- Heterotopic Ossification Wikipedia
- Paraphimosis Wikipedia
-
Lipomatosis, Multiple Symmetric
Omim
Enzi et al. (1985) documented the high frequency of somatic and autonomic neuropathies. In 28 of 33 male patients changes varying from vibratory sensory loss to incapacitating trophic ulcers or Charcot arthropathy were found. ... The other patients declared that none of their sibs (34 brothers, 28 sisters) or parents was affected.
- Imperforate Hymen Wikipedia
-
Gaba-Transaminase Deficiency
Omim
He died at 5 months of age. Tsuji et al. (2010) reported a 28-month-old Japanese female, born of nonconsanguineous parents, with GABA-aminotransferase deficiency. ... Molecular Genetics In 2 unrelated patients with GABA-aminotransferase deficiency, Medina-Kauwe et al. (1999) identified mutations in the ABAT gene (137150.0001 and 137150.0002). In a 28-month-old Japanese female with GABA-aminotransferase deficiency, Tsuji et al. (2010) identified compound heterozygous mutations in the ABAT gene (137150.0003-137150.0004).
-
Foreign Animal Disease
Wikipedia
A Foreign animal disease ( FAD ) is an animal disease or pest, whether terrestrial or aquatic, not known to exist in the United States or its territories. [1] When these diseases can significantly affect human health or animal production and when there is significant economic cost for disease control and eradication efforts, they are considered a threat to the United States. [2] Another term gaining preference to be used is Transboundary Animal Disease (TAD), [3] which is defined as those epidemic diseases which are highly contagious or transmissible and have the potential for very rapid spread, irrespective of national borders, causing serious socio-economic and possibly public health consequences. [4] An Emerging Animal Disease " may be defined as any terrestrial animal, aquatic animal, or zoonotic disease not yet known or characterized, or any known or characterized terrestrial animal or aquatic animal disease in the United States or its territories that changes or mutates in pathogenicity, communicability, or zoonotic potential to become a threat to terrestrial animals, aquatic animals, or humans." [5] A foreign animal disease in the United States has the potential to threaten food security, cause production losses for livestock producers while significantly increasing livestock production costs through costly disease control measures, affect the income of livestock producers, disrupt movement of livestock and livestock products, cause animal welfare problems in affected animals, possibly cause public health issues, and cause environmental consequences with the wildlife populations. [3] [4] Contents 1 Protecting US from FAD 1.1 Agencies involved in response to outbreak 2 Diseases considered FAD in the United States 2.1 African Swine Fever 2.2 Classical swine fever (hog cholera) 2.3 Contagious bovine pleuropneumonia 2.4 Contagious equine metritis 2.5 Dourine 2.6 Foot-and-mouth disease 2.7 Glanders 2.8 Rinderpest 2.9 Teschen disease 2.10 Screwworms 3 References Protecting US from FAD [ edit ] Agencies involved in response to outbreak [ edit ] World Organization for Animal Health [6] (historical acronym OIE- the Office International des Epizooties) The OIE originated in 1924 with the ratification of an international agreement of 28 States on January 25, 1924. The membership currently shown (2017) is 181 members countries. ... Dourine has been eradicated from many countries but is still present in horses in Asia, Africa, South America, Southern and Eastern Europe, Mexico, and Russia. [27] [28] Transmission of dourine is almost exclusively during breeding, more commonly from stallions to mares, but can also occur from mares to stallions. [27] Clinical signs are characterized mainly by swelling of the genitalia, cutaneous plaques, and neurological signs often ending in death, with the severity varying depending on the virulence of the strain, the nutritional status of the horse, and stress factors. [29] The mortality rate is believed to be higher than 50%, and some feel that nearly all cases are eventually fatal. [27] [28] The wide use of artificial fertilization technology has resulted in few cases being reported. [28] Dourine can be an economically important disease, and is a well documented trade barrier for the movement of horses. [28] Diagnosis of dourine is based on clinical evidence but requires confirmation by parasitological, serological, and molecular techniques. [28] There is no vaccine available for this disease, and pharmaceutical therapy is not recommended because animals may improve clinically but will remain carriers.
-
Complicated Grief Disorder
Wikipedia
Six months is considered to be the appropriate point of CGD consideration, since studies show that most people are able to integrate bereavement into their lives by this time. [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] Symptoms [ edit ] The symptoms of complicated grief are mentioned in the most-recently proposed diagnostic criteria; they include maladaptive thoughts and behaviors related to the death or the deceased, continuous emotional dysregulation about the death, social isolation and suicidal ideation . [17] Central to complicated grief is the presence of yearning. [1] Causes and predictors [ edit ] Although more research is needed to determine the multiple pathways to complicated grief disorder, preexisting conditions (such as major depression, PTSD, and sleep disorders ) are thought to exacerbate the interruption of the natural healing process. [17] There are some known predictive characteristics for CGD. [17] An individual is at increased risk for CGD if they are: Female [5] [18] and Age of 61 or older [19] Pessimistic [20] [21] Previously diagnosed with a mood disorder [4] [6] Low self-reported social support [22] An insecure attachment [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] High stress [22] A positive caregiving experience and dependency on the deceased [28] [29] [30] Have had an early pregnancy loss ( miscarriage ) [31] [32] Monthly income below €1250 [19] Consequences [ edit ] Untreated CGD has clinically significant consequences. A high level of impairment can be pervasive, [3] [4] [6] [10] [18] [33] [34] [35] [36] [37] [38] [39] [40] including destructive thoughts and behaviors (such as substance abuse ). [16] [41] CGD may worsen the course of preexisting disorders and contribute to the development of new ones. [42] [43] Incidence [ edit ] CGD is an atypical grief response, occurring only in a minority of the bereaved population. [16] [24] It is considered more common in those experiencing disasters, [5] [18] [44] [45] violence, [46] [47] [48] [49] the loss of a child, [50] [51] [52] and the loss of a spouse. [19] [53] It has also been found in family members (or friends) of: Patients with life-threatening illnesses [28] [54] [55] [56] Suicides and homicides [48] [57] CGD is found to be prevalent cross-culturally in Europe, [20] [23] [58] [59] [60] [61] [62] [63] [64] the Middle East, [44] [65] Africa, [66] and Asia. [28] [67] [68] [69] [70] [71] Treatment [ edit ] CGD is relatively unresponsive to antidepressants [72] or interpersonal psychotherapy ; [73] however, recent studies support the use of CG-targeted psychotherapy [54] [74] [75] (similar to PTSD-targeted psychotherapy). ... Furthermore, despite the possibility of diagnosis-related stigma the clinical necessity for treatment is a priority for those suffering from CGD. [17] Cultural norms for grief [ edit ] An individual’s culture plays a large role in determining an inappropriate pattern of grief, and it is necessary to consider cultural norms before reaching a CGD diagnosis. [17] There are cultural differences in expected emotional levels, their expression and duration; the external symptoms of grief differ in non-Western cultures, presenting increased somatization . [81] See also [ edit ] Ghost sickness References [ edit ] ^ a b c "Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5 (5th edition)2014 102 Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5 (5th edition) Washington, DC American Psychiatric Association 2013 xliv+947 pp. 9780890425541(hbck);9780890425558(pbck) £175 $199 (hbck); £45 $69 (pbck)" . Reference Reviews . 28 (3): 36–37. 2014-03-11. doi : 10.1108/rr-10-2013-0256 . ... "Complicated grief and related bereavement issues for DSM-5" . Depression and Anxiety . 28 (2): 103–17. doi : 10.1002/da.20780 . ... COMPLICATED GRIEF ASSOCIATED WITH HURRICANE KATRINA. Depression and Anxiety, 28(8), 648-657. doi:10.1002/da.20865 ^ Mancini A, Prati G, Black S.
-
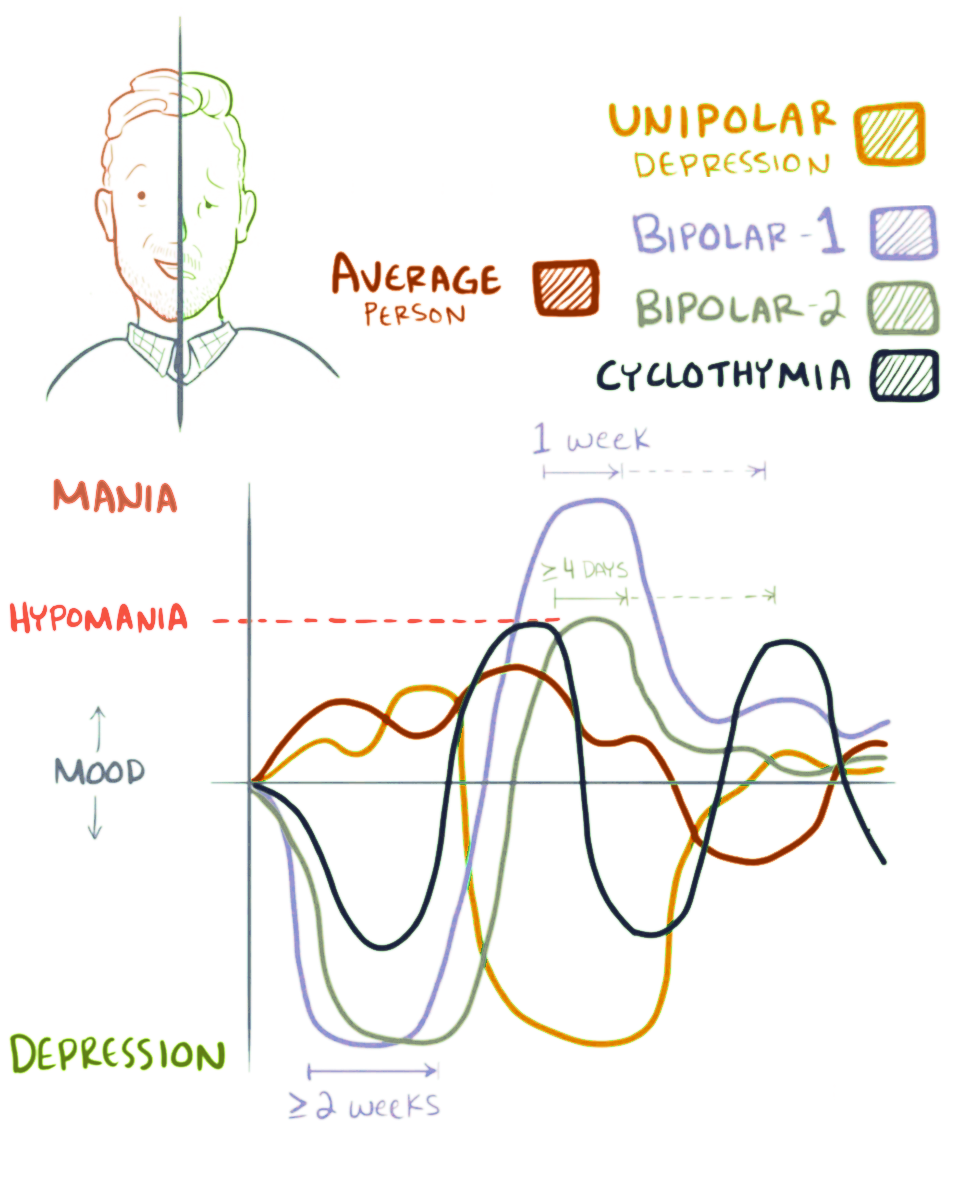
Bipolar Ii Disorder
Wikipedia
Relapse can still occur, even with continued medication and therapy. [25] Prognosis [ edit ] There is evidence to suggest that bipolar II has a more chronic course of illness than bipolar I disorder . [26] This constant and pervasive course of the illness leads to an increased risk in suicide and more hypomanic and major depressive episodes with shorter periods between episodes than bipolar I patients experience. [26] The natural course of bipolar II disorder, when left untreated, leads to patients spending the majority of their lives unwell with much of their suffering stemming from depression . [20] Their recurrent depression results in personal suffering and disability. [20] This disability can present itself in the form of psychosocial impairment, which has been suggested to be worse in bipolar II patients than in bipolar I patients. [27] Another facet of this illness that is associated with a poorer prognosis is rapid cycling , which denotes the occurrence of four or more major Depressive, Hypomanic, and/or mixed episodes in a 12-month period. [26] Rapid cycling is quite common in those with Bipolar II, much more so in women than in men (70% vs. 40%), and without treatment leads to added sources of disability and an increased risk of suicide. [20] To improve a patient's prognosis, long-term therapy is most favorably recommended for controlling symptoms, maintaining remission and preventing relapses. [28] With treatment, patients have been shown to present a decreased risk of suicide (especially when treated with lithium ) and a reduction of frequency and severity of their episodes, which in turn moves them toward a stable life and reduces the time they spend ill. [29] To maintain their state of balance, therapy is often continued indefinitely, as around 50% of the patients who discontinue it relapse quickly and experience either full-blown episodes or sub-syndromal symptoms that bring significant functional impairments. [28] Functioning [ edit ] The deficits in functioning associated with Bipolar II disorder stem mostly from the recurrent depression that Bipolar II patients suffer from. Depressive symptoms are much more disabling than hypomanic symptoms and are potentially as, or more disabling than mania symptoms. [27] Functional impairment has been shown to be directly linked with increasing percentages of depressive symptoms, and because sub-syndromal symptoms are more common—and frequent—in Bipolar II disorder, they have been implicated heavily as a major cause of psychosocial disability. [20] There is evidence that shows the mild depressive symptoms, or even sub-syndromal symptoms, are responsible for the non-recovery of social functioning, which furthers the idea that residual depressive symptoms are detrimental for functional recovery in patients being treated for Bipolar II. [30] It has been suggested that symptom interference in relation to social and interpersonal relationships in Bipolar II Disorder is worse than symptom interference in other chronic medical illnesses such as cancer. [30] This social impairment can last for years, even after treatment that has resulted in a resolution of mood symptoms. [30] The factors related to this persistent social impairment are residual depressive symptoms, limited illness insight (a very common occurrence in patients with Bipolar II Disorder), and impaired executive functioning. [30] Impaired ability in regards to executive functions is directly tied to poor psychosocial functioning, a common side-effect in patients with Bipolar II. [31] The impact on a patient's psychosocial functioning stems from the depressive symptoms (more common in Bipolar II than Bipolar I). [27] An increase in these symptoms' severity seems to correlate with a significant increase in psychosocial disability. [31] Psychosocial disability can present itself in poor semantic memory , which in turn affects other cognitive domains like verbal memory and (as mentioned earlier) executive functioning leading to a direct and persisting impact on psychosocial functioning. [32] An abnormal semantic memory organization can manipulate thoughts and lead to the formation of delusions and possibly affect speech and communication problems, which can lead to interpersonal issues. [32] Bipolar II patients have also been shown to present worse cognitive functioning than those patients with Bipolar I, though they demonstrate about the same disability when it comes to occupational functioning, interpersonal relationships, and autonomy . [31] This disruption in cognitive functioning takes a toll on their ability to function in the workplace, which leads to high rates of work loss in Bipolar II patient populations. [27] After treatment and while in remission, Bipolar II patients tend to report a good psychosocial functioning but they still score less than patients without the disorder. [20] These lasting impacts further suggest that a prolonged exposure to an untreated Bipolar II disorder can lead to permanent adverse effects on functioning. [30] Recovery and recurrence [ edit ] Bipolar II Disorder has a chronic relapsing nature. [28] It has even been suggested that Bipolar II patients have a higher degree of relapse than Bipolar I patients. [26] Generally, within four years of an episode, around 60% of patients will relapse into another episode. [28] Some patients are even symptomatic half the time, either with full on episodes or symptoms that fall just below the threshold of an episode. [28] Because of the nature of the illness, long-term therapy is the best option and aims to not only control the symptoms but to maintain sustained remission and prevent relapses from occurring. [28] Even with treatment, patients do not always regain full functioning, especially in the social realm. [30] There is a very clear gap between symptomatic recovery and full functional recovery for both Bipolar I and Bipolar II patients. [31] As such, and because those with Bipolar II spend more time with depressive symptoms that do not quite qualify as a major depressive episode, the best chance for recovery is to have therapeutic interventions that focus on the residual depressive symptoms and to aim for improvement in psychosocial and cognitive functioning. [31] Even with treatment, a certain amount of responsibility is placed in the patient's hands; they have to be able to assume responsibility for their illness by accepting their diagnosis, taking the required medication, and seeking help when needed to do well in the future. [33] Treatment often lasts after remission is achieved, and the treatment that worked is continued during the continuation phase (lasting anywhere from 6–12 months) and maintenance can last 1–2 years or, in some cases, indefinitely. [34] One of the treatments of choice is Lithium , which has been shown to be very beneficial in reducing the frequency and severity of depressive episodes. [29] Lithium prevents mood relapse and works especially well in Bipolar II patients who experience rapid-cycling. [29] Almost all Bipolar II patients who take lithium have a decrease in the amount of time they spend ill and a decrease in mood episodes. [29] Along with medication, other forms of therapy have been shown to be beneficial for Bipolar II patients.
-
Mullerian Anomalies
Wikipedia
An array of Mullerian anomalies can occur if any of these processes are arrested or impaired. [6] [27] [28] The first stage of Mullerian duct development is organogenesis , where both Mullerian ducts are formed. [27] If the formation of the Mullerian ducts is impaired or does not occur, this can give rise to uterine, cervical and/or vaginal hypoplasia or agenesis . [6] Mullerian agenesis , also known as the Mayer–Rokitansky–Kuster–Hauser ( MRKH ) syndrome, results in the congenital absence of the vagina or uterus. [29] Women with MRKH syndrome commonly present with primary amenorrhea , where menstruation does not occur by the age of 16. ... More than 50% of women with reported Mullerian anomalies have septate uteri. [26] It is common for other developmental defects to occur in conjunction with Mullerian anomalies, including renal, skeletal, auditory and cardiac abnormalities. [28] [29] Causes [ edit ] The causes of Mullerian anomalies are not well-understood. [27] [28] [29] [30] The aetiology of this congenital disease may be multifactorial, with genetics , socioeconomic factors and geographic factors playing a role in dysfunctional Mullerian duct development. [27] Mullerian anomalies likely occur early in development, as the congenital disorder often occurs in association with renal and anorectal disorders. [28] [29] Typically, women with Mullerian abnormalities have a normal female karyotype (46, XX). Most incidences of Mullerian anomalies occur sporadically, with instances of familial inheritance patterns being less common. [28] The genetic component of the disease classically follows an autosomal dominant pattern, with variable rates of genotypic expression. ... Mutations in WNT4 gene are not always present in individuals with Mullerian anomalies or MRKH syndrome, but the WNT4 gene is the only gene that has been clearly implicated in MRKH. [28] TP63 [ edit ] TP63 is a tumour protein encoded by the EMX2 gene, which is expressed in uterine and vaginal epithelium . [30] The TP63 protein is required for epithelial differentiation during Mullerian duct development in utero , by promoting the transcription of particular genes.
-
Pneumothorax
Wikipedia
The tube is left in place until no air is seen to escape from it for a period of time, and X-rays confirm re-expansion of the lung. [14] [18] [28] If after 2–4 days there is still evidence of an air leak, various options are available. ... Professional guidelines suggest that pleurectomy be performed on both lungs and that lung function tests and CT scan normalize before diving is resumed. [14] [28] Aircraft pilots may also require assessment for surgery. [14] Prevention [ edit ] A preventative procedure ( thoracotomy or thoracoscopy with pleurodesis) may be recommended after an episode of pneumothorax, with the intention to prevent recurrence. ... "Management of spontaneous pneumothorax: state of the art" . European Respiratory Journal . 28 (3): 637–50. doi : 10.1183/09031936.06.00014206 . ... Archived from the original on 8 April 2015 . Retrieved 28 September 2017 . ^ a b Neuman TS (2003). ... Merck Veterinary Manual, 9th edition (online version) . 2005. Archived from the original on 28 October 2011 . Retrieved 5 June 2011 . ^ Au, JJ; Weisman, DL; Stefanacci, JD; Palmisano, MP (1 March 2006).FLCN, ELN, TSC1, SMAD3, CLPB, BTNL2, SLC25A24, MFAP5, TSC2, CHST14, LOX, TGFBR2, TGFBR1, TGFB3, TGFB2, ACTA2, MYLK, MYH11, MAT2A, ABL1, PRKG1, COL5A1, HRAS, COL5A2, HLA-DRB1, COL3A1, ATP6V1E1, FOXE3, FBN1, COL1A1, BHD, SLIT2, TECR, RIDA, FASTK, SMUG1, IL10, FEV, PGPEP1, TST, CENPJ, CD40LG, IFIH1, BMP1, EMB, BPIFA2, ALK, TESC, TNF, SMAD2, ERBB2, SMAD4, MMP1, MMP9, MSMB, GABPA, NFE2L2, POMC, PRCP, FGA, PSPN, PSPH, PRPH2, REG1A, SLC12A3, STXBP3, ERBB4, ERBB3, SMIM20
-
Abortion In Ghana
Wikipedia
Another study carried out in the 1990s suggested that in southern Ghana, the number is marginally higher, at 17 abortions for every 1,000 women. [4] This number is lower than the statistics available for West Africa as a whole: abortions rates are at 28 per 1,000 women [5] Ghanaian women of the following demographics are more likely to have abortions: women who have never been married; women in their twenties; women with no children; wealthy women; and women from urban areas. ... According to a paper, the number of abortions in Ghana is more likely to be closer to the West African rate of 28 per 1,000 women. [6] Abortion and Contraceptives [ edit ] The low rate of contraceptive use is part of the driver for abortions. [6] According to national statistical data, contraceptive use has increased over the decades, but from 13% use by married women in 1988, to just 25% by this demographic in 2003 followed by a slight decline to 24% in 2008. [8] A much higher proportion of sexually active unmarried women use modern contraceptives, but in 2008, this number was just 28% of the population.
-
Herpes Gladiatorum
Wikipedia
Lesions were on the head in 73 percent of the wrestlers, the extremities in 42 percent, and the trunk in 28 percent. [3] Physical symptoms sometimes recur in the skin. [4] Previous adolescent HSV-1 seroconversion would preclude most herpes gladiatorum, but being that stress and trauma are recognized triggers, such a person would be likely to infect others. ... Prophylactic Valacyclovir to Prevent Outbreaks of Primary Herpes Gladiatorum at a 28-day camp: a 10-year review. Clin J Sports Med . 2016. 26:4: 272–8. ^ Anderson, BJ (April 1999). ... "Prophylactic valacyclovir to prevent outbreaks of primary herpes gladiatorum at a 28-day wrestling camp". Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases . 59 (1): 6–9.
-
Interrupted Aortic Arch
Wikipedia
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center. July 2015 . Retrieved 28 April 2018 . ^ a b Börcek, Alp Özgün; Egemen, Emrah; Güngör, Günhan; Baykaner, Mustafa Kemali (6 November 2012). ... University of Michigan . Retrieved 28 April 2018 . ^ "Interrupted Aortic Arch" . Cleveland Clinic . Cleveland Clinic . Retrieved 28 April 2018 . ^ a b c Lie, J.T. (May 1967).
-
Sex Differences In Medicine
Wikipedia
Diseases of X-linked recessive inheritance , such as colour blindness , occur more frequently in men, and haemophilia A and B occur almost exclusively in men. [21] Abdominal aortic aneurysms are six times more common in men, and thus some countries have introduced screening for males at risk of suffering the condition. [22] Autism is approximately 4 times more prevalent in males than females. [23] Schizophrenia is about 1.4 times more common in males and on average starts 2 years earlier and has more severe symptoms. [24] More than two times more men than women are affected by antisocial personality disorder and substance use disorder . [25] [26] Several cancers, including stomach cancer (2:1), [27] oesophageal cancer (3:1), [28] liver cancer (2:1 to 4:1) [29] and oral cancer (2:1 to 3:1), [30] which have mostly lifestyle-based risk factors, are more common in men. ... Vascular Health and Risk Management . 10 : 115–28. doi : 10.2147/vhrm.s45181 . PMC 3956880 . ... Annu Rev Public Health . 2007 [ archived 2013-09-03];28:235–58. doi : 10.1146/annurev.publhealth.28.021406.144007 .
-
Bright's Disease
Wikipedia
Ellen Axson Wilson , first wife of Woodrow Wilson , died on 6 August 1914. [28] Richard Warren Sears , an American businessman and founder of the department store chain Sears, Roebuck and Company , died on 28 September 1914 in Waukesha, Wisconsin . Woodsman Louis " French Louie " Seymour died on 28 February 1915. John Bunny , comic star of the early motion picture era, died on 26 April 1915.
- Leontiasis Ossea Wikipedia
-
Sodoku
Wikipedia
Local transmission has been reported in US. [2] The incubation period is 4 to 28 days. Prognosis [ edit ] Mortality is 6–10%.
-
Electroencephalographic Pattern, Beta Frequency, Quantitative Trait Locus
Omim
Mapping To identify genes underlying the heritability of EEG, Porjesz et al. (2002) conducted a linkage and linkage-disequilibrium study concerning the 3 beta frequency bands (13 to 28 Hz) of the human EEG. Their studies demonstrated maximum lod scores with the GABRB1 gene (137190) on chromosome 4p13-p12 between markers D4S1627 and D4S1645.
-
Neutropenia, Severe Congenital, 6, Autosomal Recessive
Omim
One patient died at age 5 years; the others, aged 5 to 28 years, were alive and well. Two patients underwent hematopoietic bone marrow transplantation.
-
Joseph And Luka Banda
Wikipedia
In 1997, Ben Carson led a team of 50 Zambian and South African specialists to separate the 11-month-old twins in a 28-hour operation. [2] They did not share any organs, but shared intricate blood vessels that flowed into each other's brains.