-
Electrolyte Imbalance
Wikipedia
., spinach, kale) Apples Apricots Potatoes Squash Bananas Dates Calcium [ edit ] Dairy is a major contributor of calcium to diet in the United States. [26] The recommended calcium intake for adults range from 1,000 mg to 1,300 mg depending on age and gender. [26] Yogurt Cheese Milk Tofu Canned sardines Magnesium [ edit ] Magnesium is found in a variety of vegetables, meats, and grains. [27] Foods high in fiber generally are a source of magnesium. [28] The recommended magnesium intake for adults range from 360 mg to 420 mg depending on age and gender. [28] Epsom salt Nuts and seeds (e.g., pumpkin seeds, almonds, peanuts) [27] Dark leafy greens (e.g., spinach) [27] Beans [27] Fortified cereals See also [ edit ] Acidosis Alkalosis Dehydration Malnutrition Starvation Sports drink References [ edit ] ^ Alfarouk, Khalid O.; Ahmed, Samrein B.
-
Toothache
Wikipedia
Typical signs and symptoms of a pericoronal abscess include severe, throbbing pain, which may radiate to adjacent areas in the head and neck, [21] [26] : 122 redness, swelling and tenderness of the gum over the tooth. [27] : 220–222 There may be trismus (difficulty opening the mouth), [27] : 220–222 facial swelling, and rubor (flushing) of the cheek that overlies the angle of the jaw. [21] [26] : 122 Persons typically develop pericoronitis in their late teens and early 20s, [28] : 6 as this is the age that the wisdom teeth are erupting. ... Accordingly, there is no single test or combination of symptoms that accurately diagnose a fracture or crack, although when pain can be stimulated by causing separation of the cusps of the tooth, it's highly suggestive of the disorder. [10] : 27–31 Vertical fractures can be very difficult to identify because the crack can rarely be probed [10] : 27 or seen on radiographs, as the fracture runs in the plane of conventional films (similar to how the split between two adjacent panes of glass is invisible when facing them). [10] : 28–9 When toothache results from dental trauma (regardless of the exact pulpal or periodontal diagnosis), the treatment and prognosis is dependent on the extent of damage to the tooth, the stage of development of the tooth, the degree of displacement or, when the tooth is avulsed, the time out of the socket and the starting health of the tooth and bone. ... The success rate of root canal treatment also depends on the degree of disease (root canal therapy for irreversible pulpitis has a generally higher success rate than necrosis with periapical abscess) and many other technical factors. [10] : 77–82 Epidemiology [ edit ] In the United States, an estimated 12% of people reported that they had a toothache at some point in the six months before questioning. [10] : 40 Individuals aged 18–34 reported much higher rates toothache than those aged 75 or over. [28] : 6 In a survey of Australian schoolchildren, 12% had experienced toothache before the age of five, and 32% by the age of 12. [28] : 6 Dental trauma is extremely common and tends to occur more often in children than adults. [25] Toothache may occur at any age, in any gender and in any geographic region. ... The prevalence of caries in a population is dependent upon factors such as diet (refined sugars), socioeconomic status, and exposure to fluoride (such as areas without water fluoridation ). [28] : 6 History, society and culture [ edit ] Saint Apollonia , patron saint for toothaches, holds one of her own extracted teeth in a pair of forceps ( Nuremberg Chronicle , Hartmann Schedel , 1493) American advertisement from 1885 offering "instantaneous cure" for toothache with "Cocaine toothache drops". [53] Cocaine was the first local anesthetic , but its addictive and other dangerous side effects eventually led to its use being virtually abandoned by modern health care.
-
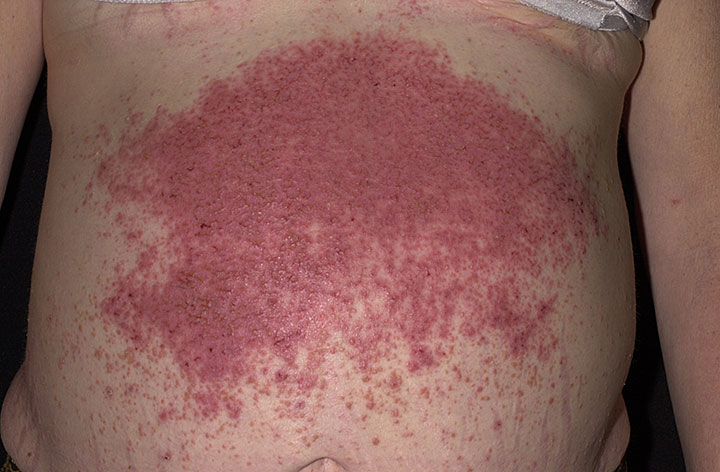
Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Wikipedia
In 2010, Cutis reported an eruption labelled gluten-sensitive dermatitis which is clinically indistinguishable from dermatitis herpetiformis, but lacks the IgA connection, [27] similar to gastrointestinal symptoms mimicking coeliac disease but without the diagnostic immunological markers. [28] Treatment [ edit ] First-line therapy [ edit ] A strict gluten-free diet must be followed, [25] and usually, this treatment will be a lifelong requirement. ... Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology . 28 (3): 505–506. doi : 10.1016/S0190-9622(08)81769-0 .
-
Concussion
Wikipedia
Loss of consciousness may occur, but is not necessarily correlated with the severity of the concussion if it is brief. [28] Post-traumatic amnesia , in which events following the injury cannot be recalled, is a hallmark of concussions. [21] Confusion , another concussion hallmark, may be present immediately or may develop over several minutes. [21] A person may repeat the same questions, [29] be slow to respond to questions or directions, have a vacant stare, or have slurred [21] or incoherent speech. [30] Other mTBI symptoms include changes in sleeping patterns [24] and difficulty with reasoning, [25] concentrating, and performing everyday activities. [21] A concussion can result in changes in mood including crankiness, loss of interest in favorite activities or items, [31] tearfulness, [32] and displays of emotion that are inappropriate to the situation. [30] Common symptoms in concussed children include restlessness, lethargy, and irritability. [33] Mechanism Rotational force is key in a concussion. ... For example, post-concussion symptoms such as cognitive problems may be misattributed to brain injury when, in fact, due to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). [74] There are no fluid biomarkers (i.e., blood or urine tests) that are validated for diagnosing concussion in children or adolescents. [75] Classification No single definition of concussion, minor head injury, [76] or mild traumatic brain injury is universally accepted. [77] In 2001, the expert Concussion in Sport Group of the first International Symposium on Concussion in Sport [54] defined concussion as "a complex pathophysiological process affecting the brain, induced by traumatic biomechanical forces." [28] It was agreed that concussion typically involves temporary impairment of neurological function that heals by itself within time, and that neuroimaging normally shows no gross structural changes to the brain as the result of the condition. [38] However, although no structural brain damage occurs according to the classic definition, [78] some researchers have included injuries in which structural damage has occurred and the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence definition includes physiological or physical disruption in the brain's synapses . [79] Also, by definition, concussion has historically involved a loss of consciousness. ... Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine . 36 (43 Suppl): 28–60. doi : 10.1080/16501960410023732 . ... Ontario Neurotrauma Foundation. ^ a b "CDC Pediatric mTBI Guideline | Concussion | Traumatic Brain Injury | CDC Injury Center" . www.cdc.gov . 2020-07-28 . Retrieved 2020-08-05 . ^ Halstead ME, Walter KD, Moffatt K (December 2018).
-
Mushroom Poisoning
Wikipedia
It is not uncommon for an individual person to experience gastrointestinal upset associated with one particular mushroom species or genus. [27] Some mushrooms might concentrate toxins from their growth substrate, such as Chicken of the Woods growing on yew trees. [28] Poisonous mushrooms [ edit ] See also: List of deadly fungus species and List of poisonous fungus species Of the most lethal mushrooms, five—the death cap ( A. phalloides ), the three destroying angels ( A. virosa , A. bisporigera , and A. ocreata ), and the fool's mushroom ( A. verna )—belong to the genus Amanita , and two more—the deadly webcap ( C. rubellus ), and the fool's webcap ( C. orellanus )—are from the genus Cortinarius . ... PMID 16188280 . ^ "Death due to Galerina". Seattle Post-Intelligencer . 28 December 1981. ^ Calviño, Jesus; Romero, Rafael; Pintos, Elena; Novoa, Daniel; Güimil, Dolores; Cordal, Teresa; Mardaras, Javier; Arcocha, Victor; Lens, XoseM.; Sanchez-Guisande, Domingo (1998).
-
Anorexia Nervosa
Wikipedia
Excessive exercise [27] including micro-exercising, for example making small persistent movements of fingers or toes. [28] Perception of self as overweight, in contradiction to an underweight reality. ... Anorexia nervosa is highly heritable . [50] Twin studies have shown a heritability rate of between 28 and 58%. [51] First-degree relatives of those with anorexia have roughly 12 times the risk of developing anorexia. [52] Association studies have been performed, studying 128 different polymorphisms related to 43 genes including genes involved in regulation of eating behavior, motivation and reward mechanics , personality traits and emotion .HTR2A, HTR4, EBF1, NCKIPSD, CADM1, SORCS2, CARMIL1, ASB3, LEP, FOXP1, MGMT, ERLEC1, TAFA2, SOX2-OT, BDNF, SLC6A4, COMT, AGRP, LEPR, OPN1SW, DRD4, DRD2, PYY, GHRL, ADIPOQ, RETN, ESR1, TNF, BEST1, DMD, OXTR, MC4R, SCLY, IFNG, CRH, TPH2, HTR1D, KRT7, TAL1, EPHX2, ESR2, CNR1, UCP3, IGF1, UCP2, POMC, OPRD1, NTRK2, HTR2C, SLC6A2, SLC6A3, CNTN4, MAOA, BED, FGF21, DPP4, MBOAT4, CD38, NUCB2, KCNN3, SMIM20, APOB, PTGS2, BMS1, HDAC4, DNTT, ACACA, SPX, NR3C1, GCG, ZDHHC2, GHSR, RBPJP4, CYP2B6, FTO, IL15, IL6, SPAG9, GRAP2, NR1H3, AIMP2, BAS, ADIPOR2, CARF, CLOCK, PARP9, AKAP6, CGB5, HTR3B, PANK2, ANGPTL6, CEP70, OLIG2, PPIG, GPR55, PDLIM7, ZW10, NT5C1B, MTCO2P12, OR2AG1, POSTN, NBEAL1, RSPO1, ANGPTL4, DLL1, YY1, ANGPTL3, CNTN6, NIPA1, ATP8A2, CNTN5, NPW, SYTL5, POLDIP2, GDF11, SS18L1, RNF19A, NTNG1, CSGALNACT1, TREX1, CGB8, WDHD1, SDS, C1QL1, AHSA1, NPB, PTH, WAS, DBI, ELK3, EPHB1, EPHB2, ETFA, FAAH, MSTN, GFER, GJA1, GPT, GRIA3, GRIN2B, HCRT, HSD11B2, HTC2, HTR3A, DRD3, CYP19A1, IL1B, CYP17A1, AMY1A, AMY1B, AMY1C, ARVCF, CCKAR, CCNE1, CDH9, CGA, CGB3, CPN1, CPN2, CRK, CRYGD, MAPK14, CTBP2, IGFBP1, IL18, VEGFA, PRL, TAS2R38, PTPN11, RAN, S100B, SCD, CX3CL1, SGSH, SHBG, SLC18A1, SNCA, STATH, TACR1, TNXB, UCN, VDR, PSMB6, MAPK1, INHBB, ABCB1, STMN1, LDLR, LTB, LYZ, MC3R, MCL1, MDK, MMP9, COX2, MUC1, NEFL, NNAT, NTRK3, PEPB, PGC, LOC110806262
-
Sleepwalking
Wikipedia
Genome-wide multipoint parametric linkage analysis for sleepwalking revealed a maximum logarithm of the odds score of 3.14 at chromosome 20q12-q13.12 between 55.6 and 61.4 cM. [23] Sleepwalking has been hypothesized to be linked to the neurotransmitter serotonin , which also appears to be metabolized differently in migraine patients and people with Tourette syndrome , both populations being four to nine times more likely to experience an episode of sleepwalking. [24] Hormonal fluctuations have been found to contribute to sleepwalking episodes in women, with the likeliness to sleepwalk being higher before the onset of menstruation. [25] It also appears that hormonal changes during pregnancy decrease the likelihood of engaging in sleepwalking [26] Medications, primarily in four classes—benzodiazepine receptor agonists and other GABA modulators, antidepressants and other serotonergic agents , antipsychotics , and β-blockers — have been associated with sleepwalking. [27] The best evidence of medications causing sleepwalking is for Zolpidem and sodium oxybate —all other reports are based on associations noted in case reports. [27] A number of conditions, such as Parkinson's disease , are thought to trigger sleepwalking in people without a previous history of sleepwalking. [28] [ needs update ] Diagnosis [ edit ] Polysomnography is the only accurate assessment of a sleepwalking episode. ... PMID 2106985 . ^ Orme, J.E. (1967), "The Incidence of Sleepwalking in Various Groups", Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, Vol 43, Iss 3, pp 279–28. ^ Milliet N, Ummenhofer W. Somnambulism and trauma: case report and short review of the literature. ... Yeates (2013), p.788. ^ For example, Pritchard J.C., A Treatise on Insanity and Other Disorders Affecting the Mind , Sherwood, Gilbert and Piper, (London), 1835, p.p.410. ^ "Jenny Lind at the Manufacturing Establishments", Manchester Guardian , No.1947, (Saturday, 4 September 1847), p.7, col.C; "Jenny Lind and the Hypnotic Somnambulist", Manchester Guardian , No.1948, (Wednesday, 8 September 1847), p.5, col.F; "Jenny Lind and the Manchester Somnambulists", Newcastle Courant , No.9015, (Saturday, 17 September 1847), p.2, col.E; "Jenny Lind and Hypnotism", The Medical Times , Vol.16, No.416, (18 September 1847), p.602; and "Jenny Lind and Mesmerism", The Lady's Newspaper , No.39, (Saturday, 25 September 1847) p.294, col.A. ^ Storer, H., "Jenny Lind and the Somnambulist", The Critic: A Journal for Readers, Authors, and Publishers , Vol.6, No.145, (9 October 1847), p.238; Braid, J., "(Letter to Dr. Storer, written on 28 September 1847)", The Critic: A Journal for Readers, Authors, and Publishers , Vol.6, No.145, (9 October 1847), p.238. ^ Popat, S; Winslade, W (2015).
-
Lesch–nyhan Syndrome
Wikipedia
"Hypothesized deficiency of guanine-based purines may contribute to abnormalities of neurodevelopment, neuromodulation, and neurotransmission in Lesch–Nyhan syndrome". Clin. Neuropharmacol . 28 (1): 28–37. doi : 10.1097/01.wnf.0000152043.36198.25 .
-
Abortion In Minnesota
Wikipedia
Only Iowa successfully passed such a bill, but it was struck down by the courts. [22] As of May 14, 2019, the state prohibited abortions after the fetus was viable, generally some point between week 24 and 28. This period uses a standard defined by the US Supreme Court in 1973 with the Roe v. ... That year, 59% of women in the state aged 15 – 44 lived in a county without an abortion clinic. [28] In March 2016, there were eighteen Planned Parenthood clinics in the state. [29] In 2017, there were eighteen Planned Parenthood clinics in a state with a population of 1,227,431 women aged 15 – 49 of which one offered abortion services. [30] Statistics [ edit ] In the period between 1972 and 1974, there were zero recorded illegal abortion death in the state. [31] In 1990, 529,000 women in the state faced the risk of an unintended pregnancy. [26] In 2013, among white women aged 15–19, there were abortions 510, 260 abortions for black women aged 15–19, 80 abortions for Hispanic women aged 15–19, and 140 abortions for women of all other races. [32] In 2014, 52% of adults said in a poll by the Pew Research Center that abortion should be legal in all or most cases. [33] In 2017, the state had an infant mortality rate of 4.8 deaths per 1,000 live births. [9] Number of reported abortions, abortion rate and percentage change in rate by geographic region and state in 1992, 1995 and 1996 [34] Census division and state Number Rate % change 1992–1996 1992 1995 1996 1992 1995 1996 West North Central 57,340 48,530 48,660 14.3 11.9 11.9 –16 Iowa 6,970 6,040 5,780 11.4 9.8 9.4 –17 Kansas 12,570 10,310 10,630 22.4 18.3 18.9 –16 Minnesota 16,180 14,910 14,660 15.6 14.2 13.9 –11 Missouri 13,510 10,540 10,810 11.6 8.9 9.1 –21 Nebraska 5,580 4,360 4,460 15.7 12.1 12.3 –22 North Dakota 1,490 1,330 1,290 10.7 9.6 9.4 –13 South Dakota 1,040 1,040 1,030 6.8 6.6 6.5 –4 Number, rate, and ratio of reported abortions, by reporting area of residence and occurrence and by percentage of abortions obtained by out-of-state residents, US CDC estimates Location Residence Occurrence % obtained by out-of-state residents Year Ref No.
-
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Wikipedia
These therapies are aimed at relieving symptoms such as itching with antipruritics (e.g. bile acid sequestrants such as cholestyramine ); antibiotics to treat episodes of ascending cholangitis ; and vitamin supplements, as people with PSC are often deficient in fat-soluble vitamins ( vitamin A , vitamin D , vitamin E , and vitamin K ). [28] ERCP and specialized techniques may also be needed to help distinguish between a benign PSC stricture and a bile duct cancer ( cholangiocarcinoma ). [29] Liver transplantation is the only proven long-term treatment of PSC. ... There is relatively little data on the prevalence and incidence of primary sclerosing cholangitis, with studies in different countries showing annual incidence of 0.068–1.3 per 100,000 people and prevalence 0.22–8.5 per 100,000; given that PSC is closely linked with ulcerative colitis, it is likely that the risk is higher in populations where UC is more common.< |vauthors=Feld JJ, Heathcote EJ |title=Epidemiology of autoimmune liver disease |journal= Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology|volume=18 |issue=10 |pages=1118–28 |date=October 2003 |pmid=12974897 |doi=10.1046/j.1440-1746.2003.03165.x |s2cid=24075827 |doi-access=free }} In the United States, an estimated 29,000 individuals have PSC. [1] Research directions [ edit ] Although there is no curative treatment, several clinical trials are underway that aim to slow progression of this liver disease. [35] Obeticholic acid is being investigated as a possible treatment for PSC due to its antifibrotic effects.MST1, ABCB4, UBASH3A, TCF4, BCL2L11, HIF1A, GPR35, NOS2, IL2RA, SH2B3, ATXN2, RMI2, RBM45, KIAA1109, BSN, PUS10, MMEL1, SIK2, MIR4435-2HG, HLA-DRB1, RIC8B, HDAC7, CD226, ACAD8, PRKD2, PHLDB1, CFTR, HLA-B, GPBAR1, FUT2, MICA, CCR5, IL2, TNF, PSC, HLA-DQA1, MET, IL10, DLAT, HLA-DRB3, HLA-C, NR1H4, GP2, CD28, FBN2, GGTLC1, ALB, NLRP3, NOTCH1, LOC102724197, MMP3, CDKN2A, FGF19, IFNG, DEFB4B, STS, HLA-DQB1, HP, ICAM1, TLR4, TLR9, ARSA, TP53, CXCL8, FOXP3, LOXL2, PYCARD, SLC17A5, VDR, IL6, H3P10, CEACAM5, PTGS2, NR1I2, TNFSF10, STAT4, DEFB4A, EGFR, ETS1, PNPLA3, CD14, MIR200B, IL21, HAMP, HLA-A, MAPK3, GPT, CASP3, NOD1, TNFRSF25, PTGES, TBC1D9, HSPB3, PDZD2, NOL3, ARID1A, SOCS1, XPR1, GRAP2, KLRK1, DLG5, MGLL, KMT2B, BTG3, CCR9, SLC9A3R1, TXNIP, ABCB11, AHSA1, AOC3, CFLAR, KRT20, WWC1, SARNP, KIF12, CTHRC1, KCNH8, DEFB104A, HT, CCBE1, NANOS2, MIR122, MIR150, MIR200C, MIR21, MIR222, DEFB104B, MIR483, CCR2, PBC2, KLRC4-KLRK1, GATD3B, MTCO2P12, RSPO3, JAM3, KCNH4, AGBL2, TXN2, RNF19A, POLDIP2, B3GAT1, CD274, ICOS, IL22, CUZD1, NEUROG3, IL23A, TM6SF2, MADCAM1, WDR11, USE1, RETN, AICDA, NOD2, UBE2Z, NEIL1, GATD3A, ABCA4, AIMP2, CX3CR1, DDC, DEFB1, DNASE1, SLC26A3, ELK1, ERBB2, FBL, F3, PTK2B, FOXO1, FOXO3, FUT3, GABPA, GCLC, GCLM, NR3C1, GSTT1, HCLS1, HLA-DOA, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DRB5, HES1, IL1A, DCT, CTNNB1, VIM, CTLA4, AGA, JAG1, AKT1, ABCD1, ANXA2, AIRE, AREG, ADGRB3, BCL2, BCL2L1, BCL3, CFB, C3, MS4A1, ENTPD1, CD40LG, CD47, CD68, CEACAM3, CEACAM7, CHRM3, CRK, MAPK14, IL1B, IL1RN, IL12A, IL13, ABCB1, PIK3CD, POLR2G, PPARA, MAPK1, PSG2, AFP, S100A8, S100A12, CCL20, CCL21, CCL25, SDC1, SLC10A2, SOD2, SPP1, SPTBN1, SRY, SULT2A1, TERC, TFF3, TXN, TXNRD1, PDZK1, PAEP, ORM2, KMT2A, IL15, IL17A, INSRR, ISG20, LGALS3BP, LSS, MCL1, MEFV, MEN1, MICB, MME, DDR2, MMP1, MMP2, MMP9, MMP14, MPO, COX2, NCAM1, NFE2L2, NOTCH3, NRAS, RLN2
-
Oxygen Toxicity
Wikipedia
The symptoms appear in the upper chest region ( substernal and carinal regions). [25] [26] [27] This begins as a mild tickle on inhalation and progresses to frequent coughing. [25] If breathing increased partial pressures of oxygen continues, patients experience a mild burning on inhalation along with uncontrollable coughing and occasional shortness of breath ( dyspnoea ). [25] Physical findings related to pulmonary toxicity have included bubbling sounds heard through a stethoscope (bubbling rales ), fever, and increased blood flow to the lining of the nose ( hyperaemia of the nasal mucosa ). [27] X-rays of the lungs show little change in the short term, but extended exposure leads to increasing diffuse shadowing throughout both lungs. [25] Pulmonary function measurements are reduced, as noted by a reduction in the amount of air that the lungs can hold ( vital capacity ) and changes in expiratory function and lung elasticity. [27] [28] Tests in animals have indicated a variation in tolerance similar to that found in central nervous system toxicity, as well as significant variations between species. ... Prematurity, low birth weight and a history of oxygen exposure are the principal indicators, while no hereditary factors have been shown to yield a pattern. [64] Prevention [ edit ] The label on the diving cylinder shows that it contains oxygen-rich gas (36%) and is boldly marked with a maximum operating depth of 28 metres. The prevention of oxygen toxicity depends entirely on the setting. ... Journal, Indian Academy of Clinical Medicine . 4 (3): 234–237 . Retrieved 28 September 2008 . ^ Clark & Lambertsen 1970 , p. 159. ^ a b Clark & Thom 2003 , p. 376. ^ a b c U.S. ... Department of Health & Human Services . Retrieved 28 September 2008 . ^ Regillo, Brown & Flynn 1998 , p. 178. ^ a b Mitchell, Simon J ; Bennett, Michael H; Bird, Nick; Doolette, David J; Hobbs, Gene W ; Kay, Edward; Moon, Richard E; Neuman, Tom S; Vann, Richard D; Walker, Richard; Wyatt, HA (2012).
-
Multiple Chemical Sensitivity
Wikipedia
Through behavioral conditioning, it has been proposed that people with MCS may develop real, but unintentionally psychologically produced, symptoms, such as anticipatory nausea, when they encounter certain odors or other perceived triggers. [21] [19] [ non-primary source needed ] It has also been proposed in one study that individuals may have a tendency to "catastrophically misinterpret benign physical symptoms" [22] [19] [ non-primary source needed ] or simply have a disturbingly acute sense of smell. [ medical citation needed ] The personality trait absorption , in which individuals are predisposed to becoming deeply immersed in sensory experiences, may be stronger in individuals reporting symptoms of MCS. [23] [19] [ non-primary source needed ] In the 1990s, behaviors exhibited by MCS sufferers were hypothesized by some to reflect broader sociological fears about industrial pollution and broader societal trends of technophobia and chemophobia . [24] [19] These theories have attracted criticism. [8] [25] In Canada, in 2017, following a three-year government inquiry into environmental illness, it was recommended that a public statement be made by the health department. [26] [ needs update ] A 2018 systematic review concluded that the evidence suggests that abnormalities in sensory processing pathways combined with peculiar personality traits best explains this condition. [27] Diagnosis [ edit ] In practice, diagnosis relies entirely upon the self-reported claim that symptoms are triggered by exposure to various substances. [11] Many other tests have been promoted by various people over the years, including testing of the immune system, porphyrin metabolism , provocation-neutralization testing, autoantibodies , the Epstein–Barr virus , testing for evidence of exposure to pesticides or heavy metals, and challenges involving exposure to chemicals, foods, or inhalants. [11] None of these tests correlate with MCS symptoms, and none are useful for diagnosing MCS. [11] The stress and anxiety experienced by people reporting MCS symptoms are significant. [11] Neuropsychological assessments do not find differences between people reporting MCS symptoms and other people in areas such as verbal learning, memory functioning, or psychomotor performance . [11] Neuropsychological tests are sensitive but not specific , and they identify differences that may be caused by unrelated medical, neurological, or neuropsychological conditions. [11] Another major goal for diagnostic work is to identify and treat any other medical conditions the person may have. [11] People reporting MCS-like symptoms may have other health issues, ranging from common conditions, such as depression or asthma , to less common circumstances, such a documented chemical exposure during a work accident . [11] These other conditions may or may not have any relationship to MCS symptoms, but they should be diagnosed and treated appropriately, whenever the patient history , physical examination , or routine medical tests indicates their presence. [11] The differential diagnosis list includes solvent exposure , occupational asthma , and allergies. [11] Definitions [ edit ] Different researchers and proponents use different definitions, which complicates research and can affect diagnosis. [28] For example, the 1987 definition that requires symptoms to begin suddenly after an identifiable, documented exposure to a chemical, [29] but the 1996 definition by the International Programme on Chemical Safety says that the cause can be anything, including other medical conditions or psychological factors. [30] [29] In Japan, MCS is called chemical hypersensitivity or chemical intolerance ( 化学物質過敏症 ; kagaku kando), and the 1999 Japanese definition requires one or more of four major symptoms – headaches; malaise and fatigue; muscle pain; joint pain – combined with laboratory findings and/or some minor symptoms, such as mental effects or skin conditions. [30] The defined lab findings are abnormalities in parasympathetic nerves , cerebral cortical dysfunction diagnosed by SPECT testing, visuospatial abnormalities, abnormalities of eye movement , or a positive provocation test . [30] Recognition [ edit ] In 1996, an expert panel at WHO /ICPS (International Classification for Patient Safety) was set up to examine MCS. [31] The panel: "accepted the existence of a disease of unclear pathogenesis", proposed that the disease was acquired, that its symptoms were "in close relationship to multiple environmental influences, which are well tolerated by the majority of the population," and that it "could not be explained by a known clinical or psychic disorder," suggested that the broader term "idiopathic environmental intolerances" (IEI) be adopted instead of MCS, to incorporate MCS and several other conditions under a single umbrella term. [31] The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD), maintained by the World Health Organization , is a medical coding system used for medical billing and statistical purposes – not for deciding whether any person is sick, or whether any collection of symptoms constitutes a single disease. ... The Environmental Health Policy Committee is currently inactive, and the workgroup document has not been finalized. [45] The different understandings of MCS over the years have also resulted in different proposals for names. [30] For example, in 1996 the International Programme on Chemical Safety proposed calling it idiopathic environmental illness , because of their belief that chemical exposure may not the sole cause, [28] while another researcher, whose definition includes people with allergies and acute poisoning, calls it chemical sensitivity . [30] [ clarification needed ] See also [ edit ] Electromagnetic hypersensitivity Sick building syndrome Sensory processing disorder Sensory processing sensitivity List of questionable diseases References [ edit ] ^ a b c Genuis, SJ (May 2013).
-
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Wikipedia
Specialty Psychiatry , pediatrics Symptoms Difficulty paying attention , excessive activity, difficulty controlling behavior Usual onset Before age 6–12 Causes Both genetic and environmental factors Diagnostic method Based on symptoms after other possible causes ruled out Differential diagnosis Normally active young child, conduct disorder , oppositional defiant disorder , learning disorder , bipolar disorder , fetal alcohol spectrum disorder Treatment Counseling , lifestyle changes, medications Medication Stimulants , atomoxetine , guanfacine , clonidine Frequency 84.7 million (2019) Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder ( ADHD ) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by inattention , or excessive activity and impulsivity , which are otherwise not appropriate for a person's age. [1] [2] [3] [4] Some individuals with ADHD also display difficulty regulating emotions or problems with executive function . [5] [6] [7] [1] For a diagnosis, the symptoms should appear before a person is twelve years old, be present for more than six months, and cause problems in at least two settings (such as school, home, or recreational activities). [1] [2] In children, problems paying attention may result in poor school performance . [8] Additionally, there is an association with other mental disorders and substance misuse . [9] Although it causes impairment, particularly in modern society, many people with ADHD can have sustained attention for tasks they find interesting or rewarding (known as hyperfocus ). [10] [11] Despite being the most commonly studied and diagnosed mental disorder in children and adolescents, the precise cause or causes are unknown in the majority of cases. [12] Genetic factors are estimated to make up about 75% of the risk. [13] Nicotine exposure during pregnancy may be an environmental risk. [14] It does not appear to be related to the style of parenting or discipline. [15] It affects about 5–7% of children when diagnosed via the DSM-IV criteria [1] [16] and 1–2% when diagnosed via the ICD-10 criteria. [17] As of 2019, it was estimated to affect 84.7 million people globally. [18] Rates are similar between countries and differences in rates depend mostly on how it is diagnosed. [19] ADHD is diagnosed approximately two times more often in boys than in girls, [1] although the disorder is often overlooked in girls because their symptoms are often less disruptive. [20] [21] [22] About 30–50% of people diagnosed in childhood continue to have symptoms into adulthood and between 2–5% of adults have the condition. [23] [24] [25] In adults, inner restlessness, rather than hyperactivity, may occur. [26] Adults often develop coping skills which compensate for some or all of their impairments. [27] The condition can be difficult to tell apart from other conditions, as well as from high levels of activity within the range of normal behavior. [28] ADHD management recommendations vary by country and usually involve some combination of medications, counseling , and lifestyle changes. [8] The British guideline emphasises environmental modifications and education for individuals and carers about ADHD as the first response. ... In children with ADHD, there is a general reduction of volume in certain brain structures, with a proportionally greater decrease in the volume in the left-sided prefrontal cortex . [129] [133] The posterior parietal cortex also shows thinning in individuals with ADHD compared to controls. [129] Other brain structures in the prefrontal-striatal-cerebellar and prefrontal-striatal-thalamic circuits have also been found to differ between people with and without ADHD. [129] [131] [132] The subcortical volumes of the accumbens , amygdala , caudate , hippocampus , and putamen appears smaller in individuals with ADHD compared with controls. [134] Inter-hemispheric asymmetries in white matter tracts have also been noted in children with ADHD, suggesting that disruptions in temporal integration may be related to the behavioral characteristics of ADHD. [135] Neurotransmitter pathways [ edit ] Previously it was thought that the elevated number of dopamine transporters in people with ADHD was part of the pathophysiology but it appears that the elevated numbers are due to adaptation to exposure to stimulants. [136] Current models involve the mesocorticolimbic dopamine pathway and the locus coeruleus-noradrenergic system . [128] [129] [130] ADHD psychostimulants possess treatment efficacy because they increase neurotransmitter activity in these systems. [129] [130] [137] There may additionally be abnormalities in serotoninergic , glutamatergic , or cholinergic pathways. [137] [138] [139] Executive function and motivation [ edit ] The symptoms of ADHD arise from a deficiency in certain executive functions (e.g., attentional control , inhibitory control , and working memory ). [65] [129] [130] [140] Executive functions are a set of cognitive processes that are required to successfully select and monitor behaviors that facilitate the attainment of one's chosen goals. [65] [130] [140] The executive function impairments that occur in ADHD individuals result in problems with staying organized, time keeping, excessive procrastination , maintaining concentration, paying attention, ignoring distractions, regulating emotions, and remembering details. [65] [129] [130] People with ADHD appear to have unimpaired long-term memory, and deficits in long-term recall appear to be attributed to impairments in working memory. [65] [141] The criteria for an executive function deficit are met in 30–50% of children and adolescents with ADHD. [142] One study found that 80% of individuals with ADHD were impaired in at least one executive function task, compared to 50% for individuals without ADHD. [143] Due to the rates of brain maturation and the increasing demands for executive control as a person gets older, ADHD impairments may not fully manifest themselves until adolescence or even early adulthood. [65] ADHD has also been associated with motivational deficits in children. [144] Children with ADHD often find it difficult to focus on long-term over short-term rewards, and exhibit impulsive behavior for short-term rewards. [144] Diagnosis [ edit ] ADHD is diagnosed by an assessment of a child's behavioral and mental development, including ruling out the effects of drugs, medications and other medical or psychiatric problems as explanations for the symptoms. [61] It often takes into account feedback from parents and teachers [28] with most diagnoses begun after a teacher raises concerns. [116] It may be viewed as the extreme end of one or more continuous human traits found in all people. [145] Whether someone responds to medications does not confirm or rule out the diagnosis.DRD5, COMT, DRD4, STS, GRM5, FGD1, AS3MT, MED13, ADGRL3, DRD2, CIC, SLC6A3, TPH2, CHRNA4, GRM7, GIT1, CNR1, TACR1, GRM8, CALY, PTPRD, CHRNB2, GRM1, ZNF292, DHDDS, CHRNA7, GRIN2A, ASTN2, MECP2, UPF3B, PTCHD1, SYP, CACNA1C, FOXP2, ST3GAL3, GJB2, PTEN, ITIH3, FAS, AUTS2, THRB, NTRK2, CPLX2, SLC6A8, DMD, IFNG, PIK3CA, PRKG1, FMR1, SLITRK1, PTPRG, GABRB3, PAH, IQSEC2, SMC3, TRNS2, TRNW, NBN, SEC24C, GTF2IRD1, ARHGEF6, SYNGAP1, NCL, SYNJ1, BAZ1B, BRSK2, PPM1D, HERC2, SEMA3E, IKBKG, CACNA1H, JRK, FEZ1, NOP56, FRMPD4, MID2, ND6, TRNF, MKRN3-AS1, GNB5, RAI1, GPC6, TRNH, GNE, TRNL1, TRNQ, USP9X, TRNS1, MED12, KIF14, ATP2C2, CPLX1, NUAK1, DEAF1, MAGED2, TLK2, HDAC4, SMC1A, PAK3, CHAF1B, AP3B2, SLC6A9, SLC6A4, OCRL, SLC6A2, SLC2A1, SLC1A2, SIM1, SDHA, SCN8A, SCN3A, OPHN1, RXRG, RREB1, RPS20, RPS6KA3, RFC2, RAD21, PTPRF, PRNP, MAPK1, PRKCG, PPP3CA, POLG, PMS2, PMS1, SMPD1, SNAP25, SNRPN, TSC2, ADAM12, TRIM26, PCGF2, MKRN3, ZNF41, ZNF711, YWHAG, CLIP2, PCNT, UBE3A, HIRA, TSC1, SOX5, TRIO, NDN, TSPAN7, IL1RAPL1, TGFBR2, NDP, TCF20, TCF4, TBX1, STXBP1, SPG7, UFD1, VPS13A, ITGA11, AK8, FBXL16, PWAR1, PIWIL4, MUCL3, IRAK1BP1, OSR1, MTFMT, RAB39B, NUS1, CSMD2, C12orf57, ALKBH8, MLIP, SLC9A7, ASCC2, FERMT3, TMEM47, CSRNP3, SEMA6D, PANK2, UBA5, ALG13, SPAG16, ARV1, CSMD1, SEMA4A, CXorf56, VPS13B, SPRED1, BCORL1, ARX, LINC01572, OBI1-AS1, P2RX5-TAX1BP3, BORCS7-ASMT, KDM4A-AS1, TAF9BP2, SNORD116-1, PWRN1, LINC00461, MIR137HG, USP27X, SFTA2, MIR99AHG, CEP85L, KIF7, HCN1, TUBB2B, ZNF81, SNORD115-1, ZNF615, LAMA1, SLC13A5, ASPM, JMJD1C, CEP112, CFAP221, ARID2, PIEZO2, SORCS2, PUF60, SH3KBP1, MLH3, CYFIP2, TBL2, SETBP1, TENM4, NECAP1, PARS2, SH2B1, SIN3A, NIPBL, FTSJ1, NPAP1, CDK20, ZFPM2, ADNP, MED13L, SYNE1, SZT2, SATB2, ND4, SORCS3, NT5C2, SHANK2, FAN1, TRAK1, NLGN1, CNKSR2, SRPX2, ZNRD1, TBC1D24, TAX1BP3, SLC4A10, C12orf4, HDAC8, MCTP2, CHD7, DHTKD1, PI4K2B, ACOXL, MAP11, SETD5, PHIP, NSUN2, DYM, CNNM2, RBFOX1, MAGEL2, WWOX, MPP6, ACTL6B, WAC, RSRC1, CRBN, ZDHHC9, MLXIPL, WDPCP, NTM, SCAPER, ND5, AARS1, ND1, IPW, BDNF, BMPR1A, BRCA2, CACNA1A, CACNA1B, IGF1, CACNB2, DNM1, HTR2A, HTR1B, HSPG2, HOXA2, HLA-DPB2, HLA-DMB, HIVEP1, BCR, ITGAE, AGTR2, ATP6V1A, LIMK1, LIG4, LHCGR, ANK3, KRAS, KIF11, KIF5B, ARF1, ARSD, KCNB1, KCNA2, ARVCF, ITPR3, STT3A, RERE, CHD2, CLCN4, HDC, HCFC1, CSNK2A1, FLII, FLI1, FGF12, ACSL4, EMP2, ELN, EEF1A2, DBH, DPP6, DDX3X, TIMM8A, DHCR7, DYNC1I2, DLG3, GABRA1, GABRB2, GABRG2, GRIA4, GTF2I, MSH6, CLTC, GRIN2D, COL2A1, COL11A2, GP1BB, GATA4, GNAS, GNAQ, GLUD1, CREBBP, CRKL, GDI1, ABCD1, DYNC1H1, MOBP, MEF2C, ADCY2, KMT2A, MAOB, ADRA2A, MAOA, MSH2, MANBA, EPCAM, COX1, MAN2A2, MLH1, COX2, COX3, MITF, DRD1, CDH13, CLOCK, ELK3, CYP2D6, DNTT, MTHFR, NTF3, STX1A, WASF2, ADRA1A, EPHB1, SLC9A9, NGF, CHPT1, HTR1A, LOC110806262, RSS, NR3C1, SSTR4, LPAR2, ADRA2B, HTR2C, SMS, ADRA2C, MC4R, GTS, BAIAP2, GRIN2B, CXCR6, REM1, DDC, DRD3, LOC107987479, EDNRA, NOS1, GPR42, NPY, BRS3, TPH1, NET1, ACKR3, HCRT, VEGFA, DISC1, SHANK3, CES1, ABCB10P1, WASF1, DIRAS2, NR4A2, IMPACT, STUB1, ADIPOQ, CHRNA3, ZNF804A, AMPH, SLC1A3, VAMP2, ANKK1, SHBG, MIRLET7D, ADORA2A, CDK5, FLRT3, DCDC2, NDRG2, CFP, HLA-DRB1, PART1, PER2, ATXN1, CRP, TSPAN31, NCAM1, DTNBP1, LOC102723407, GUCY2C, CNTNAP2, SCLY, RBM12, ADHD5, OPN1SW, BAG3, LOC102724971, OXTR, CHRNA5, ERICD, SPN, COA7, F2R, APOE, CYBC1, NANS, DCLK1, GAD1, SOD1, DNAAF4, TERF1, PRS, GNPAT, GRIA1, INSRR, BTBD9, C4B, SLC9A6, INS, IL1B, IL1RN, SLC2A3, NPSR1, IL5, IL6, TRH, TPO, TERC, KRT7, IL10, DNMT3B, BDNF-AS, SYN3, EBPL, RFC1, CAT, SYT1, BCHE, INTS8, MTR, TAL1, PIK3CG, POMC, POLR3A, ZFPM2-AS1, CSF2, PSC, APP, ACACA, CSE1L, FBXO33, CRY1, SLC30A10, CREM, NPNT, MIR5692B, PIDD1, TTC12, CYP3A4, PRTG, NCAN, AGA, IPO11, NAT8L, COL6A4P1, ALDH2, FEZF1, ALB, AKT1, GAL, NR0B1, ASCC1, DLG2, SPOCK3, STIN2-VNTR, DLX4, LOC390714, AMH, BRINP1, CCHCR1, CTNND1, TRIT1, ELFN1, CYP2B6, P4HTM, CYP2D7, CNTN5, PLA1A, AMPD1, GPRC5B, CPT2, THRA1/BTR, DAPK3, LOC105379528, ADRB2, CNTFR, ADM, BPIFA2, CBS, PPP1R1B, KYAT1, CCT, LMAN2L, KCNIP4, CD38, CD40, AGT, NRSN1, CD79A, CDH11, MIR34B, MIR320A, RNF122, MICALL2, NTPCR, STXBP5-AS1, AVP, ZGPAT, MIR148B, RBM45, SYT2, BHMT, DCD, THEM4, ADHD2, ADHD4, XKR4, MIR34C, MIR378A, NDUFAF2, SLC39A13, CASP3, CLEC19A, ZBBX, ATM, EAF2, KLK3, DGKH, TMX2-CTNND1, MIR107, CNTN1, OXER1, ARNTL, PRXL2C, APRT, FEZF1-AS1, LXN, C9orf72, DNAJC12, DYX8, KYAT3, ASH1L, CORD1, KIDINS220, NUFIP2, LUCAT1, MIR138-1, MBOAT7, FTO, ADRA1B, ASMT, NSD1, CHRNB3, SLC39A8, CHRNB4, CLTA, MIR3171, MIR142, LINC01672, HAMP, DPP10, LRRC7, SNORC, NUDT3, NT5C, VDR, SLC18A2, SLC16A1, KCNC1, KCNJ5, KCNJ6, KCNJ11, SLC6A1, SLC5A4, SKI, LAIR1, SDHD, LAMB2, CCL11, SCT, LAMC2, LGALS3, SCD, ATXN7, S100B, FADS1, LMNA, REG1A, RARA, SMN1, SMN2, SNCA, THAS, IL1A, TXN, TWIST1, PHLDA2, IL2, TNR, TSPAN8, THRSP, THRA, THBS3, TH, ITPA, IL16, ABCA4, ITGA1, SULT2A1, STXBP3, CDKL5, STATH, STAT6, SST, SRY, LMX1B, RAB3A, PEX2, NGFR, PDE4A, PDE2A, MFAP1, PC, PRKN, MFGE8, MIP, OPRM1, NTRK3, NTRK1, NFKB1, PFN1, NF1, NR3C2, MNT, MOG, MYT1, MYO5B, MPP2, MSMB, MTHFD1, MTNR1A, PDE4D, SERPINA1, PTPRN2, PROC, LRP6, LRP5, CYP4F3, PTPRC, PTH, PTGDS, PSPH, PSG5, PSD, RELN, PSPN, PIK3CB, MXD1, PRKCD, PRKCB, PPIA, PON1, MAP1B, MARK1, PMCH, SERPINF2, PIK3CD, IGFALS, VIPR2, KCNIP1, IGF2, RRS1, CYFIP1, FN1, VWA8, GAST, TRIM32, GALR1, GCH1, GFI1, PARK7, HRH3, SEC23IP, NISCH, CORO1A, TRIM31, RAB40B, PDE10A, GPER1, WASF3, NRG3, GRIA2, SH2B2, GRIK5, FKBP5, FHIT, FGF2, EGF, PADI1, ZCCHC4, IGHV3-69-1, IGHV3OR16-7, HTRA2, ZNF544, CNTN6, DOCK3, AGO1, EDA, EIF4EBP1, SYNM, TPSG1, PRPF6, EPHA5, FRRS1L, CADM1, SMUG1, OTP, KCNH3, ERBB2, FAAH, CIB1, CACNG2, RIDA, HPRT1, HK1, KALRN, SELENBP1, CHRNA6, ARHGEF7, HP, NRP1, NRP2, LIN7A, B4GALT2, USO1, PKMYT1, BHLHE40, HRC, HTR1D, HTR1E, ZMYM2, TRIM25, HTR3A, HTR4, HTR5A, HTR6, ARTN, PDLIM1, GPHN, HFE, PSMD14, TSHZ1, RASGRP1, BCL2L10, SLC12A6, GSK3B, BMS1, GYPA, GUCY2D, CARTPT, BCAR1, LGI1, ADAMTS2, HGF, ITM2B, FADS2, NRXN1, TGM5, PDLIM7, GPR50, DLGAP1, MTA2, H3P40
-
Pseudobulbar Affect
Wikipedia
It is hypothesized that these primary neurologic injuries and diseases affect chemical signaling in the brain, which in turn disrupts the neurologic pathways that control emotional expression. [20] [21] [22] Stroke [ edit ] PBA is one of the most frequently reported post-stroke behavioral syndromes , with a range of reported prevalence rates from 28% to 52%. [23] [24] [25] The higher prevalence rates tend to be reported in stroke patients who are older or who have a history of prior stroke. [26] [27] The relationship between post-stroke depression and PBA is complicated, because the depressive syndrome also occurs with high frequency in stroke survivors. Post-stroke patients with PBA are more depressed than post-stroke patients without PBA, and the presence of a depressive syndrome may exacerbate the weeping side of PBA symptoms. [23] [28] Multiple sclerosis [ edit ] Recent studies suggest that approximately 10% of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) will experience at least one episode of emotional lability. [29] [30] PBA is generally associated with later stages of the disease (chronic progressive phase). [25] PBA in MS patients is associated with more severe intellectual deterioration, physical disability, and neurological disability. [31] Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [ edit ] A study designed specifically to survey for prevalence found that 49% of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) also had PBA. [9] PBA does not appear to be associated with duration of ALS. [32] [33] It is a symptom of ALS that many patients are unaware of and do not receive information about from their physician. [34] Traumatic brain injury [ edit ] One study of 301 consecutive cases in a clinic setting reported a 5% prevalence.
-
Test Anxiety
Wikipedia
Students often report "blanking out" even though they have studied sufficiently for the test. [26] Emotional – low self-esteem, depression, anger, and a feeling of hopelessness. [26] Causes [ edit ] Research shows that parental pressure is associated with greater worry, test irrelevant thoughts, and stronger bodily symptoms relating to anxiety during a test. [21] Other causes of test anxiety may include fear of failure, procrastination , and previous poor test performance. [27] As well, characteristics of the test environment such as: nature of the task, difficulty, atmosphere, time constraints, examiner characteristics, mode of administration and physical setting can affect the level of anxiousness felt by the student. [5] [21] Researchers Putwain & Best (2011), [28] examined test performance among elementary children when the teacher put pressure on the students in an attempt to create a more high stress environment. ... Journal of College Student Development . 44 : 18–28. doi : 10.1353/csd.2003.0008 . S2CID 16769612 . ^ Vaez, M.; Laflamme, L. (2008).
-
Hospital-Acquired Infection
Wikipedia
"Control of an outbreak of pandrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii colonization and infection in a neonatal intensive care unit". Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol . 28 (4): 423–9. doi : 10.1086/513120 . ... Retrieved 2018-12-06 . ^ "11 Investigates: Surgical implants raising contamination concerns" . wtol.com . Retrieved 2020-07-28 . ^ "Ban 'Reprocessing' of Spinal Surgery Screws, Experts Say" . Medscape . Retrieved 2020-07-28 . ^ Hudson, Jocelyn (2019-01-16). ... Spinal News International . Retrieved 2020-07-28 . ^ World Alliance for patient safety. ... Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 December 2015 . Retrieved 28 November 2015 . ^ "Deadly hospital infections quadruple as staff struggle to fight superbugs" .
-
Tuberculosis In India
Wikipedia
Economics [ edit ] Some legal advocates have argued that public interest litigation in India must be part of the TB response strategy to ensure that available resources actually fund the necessary health response. [25] India has a large burden of the world's TB, with an estimated economic loss of US $43 billion and 100 million lost annually directly due to this disease. [26] Special populations [ edit ] The most certain knowledge about how Scheduled Tribes and other Adivasi experience TB is that there is a lack of research and understanding of the health of this demographic. [27] [28] There is recognition that this community is more vulnerable and has less access to treatment, but details are lacking on how TB affects tribal communities. [27] [28] References [ edit ] ^ World Health Organization (2009).
-
Hemispatial Neglect
Wikipedia
Further research is mandatory in this field of research in order to provide more support in evidence-based practice. [27] In a review article by Pierce & Buxbaum (2002), they concluded that the evidence for Hemispheric Activation Approaches, which focuses on moving the limb on the side of the neglect, has conflicting evidence in the literature. [28] The authors note that a possible limitation in this approach is the requirement for the patients to actively move the neglected limb, which may not be possible for many patients. ... Some less studied treatment possibilities include treatments that target Dorsal Stream of visual processing, Mental Imagery Training, and Neck Vibration Therapy. [28] Trunk rotation therapies aimed at improving postural disorders and balance deficits in patients with unilateral neglect, have demonstrated optimistic results in regaining voluntary trunk control when using specific postural rehabilitative devices.
-
Poisoning Of Alexei Navalny
Wikipedia
He also alleged that the attacker was Aleksandr Petrunko, a man who he claimed had ties with State Duma deputy speaker Pyotr Olegovich Tolstoy . [23] [24] Navalny accused the Kremlin of orchestrating the attack. [25] [26] Another incident occurred in July 2019, when Navalny was arrested and imprisoned. On 28 July, he was hospitalized with severe damage to his eyes and skin. At the hospital, he was diagnosed with an allergic reaction, although this diagnosis was disputed by Anastasia Vasilieva, one of his personal doctors. [27] Vasilieva questioned the diagnosis and suggested the possibility that Navalny's condition was the result of "the damaging effects of undetermined chemicals". [28] On 29 July 2019, Navalny was discharged from hospital and taken back to prison, despite the objections of his personal physician who questioned the hospital's motives. [27] [29] In August 2020, in the days leading up to the poisoning, Navalny had been publishing videos on his YouTube channel in which he expressed support for the pro-democracy 2020 Belarusian protests , which were triggered by the heavily contested 2020 Belarusian presidential election . [30] Navalny had also written that the kind of 'revolution' that was taking place in neighbouring Belarus would soon happen in Russia. [31] Local news site Tayga.Info reported that during his Siberia trip, Navalny had been carrying out an investigation, as well as meeting local candidates and volunteers.
-
Abortion In Pennsylvania
Wikipedia
Casey , the Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit affirmed in part and reversed in part, upholding all of the regulations except for the husband notification requirement. [27] The Third Circuit concluded that the husband notification was unduly burdensome because it potentially exposed married women to spousal abuse, violence, and economic duress at the hands of their husbands. [28] In the 1992 United States Supreme Court ruling on Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v. ... The Roe trimester framework completely forbade states from regulating abortion during the first trimester of pregnancy, permitted regulations designed to protect a woman's health in the second trimester, and permitted prohibitions on abortion during the third trimester (when the fetus becomes viable) under the justification of fetal protection, and so long as the life or health of the mother was not at risk. [31] The plurality found that continuing advancements in medical technology had proven that a fetus could be considered viable at 23 or 24 weeks rather than at the 28 weeks previously understood by the Court in Roe . [32] The plurality thus redrew the line of increasing state interest at viability because of increasing medical accuracy about when fetus viability takes place.