-
Image Syndrome
Gene_reviews
Clinical Characteristics Clinical Description Twenty-eight individuals reported from 16 families have features consistent with the clinical diagnosis of IMAGe syndrome [Vilain et al 1999, Lienhardt et al 2002, Pedreira et al 2004, Bergadá et al 2005, Hutz et al 2006, Tan et al 2006, Ko et al 2007, Amano et al 2008, Balasubramanian et al 2010, Arboleda et al 2012, Hamajima et al 2013, Bodian et al 2014, Kato et al 2014]. Of these 28 individuals, 17 from nine unrelated families have had the diagnosis confirmed molecularly [Arboleda et al 2012, Hamajima et al 2013]. ... A diagnosis of IMAGe syndrome has been considered in other published cases; however, the clinical information was either significantly different from the 28 typical cases or insufficient to determine the diagnosis with certainty, and pathogenic CDKN1C variants were not reported [Blethen et al 1990, Hall & Stelling 1991, Le & Kutteh 1996, Coman et al 2007, McDonald et al 2010, Lindemeyer et al 2014]. ... Reported abnormalities include cryptorchidism (usually bilateral), micropenis, and hypospadias. Of the 28 individuals reported with IMAGe syndrome 20 are male, which may represent ascertainment bias due to the presence of genital abnormalities in males only. ... Prevalence The prevalence of IMAGe syndrome is currently unknown. A total of 28 affected individuals from 16 families have been reported to date.
-
Trichomoniasis
Wikipedia
Specialty Gynecology Symptoms Itching in the genital area , bad smelling thin vaginal discharge , burning with urination, pain with sex [1] [2] Usual onset 5 to 28 days after exposure [1] Causes Trichomonas vaginalis (typically sexually transmitted ) [2] [1] Diagnostic method Finding the parasite in vaginal fluid, microbial culture , testing for the parasites DNA [1] Prevention Not having sex, using condoms, not douching [1] Medication Antibiotics ( metronidazole or tinidazole ) [1] Frequency 122 million (2015) [3] Trichomoniasis ( trich ) is an infectious disease caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis . [2] About 70% of women and men do not have symptoms when infected. [2] When symptoms do occur they typically begin 5 to 28 days after exposure. [1] Symptoms can include itching in the genital area , a bad smelling thin vaginal discharge , burning with urination, and pain with sex. [1] [2] Having trichomoniasis increases the risk of getting HIV/AIDS . [1] It may also cause complications during pregnancy . [1] Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) which is most often spread through vaginal, oral, or anal sex. [1] It can also spread through genital touching. [1] People who are infected may spread the disease even when symptoms are not present. [2] Diagnosis is by finding the parasite in the vaginal fluid using a microscope , culturing the vagina or urine, or testing for the parasite's DNA . [1] If present other STIs should be tested for. [1] Methods of prevention include not having sex , using condoms , not douching , and being tested for STIs before having sex with a new partner. [1] Trichomoniasis can be cured with antibiotics , either metronidazole or tinidazole . [1] Sexual partners should also be treated. [1] About 20% of people get infected again within three months of treatment. [2] There were about 122 million new cases of trichomoniasis in 2015. [3] In the United States, there are about 2 million women affected. [1] It occurs more often in women than men. [1] Trichomonas vaginalis was first identified in 1836 by Alfred Donné . [4] It was first recognized as causing this disease in 1916. [5] Contents 1 Signs and symptoms 1.1 Complications 2 Causes 2.1 Genetic sequence 3 Diagnosis 4 Prevention 4.1 Screening 5 Treatment 6 Epidemiology 7 References 8 External links Signs and symptoms [ edit ] Play media Trichomonas vaginalis as seen by phase contrast microscopy Most people infected with Trichomonas vaginalis do not have any symptoms and can be undetected for years. [6] Symptoms experienced include pain, burning or itching in the penis, urethra ( urethritis ), or vagina ( vaginitis ). ... Symptoms usually appear within 5 to 28 days of exposure. [7] Sometimes trichomoniasis can be confused with chlamydia because the symptoms are similar. [8] Complications [ edit ] Trichomoniasis is linked to two serious complications. ... Infection with trichomoniasis through water is unlikely because Trichomonas vaginalis dies in water after 45–60 minutes, in thermal water after 30 minutes to 3 hours and in diluted urine after 5–6 hours. [23] Currently there are no routine standard screening requirements for the general U.S. population receiving family planning or STI testing. [24] [25] The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends trichomoniasis testing for females with vaginal discharge [26] and can be considered for females at higher risk for infection or of HIV-positive serostatus . [24] The advent of new, highly specific and sensitive trichomoniasis tests present opportunities for new screening protocols for both men and women. [24] [27] Careful planning, discussion, and research are required to determine the cost-efficiency and most beneficial use of these new tests for the diagnosis and treatment of trichomoniasis in the U.S., which can lead to better prevention efforts. [24] [27] A number of strategies have been found to improve follow-up for STI testing including email and text messaging as reminders of appointments. [28] Screening [ edit ] Evidence from a randomized controlled trials for screening pregnant women who do not have symptoms for infection with trichomoniasis and treating women who test positive for the infection have not consistently shown a reduced risk of preterm birth . [29] [30] Further studies are needed to verify this result and determine the best method of screening.
-
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
Wikipedia
If the sample is sent in a plain sterile container 40% of samples will identify an organism, while if the sample is sent in a bottle with culture medium , the sensitivity increases to 72–90%. [10] Prevention [ edit ] All people with cirrhosis might benefit from antibiotics (oral fluoroquinolone norfloxacin) if: Ascitic fluid protein <1.0 g/dL. [21] Patients with fluid protein <15 g/L and either Child-Pugh score of at least 9 or impaired renal function may also benefit. [24] Previous SBP [25] People with cirrhosis admitted to the hospital should receive prophylactic antibiotics if: They have bleeding esophageal varices [26] Studies on the use of rifaximin in cirrhotic patients, have suggested that its use may be effective in preventing spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. [9] [27] Treatment [ edit ] Antibiotics [ edit ] Although there is no high-quality evidence, the third generation cephalosporins are considered the standard empirical treatment for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in people with cirrhosis. [28] In practice, cefotaxime is the agent of choice for treatment of SBP. ... PMID 19266595 . ^ a b Fiore, Marco; Maraolo, Alberto Enrico; Gentile, Ivan; Borgia, Guglielmo; Leone, Sebastiano; Sansone, Pasquale; Passavanti, Maria Beatrice; Aurilio, Caterina; Pace, Maria Caterina (2017-10-28). "Current concepts and future strategies in the antimicrobial therapy of emerging Gram-positive spontaneous bacterial peritonitis" . ... Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology . 28 (2): 235–42. doi : 10.1111/jgh.12065 .
-
Migrainous Infarction
Wikipedia
A diagnosis is confirmed when neuroimaging of the patient's brain exhibits an ischaemic infarction in an area associated with the migraine. [20] Overall, only 18% of patients with MA will experience any aura symptoms for longer than 60 minutes. [6] Localisation [ edit ] CT scans , Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) are all common techniques which allow the localisation of brain lesions after stroke. [28] Approximately 82% of migrainous infarction patients experience lesions in the posterior circulation , with 21% of patients also experiencing lesions in the cerebellum . [2] Treatment [ edit ] Clot-busting agents [ edit ] Clot busting agents or thrombolytic therapy are a treatment option for migrainous infarction caused by enhanced platelet activation leading to thrombosis. [29] Streptokinase [ edit ] Streptokinase is a thrombolytic agent which aims to permit reperfusion , allowing the restoration of blood flow to the ischaemic areas. [30] Recent trials indicate that Streptokinase can improve function after a 6 month period, however, the risk of mortality due to intracerebral haemorrhage resulting from use of this thrombolytic agent is extremely high and therefore, treatment using streptokinase is not recommended. [30] Alteplase [ edit ] Alteplase is a recombinant tissue plasminogen activator which enhances the conversion of plasminogen into plasmin to aid in the degradation of blood clots. [31] Effectiveness depends highly on swift administration of the medication, notably, the treatment should be administered within 3 to 4.5 hours of onset of the ischaemic stroke for the most effective results. [32] In a similar manner to Streptokinase, Alteplase increases the risk of intracranial haemorrhage, however, mortality rate is not affected. [32] Aspirin [ edit ] Aspirin is a class anti-aggregation drug, often used to treat headaches in patients with MA. [22] Administration of aspirin in patients with MA has been shown to be effective in reducing platelet factor 4 (PF4) concentration. ... PMID 1557011 . ^ Stam, J. (2005-04-28). "Thrombosis of the Cerebral Veins and Sinuses" . ... Headache: The Journal of Head and Face Pain . 28 (3): 183–186. doi : 10.1111/j.1526-4610.1988.hed2803183.x .
-
Post-Acute-Withdrawal Syndrome
Wikipedia
For some individuals, these withdrawal symptoms are short-lived and make a full recovery, for others a protracted withdrawal syndrome may occur with withdrawal symptoms persisting for months or years. [22] Cause [ edit ] The syndrome may be in part due to persisting physiological adaptations in the central nervous system manifested in the form of continuing but slowly reversible tolerance , disturbances in neurotransmitters and resultant hyperexcitability of neuronal pathways. [23] [24] [25] [26] However, data supports “neuronal and overwhelming cognitive normalization” in regards to chronic amphetamine use and PAWS. [27] [28] Stressful situations arise in early recovery, and the symptoms of post acute withdrawal syndrome produce further distress. ... J Subst Abuse Treat . benzo.org.uk. 8 (1–2): 19–28. doi : 10.1016/0740-5472(91)90023-4 . ... Brain Res Brain Res Rev . 49 (3): 505–28. doi : 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2005.01.007 .
-
Adhesive Capsulitis Of The Shoulder
Wikipedia
Symptoms in people with diabetes may be more protracted than in the non-diabetic population. [28] See also [ edit ] Calcific tendinitis Milwaukee shoulder syndrome References [ edit ] ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u Ramirez, J (1 March 2019). ... PMID 30632986 . ^ "Your Orthopaedic Connection: Frozen Shoulder" . Retrieved 28 January 2008 . ^ a b c Kelley MJ, Shaffer MA, Kuhn JE, Michener LA, Seitz AL, Uhl TL, et al. ... PMID 29683834 . ^ "Questions and Answers about Shoulder Problems" . Retrieved 28 January 2008 . External links [ edit ] Classification D ICD - 10 : M75.0 ICD - 9-CM : 726.0 DiseasesDB : 34114 External resources MedlinePlus : 000455 eMedicine : orthoped/372 v t e Soft tissue disorders Capsular joint Synoviopathy Synovitis / Tenosynovitis Calcific tendinitis Stenosing tenosynovitis Trigger finger De Quervain syndrome Transient synovitis Ganglion cyst osteochondromatosis Synovial osteochondromatosis Plica syndrome villonodular synovitis Giant-cell tumor of the tendon sheath Bursopathy Bursitis Olecranon Prepatellar Trochanteric Subacromial Achilles Retrocalcaneal Ischial Iliopsoas Synovial cyst Baker's cyst Calcific bursitis Noncapsular joint Symptoms Ligamentous laxity Hypermobility Enthesopathy / Enthesitis / Tendinopathy upper limb Adhesive capsulitis of shoulder Impingement syndrome Rotator cuff tear Golfer's elbow Tennis elbow lower limb Iliotibial band syndrome Patellar tendinitis Achilles tendinitis Calcaneal spur Metatarsalgia Bone spur other/general: Tendinitis / Tendinosis Nonjoint Fasciopathy Fasciitis : Plantar Nodular Necrotizing Eosinophilic Fibromatosis / contracture Dupuytren's contracture Plantar fibromatosis Aggressive fibromatosis Knuckle pads Authority control NDL : 00562580
-
Menstrual Disorder
Wikipedia
In secondary amenorrhea, or the absence of menstruation for greater than 6 months, can be caused by the same reasons as primary amenorrhea, as well as polycystic ovary syndrome , pregnancy, chronic illness, and certain drugs like cocaine and opioids. [25] Hypomenorrhea [ edit ] Causes of hypomenorrhea , or irregular light periods, include periods around menopause , eating disorders , excessive exercise, thyroid dysfunction , uncontrolled diabetes , Cushing's syndrome , hormonal birth control , and certain medications to treat epilepsy or mental health conditions. [26] Menorrhagia [ edit ] Causes of menorrhagia , or heavy menstrual bleeding, include polycystic ovary syndrome , uterine fibroids , endometrial polyps , bleeding disorders , and miscarriage. [26] Dysmenorrhea [ edit ] Causes of dysmenorrhea , or menstrual pain, include endometriosis , pelvic scarring due to chlamydia or gonorrhea , and intrauterine devices or IUDs . [26] Primary dysmenorrhea is when there is no underlying cause that is identified, and secondary dysmenorrhea is when the menstrual pain is caused by other conditions such as endometriosis , fibroids , or infection. [27] Diagnosis of menstrual disorders [ edit ] Pelvic exam Diagnosis begins with an in-depth medical history and physical exam, including a pelvic exam and sometimes a Pap smear . [28] Additional testing may include but are not limited to blood tests, hormonal tests, ultrasound , gynecologic ultrasound , magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) , hysteroscopy , laparoscopy , endometrial biopsy , and dilation and curettage (D&C). [28] Treatment of menstrual disorders [ edit ] Premenstrual syndrome and premenstrual dysphoric disorder [ edit ] Due to the unclear etiology of premenstrual syndrome and premenstrual dysphoric disorder, symptom relief is the primary goal of treatment. ... Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 2015 . Retrieved 2020-07-28 . ^ Costlow LS (May 2020). "Heavy Menstrual Bleeding in Adolescents: ACOG Management Recommendations".
-
Osteopenia
Wikipedia
Once a person loses bone density, the loss is usually irreversible, so preventing (greater than normal) bone loss is important. [23] Actions to maximize bone density and stabilize loss include: [24] [25] [26] [27] Exercise, particularly weight-bearing exercise and resistance exercises Adequate caloric intake Sufficient calcium in diet: older adults may have increased calcium needs—of note, medical conditions such as Celiac and hyperthyroidism can affect absorption of calcium [25] Sufficient Vitamin D in diet Estrogen replacement Avoidance of steroid medications Limit alcohol use and smoking Pharmaceutical treatment [ edit ] The pharmaceutical treatment of osteopenia is controversial and more nuanced than well-supported recommendations for improved nutrition and weight-bearing exercise. [28] [29] [5] The diagnosis of osteopenia in and of itself does not always warrant pharmaceutical treatment. [30] [31] Many people with osteopenia may be advised to follow risk prevention measures (as above). ... Eating Disorders Catalogue . 2018-02-28 . Retrieved 2019-12-03 . ^ a b "2019 ISCD Official Positions – Adult – International Society for Clinical Densitometry (ISCD)" . ... Retrieved 2019-12-08 . ^ Kolata G (September 28, 2003). "Bone Diagnosis Gives New Data But No Answers" .ESR1, IGF1, MMP2, CTC1, PHOSPHO1, ALPL, DHCR7, SLC20A1, ANKRD11, LRP2, SLC5A6, GC, KCNMA1, CYP2R1, CYP27A1, PPARG, CYP19A1, LRP5, COL1A1, NOTCH2, FSHR, FBN1, CAV1, SLC20A2, STAT3, B3GAT3, GNPTAB, EFL1, CREB3L1, COL1A2, LMNA, ADCY10, SBDS, GORAB, PROP1, PLS3, PTPN11, GTF2I, PYCR1, GBA, NRAS, TMEM67, TRPV6, WDR11, NPR2, POU1F1, PROK2, PRKACA, FKBP10, PRKAR1A, TNFRSF11B, OTX2, SLC39A13, IARS2, P4HB, NUP107, MRPS22, PDGFRB, PEX6, CHD7, TONSL, PMM2, PLOD2, CDH23, TUBB6, SLC39A8, LIMK1, LHX4, STN1, DCAF17, HSD17B4, KRAS, KISS1, PIGY, COX4I2, KCNJ1, ANOS1, IL17A, KISS1R, IL6, SPRY4, IL1B, LIFR, ALG13, NFATC1, HRAS, RSPRY1, NAGA, IL1A, MTAP, P3H1, NSD1, GZF1, MMP14, HPGD, MMP1, MGAT2, MEN1, MECP2, CDC73, FAT4, XYLT2, SMARCD2, TMEM38B, HESX1, B4GALT7, BMP15, SLC7A7, AIP, BAZ1B, EXOC6B, PLOD3, FGF17, DPM2, SLC9A3R1, SPIDR, TNFRSF11A, GPAA1, EED, ATP6V0A2, DCHS1, TNFSF11, GNPAT, GCM2, COG1, NSMF, PLEKHM1, CRTAP, TCIRG1, ZMPSTE24, IRX5, AGPAT2, FARSB, MAFB, SEC24D, AFG3L2, HS6ST1, ADAMTSL2, GTF2IRD1, ADAMTS2, CHST3, POLR3A, EIF2AK3, CRIPT, RECQL4, USP9X, RNF113A, FKBP14, RFC2, SMARCAL1, SKI, GEMIN4, PDE11A, SOST, MLXIPL, MBTPS2, RPL11, PIGT, SLC34A1, ALDH18A1, PURA, PTH1R, PTH, PSMB8, PSAP, PRLR, RNF125, SLC12A1, SMPD1, PHGDH, TRPS1, CLIP2, BEST1, SLC17A5, VDR, UROS, SLC35A2, BSCL2, TBL2, TNF, SOX3, TCF4, TAF1, TACR3, TAC3, PSMC3IP, PSAT1, STAT1, SRP54, MAGEL2, MST1, NR5A1, SH3PXD2B, DUSP6, FLG, MPLKIP, FOS, BGLAP, CCND1, AVP, DNAJC21, FUT8, GATA1, PROKR2, GFI1, ATP7A, CAVIN1, COL7A1, BMP2, FGFR2, FGFR1, ENG, ERCC2, ERCC3, ANO5, SERPINH1, RUNX2, EXT2, ELN, FGF8, SGMS2, ELANE, FBN2, SCARB2, BTF3P11, BRAF, UNC80, TAPT1, CTSK, DDOST, GNRHR, GNAS, GTF2E2, GLI2, GNRH1, DMD, FLG-AS1, RNU4ATAC, GTF2H5, GPR35, CTNNB1, IFITM5, ANTXR2, DKK1, APOE, KL, CCL2, GH1, MBL2, SH3BP2, MAPK1, MBL3P, TLR2, TRPV1, P2RX7, DMP1, CALCA, FGF23, TRAP, IL10, CBL, BRD2, TRAF6, LEP, FGF21, AIMP2, RNF19A, POLDIP2, CD6, MMP9, PTHLH, ACP5, AHSA1, NFE2L2, MAPK14, CD38, IL11, IL1RN, ACE, CRK, GABPA, IFNG, AKT1, GRAP2, ATP6V1H, MIR21, MIR146A, EPHB2, CSF1, SLIT3, MIR29A, SERPINE1, PRL, FBLIM1, SIRT6, GOPC, HAMP, IL23A, CD40LG, SPP1, CSF3, GJA1, MGP, MYD88, HSPD1, PTRH1, CALCR, AR, SATB2, SIRT1, NLRP3, ADIPOQ, AGT, APP, TSC1, KIF3A, S1PR2, MSC, IL32, ATF4, RPS6KA3, P2RX5-TAX1BP3, RELA, CRP, ALB, ATM, PPARGC1A, EMCN, AHR, CRYGD, TNFSF15, TNFSF13B, ABCB6, ANP32B, ACTB, ABO, PTGS2, HSPA14, CCL3, P2RX6, TNFRSF25, UCP1, CASR, WNT1, AGO2, TGFB1, ZFP36, TFRC, CST3, GDF5, NCOA1, SYT1, CD40, TNKS, SRY, CNR2, SRC, TNFSF13, VSX1, BMP4, BMI1, CCN6, SIRT3, SLA, SHBG, P2RX2, FOXP3, TRAF3, RGN, MIR451A, SEMA3A, ZNF384, NOD2, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, PIK3CA, SERPINA1, SMAD1, MTHFR, PECAM1, MYC, ASXL1, IKBKB, GIP, FNDC5, PAX5, EPO, HSD11B2, NPY, P2RY2, CD109, P2RY1, P2RX5, P2RX4, FSHB, P2RX3, P2RX1, IL15, LGALS8, TRPV4, LGALS3, PIK3CG, MSTN, HIF1A, GSK3B, DNER, CD46, CYP27B1, IL33, HMOX1, HSD11B1, NR3C1, HPD, DDIT3, FCGR2B, FGF2, WNK1, GORASP1, PLCG2, PTK2B, F2RL1, MFGE8, HBZ, GGTLC4P, SMUG1, CARD14, MIR885, TPX2, DOK3, BRD4, RIOX1, TSG1, AGBL2, GGTLC5P, ANGPTL2, CCR2, GGTLC3, RHBDF2, IGSF23, RBFOX2, WLS, DOCK11, GGT2, TREM1, DCSTAMP, ARMC9, COMMD3-BMI1, ADAMTS5, SCIN, DUSP14, IMMT, PGR-AS1, C1QTNF4, CYSLTR1, MYSM1, CBSL, TOB2, PERCC1, GNA13, KHDRBS1, LRP1-AS, RSAD2, SEMA4D, MTCO2P12, DOCK7, LINC01672, RAB3GAP1, MRGPRF, TET1, PIFO, CILK1, VSIG4, PPP1R2C, WNT10A, MIR497, MIR543, WIF1, RNF146, WDHD1, QRFPR, ASCC2, FNDC1, MIR1234, TRIM63, ORAI1, MIR503, ERAL1, NUP62, SLC13A5, NGLY1, PLEKHO1, DCTN4, MIR155, ADIPOR1, TXLNG, DEFB103B, MIR185, MIR188, MIR29B1, MIR19B1, IL22, IL20, MIR203A, TEX11, MIR214, MIR23B, ERVW-1, CRBN, RSPO1, LIMS2, WNT16, EGLN1, MIR106B, MIR130A, TLR9, IMMTP1, MIR132, IL17D, P4HTM, RPS19BP1, MIR100, MSTO1, KLF13, MIR140, STING1, FBXW7, LGR4, SLC39A4, MIR296, IL27, GPBAR1, PRMT5, PIKFYVE, DEFB103A, MIR151A, MIR325, MIR335, MIR376C, GLIS3, MIR384, MIR10B, ATP6V0D2, DEPTOR, MIR496, P2RY12, AGXT2, ASF1A, SLC39A6, VKORC1, IL17RA, HAVCR1, ACAD8, SND1, KCNMB3, MIR29B2, MIR30B, MIR31, NCOA5, MIR33A, SNX10, MPEG1, MIR34A, IL21, HIVEP3, PYCARD, SETD2, OSTM1, IL17B, IL37, ACE2, TGIF2, NLRP12, NAT2, YAP1, HBA2, FFAR1, FFAR2, GRN, CXCL2, GTF2H1, HBA1, HFE, AKR1A1, HGF, HLA-B, NR4A1, HOXC6, HP, PRMT1, CXCR3, GHR, GGT1, GGCX, KAT2A, FTH1, MTOR, FN1, FOXO3, FHL2, FGFR3, FCGR3A, FASN, FABP4, MECOM, ETV6, ESRRG, HES1, HSPA1A, HSPA1B, LCN2, MIF, CIITA, MFAP2, MET, MAOA, SMAD7, SMAD6, SMAD3, LRP6, LRP4, LIMS1, LGALS1, LEPR, LDLR, KRT8, HSPA2, IRF4, IL18, IL13, IL9, CXCL8, IL7, IL4, IL3, IGFBP1, IGFALS, IFRD1, IDH2, ICAM1, HSPA6, ESR2, ERBB2, EPAS1, BMP3, CBS, RUNX3, RUNX1, CASP8, CASP3, CASP1, CAMP, C4BPA, TSPO, ZFP36L1, BRCA2, BRCA1, BMP7, BMP6, PRDM1, ENTPD1, BGN, BCL6, ART4, STS, ARNTL, FAS, AMELX, AMBP, ALDH2, AHSG, AGTR1, AGER, ADORA2B, ACR, CD28, CD44, EGR2, CTLA4, EGFR, S1PR1, DYRK1A, DUSP2, TSC22D3, DPAGT1, DOK1, DNMT3B, DLX3, DCN, CYP11A1, CYP2B6, CUX1, CTNS, CSF2, CD74, CSF1R, CRX, CREM, CREBBP, CNR1, ACKR2, CCR3, CCR1, CHRNA4, CHRM3, CHAD, CFTR, CDX2, CDKN1A, CXCL9, MAP3K10, MMP8, TXN, SOCS1, PIP5K1B, TAM, FOSL1, ARHGEF5, TFEB, SEMA3B, CXCR4, WNT10B, WNT5A, WNT3, VIP, VIM, TYROBP, HSP90B2P, DLK1, TP53, TNXB, TNFRSF1B, KLF10, THY1, THBD, THAS, TGM2, TGFBR1, PRDX2, TAT, SYK, SULT2A1, SOX9, IRS2, TRIM24, SLC6A4, PTGES, STUB1, KCNMB2, PRMT3, EBI3, EDIL3, DPP3, ABI1, NR1H4, RB1CC1, KEAP1, PIEZO1, HDAC4, SART3, CLOCK, IL27RA, IL18R1, PPIG, MAPKAPK2, XPR1, SLC33A1, IL1RL1, USP6, PSTPIP2, DOK2, RHBDL1, SOCS3, TIMELESS, SQSTM1, SPHK1, SOCS2, ABCA1, SLC5A2, MMP13, OXA1L, PRKAA1, PPARA, PON1, PRRX1, PLG, PLCG1, PKD2, PKD1, PIK3R2, PIK3R1, PDK4, PCNA, PAH, PRDX1, CLDN11, PRKAB1, OSM, OAS3, NT5E, CCN3, NOTCH3, NOTCH1, NOS3, NOS2, NFKB2, NCK1, COX2, MST1R, MPST, MPO, PRKAA2, PRKG2, SLC2A1, RGS12, PMEL, SGK1, SFRP5, CXCL12, SCT, SCN8A, S100A12, S100A9, S100A8, S100A4, RRBP1, RPS19, RPL29, RNU1-4, REN, MAPK8, RCN1, RBP4, KDM5A, RARRES2, PTPRA, PTPN2, PTN, PTEN, PYY, PSG5, PRNP, MAP2K7, MAP2K6, MAP2K1, LINC02605
-
Eclabium
Wikipedia
Lateral columella base-labrum transposition flap [28] results in soft linear scars without hyperplasia. [29] It is an easy, minimally invasive and nearly no secondary malformation method. a type of flap used is the Limberg/Rhomboid flap. [28] The flap is made up of Cutaneous tissue [13] to close defects anywhere on the body. ... Some patients might get further cosmetic surgery [28] to fix the scarring. Eclabium caused by Periodontitis is almost always treatable and if it has advanced severely, surgery can help to treat it.
-
Upskirt
Wikipedia
The maximum sentence for the offence is two years' imprisonment and in the more serious sexual cases those convicted are added to the Violent and Sex Offender Register . [22] [23] [24] Before 2019, there were no specific laws against upskirting in England and Wales . [25] When upskirting took place in public, it was outside of the scope of the offence of voyeurism under the Sexual Offences Act 2003. [26] Nevertheless, prosecutions for upskirting were successful under the common law offence of outraging public decency , which requires the presence of at least two other people and for the act to be done in a public place. [27] Following a public campaign to change the law, a government bill was introduced to the House of Commons on 21 June 2018. [28] [29] Speaking on the government's behalf in the House of Lords, Baroness Vere of Norbiton said that the legislation would also protect men wearing kilts . [30] [31] The Voyeurism (Offences) Act 2019 received royal assent on 12 February 2019, taking effect two months later. ... United Kingdom. ^ "Upskirting to become a crime" . smh.com.au . The Sydney Morning Herald. 28 July 2006 . Retrieved 10 June 2007 . ... Retrieved 17 May 2018 . ^ "Northern Ireland teen to fight 'upskirting' charges" . Belfast Telegraph . 28 June 2018 . Retrieved 12 February 2019 . ^ "S. 1301 [108th]: Video Voyeurism Prevention Act of 2004" .
-
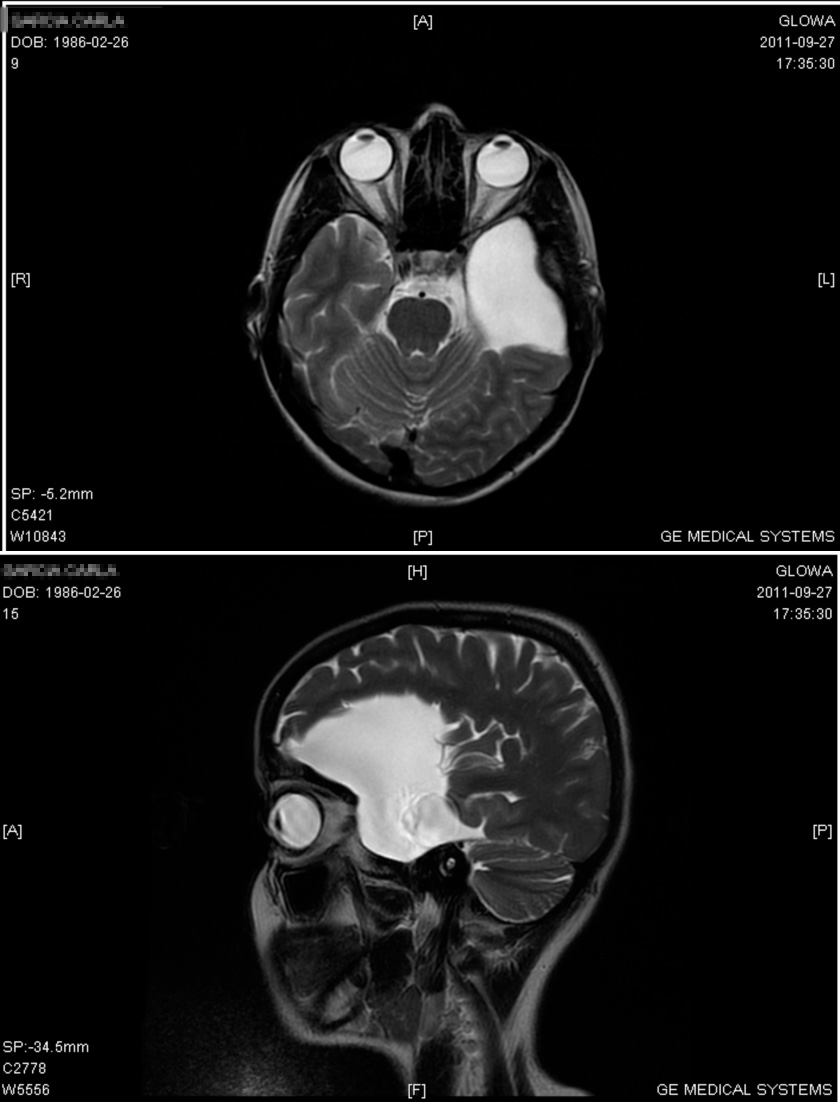
Arachnoid Cyst
Wikipedia
Surgical placement of a cerebral shunt : [25] An internal shunt drains into the subdural compartment. [26] A cystoperitoneal shunt drains to the peritoneal cavity . [27] Fenestration : Craniotomy with excision [28] Various endoscopic techniques are proving effective, [29] including laser-assisted techniques. [30] Drainage by needle aspiration or burr hole . ... Action=View&Archive=True&ID=67&GroupID=&Page=11 Archived September 28, 2007, at the Wayback Machine ^ Griffiths TD (October 2000). ... Action=View&Archive=True&ID=29&GroupID=&Page=18 Archived September 28, 2007, at the Wayback Machine ^ a b Yamakawa H, Ohkuma A, Hattori T, Niikawa S, Kobayashi H (1991).
-
Contrast-Induced Nephropathy
Wikipedia
Several studies have shown that Intravenous contrast material administration was not associated with excess risk of acute kidney injury (AKI), dialysis, or death, even among patients with comorbidities reported to predispose them to nephrotoxicity. [4] Moreover, hydration, the most established prevention measure to prevent contrast induced nephropathy was shown to be ineffective in the POSEIDON trial, [26] raising further doubts regarding the significance of this disease state. [27] A meta-analysis of 28 studies of AKI after CT with radiocontrast showed no causal relationship between the use of radiocontrast and AKI. [3] References [ edit ] ^ Barrett BJ, Parfrey PS (2006). ... "Preventing contrast medium-induced acute kidney injury". European Radiology . 28 (12): 5384–5395. doi : 10.1007/s00330-018-5678-6 . ... S2CID 7882106 . ^ "Medscape" . www.medscape.com . Retrieved 2017-09-28 . External links [ edit ] Classification D ICD - 10 : N99.0 ICD - 9-CM : 586 v t e Kidney disease Glomerular disease See Template:Glomerular disease Tubules Renal tubular acidosis proximal distal Acute tubular necrosis Genetic Fanconi syndrome Bartter syndrome Gitelman syndrome Liddle's syndrome Interstitium Interstitial nephritis Pyelonephritis Balkan endemic nephropathy Vascular Renal artery stenosis Renal ischemia Hypertensive nephropathy Renovascular hypertension Renal cortical necrosis General syndromes Nephritis Nephrosis Renal failure Acute renal failure Chronic kidney disease Uremia Other Analgesic nephropathy Renal osteodystrophy Nephroptosis Abderhalden–Kaufmann–Lignac syndrome Diabetes insipidus Nephrogenic Renal papilla Renal papillary necrosis Major calyx / pelvis Hydronephrosis Pyonephrosis Reflux nephropathy
-
Abortion In Idaho
Wikipedia
The cut off point for getting a legal abortion in the state was generally some point between week 24 and 28. This period uses a standard defined by the United States Supreme Court in 1973 with the Roe v. ... This was on top of the fact that many had other menstrual issues including bleeding, cramps and other menstrual induced health issues. [10] This state was one of a majority that taxed essential hygiene products like tampons and menstrual pads as of November 2018. [11] [12] [13] [14] History [ edit ] Legislative history [ edit ] By 1950, the state legislature passed a law stating that a woman who had an abortion or actively sought to have an abortion regardless of whether she went through with it were guilty of a criminal offense. [15] The state passed a law in the 2000s banning abortions after 22 weeks because they alleged that fetus can feel pain. [16] The state was one of 23 states in 2007 to have a detailed abortion-specific informed consent requirement. [17] In the informed consent materials given to women in Idaho, Oklahoma, South Dakota and Texas required by statute, the materials used graphic and inflammatory language. [18] Idaho was the only state of 23 with detailed informed consent requirements by statute that did not require the woman be told how far advanced her pregnancy was. [18] Georgia, Michigan, Arkansas and Idaho all required in 2007 that women must be provided by an abortion clinic with the option to view an image their fetus if an ultrasound is used prior to the abortion taking place. [18] As of May 14, 2019, the state prohibited abortions after the fetus was viable, generally some point between week 24 and 28. This period uses a standard defined by the United States Supreme Court in 1973 with the Roe v. ... That year, 68% of women in the state aged 15 – 44 lived in a county without an abortion clinic. [25] In March 2016, there were three Planned Parenthood clinics in the state. [26] In 2017, there were three Planned Parenthood clinics in a state with a population of 365,502 women aged 15 – 49 of which 3 offered abortion services. [27] Emerg-A-Care in Jackson Hole , Wyoming also served women from Eastern Idaho in 2017. [28] Statistics [ edit ] In the period between 1972 and 1974, there was only no recorded illegal abortion death in the state. [ clarification needed ] [29] In 1990, 106,000 women in the state faced the risk of an unintended pregnancy. [23] The lowest number of legal induced abortions by state in 2000 occurred in Idaho with 801, while South Dakota was second with 878, and North Dakota was third with 1,341. [30] Idaho had the fewest induced abortions in 2001 with 738, while South Dakota was second with 895, and North Dakota was third with 1,216.
-
Primary Myelofibrosis
Wikipedia
These data showed that the treatment significantly reduced spleen volume, improved symptoms of myelofibrosis, and was associated with much improved overall survival rates compared to placebo. [26] [27] However, the beneficial effect of ruxolitinib on survival has been recently questioned. [28] In August 2019, the FDA approved fedratinib as a treatment for adults with intermediate-2 or high-risk primary or secondary (post-polycythemia vera or post-essential thrombocythemia) myelofibrosis (MF). [29] History [ edit ] Myelofibrosis was first described in 1879 by Gustav Heuck . [30] [31] Eponyms for the disease are Heuck-Assmann disease or Assmann's Disease, for Herbert Assmann , [32] who published a description under the term "osteosclerosis" in 1907. [33] It was characterised as a myeloproliferative condition in 1951 by William Dameshek . [34] [35] The disease was also known as myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia and agnogenic myeloid metaplasia [36] The World Health Organization utilized the name chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis until 2008, when it adopted the name of primary myelofibrosis . ... "CALR vs JAK2 vs MPL-mutated or triple-negative myelofibrosis: clinical, cytogenetic and molecular comparisons". Leukemia . 28 (7): 1472–1477. doi : 10.1038/leu.2014.3 . ... Springer Science+Business Media, LLC. pp. 28–. ISBN 978-0-387-73744-7 . ^ Judith E.MPL, JAK2, CALR, TET2, GATA1, NCOR2, MYB, ABL1, JAK1, BCR, THPO, CD34, SOAT1, TGFB1, ASXL1, STAT5A, STAT5B, HMGA2, SRSF2, CXCL8, EPO, MVD, TP53, DERL1, TNFRSF11B, PDGFRA, GLI1, CD177, PRB1, FN1, CXCL12, CDKN2A, VPS45, AURKA, TNF, CXCR4, PDGFRB, LINC01152, NBEAL2, MPIG6B, NOG, WT1, WNT1, AKT1, TAC1, PIK3CB, PIK3CD, VEGFA, INTS2, PIK3CG, FXYD5, SCT, IRAK1, PIK3CA, H3P10, RUNX1, ETV6, CSF3, FGF2, FGF3, FLT1, FLT3, CD47, DNMT3A, IFNA2, IFNA13, IFNA1, ALB, IFNG, MAGT1, SHOC2, SOCS3, HSPB3, IL18R1, ALPI, GFI1B, CHIT1, CRP, CHI3L1, ZMYM2, H3P9, CSF3R, CTNNB1, VDR, TPO, CUX1, TNFRSF1B, DAPK1, MYOM2, CDKN2B, PRSS27, TBK1, ALPP, BORA, AMCN, CIP2A, XIAP, STS, BMP6, BMF, SCLY, PYCARD, EBI3, NXT1, SGSM3, INTS1, SETBP1, SF3B1, TLR4, CDK2, SUB1, MRPL28, TBC1D9, IL1A, THY1, HMGA1, ABCB1, HPGD, HSPB1, PAEP, HSPB2, NRAS, NFE2L2, NFE2, IAPP, IDH1, IDH2, MMP8, LOX, LIG3, LEPR, LEP, KRT7, KIT, CXCR2, IL2RA, IL1RN, HP, NR3C1, THBS2, GABPA, THBS1, TGFBR1, IL1B, TAL1, EDA, ELN, EZH2, STAT3, STAT1, SPP1, SPARC, SLCO2A1, SELP, RPS14, RARS1, RARB, PTHLH, PTH, MAPK8, FZD2, PLK1, ATN1
-
1957–1958 Influenza Pandemic
Wikipedia
The World Health Organization and the UK government estimate the death toll to be between one and four million, [3] [25] [26] while a paper published in The Journal of Infectious Diseases estimates 1.1 million. [6] [19] [27] According to the 2016 study in The Journal of Infectious Diseases , the highest excess mortality occurred in Latin America . [27] About 70,000 to 116,000 people died in the United States , and an estimated 33,000 deaths in the United Kingdom were attributed to the 1957–58 flu outbreak. [6] [23] [25] [28] It caused many infections in children, spread in schools, and led to many school closures. However, the virus was rarely fatal in children and was most deadly in pregnant women, the elderly, and those with pre-existing heart and lung disease. [6] In Germany, around 30,000 people died of the flu between September 1957 and April 1958. [29] Economic effects [ edit ] The Dow Jones Industrial Average lost 15% of its value in the second half of 1957. [28] In the United Kingdom , the government paid out £10,000,000 in sickness benefit , and some factories and mines had to close. [15] Many schools had to close in Ireland , including seventeen in Dublin . [30] References [ edit ] ^ a b Pennington, T H (2006). ... PMID 26908781 . ^ a b Pinsker, Joe (28 February 2020). "How to Think About the Plummeting Stock Market" .
-
Pharyngitis
Wikipedia
Some medications may produce pharyngitis, such as pramipexole and antipsychotics . [24] [25] Diagnosis [ edit ] Modified Centor score Points Probability of Strep Management 1 or less <10% No antibiotic or culture needed 2 11–17% Antibiotic based on culture or rapid antigen detection test 3 28–35% 4 or 5 52% Empiric antibiotics Throat swab Differentiating a viral and a bacterial cause of a sore throat based on symptoms alone is difficult. [26] Thus, a throat swab often is done to rule out a bacterial cause. [27] The modified Centor criteria may be used to determine the management of people with pharyngitis. ... Aspirin may be used in adults, but is not recommended in children due to the risk of Reye syndrome . [28] Steroids (such as dexamethasone ) may be useful for severe pharyngitis. [29] [8] Their general use, however, is poorly supported. [7] Viscous lidocaine relieves pain by numbing the mucous membranes. [30] Antibiotics are useful if a bacterial infection is the cause of the sore throat. [31] [32] For viral infections, antibiotics have no effect. ... Archived from the original on 17 March 2010 . Retrieved 28 April 2010 . ^ a b Bisno AL (January 2001).
-
Skin Cancer In Horses
Wikipedia
However, the actual prevalence of metastatic melanoma may be lower due to infrequent submission of melanotic tumors for diagnosis. [28] Common sites for metastasis include lymph nodes, the liver, spleen, lung, skeletal muscle, blood vessels and parotid salivary gland. [28] Clinical signs [ edit ] The most common sites for melanotic tumors are on the under-side of the tail near the base, on the prepuce, around the mouth or in the skin over the parotid gland (near the base of the ear). [24] Tumors will initially begin as single, small raised areas that may multiply or coalesce into multi-lobed masses (a process called melanomatosis) over time. [3] Horses under 2-years-old can be born with or acquire benign melanotic tumors (called melanocytomas), but these tumors are often located on the legs or trunk, not beneath the tail as in older animals. [29] Treatment of melanoma [ edit ] Treatment of small melanomas is often not necessary, but large tumors can cause discomfort and are usually surgically removed. ... "Congenital and Acquired Melanocytomas (Benign Melanomas) in Eighteen Young Horses" . Veterinary Pathology . 28 (5): 363–369. doi : 10.1177/030098589102800503 .
-
Treatment-Resistant Depression
Wikipedia
There have also been a number of meta-analyses of RCTs [25] confirming the efficacy of rTMS in treatment-resistant major depression, as well as naturalistic studies showing its effectiveness in "real world" clinical settings. [26] [27] dTMS [ edit ] dTMS ( deep transcranial magnetic stimulation ) is a continuation of the same idea as rTMS, but with the hope that deeper stimulation of subcortical areas of the brain leads to increased effect. [28] A 2015 systematic review and health technology assessment found lacking evidence in order to recommend the method over either ECT or rTMS because so few studies had been published. [28] Psychotherapy [ edit ] There is sparse evidence on the effectiveness of psychotherapy in cases of treatment-resistant depression. [8] However, a review of the literature suggests that it may be an effective treatment option. [29] Psychotherapy may be effective in people with TRD because it can help relieve stress that may contribute to depressive symptoms. [30] A Cochrane systematic review has shown that psychological therapies (including cognitive behavioural therapy , dialectal behavioural therapy, interpersonal therapy and intensive short-term dynamic psychotherapy) added to usual care (with antidepressants) can be beneficial for depressive symptoms and for response and remission rates over the short term (up to six months) for patients with TRD. ... "Augmentation strategies for treatment-resistant depression: a literature review" . J Clin Pharm Ther . 32 (5): 415–28. doi : 10.1111/j.1365-2710.2007.00846.x .SLC6A4, SLC6A2, VEGFA, MAOA, MAP2K1, RGS4, WDR64, BDNF, SLIT3, OPN3, ZNF385D-AS1, LINC01643, ZNF385D, STAR, TNF, IL6, LRP2, MCF2L, CRP, CREB1, GRIN2B, UGT2B7, TYMS, MLXIP, TXN, CHL1, MYLIP, SMUG1, PYCARD, MARCHF5, ZNF804A, TPH2, MARCHF8, MIRLET7B, MIRLET7C, MIR155, MDD1, ECT, TNFRSF1A, FAS, TRD, TAC1, CACNA1C, CDK9, COMT, CSF2, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, DBT, FKBP5, MSTN, GRM2, HTR1A, IL1B, IL6R, IL18, LAMC2, COX2, NHS, NTRK2, OPRK1, OXTR, POMC, PSMD13, PTGS2, MTCO2P12
-
Bluetongue Disease
Wikipedia
However, immunization with any of the available vaccines preclude later serological monitoring of affected cattle populations, a problem which could be resolved using next-generation subunit vaccines currently in development. [26] In January 2015, Indian researchers launched a vaccine named 'Raksha Blu' that is designed to protect livestock against five strains of the bluetongue virus prevalent in the country. [27] History [ edit ] Although bluetongue disease was already recognized in South Africa in the early 19th century, a comprehensive description of the disease was not published until the first decade of the 20th century. [28] In 1906 Arnold Theiler showed that bluetongue was caused by a filterable agent. ... The first confirmed outbreak outside of Africa occurred in Cyprus in 1943. [28] Related diseases [ edit ] African horse sickness is related to bluetongue and is spread by the same midges ( Culicoides species). ... Retrieved 2006-08-21 . ^ "Lethal horse disease knocking on Europe's door" (Press release). Horsetalk.co.nz. 2007-03-28 . Retrieved 2007-03-27 . ^ "Bluetongue dobývá Evropskou unii" .
-
Fluoride Toxicity
Wikipedia
Compared to unfluoridated water, fluoridation to 1 mg/L is estimated to cause fluorosis in one of every 6 people (range 4–21), and to cause fluorosis of aesthetic concern in one of every 22 people (range 13.6–∞). [19] Thyroid [ edit ] Fluoride's suppressive effect on the thyroid is more severe when iodine is deficient, and fluoride is associated with lower levels of iodine . [ clarification needed ] [28] Thyroid effects in humans were associated with fluoride levels 0.05–0.13 mg/kg/day when iodine intake was adequate and 0.01–0.03 mg/kg/day when iodine intake was inadequate. [20] : 263 Its mechanisms and effects on the endocrine system remain unclear. [20] : 266 Testing on mice shows that the medication gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) can be used to treat fluoride toxicity of the thyroid and return normal function. [29] Effects on aquatic organisms [ edit ] Fluoride accumulates in the bone tissues of fish and in the exoskeleton of aquatic invertebrates. ... Toxicity, Fluoride . eMedicine. Retrieved 2008-12-28. ^ Augenstein WL, Spoerke DG, Kulig KW, et al. ... "Marked hypocalcemia and ventricular fibrillation in two pediatric patients exposed to a fluoride-containing wheel cleaner". Annals of Emergency Medicine . 28 (6): 713–8. doi : 10.1016/S0196-0644(96)70097-5 .