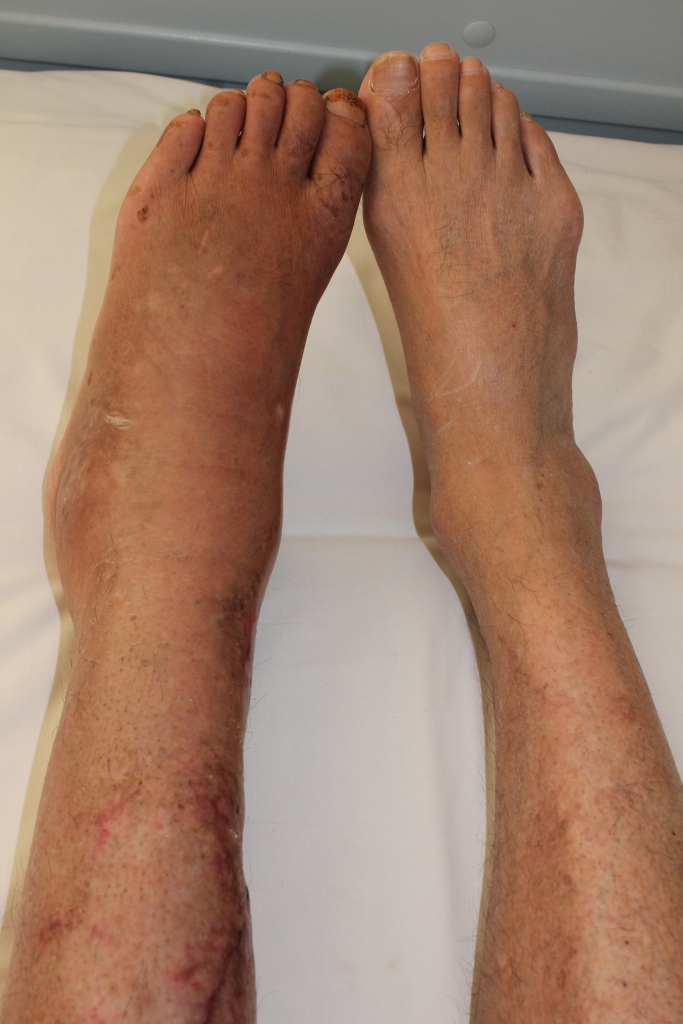
Pre-operative imaging can be helpful for diagnosis, but intra-operative findings are required for confirmation. [24] Inflammation [ edit ] It is increasingly recognized that back pain resulting from disc herniation is not always due solely to compression of the spinal cord or nerve roots, but may also be caused by chemical inflammation. [25] [26] [27] [28] There is evidence that points to a specific inflammatory mediator in back pain: [29] [30] an inflammatory molecule, called tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF), is released not only by a herniated disc, but also in cases of disc tear ( annulus tear) by facet joints , and in spinal stenosis . [25] [31] [32] [33] In addition to causing pain and inflammation, TNF may contribute to disc degeneration. [34] Diagnosis [ edit ] Terminology [ edit ] Terms commonly used to describe the condition include herniated disc , prolapsed disc , ruptured disc , and slipped disc .
-
Cerebral Cavernous Malformations
Omim
Clark (1970) described cavernous angioma of the brain in a man who died in 1945 at age 27 and in his daughter who died in 1969 at age 28. Hayman et al. (1982) examined 43 relatives in 1 kindred by cranial computed tomography (CCT) and found 15 affected with cerebral vascular angiomas.
-
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
Wikipedia
Potential explanations include a dysbalance of the activities of sympathetic and parasympathetic autonomic nervous system [26] [27] [28] and mild secondary hyperparathyroidism . [29] However, the trigger of secondary hyperparathyroidism has not yet been identified. [ citation needed ] In summary, the pathophysiology of complex regional pain syndrome has not yet been defined; CRPS, with its variable manifestations, could be the result of multiple pathophysiological processes. [16] Diagnosis [ edit ] Diagnosis is primarily based on clinical findings. ... Retrieved 2013-12-23 . ^ O'Connell, NE; Wand, BM; Gibson, W; Carr, DB; Birklein, F; Stanton, TR (28 July 2016). "Local anaesthetic sympathetic blockade for complex regional pain syndrome" . ... "Efficacy and safety of ketamine in patients with complex regional pain syndrome: a systematic review". CNS Drugs . 26 (3): 215–28. doi : 10.2165/11595200-000000000-00000 .HLA-DQB1, KRT16, ADRB2, TSPO, B3GAT1, CD160, ZNF35, MIR34A, SCN9A, MBP, MME, MMP9, NFE2L2, POMC, MAPK8, MIR338, CCL2, STAT3, LAMC2, STAT5B, TWIST1, ADAMTS1, MCF2L2, TWSG1, STAT5A, KNG1, ITGAM, GNAO1, DDR1, CALCA, CREBBP, CRHR1, CSF2, CSF3, ACE, GABPA, HLA-B, IL10, HLA-DQB2, HLA-DRB1, HLA-DRB6, IGHG3, IL1B, IL1R1, IL1RN, IL6, MIR939
-
Hereditary Haemochromatosis
Wikipedia
The worldwide prevalence rates for H63D, C282Y and S65C (minor allele frequencies) are 10%, 3% and 1% respectively. [25] [26] [27] The C282Y allele is a transition point mutation from guanine to adenine at nucleotide 845 in HFE , resulting in a missense mutation that replaces the cysteine residue at position 282 with a tyrosine amino acid. [28] Heterozygotes for either allele can manifest clinical iron overload, if they have two of any alleles. ... Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology . 28 (4): 198–202. doi : 10.1155/2014/468521 . ... Retrieved 2007-03-17 . ^ Adams, PC; Reboussin, DM; Barton, JC; McLaren, CE; Eckfeldt, JH; McLaren, GD; Dawkins, FW; Acton, RT; Harris, EL; Gordeuk, VR; Leiendecker-Foster, C; Speechley, M; Snively, BM; Holup, JL; Thomson, E; Sholinsky, P; Hemochromatosis and Iron Overload Screening (HEIRS) Study Research, Investigators (28 April 2005). "Hemochromatosis and iron-overload screening in a racially diverse population" .HFE, HAMP, TFR2, HJV, SLC40A1, SLC11A2, TNF, BMP6, CP, HP, BMP2, AKR1D1, B2M, HMOX1, ALAD, HLA-A, TFRC, HLA-H, CYBRD1, FTL, HLA-B, TMPRSS6, APOE, TF, UBE2D1, TIMP1, GNPAT, TLR4, ACO1, MMP2, HEPH, FTH1, EPO, SUCNR1, COX8A, F5, PPP1R11, SOD2, SOD1, SHBG, ADIPOQ, TP53, UROD, ZKSCAN8, PCSK7, S100A9, GDF15, PIEZO1, TRIM31, NUP42, TNMD, SLC46A1, BTBD9, MCIDAS, LINC01194, CCL2, MDM2, UBL3, SERPINA1, GABPA, GAST, FXN, FOXC2, ELANE, CYLD, CTNNB1, CFTR, CELP, CD68, CALR, ARNTL, ALDH2, ALB, ALAS2, GAPDH, GNRH1, GPT, SMAD1, PGF, NMBR, NFE2L2, MPO, MMP3, SMAD7, IREB2, GSTP1, IL10, IL6, IGHG3, IGFALS, IFNG, HLA-F, MFT2
-
Li-Fraumeni Syndrome
Omim
Varley (2003) reviewed the findings of Birch et al. (2001), who studied the distribution of cancers in carriers of germline TP53 mutations from 28 families in which all cancers were verified and the ages of all family members, affected and unaffected, were known.TP53, CHEK2, MDM2, CDKN2A, BRCA2, BRCA1, EGFR, ERBB2, PTEN, PKM, RPS19, IDH1, H2AX, RNASE3, CYP19A1, RAF1, DDX41, MIR605, RUNX1, ANKRD26, AHSA2P, OCLN, DOCK11, SFRP2, SHH, SKP2, SMARCB1, SRP72, TERC, TOP2B, RBM17, ZDHHC9, WT1, BAP1, TWSG1, CREG1, BCL10, RECQL4, PLXNA3, DLL4, AHSA1, RALBP1, CPSF6, AR, NF1, RB1, DCN, B2M, BCL2, CAV1, CD44, CDH1, CDK2, CDKN1A, CDKN2B, CEBPA, CHEK1, CMM, ATF2, DCK, DNA2, PCNA, ESR1, ETV6, GATA2, HIF1A, HSP90AA1, IFNA1, IFNA13, IGFBP7, IRF7, MLH1, MUTYH, ATM, NF2, H3P10
-
Polycystic Kidney Disease 1 With Or Without Polycystic Liver Disease
Omim
They concluded that there is no evidence for genetic heterogeneity of APKD in families with early- and later-onset disease. In 28 northern European pedigrees from England, Scotland, Holland, and eastern Finland, Reeders et al. (1987) found no evidence of heterogeneity of the linkage of PKD1 with alpha-globin.
-
Adrenal Hyperplasia, Congenital, Due To 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency
Omim
Blankstein et al. (1980) reported a possible allelic form of 21-hydroxylase deficiency in 2 sisters, aged 28 and 30 years, who had primary infertility and mild hirsutism but normal puberty, regular menses, and normal female sexual characteristics.CYP17A1, HSD3B2, CYP21A2, POR, PDE8B, PRKAR1A, AVPR2, HTR4, AVPR1A, CYP11B1, STAR, CYP11B2, PDE11A, KCNJ5, PRKACA, USP8, CDH23, CYP21A1P, CYP2B6, POMC, NR3C1, GML, AIRE, CACNA1D, TBC1D24, TNXB, AR, HSD3B1, CHST3, CYP19A1, GLO1, HLA-A, CYP4F3, NR0B1, MC2R, HSD11B2, TNXA, SRY, REN, GIP, HLA-B, GH1, CYP2C19, CRH, RNU1-4, TWIST1, SDHD, TP53, PPIG, SCO2, VWF, TGM5, SULT2A1, ARMC5, COASY, CGB5, CGB8, RBM45, OTOA, EYS, ACADVL, SDHB, PROP1, ATP7B, AVP, AZF1, BCL2, C4B, CGA, CGB3, CRYGD, CYP3A7, CYP2B7P, CYP11A1, ENPEP, FH, GRB7, HADHA, HLA-DRB1, HTC2, TNC, LEP, MDH2, MEN1, SERPINA1, PRKACB, LOC110673972
-
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Due To 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency
Wikipedia
The salt-wasting and simple virilizing types are sometimes grouped together as "classical". [28] Newborn Screening [ edit ] Conditions justifying newborn screening for any disorder include (1) a simple test with an acceptable sensitivity and specificity , (2) a dire consequence if not diagnosed early, (3) an effective treatment if diagnosed, and (4) a frequency in the population high enough to justify the expense.CYP21A2, POMC, CYP21A1P, HLA-B, AR, C4B, TNXB, HSD3B2, CYP2B6, GLO1, DKK1, NR3C1, C4B_2, CYP2C19, C4A, CYP17A1, TNFSF11, PRKAR1A, TRIM27, BRD2, SPG7, TNFRSF1B, TNXA, NR1I2, TNFRSF11B, NR1I3, TRIM13, CAPN10, AZF1, CFC1, CXADRP1, CASR, NR3C2, CYP11B1, HLA-A, CYP3A4, FPR2, GH1, GNRH1, GRB7, CYP3A7, CXADR, IRS1, HLA-DOA, ARR3, CRH, HSD17B1, IDS, IGF2, HSD3B1
-
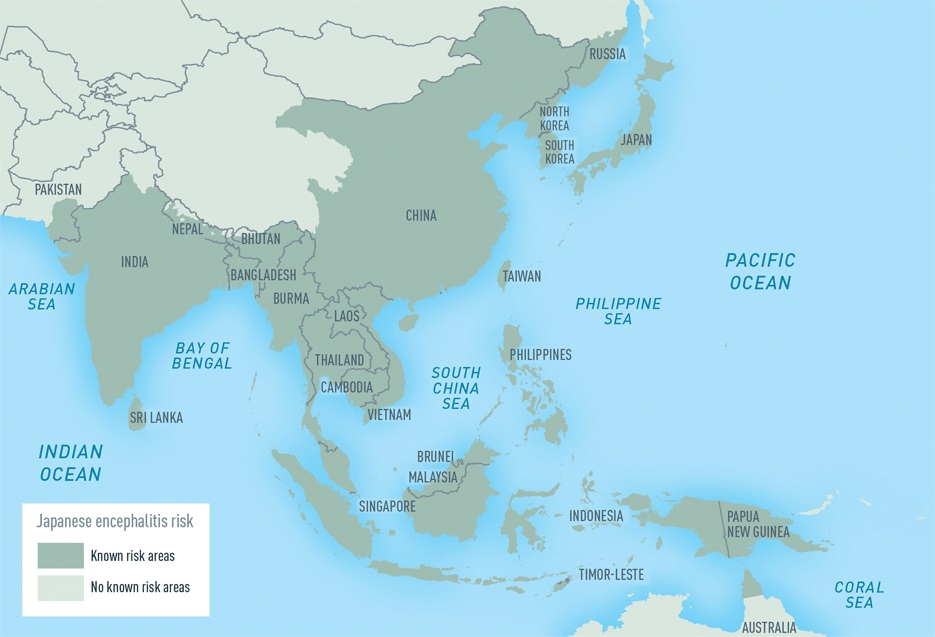
Japanese Encephalitis
Wikipedia
The natural hosts of the Japanese encephalitis virus are birds, not humans, and many believe the virus will therefore never be completely eliminated. [27] In November 2011, the Japanese encephalitis virus was reported in Culex bitaeniorhynchus in South Korea . [28] Recently whole genome microarray research of neurons infected with the Japanese Encephalitis virus has shown that neurons play an important role in their own defense against Japanese Encephalitis infection.ERVK-6, ERVK-32, IFNB1, CCL2, RAF1, TLR7, IVNS1ABP, PTPN11, AMFR, CCR2, TNF, CCR5, ERVK-20, ERVW-1, IL6, IL1B, CCL5, CSF2, MIR15B, IFNA1, ACTB, CXCL10, NLRP3, CD40LG, ROBO3, IFNG, MIR146A, IFNA13, STAT1, DDX58, HSPA5, MIR301A, PLAAT4, ATF3, AGO2, CD274, SPCS1, CASP4, SOCS7, ELAVL2, CLEC5A, LAMP3, HAVCR1, BST2, ANGPTL2, ATF6, DDX42, CHEK2, CAV1, HSPA14, BCL2, DDX56, RNF125, MIR374B, ATF4, MIR432, MIR29B2, MIR29B1, MIR19B1, STING1, PPP1R42, MLKL, RSAD2, IL33, TSLP, SESN2, ZC3H12A, IFIH1, ACTR2, AICDA, NKRF, CCDC88A, PAK4, TIMELESS, DNAJB6, LAMC2, KPNA4, ITGB3, ITGAX, ITGAM, IRF1, ILF2, IL10, DDX3X, DHX9, HBEGF, ICAM1, HSPD1, HSP90AB1, HSPA4, DNAJA1, AGFG1, HLA-DRB1, GRIN2B, CXCR3, KRAS, LSAMP, SOCS6, CAPRIN1, MYOM2, SOCS3, EPHB2, RAB11A, ARHGEF5, XBP1, VIM, TLR3, CXCL11, CCL3, RNASE3, DDIT3, RAB5A, DDT, MAPK1, PF4, NPM1, NEDD4, MYD88, ACHE
-
Niemann-Pick Disease, Type C1
Omim
Three recombinants detected among the 28 informative individuals represented a recombination fraction of 0.07.NPC1, LIPA, NPC2, PDLIM7, APP, SMPD1, PSMB9, ABCA1, RASSF1, CDKN2A, TNF, CHIT1, LINC01193, ERCC2, FCER2, IFNG, LAMP1, LDLR, CD274, MAPT, VEGFA, BACE1, PTCH1, CCL2, SOX2, TP53, ERCC1, H3P10, ATM, CKS1B, SRRM2, APOE, POSTN, APOD, WIF1, CUL9, NBEAL2, SIRT1, TARDBP, SEZ6L, SCO2, ARL2BP, DDX58, APC, TRIM29, DKK3, PDCD4, TMEM97, ANXA6, HDAC6, RAB9A, ATP7B, CD163, TRAF1, UBE2N, UGCG, VHL, VIM, VIP, ZNF154, BSND, ARID1A, ULK1, NR0B2, BECN1, CDK5R1, PER2, ST3GAL5, SPHK1, ARF6, FOXP3, ZMYND10, GDE1, MIR185, NEGR1, NPCA1, H19, STPG4, CELIAC2, ANXA1, MIR10B, MIR130A, MIR203A, RTRAF, MIR31, POU5F1P3, POU5F1P4, UCA1, MIR663A, APOBEC3A_B, UPK3B, CNE-2, NPB, APOBEC3A, ARHGAP42, CKS1BP7, NLK, OTUD4, NLRP2, LPAR5, GBA2, OVOL2, NEUROG2, ROBO3, GORASP1, WNK1, SPNS1, HAVCR2, FATE1, SCGB3A1, CDCA5, SEZ6, OSCP1, TP73, B2M, CP, CD58, GCHFR, GFAP, HCRT, HDAC2, HLA-A, HOXC6, HSPB1, HSP90AA1, IGFBP6, XRCC6, IL1A, IL1B, IL12A, IL17A, JAK2, JUN, JUNB, JUND, GBA, FOSB, THBS1, EGR1, CPT1A, CRP, CTLA4, CTNNB1, DAP, DAPK1, TYMP, S1PR3, EPHA2, FOS, EIF4E, CDKN2B, CDK5, FASN, CDH1, FCN2, FGF2, FOXM1, CD40, SCARB1, LGALS9, SLC6A8, RBM3, RELA, REST, SATB1, BSG, ALB, CCL18, SFRP1, SLPI, CCK, BMP2, BCL2, STAR, STAT3, SYT1, TRBV20OR9-2, TERT, TGFBR1, PLAAT4, PVALB, PTPN12, PTPN6, CAV1, MGMT, MLH1, MMP1, MNAT1, MYC, NBN, CASP8, OSM, OTC, PAK1, ABCB1, PIK3CA, POU5F1, CALR, CALCR, PTK2, CCL5
-
Metachromatic Leukodystrophy
Omim
Betts et al. (1968) described a man who was 28 when admitted to a psychiatric hospital for 'acute schizophrenia' and 35 when he died of bronchopneumonia.
- Refsum Disease Gene_reviews
-
Dopamine Beta-Hydroxylase Deficiency
Gene_reviews
Her listed cause of death at an assisted living facility was cardiac arrhythmia. Autopsy of a male age 28 years reported "scattered pyknotic cerebral neurons, isolated microfoci of cortical gliosis, cardiac arteriolar smooth muscle hypertrophy, scattered fibrosis in the cardiac conduction system, and sclerotic renal glomeruli."
-
Pemphigoid
Wikipedia
Two European studies have also suggested the increased risk of bullous pemphigoid with advancing age. [28] [29] According to the results of several retrospective studies, there is an increasing incidence of bullous pemphigoid. [30] [31] [32] Bullous pemphigoid can be considered as the most common autoimmune blistering disease in Europe, while pemphigus may be more common in locations such as Thailand and Malaysia. ... Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology . 28 (1): 74–7. doi : 10.1016/0190-9622(93)70013-J .HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRB1, CXCL8, COL17A1, DPP4, ZAP70, DST, MMP9, DSPP, IL17A, IL5, CCL18, FOXP3, CD274, IGHE, IL23A, PLG, IFNA1, IFNA13, RNASE2, PLEC, IL2RA, ABCB1, HLA-DQA1, IL10, ISG20, TGFB1, SELL, SELE, MRC1, RNASE3, DSG3, IL31, C3, RBM45, IL17RA, ABCC8, SOAT1, SLC5A2, SELPLG, SELP, DPP9, HT, CXCL5, TNF, CCL22, CCL17, C9orf72, CCL11, CELIAC2, S100A9, S100A8, TSLP, ABCC11, PRPF6, TXNRD1, IL24, POSTN, IL17B, C5AR2, DPP7, IL22, CCL26, CD163, TNFSF12, HSD17B6, TNFRSF12A, KRT20, IL17RB, SEMA6A, VEGFA, IL17RC, VCAM1, SEMA4D, ADAM10, RAC1, MAPK1, HSP90AA1, HLA-C, NR3C1, GPT, GLP1R, GLB1, FCGR3A, EPHB2, DSP, DSG1, DOCK3, TIMM8A, CD55, CYP2D6, CYP2B6, CSF2, CD40, CD22, MS4A1, CASP3, BDNF, BCL2, AQP3, ICAM1, IFNG, IGHG3, CD46, PPBP, MED1, PKD1, PDCD1, PEBP1, MUC1, FAS, MMP12, MMP3, MIF, LAD1, IL1A, ITGB4, ITGB3, ITGB1, ITGAM, ITGA6, CXCL10, IL13, IL4, IL1RN, IL1B, TNFSF12-TNFSF13
-
Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex
Gene_reviews
Horn and colleagues estimate a prevalence of 28.6 per million in Scotland, and prevalence estimates from other countries range from one to 28 per million [Horn et al 1997]. Differential Diagnosis According to the 2014 classification system, the four major types of epidermolysis bullosa (EB), caused by pathogenic variants in 18 different genes, are EB simplex (EBS), junctional EB (JEB), dystrophic EB (DEB), and Kindler syndrome [Fine et al 2014].
-
Dyskeratosis Congenita, X-Linked
Omim
As a result of large-scale positional cloning and sequencing of the region of Xq28 containing the DKC1 gene, virtually all DKC positional candidates had been identified. By hybridization screening with 28 candidate cDNAs, Heiss et al. (1998) detected a 3-prime deletion in 1 DKC patient with a cDNA probe derived from XAP101.
-
Silver-Russell Syndrome
Gene_reviews
Luk et al [2016b] described one group of 28 individuals with SRS who had UPD11. 13.IGF2, H19, HMGA2, CDKN1C, PLAG1, IGFBP3, CSH1, IGFBP1, FOXP2, GH2, RIT1, RAF1, PTPN11, ATR, LZTR1, KRAS, SOS1, CEP63, CENPJ, UROD, GRB10, BSCL2, H19-ICR, INS-IGF2, RSS, SMS, TGM1, MEST, WDR20, IGF1, IGF1R, GH1, KCNQ1OT1, WASHC5, KCNQ1, PLAGL1, CTCF, PCNA, ZFP57, TSPO, EGFR, CPA4, SPG38, SGCE, IGF2-AS, ZACN, MBD3, COPG2IT1, PHLDA2, HSP90B2P, TLR3, AIFM1, MAD2L1BP, COPG2, PEG10, MEG3, NSD1, CTCFL, OBSL1, HSPB8, OSBPL5, KCNIP1, CCDC22, KIF1B, AIF1, SRF, FGFR3, GHR, GFAP, GDNF, GCSH, GART, GARS1, FOLR1, EGF, GNAS, RCAN1, DES, DDC, COL1A1, CHRM3, BAAT, ANXA1, GLDC, GPI, SPAST, PGR, RASGRF1, PTCH1, AMT, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, PIK3CA, PDGFRB, NR3C1, NFE2L2, NEUROD1, KPNA2, KCNE1, HSPB1, HOXA4, HIC1, LOC105274310
-
Mitochondrial Short-Chain Enoyl-Coa Hydratase 1 Deficiency
Gene_reviews
Common Clinical Manifestations of ECHS1 Deficiency View in own window Clinical Manifestation Frequency Neurologic 1 Signal abnormalities in the basal ganglia 28/32 (88%) Developmental delay 27/32 (84%) Hypotonia 21/30 (70%) Dystonia 15/29 (52%) Seizures 12/23 (52%) Encephalopathy 12/31 (39%) Ataxia/choreoathetosis 5/25 (20%) Growth Failure to thrive 20/32 (62%) Microcephaly 7/30 (23%) Intrauterine growth restriction 5/27 (18%) Cardiovascular Cardiomyopathy 9/15 (60%) Pulmonary hypertension 3/14 (21%) Ophthalmologic Nystagmus 10/31 (32%) Optic atrophy 8/27 (30%) Corneal clouding 1/27 (4%) Other Sensorineural hearing loss 13/27 (48%) Apnea 7/37 (19%) Liver steatosis &/or hepatomegaly 5/6 (83%) Biochemical/ Enzymatic Lactic acidemia 27/36 (75%) Low PDC activity (in cultured fibroblasts) 5/12 (42%) 1.
-
Mutyh Polyposis
Gene_reviews
Percentage of Persons with MAP by Age at Diagnosis of CRC View in own window Persons with Biallelic MUTYH Pathogenic Variants Age at Diagnosis of CRC % (n) Range 1.3% (52/3,976) 0.5%-6.2% <50 years 0.3% (28/11,150) 0.0%-0.6% >50 years Review of literature, Nielsen et al [2011], Landon et al [2015], Pearlman et al [2017] CRC = colorectal cancer Differential Diagnosis MUTYH polyposis (MAP) can be distinguished from other inherited polyposis and colon cancer conditions by clinical findings, pathologic findings, mode of inheritance, and molecular genetic testing.
-
Lrrk2 Parkinson Disease
Gene_reviews
Age at onset is typically in the 50s and 60s but varies, even within the same family. The range of disease onset is 28-95 years with a mean of 58-61 years – similar to or slightly younger than in individuals with IPD [Ishihara et al 2006, Healy et al 2008, San Luciano et al 2010, Trinh et al 2014b, Marder et al 2015, San Luciano et al 2017].