-
Hellp Syndrome
Wikipedia
Placental components, such as inflammatory cytokines and syncytiotrophoblast particles interact with the maternal immune system and endothelial cells, further promoting coagulation and inflammation. [26] [27] These interactions also elevate leukocyte numbers and interleukin concentrations, as well as increase complement activity. [28] [29] Low platelet count [ edit ] vWF degradation in HELLP syndrome is inhibited due to decreased levels of degrading proteins, leading to an increased exposure of platelets to vWF.CD46, CFH, CFI, HELLPAR, FASLG, FAS, PGF, F5, LEP, HADHA, F2, TNF, HPGDS, LGALS13, FLT1, VEGFA, MTHFR, MAPK14, TLR4, AIMP2, TLR2, MAPK3, TPBG, VEGFC, TGFB3, VWF, MAPK1, ABCG2, TFPI2, IL18R1, GRAP2, EBI3, AHSA1, ADAMTS13, SIRT4, RNF19A, POLDIP2, SLC17A5, ERVW-1, MBL3P, AHSP, NOD2, POTEF, SERPINE2, ACTB, SERPINE1, PAH, APC, CFB, CA9, CD40LG, CD59, CDKN1C, COX8A, CP, CRK, ENG, EPHX1, GAPDH, GNB3, GPT, NR3C1, GSTM1, GSTT1, HSPA4, HSPG2, IFNG, IL1B, IL1RN, CXCL8, IL10, LEPR, LNPEP, ADM, NOS3, PAEP, MBL2
-
Abortion In Alabama
Wikipedia
The bill passed the Lower House on April 30 (74-3), [25] the Senate on 14 May, [26] and was signed into law by Governor Kay Ivey on 16 May. [27] The state was one of 23 states in 2007 to have a detailed abortion-specific informed consent requirement. [28] By law, abortion providers in Alabama, Louisiana and Mississippi were required to perform ultrasounds before providing women with ultrasounds, even in situations like in the first trimester where an ultrasound has no medical necessity. [29] In 2013, state Targeted Regulation of Abortion Providers (TRAP) law applied to medication induced abortions and private doctor offices in addition to abortion clinics. [30] Dates of when heartbeat laws come into effect (as of May 25, 2019) The state legislature was one of five states nationwide that tried, and failed, to pass a fetal heartbeat bill in 2014. [31] House Bill 490 prohibiting abortions once a cardiogenesis or "fetal heartbeat" is detected passed the Lower House (73-29) on 4 March 2014. [32] The bill later died in committee. [33] Despite this, Alabama's Lower House was the first state in the nation to pass such a bill. [32] The state legislature tried and failed again in 2015 to pass similar legislation where they were one of three states, again in 206 when they were one of four states, and again in 2017 when they were one of eight states to attempt to pass a fetal heartbeat bill. [31] The law as of March 2019 required women wait 24 hours after their initial appointment for an abortion before they could have a second appointment for the actual procedure. [34] State law at the time prohibited health insurance companies on public exchanges from offering abortion services unless the life of the woman was at risk, or the pregnancy was a result of rape or incest. [34] Nationally, 2019 was one of the most active years for state legislatures in terms of trying to pass abortion rights restrictions. ... Retrieved May 25, 2019 . ^ Romo, Vanessa (June 28, 2019). "Woman Indicted For Manslaughter After Death Of Her Fetus, May Avoid Prosecution" .
-
Tuberculosis
Wikipedia
Since MTB retains certain stains even after being treated with acidic solution, it is classified as an acid-fast bacillus . [14] [26] The most common acid-fast staining techniques are the Ziehl–Neelsen stain [28] and the Kinyoun stain , which dye acid-fast bacilli a bright red that stands out against a blue background. [29] Auramine-rhodamine staining [30] and fluorescence microscopy [31] are also used.SLC11A1, TIRAP, HP, CORO1A, ASAP1, RGS12, MFN2, SLC14A2, HLA-DRB3, CD14, CCL5, CCL2, NAT2, CFP, P4HB, STAT3, NOS2, MT1JP, P2RX7, TLR2, TGFB1, TLR1, MMP1, TLR4, CAT, TNF, ELF3, TSC1, TSC2, VDR, CAMP, CCN6, MMP9, LSAMP, MBL2, ARTN, CYP2E1, CYP2B6, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRB1, HLA-DRB5, HPD, HSPD1, SP110, CRP, IFNA1, IFNA13, IFNG, IFNGR1, IL1A, IL1B, IL2, IL2RB, IL4, IL6, CXCL8, IL10, IL12B, IL12RB1, IL17A, IL18, INHA, CXCL10, SOCS3, TOP2A, ESAT, RHOF, LINC02618, TGM6, CD209, IL22, MBL3P, FOXP3, ADA, TLR9, NCAPG2, LAMP3, ZNF630, IRGM, NOD2, DYNC2H1, RNF34, ESX1, RBM45, AGRP, AGO2, VSX1, BCAR1, SLC14A2-AS1, LINC02211, NEBL, C2CD2, SMUG1, MAPK1, IL23A, INTS4, CSF2, NR1I2, GNLY, FCGR1A, WNT3, TRBV20OR9-2, CDR3, GC, TST, CISH, CTNND1, NTM, HSPA4, IL1RN, CD274, NLRP3, CSE1L, TMX2-CTNND1, IL15, FCGR3A, PTBP2, MAPK14, IL27, CD1B, CHP1, CD27, MAS1, MIF, GSTM1, SPP1, CLEC4E, TPPP, MIR29A, PTBP1, HPGDS, HLA-A, GEM, GSTK1, HIF1A, THEMIS, HSPE1, IL32, CACNA1G-AS1, POLDIP2, GRAP2, MARCO, EBI3, AIMP2, TLR6, AHSA1, MASP2, TMED2, RNF19A, IL37, NRSN1, PDCD1, MT1E, IL17D, KIR3DL1, CD163, IL13, HAMP, IL17F, SLCO6A1, IRF1, H3P19, CRK, CD9, CCR5, ALB, AKT1, BRCA1, SIRT1, CPAT1, GZMB, BMS1, ISG15, ABCG2, IFNB1, PTGS2, SFTPA2, CXCR3, FCGR3B, ABCB1, ARG1, SAT1, SFTPA1, IL2RA, SOCS1, CYP3A4, MYDGF, SFTPD, ACTB, IL18R1, HSPA14, MIR155, HMOX1, HLA-C, NDUFAB1, MYD88, MRC1, ACACA, HLA-DQA1, IL9, SDHD, NFKB1, ITGAX, IL5, SLCO1B1, ISG20, AHR, IL21, TYMS, DHFR, CDX2, BATF2, IL7, DEFB4A, MC3R, DEFB1, GAPDH, CGAS, MTOR, PPARG, TLR8, RPSA, CMPK1, CD44, MCL1, PIK3CG, HSPG2, TOLLIP, BCL2, HLA-B, PTPN22, TAP1, LAMP1, CCR6, CCR4, MIR144, HLCS, TNFRSF1A, IFNAR1, CCL4L1, TICAM2, TAP2, CORD1, KRIT1, STING1, ICAM3, CR1, TXN, SMS, TNFRSF1B, BTNL2, CD36, IL23R, LTA4H, PIK3CD, LTB, PIK3CB, PIK3CA, SH2D1A, LYZ, PC, SMARCAD1, MFAP1, NTRK1, CXCL9, CD48, CD40, CMPK2, COX2, CD40LG, LPA, TLR10, POMC, LCN2, IL7R, CXCR2, CCL4, CCL3, SRL, S100A6, INSRR, ALOX5, TXNRD1, COPD, CLEC7A, KIR2DS1, MAPK8, CAMKMT, LAG3, PDCD1LG2, LAMC2, HLA-E, MT1A, LARS1, CALM2, GPT, KLRC4-KLRK1, SIT1, FASN, KLRG1, ACAD8, MIR20B, CYP2C9, EGFR, GATA3, ABCB6, PRDX5, SQSTM1, TST1, LINC01672, FPR1, SEC14L2, ARHGEF2, EPHB2, CARD8, FOXO3, KLRK1, CCL4L2, CTSZ, DEFB4B, POTEF, CCR2, F3, TBC1D9, CALM1, ST11, MTCO2P12, CYBB, DEFB103A, IRAK4, LINC02605, SARDH, GSTT1, VIM, DECR1, VEGFA, DHX9, APRT, CALM3, TLR7, TYS, SETX, MUC1, PARP9, PLG, INO80B, HCST, SPATA2, DBA2, PRKCD, IL27RA, NCR1, CEP290, ATP6AP1, AIM2, CXCL13, PPID, LILRB1, PLA2G2A, IL33, PHB2, PGM1, SLC9A6, HAVCR2, KLF2, EBPL, LANCL1, RABEPK, NXF1, PDE6B, PDR, SLC27A5, NPPA, SDS, HDAC6, NOTCH4, EBNA1BP2, WASF2, SERPINA1, ZNRD2, OPTN, PPIF, MUC16, ATP2A2, NCAM1, PKP3, PRL, LARS2, PSMB8, SLC34A1, SMPD1, DEFB103B, FASLG, SNCA, SPN, STAT1, EPX, MAFK, TAT, ATG16L1, SARS2, TRIT1, UGT1A1, TGFBR2, THBD, TIMP1, HSD17B8, SCG2, ZYX, SOST, CASR, TMED7, RTEL1, CD244, TRC-GCA24-1, CASP8, CASP3, ANXA5, UGT2B7, TBX21, USO1, PSMD7, TP63, PSMD9, CD86, DST, PMPCA, TBC1D1, SIGIRR, RAB33A, RORC, RPL17, MLYCD, ZNF410, ALOX15, BRCA2, SARS1, CCL1, CD28, FCGR2C, CCL3L1, ATD, KIDINS220, CCL20, CCL22, WASF1, SELL, SFRP1, ASL, SOCS2, ART1, SLC17A5, PLA2G10, DCTN6, MIRLET7B, FCGR2A, CEBPA, IDO1, GAST, FTH1, IRF7, FN1, ADRA1D, FLNB, FOXO1, MIR582, FCN2, CYP3A5, CYP7A1, TNFRSF9, PTK2B, KIR2DL1, AFA1, CDA, KIR3DL2, CYP27B1, ERF, EREG, TMED7-TICAM2, MICA, KLRC2, LBP, CEBPB, CEL, CLYBL, IFNA2, MIR223, GZMA, MIR146A, CYP2C19, MIR140, CTLA4, NR3C1, MALAT1, IRF8, PLF, ASPG, IFI27, CREB1, IL12RB2, GLUL, IFNGR2, GLI3, ARMH1, ANO9, CLEC4D, MT1DP, LIN9, CXCR1, ARAFP2, CHIT1, CHGB, LBR, HIP1, MMP2, DTYMK, ACR, RPL17-C18orf32, LRRK2, TST2, AGER, ELANE, EMB, CD68, AGTR2, GBP5, MEN1, MMP7, H3P23, MDP1, MBP, CYP51A1, BTLA, LEP, LGALS3, NQO1, ABCA4, MIP, MPO, LGALS9, DSPP, MMP3, ACE, ELK3, H3P28, SMR3B, TBK1, SETD2, IGHV3-75, SGSM3, TOR1B, MIR381, ARNT, FASTK, MIR423, C5AR2, GSTT1-AS1, IL17B, ARSA, MIR424, DEFB104B, ERVK-19, B3GAT1, FOXP1, ARSB, H4C15, ATP2C1, RNU6-6P, ARAF, LY75-CD302, ICOS, ATP4A, MIR30B, MIR30C1, DCTN4, MIR30C2, MIR31, NRG3, MIR32, APC, APCS, MIR33A, TRAT1, APEH, MIR93, MIR96, HPSE, HILPDA, POTEKP, GEMIN4, FAS, IL21R, IL20, MIR337, NOX4, MIR376C, DUOX2, KLK12, MIR196B, HAVCR1, SLC40A1, ERVK-32, AQP4, ILVBL, HNP1, PCED1B-AS1, BRD4, ERVK-11, ATP12A, MIR579, DICER1, KIF3A, ERVK-9, SYNM, ATM, MORN2, METAP1, SIGLEC14, KIR2DS2, PTP4A3, TIMM23, SNORD104, SMG1, SPEN, H3C9P, NT5C2, SIRT2, FSTL1, WDHD1, MIR1178, IRAK3, CILK1, ACOT7, KLHL2, ATF3, DCTN3, CABIN1, DUSP14, VPS33B, NOCT, STS, PHGDH, MIR486-1, PRPF31, POTEM, LOC102724971, AKAP13, TMEM72, MOXD1, CHMP2B, SMIM10L2B, SERPINC1, PART1, MT1XP1, LOC102723407, NT5C3A, IL17RA, ACP1, MYMX, SCAT1, LY96, IL24, TMSB15A, NUP62, SPAG11A, AMACR, KLHDC2, DDX58, RIPK3, PADI4, RBFOX2, AHCY, MIR27A, CCNY, NLRP11, VKORC1, FTO, ZXDC, PAGR1, SLC52A2, AKR1B1, CRYGEP, VTCN1, SUGCT, NLRC3, AGBL2, HDAC11, STN1, ASRGL1, ALDH2, MLKL, COLEC11, MARCKSL1, MIR23A, TBATA, UBL5, RICTOR, ERVK-6, RBKS, LRRC4, SLC39A8, ALOX12, CARD9, SEMA4A, ROBO3, SIL1, ATG3, ADRB2, MARCHF7, CDK15, RNASEH1, VPS33A, ACSBG2, CLEC4C, PYHIN1, SESN2, SCAR3, TRIM4, NLRP12, ALAD, MTG1, NAF1, CLEC6A, FOXP2, DRAM2, SFXN1, OPN4, TGS1, H4-16, PRRT2, CYP2R1, MRGPRF, SLC2A13, ATG4C, ATAD1, CBR4, AGA, C1orf52, LYPD4, PWAR1, ATG10, FGFBP2, HSPE1P1, TNFSF13B, DEFB104A, TRIM63, MAGT1, CHCHD6, CARD11, UPRT, ZNF469, PACRG, RNASE7, H2BC1, NLRC4, CTDSP1, HCN1, SMIM10L2A, ANXA1, RTL1, MOV10L1, KMT5A, ACTG1, AMBP, IL31, MARCHF5, TMED9, AHI1, ALPP, RHBDL2, OXSM, ACTG2, DARS2, VPS13D, MIR155HG, MIR125A, DUOX1, MIR150, KLRF1, MAGEC2, NCKIPSD, MIR21, MIR199B, MIR18A, MIR17, SIRT6, ADAM22, MIR148A, CYRIB, MIR142, GDE1, MIR141, MIR132, ANXA2, TENT5A, RAB20, SCASI, PRPF40A, MCCC1, PLAAT1, TMSB15B, SMURF1, ALPI, NLN, MIF-AS1, CHAMP1, ARID1B, SEMA6A, TRMT5, CLEC9A, OR10A4, SPG16, IFNL3, BMP6P1, SEC14L3, MAP3K7CL, RETN, IRGC, GABRQ, INTS13, IFT122, CCL15-CCL14, IL26, EMC3, PBK, ACTBL2, ADH4, CTNNBL1, COL6A4P1, ADK, CMAS, NKRF, CFC1, ZBTB8OS, HSR, ADGRV1, CD55, KHDRBS1, CNR2, KLRB1, LAMB3, LCN1, LDHC, LIPE, LNPEP, LRP1, CD79A, LTA, CYP4F3, CD180, LY75, MARS1, CD69, MATN3, ADAM11, MEFV, MICB, CD53, MMP8, CD47, MMP10, MMP13, KLK1, KIR2DL3, KIR2DL2, CES1, CCR7, IL3RA, IL4R, IL5RA, CCR1, IL6R, TPP1, CHRM3, IL10RA, IL12A, IMPDH2, KCNMA1, CDKN1B, IRAK1, CDK9, IRF3, IRF5, IRF6, ITGA1, ITPA, JAK2, CD82, MMP14, MNAT1, MOG, PLAUR, PCNA, CDK16, PDE8A, PENK, TNFSF8, PFKM, SLC25A3, SERPINB6, SERPINB9, PIP, PMP22, PRKN, PNN, PPBP, PPIA, PPM1A, PPP1R1A, PPP2CA, PRF1, PRKAA1, PRKAA2, PRKAB1, PAWR, SERPINE1, MPG, NEDD4, ABCC1, MS, MSR1, MSX2, MUC2, MUC5AC, MMUT, NCF2, NDUFS3, NDUFS4, NFE2L2, CD38, NFKBIA, NFKBIL1, NHS, PNP, SLC11A2, NT5E, OAS1, OAS3, OPRM1, ENTPD1, IL1R1, IGHG3, PRKCA, IGHE, ESR1, EXTL3, F2, F2R, FANCC, FANCD2, FAT1, FBN2, FCGR2B, FDXR, FGFR3, FHIT, FMO2, FPGS, FUT2, GAB1, GALE, GALNS, GCNT2, MSTN, GFAP, CBLIF, GK, ESD, DMTN, ENPEP, DPAGT1, DARS1, DBP, DES, CFD, SEPTIN1, DLD, DMD, DMRT1, DYNC1H1, DNMT3B, DPP4, ENO2, DUSP3, DUSP5, DUT, EDN1, EDNRB, EEF1A1, EHHADH, MARK2, EMP2, ENO1, GLA, GLI2, GLO1, CRYZ, CTSG, CTNNB1, HPRT1, HPX, HRC, HRES1, HSPA1L, HSPA5, HSP90AA1, CTAA1, TNC, MR1, IAPP, IARS1, ICAM1, ICAM4, IFI16, CRYGC, IFNA17, IFNAR2, CPOX, IGHA1, HNRNPA1, CTSK, GLS, GTF2H1, GNA12, GOT1, UTS2R, GRB2, GRIK1, GRIK3, CXCL2, GSR, GSTP1, GSTZ1, GUSB, CTSW, HDAC1, CFH, HGF, NRG1, CYP1A1, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, CYBA, HLA-DQB2, HLA-DRA, PRKACG, PRKCB, TRIM16, ARHGEF5, BECN1, C5AR1, MBTPS1, URI1, RIPK1, TNFSF13, ADAM9, RIPK2, TNFRSF18, SUCLA2, NRP2, NRP1, GMPS, CFLAR, C3, KAT2B, CDK5R1, ALDH1A2, TSPO, TIMELESS, MBD2, SELENBP1, MAP3K14, ABCB11, OASL, HSD17B6, H4C8, CSRP3, SLC7A5, KDM5D, H4C9, H4C1, H4C4, H4C6, H4C12, H4C11, H4C3, H4C2, TNFSF11, H4C5, H4C13, H4C14, DAP, SRPX, ULK1, CAVIN2, NSMAF, FCN3, SCARF1, KLF5, BST1, USP6, SPAG11B, BCL2L10, BCL2L11, CHAF1A, IL18BP, TSPAN32, BCL2A1, LILRB2, CTPP, CLEC4M, TRIM22, IFITM3, MVP, CAP1, MYBBP1A, CIB1, BACH1, BATF, ANP32B, PROCR, BAAT, SORBS1, RBCK1, FGFBP1, MAFB, NMI, TMPRSS11D, LPAR2, HACD1, XPR1, NOG, S1PR2, CD83, KLF4, PPIG, SLC9A3R1, ADIPOQ, TJP2, BCS1L, FHL5, ADAMTS4, ADAMTS3, CXCR5, RGS6, ZNF592, SOCS5, GAB2, TLK1, SMG7, NR4A3, LAP, TNFRSF8, BAG6, RPE65, RPS4X, RPS7, RPS12, SALL1, CD19, CCL8, CCL15, CCL19, CXCL11, XCL1, SDC1, SEC14L1, SETMAR, SRSF1, SRSF3, SLAMF1, SLC2A1, SLC2A3, SLC6A3, SLC10A1, SLC22A4, SLC22A5, RPGR, RORA, BRD2, PTPRB, PROC, MASP1, HTRA1, PRTN3, PSEN1, PSMB9, PSME1, PTGER2, PTPN6, PTPRA, PTPRC, CD80, RAB27A, MOK, RAF1, PLAAT4, RASA1, RBP4, PRPH2, REL, RELA, RENBP, SLN, SMPD2, SIGLEC1, UMOD, TPI1, NR2C2, HSP90B1, TRAF6, CASP4, TUB, TWIST1, TYK2, UBE3A, UGT1A, UMPS, CASP9, UPP1, VDAC1, CASP1, CALR, WNT5A, RNF112, ZNF208, IL1R2, CXCR4, ALDH5A1, TP53, TNNI3, SNRNP70, PRDX2, CD8A, SPTAN1, CD3E, STAT4, SYK, MAP3K7, TBCA, HNF1B, TCOF1, CD1C, SERPINA3, RUNX1, TERC, TERT, TF, TFPI, TGFA, CD1A, TGFBR1, THBS4, TIMP2, CCNT1, TEK
-
Glaucoma
Wikipedia
Angle closure-induced ocular hypertension and glaucomatous optic neuropathy may also occur with these anomalies, [25] [26] [27] and has been modelled in mice. [28] Other [ edit ] Other factors can cause glaucoma, known as "secondary glaucoma", including prolonged use of steroids (steroid-induced glaucoma); conditions that severely restrict blood flow to the eye, such as severe diabetic retinopathy and central retinal vein occlusion (neovascular glaucoma); ocular trauma (angle-recession glaucoma); and inflammation of the middle layer of the pigmented vascular eye structure ( uveitis ), known as uveitic glaucoma. ... National Eye Institute . Archived from the original on 28 March 2016 . Retrieved 29 March 2016 . ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Mantravadi AV, Vadhar N (September 2015).MYOC, LTBP2, CDKN2B, SLC4A4, TGFB2, PITX2, BDNF, CDKN2A, TDRD7, MYLK, SH3PXD2B, CPAMD8, TNF, VEGFA, NTRK2, SNCG, CNTF, TXN, BAX, SQSTM1, CDKN1B, BECN1, NGF, BCL2, EPO, BAD, MAS1, CYP1B1, LGR4, BEX3, ATF2, NMNAT3, EPOR, FOXC1, CCND2, MAP1LC3A, ANXA3, NGFR, ACE2, TXNIP, NTRK1, LOXL1, GJA1, LMX1B, CDKN2B-AS1, SBF2, FBN1, TGFB1, NHS, ELN, ADAMTS10, COL1A1, TMCO1, COL11A1, PAX6, TEK, FAS, PLEKHA7, HLA-DRB1, PEX19, GNAQ, RPGR, PEX5, LIMK1, SRBD1, OCRL, FMNL2, COL2A1, NLRP3, PEX13, NOD2, FOXE3, RBBP8, ARHGEF12, AHR, ANGPT1, DDX58, TXNRD2, PRPF8, ATR, PROM1, TRAIP, OVOL2, PLXNA2, PLOD1, STUB1, RXYLT1, PIK3R1, MASP1, PIK3C2A, AFAP1, PEX14, YAP1, MERTK, PEX12, SLC7A14, PTCH1, PEX6, PRPF31, ROM1, RLBP1, RHO, RGR, RFC2, PRPH2, RBP3, OPTN, ZSWIM6, RASA1, RAD21, CNTNAP2, PEX2, TOPORS, TMEM98, KIAA1549, PEX10, PDE6B, PEX1, FAT4, PRPF6, B4GAT1, CCDC28B, PRDM5, ARL2BP, FKRP, CRB1, CEP152, AGBL5, SRD5A3, ZNF408, DHDDS, BICC1, PUS1, SNRNP200, ANKLE2, NDP, NEK2, NF1, ARHGEF18, IFT172, PDE6G, PDE6A, PCNT, POMT1, OPA1, EBP, PLK4, NRL, XYLT1, IFIH1, SEMA4A, GZF1, NIPBL, FSCN2, RP9, PTPN22, SCAPER, BEST1, BUB3, WT1, WFS1, CLIP2, LARGE1, NDUFB11, LRAT, VHL, PRPF4, TRIP13, RBFOX1, TRIM44, PDE7B, CLRN1, USH2A, UFD1, PRPF3, IFT88, RECQL4, PTCH2, PEX11B, POMT2, GMPPB, HERC2, CCDC22, BAZ1B, IMPG2, PEX3, SUFU, OFD1, YARS2, SMC3, LOH19CR1, DERA, NAA10, SMC1A, AHI1, HIRA, RP1, DHX38, KLHL7, CEP57, ANKH, IFT140, BTNL2, SKIV2L, RAPGEF5, SAG, KIZ, RS1, RREB1, RPS19, RPE65, WASHC5, RP2, NR2E3, HDAC8, CENPJ, TULP1, TBL2, TUB, KMT2A, PEX16, SETD5, ADAMTS3, ELP4, TIMP3, POMGNT1, SPATA7, GTF2IRD1, SEC24C, PEX26, AGK, TTC37, EXOC2, TBX1, BCOR, ZEB1, DHCR7, CANT1, MECOM, WDR36, FKTN, EYS, CBS, ZNF513, KDSR, CERKL, GJB3, PCARE, TBC1D20, GJB4, TTC8, HGSNAT, DNAJC24, GP1BB, CA4, GSTM1, BUB1B, BUB1, BBS2, BBS1, GTF2I, GUCA1B, HCCS, ARVCF, ETS1, FREM2, ARL3, ESCO2, VCAN, JMJD1C, THSD7A, CRYAA, CRX, ADAMTS17, CREBBP, CADM2, COX7B, COMT, DAG1, C8orf37, COL5A2, C14orf39, COL5A1, COL4A1, COL3A1, B3GALNT2, CCBE1, CNGA1, CNGB1, CLN3, RDH12, B3GLCT, EP300, CENPE, ARSB, GSN, ATRIP, ZNF469, CDHR1, ARL6, PRSS56, KIF11, CRPPA, CHRDL1, FAM161A, IDH3B, SLC25A4, ANTXR1, MAK, POMGNT2, IDH3A, ACVR1, REEP6, PRCD, MFRP, RNU4ATAC, IMPDH1, ADAMTSL1, MYOCOS, CHST14, POMK, LOXL1-AS1, ABCA4, CISD2, IDUA, IL6, GSTT1, HCAR2, TP53, TBK1, HCA1, ADCY10, MAGEC3, MMP9, MAGEE1, HCAR1, TLR4, APOE, IL1A, ACTB, FN1, CA2, EDNRB, MMRN1, MTHFR, EDN1, NOS3, HSD11B1, SIX6, CAV1, IL1B, P2RX7, ANGPTL7, CCN2, TYRP1, NR3C1, GSTP1, SPARC, MMP1, SIX1, PIK3CG, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, PIK3CA, DBA2, ATOH7, TTR, CAV2, MMP3, WWTR1, TGM2, HSPA4, AMD1P2, ASB10, NFKB1, NFE2L2, S100B, AMD1, HPGDS, NPPA, SIRT1, ADRB2, VDR, CP, AQP4, CNR1, VAV3, APRT, MIR93, MIR29B2, MIR29B1, BCHE, HEYL, RNU1-1, IL17B, SIGMAR1, SPAG11B, GSTK1, AKT1, RUNX1T1, CCT, CDK9, CDKN1A, CDR1, SPAG11A, POSTN, AKR1C4, CISH, CLU, IL20, MAP3K5, PRSS55, SPZ1, IGF1, PTEN, SLC1A3, PTGER2, PTGFR, SFRP1, GAS5, ISG20, HSPA1B, P2RY6, GABPA, CXCL8, SLCO6A1, IL2RA, FOXO1, BIRC6, EDNRA, SOD2, HSPA1A, CYP2B6, MGP, CRISP2, MAPK3, THBS1, MEG3, HIF1A, MAPK8, ABCA1, MFAP1, MTOR, OPTC, GLCCI1, B3GAT3, GPR166P, VN1R17P, HPSE2, GLC1I, CYGB, LGR6, MRGPRX3, GPATCH3, ELOVL5, MIR483, PART1, MVB12B, CPLANE1, MAP1LC3B, COL18A1, LOC110599580, TRPM3, WLS, MAGT1, LPAR3, MIR1298, CARD14, WNK2, DAPK2, MT1IP, MIR760, WNK1, IL1F10, MARCKSL1, CCR2, GORASP1, DNLZ, LINGO1, IL22RA1, PLXDC2, IL21, NLRC4, MRGPRX4, DOK5, SLC12A9, DPYSL5, FOXP3, ASAH2, ASCC1, LRRC8A, NSMCE3, TNFRSF12A, HSD17B7, GPRC5C, IL20RB, MIR29A, PDIK1L, PLB1, TMTC2, GPRC5D, MRGPRX1, OXER1, GPHA2, GPRC6A, ARID2, MARCHF1, RPGRIP1, PAK5, IL22, GPR151, MIR215, MIR211, MIR204, MIR200A, FOXD3, TUG1, NGB, MIR182, MIR149, GBA2, MIR141, MIR122, GPR158, MALAT1, TAF8, PTCHD3, MRTFB, BBS5, AICDA, GJD2, TMEM182, ANAPC1, AAVS1, RIMS1, FUT8, TLX2, HNF4A, HDAC1, HBB, GSTM3, GSTM2, GNAS, GLC3B, GLC1C, GLC1B, GLA, GDNF, FLT4, HTR1A, FOXC2, FANCF, PTK2B, FAAH, F9, ERG, EPHB6, EPHB1, ELK3, ELAVL2, EDN2, DOCK3, HSPD1, IAPP, MGLL, LTBP3, MT1F, MT1E, MT1B, MT1A, ABCC1, MMP2, CD46, MAPT, MAOA, SMAD4, SMAD3, SH2D1A, LPA, ICA1, LOX, LGALS9, LCN2, LAMC2, LAMA4, ITGAM, ITGA4, INPP5B, IL17A, IGFALS, IFNA13, IFNA1, COCH, DMXL1, DBN1, ANGPT2, BMP4, BMP2, BGLAP, BCL2L1, BAK1, ALDH7A1, ASAH1, ARSD, AQP9, AQP1, APCS, ANXA5, AMT, DBH, ALPP, ALPI, ALDH1A1, ALB, APLNR, AGTR1, AGT, AGER, AP2B1, ADCYAP1, ACHE, ABO, BTC, C3, C4BPA, CA9, CYP2J2, CYBB, CYBA, CXADR, CUX1, CSTA, CSF2, CRYBB2, CRYAB, CRMP1, CREB1, COX8A, COL8A2, CHM, CEBPD, CEBPB, CDSN, CD47, CD40, CASP3, CAPG, CAMP, CACNA2D1, CACNA1C, CA12, MT1G, MT1H, MT1JP, CDC7, MTMR2, ARHGEF7, APLN, DPM2, TNFSF14, RIPK1, AKR1C3, DENR, NCK2, SRPX, HYAL3, FZD4, USP9X, TGFBR3, XRCC1, VWF, VTN, VAV2, UTRN, TYR, PHLDA2, TRPC5, HSP90B1, TNNT3, TNFRSF1B, CLDN5, SELENBP1, PKD2L1, DCLK1, XPR1, POU6F2, PADI2, DDX20, KERA, STIP1, PDIA5, HPSE, FRS2, ARFGEF1, FST, PRG4, DHRS9, DNM1L, ABCB6, HDAC6, SLC23A2, MFN2, PRDX6, NRG2, TBPL1, GDF15, ROCK2, AIM2, CD163, S1PR2, TH, TGFBR1, MT1M, OGN, MAPK10, MAPK9, PPARG, PON1, POLG, PLG, PLA2G4A, SERPINA1, SERPINF1, PDK1, PDGFRB, PBX1, NTF3, TFRC, NRF1, NPHS1, NOS2, NMB, NFATC3, NEFL, MYP2, MTNR1A, MTHFD1, CYTB, MT1X, MT1L, PRNP, PSD, PTPN9, PTPN11, TFAP2B, PRDX2, TAP2, TAP1, TAC3, SYT1, STAT3, SPRR2A, SPINK1, SOD1, SNCA, SLCO2A1, SLC6A2, SLC1A1, SELE, CXCL6, CCL2, SALL1, SAA2, ROS1, RNASE3, RLN2, RELA, RAN, PTPRB, H3P40
-
Chronic Periodontitis
Wikipedia
However, there is some controversy over their use: "No consistent evidence supports the efficacy of laser treatment as an adjunct to non-surgical periodontal treatment in adults with chronic periodontitis." [26] Tentative links to other conditions [ edit ] There is little evidence linking progression of periodontal disease to low birth weight or preterm birth : "In these women with periodontitis and within this study's limitations, disease progression was not associated with an increased risk for delivering a pre-term or a low birthweight infant." [27] There is recently emerged evidence linking chronic periodontitis with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma : "Patients with periodontitis were more likely to have poorly differentiated oral cavity SCC than those without periodontitis (32.8% versus 11.5%; P = 0.038)". [28] There is evidence to suggest that periodontal disease may play a role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease. [29] References [ edit ] ^ a b Shaddox, Luciana M; Walker, Clay B (2010-08-11).TNFSF11, CXCL12, MMP9, MMP2, IL1A, TNF, TLR2, VDR, MMP1, IL10, CXCL8, IL6, IL4, IL1B, TLR4, IL17A, DEFB1, TNFRSF11B, IFNG, TGFB1, PTGS2, CD14, IL1RN, CRP, IL18, TIMP1, MMP3, IL17F, BTF3P11, IL2, COX2, NR1I2, NLRP3, MTCO2P12, CCR5, IL33, AGER, TIMP2, MMP8, LTA, NIN, SLC52A1, ICAM1, F2RL1, ESR1, IL13, IL4R, SELE, LXN, RETN, HLA-DRB1, RBP4, MIR146A, ADAM8, CASP1, HAP1, CTLA4, CDKN2B-AS1, SOST, FOXP3, STS, SERPINE1, AIM2, PYCARD, CASP3, DEFB4A, LEP, MPO, APEX1, CCL2, BRINP3, EDN1, AP3B2, ACE, VCAM1, ADGRE1, GCFC2, FCGR2A, TCN1, LIN28A, MIR3652, SLC23A2, NPEPPS, MIR375, CXCL14, BMS1, BCL2L11, SLC23A1, NCR2, DAB2IP, TNFRSF1B, EDIL3, MIR144, PWAR1, LRPPRC, MIR499B, VTN, VEGFA, ADIPOQ, SOCS1, CP20, CXCR4, RIPK2, SIGLEC5, TNFRSF11A, MIR142, TNFRSF10C, IL1R2, PGLYRP1, WNT5A, SMC3, IL32, CD163, MIR155, CNOT8, FGD5-AS1, ABHD12B, MLKL, MIR3609, ARHGEF28, WHAMM, THNSL2, SLC50A1, GOPC, SEMA6A, BEGAIN, HAMP, ZNF410, POPDC2, NOD2, IFIH1, MMP28, MIR1226, SLC52A2, FBXO38, NDEL1, MRGPRX2, NLRC5, ABCC11, UBE3D, UCN2, ZNF675, IFNL3, UCN3, RBM45, QPCTL, FBLIM1, TLR9, EBI3, POP1, IL24, RIPK3, DEFB104A, DKK1, SIRT1, KRT23, MIR125A, GTF2H5, PYDC2, IL37, PSAT1, DEFB4B, TBX21, C20orf181, MIR381, MZB1, AMTN, MALAT1, MIR499A, DEFB104B, IL23A, ITGA11, ACACA, TIMP3, CSF1, CTSD, CUX1, CYMD, DECR1, EGF, EGFR, ELANE, ELAVL2, ERCC2, ESR2, F2R, FAP, FCGR2B, FOXO1, FLT1, FN1, GAD1, GC, CXCR3, GPX1, GRN, HGD, HGF, HGFAC, HIF1A, CSF2, COL17A1, THRB, COL1A1, AGT, AGTR1, AHSG, APOE, KLK3, AQP3, AZU1, BDNF, BMP2, BPI, C4A, C4B, MPPED1, CAMP, CASP8, CD1A, CD4, CD19, CD38, CD59, CD68, CDKN2A, CDKN2B, CDSN, CLU, HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-DRB3, HMGB1, OSM, PRDX1, PF4, PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PIK3CD, PIK3CG, PLAG1, PLG, SERPINF2, PPARG, PTGDS, PTX3, MOK, REN, S100A8, SFTPD, SOD2, ABCC8, TAGLN, PRDX2, NR2F2, TGM1, TGM2, TGM3, NPY, NOS3, NOS2, IL12B, IFI16, IFNGR2, IGF1, IGHA1, IGHG3, IL2RA, IL3RA, IL5, IL6R, IL6ST, IL12A, IL12RB2, NM, INPP5D, KCNK1, KCNQ1, KDR, LTF, MBL2, MEFV, MICB, MMP12, MUC7, NFYA, PROS1
-
Von Willebrand Disease
Wikipedia
He ultimately assessed 66 members of her family and reported in a 1926 Swedish-language article that this was a previously undescribed bleeding disorder that differed from hemophilia. [27] He published another article on the disorder in 1931, in the German language, which attracted international attention in the disease. [28] The eponymous name was assigned to the disease between the late 1930s and the early 1940s, in recognition of Von Willebrand's extensive research. [29] In the 1950s, it became clear that a "plasma factor", factor VIII , was decreased in these persons and that Cohn fraction I-0 could correct both the plasma deficiency of FVIII and the prolonged bleeding time.VWF, P2RY12, F8, COX8A, ADAMTS13, GP1BA, F9, AK3, ABO, IL11, F11, ACTB, VWA8, ITIH1, TLR5, ITIH5, ANGPT2, POU2F3, CHRD, ALKBH1, CLEC4M, C20orf181, MUC5B, ATP6V0A2, SMPX, RABGEF1, CRISPLD2, SEC1P, PRB2, GP6, BMPER, TERF2IP, FAM20C, STXBP5, ANTXR1, ANO2, RAP1A, THPO, PDIA3, AGT, AVP, CANX, CD40, CLCA1, CSHL1, COCH, EPHA3, F2, F3, IFNA2, THBS1, RBPJ, ITGA2, ITGA2B, LRPAP1, MTHFR, CCN3, SERPINE1, PLG, POMC, SET, BOP
-
Intravascular Lymphomas
Wikipedia
Weeks, months, years, or decades thereafter, a small percentage of these carriers develop an EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disease, [25] [26] including in extremely rare cases IVNK/TL. [8] EBV is well known to infect NK- and T-cells, to express some of its genes that promote the survival and proliferation of the cells it infects, and thereby to cause various and far more common NK- and T-cell lymphomas. [27] It seems likely that the virus acts similarly to cause IVNK/TL. [8] IVNK/TL may differ from the other types of NK- and T-cell lymphomas which EBV produces because its NK- and T-cells and nearby endothelial cells have defects in the expression of proteins required for the NK/T-cells to pass through the endothelium and into the surrounding tissues (see above section on the Pathopysiology IVBCL). [28] Presentation [ edit ] Individuals (age range 23–81 years [8] ) with IVNK/TL typically have a rapidly progressive disease.
-
Abortion In New Zealand
Wikipedia
ALRANZ and other abortion rights groups shifted their attention to lobbying for sex education in schools and easing young people's access to contraceptives . [27] [18] In response, anti-abortion activists and groups picketed abortion clinics and joined forces with socially-conservative moral groups including Moral Rearmament, Family Rights Association, Society for the Protection of Community Standards (SPCS), and "Family 75" during the late 1970s and 1980s. [28] SPUC was at the forefront of opposing abortion during the 1980s. ... SPUC drew support from the Catholic Church in New Zealand and politicians from the two major parties, Labour and National. By 1975, SPUC had 28 branches and 40,000 members. Policy differences between the national leadership and the Christchurch branch led by Ken Orr led to SPUC's splintering in 2000. ... Stuff.co.nz . 31 January 2009 . Retrieved 28 September 2019 . ^ "Archived copy" .
-
Cancer Syndrome
Wikipedia
Tumors with increased risk in this disorder are colorectal cancer, gastric adenomas and duodenal adenomas. [15] [28] Micrograph showing keratocystic odontogenic tumour , a common finding in nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. ... "Correlation of phenotype/genotype in a cohort of 23 xeroderma pigmentosum-variant patients reveals 12 new disease-causing POLH mutations". Hum. Mutat . 35 (1): 117–28. doi : 10.1002/humu.22462 . PMID 24130121 . ^ a b "Genetic Testing for Hereditary Cancer Syndromes" .RET, VHL, BAP1, TP53, PTEN, BRCA1, FH, MLH1, BRCA2, CDH1, MSH2, STK11, DICER1, TSC2, SDHB, PMS2, MSH6, APC, BMPR1A, CDKN2A, SDHAF2, MRPS18C, SMARCB1, RAD51B, RAD51D, RB1, CDKN2B-AS1, RECQL, FLCN, SDHA, SDHC, SDHD, SMARCA4, C11orf65, SMARCE1, TOE1, ABRAXAS1, BRIP1, XRCC2, FBXO11, PALB2, RAD50, RAD51C, CHEK2, MPRIP, TMEM127, HOXB13, POLE, PTCH1, MUTYH, BARD1, BLM, CDK4, CTNNA1, EXT2, FANCC, HFE, SMAD4, MAX, ATM, MITF, MRE11, TH2LCRR, NBN, NF1, POLD1, NTHL1, MRC1, MEN1, CDC73, CYP19A1, ST8, PLAU, BRAF, RUNX1, PKM, PIK3CG, CTNNB1, SORD, SDS, SARDH, PIK3CD, MSH3, PART1, PIK3CA, KRAS, SERPINE1, PIK3CB
- Effects Of Alcohol On Memory Wikipedia
-
Dental Trauma
Wikipedia
Gum shields ideally have to be comfortable for users, retentive, odourless, tasteless and the materials should not be causing any harm to the body. [26] However, studies in various high-risk populations for dental injuries have repeatedly reported low compliance of individuals for the regular using of mouthguard during activities. [27] Moreover, even with regular use, effectiveness of prevention of dental injuries is not complete, and injuries can still occur even when mouthguards are used as users are not always aware of the best makes or size, which inevitably result in a poor fit. [16] Types of gum shield [26] [28] Stock ready-moulded Not recommended as it does not conform the teeth at all Poor retention Poor fit Higher risk of dislodging during contact sports and airway occlusion which may lead to respiratory distress Self-moulded/ Boil and bite Limited range of sizes, which may result in poor fitting Can be easily remoulded if distorted Cheap Custom-made Made with ethylene vinyl acetate The most ideal type of gum shield [29] Good retention Able to build in multiple layers/ laminations Expensive One of the most important measures is to impart knowledge and awareness about dental injury to those who are involved in sports environments like boxing and in school children in which they are at high risk of suffering dental trauma through an extensive educational campaign including lectures, leaflets, posters which should be presented in an easy understandable way. [30] Management [ edit ] The management depends on the type of injury involved and whether it is a baby or an adult tooth. ... Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth. Dental Traumatology . 28: 2-12. ^ ANDRESSON L., ANDREASEN J.O., DAY P., HEITHERSAY G., TROPE M., DIANGELIS A.J., KENNY D.J., SIGURDSSON A., BOURGUIGNON C., FLORES M.T., HICKS M.L., LENZI A.R., MALMGREN B., MOULE A.J. and TSUKIBOSHI M. (2012). ... Avulsion of permanent teeth. Dental Traumatology . 28(2): 88-96. ^ Lin S, Pilosof N, Karawani M, Wigler R, Kaufman AY, Teich ST (October 2016).
-
Low Back Pain
Wikipedia
Chronic low back pain is associated with sleep problems, including a greater amount of time needed to fall asleep, disturbances during sleep, a shorter duration of sleep, and less satisfaction with sleep. [24] In addition, a majority of those with chronic low back pain show symptoms of depression [13] or anxiety . [17] Causes A herniated disc as seen on MRI, one possible cause of low back pain Low back pain is not a specific disease but rather a complaint that may be caused by a large number of underlying problems of varying levels of seriousness. [25] The majority of LBP does not have a clear cause [1] but is believed to be the result of non-serious muscle or skeletal issues such as sprains or strains . [26] Obesity, smoking, weight gain during pregnancy, stress , poor physical condition, poor posture and poor sleeping position may also contribute to low back pain. [26] A full list of possible causes includes many less common conditions. [5] Physical causes may include osteoarthritis , degeneration of the discs between the vertebrae or a spinal disc herniation , broken vertebra(e) (such as from osteoporosis ) or, rarely, an infection or tumor of the spine. [27] Women may have acute low back pain from medical conditions affecting the female reproductive system, including endometriosis , ovarian cysts , ovarian cancer , or uterine fibroids . [28] Nearly half of all pregnant women report pain in the lower back or sacral area during pregnancy, due to changes in their posture and center of gravity causing muscle and ligament strain. [29] Low back pain can be broadly classified into four main categories: Musculoskeletal – mechanical (including muscle strain , muscle spasm , or osteoarthritis ); herniated nucleus pulposus, herniated disk ; spinal stenosis ; or compression fracture Inflammatory – HLA-B27 associated arthritis including ankylosing spondylitis , reactive arthritis , psoriatic arthritis , and inflammatory bowel disease Malignancy – bone metastasis from lung, breast, prostate, thyroid, among others Infectious – osteomyelitis ; abscess Low back pain can also be caused by an urinary tract infection . [30] Pathophysiology Back structures The five lumbar vertebrae define the lower back region. ... PMID 23245607 . ^ a b c d e "Use of imaging studies for low back pain: percentage of members with a primary diagnosis of low back pain who did not have an imaging study (plain x-ray, MRI, CT scan) within 28 days of the diagnosis" . 2013. Archived from the original on 4 October 2013 .PLAT, SPARC, NAB2, SPAST, HSPB8, HTRA1, ALDH18A1, STAT6, FAS, TBX6, ABCD1, NGF, IL1B, LBP, TNF, IL6, CALCA, CXCL8, COMT, IL1A, LEP, CCL2, NUBP1, EMSLR, TP63, CASP9, COASY, BDNF, CRP, CISD3, SEMA3A, SLCO6A1, COPD, RGS6, GDF15, NLRP3, MIR204, ADAMTS3, ADAMTS4, ZFYVE9, MSC, FST, ITLN1, ADAMTS5, RTN4, MCF2L2, SIRT1, PES1, SPECC1, TSKU, LCS1, F11R, DNAJC5, PER2, MARCHF1, PACC1, SPEN, ACR, GDF5, ZNF35, ACAN, AMH, BMP3, TSPO, CASP1, CAT, CD6, DNMT3B, NR3C1, IL1RN, IL6ST, MMP1, MMP9, OPRM1, FURIN, PPARG, PTGS2, RARRES2, RASA1, RHAG, RTN1, CCL4, ACP5, TAC1, TLR4, TP53, VDR, SMS
-
Hemothorax
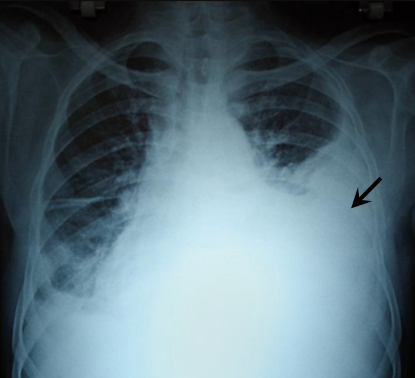
Wikipedia
However, CT is less used as a primary means of diagnosis within the trauma setting, as these scans require a critically ill person to be transported to a scanner, are slower, and require the subject to remain supine. [25] [28] Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be used to differentiate between a hemothorax and other forms of pleural effusion, and can suggest how long the hemothorax has been present for.
-
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Wikipedia
The most common symptoms of COPD are shortness of breath , and a cough that produces sputum . [22] These symptoms are present for a prolonged period of time [23] and typically worsen over time. [5] It is unclear whether different types of COPD exist. [2] [24] While previously divided into emphysema and chronic bronchitis, emphysema is only a description of lung changes rather than a disease itself, and chronic bronchitis is simply a descriptor of symptoms that may or may not occur with COPD. [3] [25] Cough [ edit ] A chronic cough is often the first symptom to develop. [22] Early on it may just occur occasionally or may not result in sputum. [22] When a cough persists for more than three months each year for at least two years, in combination with sputum production and without another explanation, it is by definition chronic bronchitis . [22] Chronic bronchitis can occur before the restricted airflow and thus COPD fully develops. [22] The amount of sputum produced can change over hours to days. [22] In some cases, the cough may not be present or may only occur occasionally and may not be productive. [22] Some people with COPD attribute the symptoms to a "smoker's cough". [22] Sputum may be swallowed or spat out, depending often on social and cultural factors. [22] In severe COPD, vigorous coughing may lead to rib fractures or to a brief loss of consciousness . [26] Those with COPD often have a history of " common colds " that last a long time. [22] Shortness of breath [ edit ] Shortness of breath is a common symptom and is often the most distressing. [27] It is commonly described as: "my breathing requires effort," "I feel out of breath," or "I can't get enough air in." [28] Different terms, however, may be used in different cultures. [22] Typically, the shortness of breath is worse on exertion of a prolonged duration and worsens over time. [22] In the advanced stages, or end stage pulmonary disease , it occurs during rest and may be always present. [29] [30] Shortness of breath is a source of both anxiety and a poor quality of life in those with COPD. [22] Many people with more advanced COPD breathe through pursed lips and this action can improve shortness of breath in some. [31] [32] Physical activity limitation [ edit ] COPD often leads to reduction in physical activity, in part due to shortness of breath. [33] In later stages of COPD muscle wasting ( cachexia ) may occur. [34] Low levels of physical activity are associated with worse outcomes. [35] Other symptoms [ edit ] In COPD, breathing out may take longer than breathing in. [36] Chest tightness may occur, [22] but is not common and may be caused by another problem. [27] Those with obstructed airflow may have wheezing or decreased sounds with air entry on examination of the chest with a stethoscope . [36] A barrel chest is a characteristic sign of COPD, but is relatively uncommon. [36] Tripod positioning may occur as the disease worsens. [23] Advanced COPD leads to high pressure on the lung arteries , which strains the right ventricle of the heart . [5] [37] [38] This situation is referred to as cor pulmonale , and leads to symptoms of leg swelling [22] and bulging neck veins . [5] COPD is more common than any other lung disease as a cause of cor pulmonale. [37] Cor pulmonale has become less common since the use of supplemental oxygen . [23] COPD often occurs along with a number of other conditions, due in part to shared risk factors. [2] These conditions include ischemic heart disease , high blood pressure , diabetes mellitus , muscle wasting , osteoporosis , lung cancer , anxiety disorder , sexual dysfunction , and depression . [2] [39] In those with severe disease, a feeling of always being tired is common. [22] Fingernail clubbing is not specific to COPD and should prompt investigations for an underlying lung cancer. [40] Exacerbation [ edit ] An acute exacerbation of COPD is defined as increased shortness of breath, increased sputum production, a change in the color of the sputum from clear to green or yellow, or an increase in cough in someone with COPD. [36] They may present with signs of increased work of breathing such as fast breathing , a fast heart rate , sweating , active use of muscles in the neck , a bluish tinge to the skin , and confusion or combative behavior in very severe exacerbations. [36] [41] Crackles may also be heard over the lungs on examination with a stethoscope. [42] Cause [ edit ] The primary cause of COPD is tobacco smoke, with occupational exposure and pollution from indoor fires being significant causes in some countries. [9] Typically, these must occur over several decades before symptoms develop. [9] A person's genetic makeup also affects the risk. [9] Smoking [ edit ] Percentage of females smoking tobacco as of the late 1990s early 2000s Percentage of males smoking tobacco as of the late 1990s and early 2000s.MMP1, SFTPD, HMOX1, HDAC2, TGFB1, MMP9, SERPINA1, FAM13A, DSP, TNF, EPHX1, MTCL1, CXCL8, EEFSEC, IL6, ELN, NOS3, SOD3, CYP1A1, NOS2, FOXO3, CXCL1, HTR2A, TRPV4, CYP1A2, RAPGEF3, TP53, TNNT2, MMP14, KLF5, CXCL2, CD8A, VEGFA, TIMP1, MUC5AC, IL17A, MIR218-2, NFE2L2, EGFR, CASP3, SERPINE1, PLAU, MUC1, SLPI, STAT4, MPO, CCN2, SMAD4, DDIT3, BNIP3, IREB2, FAIM2, CHRNA5, CHRNA3, CFTR, SMPD3, CASP8, CASP12, ERBB3, PLAUR, FAS, FASLG, NQO1, AGER, CHRNB4, MMP3, CTLA4, HSPA4, CHRM3, SCGB1A1, PLB1, PRTN3, THSD4, CYBA, RNF150, HSPA1A, NFKB1, HTR4, TNS1, PDZD2, WIPF1, PSORS1C1, HSPA1B, CDH13, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DPA1, DNAAF4, GSTCD, FTO, HSPA1L, ARHGEF38, INPP5D, GAB2, HYKK, DOCK1, CSMD1, NPNT, KCNK1, INTS12, CYBB, DNAH5, DLG2, TAFA2, RARB, GRIK4, CYS1, CFAP221, RAB4B, COPD, RSRC1, CASC15, PPARG, FAM227B, GABPA, CRACR2B, POFUT1, GP1BB, PRKCB, ZFPM2, HNF1A-AS1, GM2A, LAMA1, GC, NNT, C1orf185, NWD1, TSHZ3, NIFK-AS1, GSTT1, MIR99AHG, MKS1, GTF2I, ZBTB38, ATXN7L1, HIRA, GSTP1, GSTM1, BMP8A, SYCP2L, EFCAB5, MFHAS1, PTGS2, LINC01118, HLA-B, TGFB2, JMJD1C, PKD2L1, MMS22L, DELEC1, CFH, PKN2, FGL1, NRG1, HIF1A, MICAL3, ZKSCAN1, GLA, SCFD2, PLCE1, EML4, PCDH9, BNC2, LRMDA, ADGRV1, TNRC6A, ARMC2, ZDHHC18, HPGDS, MFAP2, ABLIM2, RBMS3, PCM1, TBX1, TOX2, PDE4A, TET2, FEV, IL33, LPO, MMP12, TSPAN14, HSBP1, SLMAP, CYBC1, HOOK2, SPAG16, HMGA2, PCDH15, SYNPO2L, DENND2D, STN1, TMEM254, NCF4, NCF2, PPP1R2C, CEP70, MYH7, SYN3, ADAM33, CASZ1, RSPH6A, BCAS3, PLXNA4, WDR20, KCNG4, ADAM19, IL13, PIK3CD, IL10, CDC123, NOL4L, PITPNA, ARHGAP42, IL5, ADIPOQ, IL1B, IL1A, LYSMD4, SLC35F3, CNTN4, IFNG, HERC1, AMZ1, SPPL2C, GLIS3, SCLT1, UBR3, TMEM219, ITPK1, PTPN22, CDRT15P1, TNPO1, SGF29, KCNMA1, CCDC69, GDAP1, BTBD9, ITGB8, IL18, KLHL32, GALNT13, SERPINE2, ITGA1, BTBD11, PIK3CA, HHIP, CXCL10, SNTG2, OR6F1, FGD6, MAPT-AS1, DIRC3, LINC00886, BTBD1, CAT, ZDHHC20P2, SLC30A10, ASTN2, CD96, C1GALT1, AMD1P3, ACE, WTAPP1, TBX4, HDAC7, BTC, TESK2, VGLL4, RREB1, SGCD, PPIEL, USP24, TLR2, CRP, SUZ12P1, LINC02869, IRF1-AS1, MAPK14, TM9SF4, CSE1L, PLF, ATP2C2, SFTPB, CCL2, TLR4, CDH11, LINC00598, SEC24C, NCF1, CCL28, FBXL7, LINC01006, CFDP1, COMT, ELANE, LINC01807, ANXA11, ANXA5, CHRM3-AS2, LINC01876, ADCY5, ADAMTSL3, LINC02863, COX10-AS1, RNASEH2A, LINC01937, LINC02625, ALB, RNPEP, LINC01997, ADRB2, HSF2BP, TOP2B, RNF220, CCDC91, PDSS2, MIA-RAB4B, RERE, DMWD, THRA, RAB4B-EGLN2, ARVCF, DPP6, WAS, NNT-AS1, CDYL, UFD1, MIR4527HG, SIRT1, ADGRG6, PIK3CG, MIR146A, STAT3, PIK3CB, MAPK1, TSLP, CHI3L1, IL1RN, SLCO6A1, EDN1, GSTK1, ICAM1, AHSA1, CDKN2A, MMP2, POLDIP2, SERPINA3, RNF19A, AIMP2, GRAP2, CRK, MYDGF, MIR21, IL22, CSF2, FOXP3, IL4, IL27, VIM, GSTM2, CTNNB1, VIP, MSTN, SPP1, CXCR2, MAPK3, ACTB, CD40, SOD2, NR3C1, HMGB1, GDF15, SOD1, CAMP, SLC6A4, IFNB1, MUC5B, SLC26A4, COX2, TIMP2, LEP, MTCO2P12, MAFD2, IFNA13, IFNA1, MIR145, CCR5, BCL2, ITGAM, VDR, IL17D, CYP2A6, MBL2, EGLN2, CTSS, DEFB4A, POSTN, NR1I2, SMAD2, GCLC, DNER, PPARGC1A, BCHE, NLRP3, CFLAR, SMAD3, NOTCH1, XRCC5, LTB, PTAFR, ADO, CHIT1, MIR34A, PTPA, PTX3, EGR1, MIR223, H3P10, CCL5, FGF7, AHR, SLC27A5, FOXO1, TLR3, PARP9, GLP1R, FN1, PTEN, PARP1, CST3, DEFB4B, AQP5, CEL, DPP4, LCN2, IL17C, PLAAT4, MRC1, FGF10, MCAM, PINK1, DEFB1, TAC1, ABCC1, CCND1, MARCO, LINC01672, NR3C2, ANPEP, CD163, ANXA1, TLR9, GCG, BTBD8, MMP7, PDCD1, EGF, BDNF, MOK, EPAS1, ITGB2, YWHAZ, CCL11, PIM3, CD68, SFTPA1, ABCB1, IL5RA, IL26, IL2, PWAR1, SLC52A2, SQSTM1, GZMB, ROBO3, PLA2G1B, CD274, FGF23, ADIPOR1, CHRNA4, TUG1, CSF3, CLCA1, CCR6, CX3CL1, TFAM, SOCS3, HP, CXCL5, ENTPD1, SAA2, MMRN1, NPPB, IL17F, KDR, NLRP1, CXCR3, F2R, KL, ABCA1, SLC2A1, JAK3, SIGLEC14, DDX58, GDF11, FBXO32, STAR, CASP4, PIGR, S100A8, S100A9, SAA1, CCR2, CD14, CD80, CD207, STAT6, SRC, P2RX7, RELA, P2RY2, SORD, HSPA14, SOX5, WNK1, PACC1, WNT5A, NAT2, CCL18, SLC6A2, IL25, SDHB, CIP2A, XRCC1, PI3, TRPV1, MAPK8, SFTPC, CCL1, IFIH1, BPIFA1, PON1, PPARA, APOM, BEST1, CCL22, CCL20, CCL13, PGF, SAGE1, PDGFRB, PDE7A, SOAT1, SNAI1, PRKN, SEMA6A, UGCG, PTPN1, RORA, PTGS1, PTH, DCTN4, IMPACT, GORASP1, PDE4B, CLEC7A, MEG3, RNASE3, HOXA6, TNFRSF11B, CYP2E1, CYP1B1, CTSG, CTH, TBC1D9, VCAN, CS, MIR29B1, MIR29B2, CPOX, COX8A, HDAC9, TIMP4, COL4A3, POTEKP, CHRNA1, CYP2B6, CYP3A5, F2RL1, MIR206, MIR126, MIR132, COX5A, EPHB1, MARK2, ELK3, MIR150, MIR155, HBEGF, SARDH, DMD, AIM2, FHL5, MIR191, DBP, HDAC5, S1PR5, POTEM, UCA1, CXCL13, ERICD, ALK, ALDH2, AKT1, AGT, ADRB1, ADM, KHDRBS1, ADAM8, ACTG2, ACTG1, CXCR6, SDS, ABCA4, APCS, SIRT6, ATF3, CAV1, MIR542, MIR570, CD34, CD86, SFTPA2, CD1C, CASP1, ATF4, CALCA, ZGLP1, SERPING1, ACOT7, GPR182, WDHD1, OGG1, MIR125A, FABP5, MBTPS1, WNT4, KRAS, KNG1, ITGAL, ITGA5, HDAC3, GSTO2, IRF3, IRAK1, INSRR, IL12B, IL11, PART1, BAMBI, MIR106B, PLA2G2D, LGALS3, HOXA13, BECN1, EHMT1, NOS1, NM, SYT1, MYOG, MYC, MUC2, COX1, MSR1, SESN2, TRIM63, MCL1, SMAD7, SIGLEC9, SH2D1A, HSPD1, TNC, HOXA11, MTOR, SMUG1, GPR15, GCLM, SUMF1, GALNS, MSC, ACTBL2, BRD4, GTF2H1, SERPINA13P, FLNA, FKBP5, FGFR4, CD83, FENDRR, FGF2, NUP62, GSR, HOXA1, HOXA@, HOXA10, HOXA9, HOXA7, HOXA5, HOXA4, HOXA3, SRF, HLA-A, HGF, CH25H, HCK, HBE1, PRKAG2, COMMD10, TLR7, TLR8, ATP6V1D, TRPV2, A2M, IRAK4, P2RX2, HEY1, RHOQ, SIRT3, TSPYL4, CYFIP1, CUL9, SARM1, PPRC1, MYCBP2, PHLPP2, SIRT2, SAR1B, KLRK1, MLXIP, TUSC2, PDAP1, PARK7, NUP42, ADAMTS13, WDR5, ABHD2, PIM2, FAM215A, PPP1R15A, PLA2G15, IL17RA, ASCC1, HEBP1, NTM, ASAP1, NOX4, DUOX2, RHOD, MYLIP, TBK1, SETD2, KLF15, DLL1, MAT2B, SIGLEC8, IL37, CYFIP2, INTS1, SH2B1, TPSG1, DCDC2, SPDEF, GULP1, YTHDC1, ISYNA1, MIR195, MIR149, MIR15A, MIR15B, MIR181A2, MIR181C, MIR186, MIR190A, MIR192, MIR197, MIR133B, MIR20A, MIR203A, MIR210, MIR212, MIR214, MIR22, MIR29C, MIR34C, MIR141, MIR134, MIR122, MIR10A, FOLH1B, ZEB1-AS1, MARCHF8, NT5DC1, IFNL2, IFNL3, IFNL1, H19, STPG4, CELIAC2, GADL1, CFAP100, SNHG5, SNHG17, PLEKHM3, MIRLET7C, MIR106A, LINC01555, MIR338, PGAM5, ELFN1-AS1, LINC00987, MIR3620, SMIM31, LINC01082, KLRC4-KLRK1, P2RX5-TAX1BP3, MIR4709, LINC-ROR, RORA-AS1, MIR374A, ADAMTS9-AS1, LOC102724334, CBSL, HLA-DQB1-AS1, ORI6, DINOL, LINC02605, COPDA1, PCNA-AS1, MIR2054, MIR664A, MIR1307, MIR380, MIR422A, MIR424, MIR146B, MIR495, MIR499A, MIR503, MIR483, MIR455, MIR552, MIR637, POTEF, MIR675, CDKN2B-AS1, MIR942, SOD2-OT1, LINC00861, CRYGEP, ADAMTS19, IL23A, MIB1, KLHL7, AGPAT3, SDHAF3, CAMK1D, PELI1, ARFGEF3, NLN, MAVS, CFAP97, TRPM8, PPP4R4, HAMP, ZNF410, CXCL16, SCAF1, IL21, SRR, NOD2, ZC4H2, ACSS2, CENPJ, ZNF692, GHRL, DUOX1, H2BS1, TREM2, TREM1, PID1, MOCOS, ATG16L1, SLC52A1, ANO1, ELP3, MTPAP, YY1AP1, HJURP, MAML3, SOX6, KLK15, DEPTOR, MMP28, AMOTL1, UCN3, RSAD2, BPIFB1, ORAI3, MUC16, ORMDL3, ARHGAP12, AZIN2, TXNRD3, MIR155HG, FSD1, SLC22A12, CD200R1, IL31RA, FUNDC1, ROMO1, LAYN, IL23R, DAB2IP, ESAM, BMF, WNT3A, PNPT1, PAGR1, ADIPOR2, NLRX1, HAND2-AS1, MAP3K19, DNAJC5, SPX, SETD7, HCG4B, FBXO38, CCNL2, FSD1L, MAGT1, DOT1L, AFAP1L2, ACCS, IL17RC, PAPOLA, SP1, MRPS30, FBL, GPER1, GPX1, GPX3, GPX4, GRIK2, CXCL3, GSK3B, GSN, GSS, GYPA, GYPB, GYPE, GZMA, HAL, HAS2, HCRT, HDLBP, CFHR1, HLA-DRB3, HMGA1, NR4A1, FOXA2, HNRNPD, HSD11B1, HSPA2, HSPB1, HSPB2, GOT2, GLRX, GLB1, FLT1, ETS2, MECOM, F10, FBLN1, FCGR1A, FDPS, FES, FGF13, FGFR1, FHL1, FKBP4, FOXC1, FOLH1, GHSR, FOS, FOSB, FPR1, FPR2, FSHMD1A, GAST, FUT8, GAD1, GALC, GATA4, GDNF, GH1, HTR2B, HYAL1, IAPP, LGALS9, KCNK3, KIT, KLK1, KLKB1, KRT5, KRT7, KRT18, KRT19, KRT34, LAMP1, LBP, LEPR, LIF, JUND, LMNB1, LOX, LRP5, LTA, LTC4S, TACSTD2, SMAD6, MAP1B, MAS1, CD46, SMCP, MDK, KCNJ2, JUNB, IDS, IL10RA, IFIT1, IGF1, IGFBP3, IGFBP7, CCN1, IGHE, IL1RAP, IL2RA, IL6R, IL7, CXCR1, IL9, IL12A, JUN, IL13RA1, IL15, IL15RA, IL16, TNFRSF9, IRF7, ISG20, ITGA2B, ITGAV, ITGB3, ITGB5, JAK1, ESR2, ERCC1, FGL2, EPO, OPN1SW, BICD1, BID, BMP4, BMP6, BMPR1A, BMPR2, BPI, BSG, BTF3P11, TSPO, C3AR1, C4A, C4BPB, C5AR1, CA2, SLC25A20, CAD, CALCR, CALR, CBS, CCNE1, CD1A, CD1D, CD5L, CD28, TNFRSF8, BAX, AZU1, AZGP1, ALPP, ACHE, ACLY, ACP3, ADA, ADCY2, ADORA2A, ADORA2B, AEBP1, AHCY, AHSG, ALOX15, ALPI, AMFR, ATP2A2, ANGPT1, ANGPT2, APEX1, APOA1, APP, AQP4, AREG, RHOA, ARSA, ARSB, STS, ATD, TNFSF8, CD33, SCARB1, DECR1, CRX, CRYGC, CSTA, CSTB, CTSD, CTSE, CTSL, CYP2A7, DAPK1, DBH, DCN, DDX1, DEFA1, CP, DHCR24, DIO1, DIO2, DIO3, DNASE1, DUSP6, DVL3, EDNRB, EIF4EBP1, ELAVL2, EPHB2, EPHX2, CREBBP, KLF6, CD38, CHRM2, CD47, CD63, CD69, CD74, CD81, CDC6, CDH3, CDK6, CDKN1B, CDKN1C, CDX2, CEACAM5, CHRNA7, COL11A1, CHUK, CIRBP, CKMT1B, TPP1, CCR7, CCR8, LTB4R, CNR2, COL1A1, COL1A2, COL6A1, COL6A2, MEF2D, MEFV, MAP3K5, MFAP4, VWF, WNT1, WNT10B, XDH, YY1, ZFP36, ZNF208, PXDN, SLBP, TFEB, NR4A3, FOSL1, MIA, FZD4, PLA2G10, ULK1, LTBP4, RECK, CUL4A, GPR65, IKBKG, PIR, PLA2G4C, STC2, HSD17B6, AOC3, DDX3Y, VTN, VIPR1, EZR, TP53BP1, TFPI, TGFB3, TGFBR3, THAS, NKX2-1, TM7SF2, CLDN5, TNFRSF1A, TNFRSF1B, TNNI3, TNNT1, TNXB, TPR, VCP, TPT1, NR2C2, TRPC1, TRPC3, TRPC6, TUFM, TULP3, TWIST1, TNFRSF4, TXN, TXNRD1, UROD, ADAM9, RIPK2, TNFRSF10C, IKZF1, KEAP1, MAGI2, MFN2, RBM8A, SRA1, ABCB6, DNM1L, EBI3, WASF2, DHRS2, EIF1, STAM2, TLR6, SOCS5, KLF2, NOD1, YAP1, MCRS1, MERTK, CAP1, CARM1, FBLN5, CIB2, CHERP, ATG7, LILRB1, HDAC4, IKBKE, IL18R1, P2RX6, CES2, NRP1, ASAP2, ARHGEF7, SPHK1, SGPL1, MBD2, WASF1, HSPB3, BTAF1, GPRC5A, SLC16A4, IL1RL1, CELSR1, MTA2, IL32, RPS6KA5, S1PR2, SLIT2, PPIG, CYP7B1, GSTO1, EIF2AK3, AKAP5, CXCL14, AKAP12, TERT, TEAD4, TRBV20OR9-2, PCBP2, NTF3, OAT, OMP, P2RX1, P2RX3, P2RX4, P2RX5, P2RY1, FURIN, PAH, PAK2, REG3A, PCNA, YBX1, PDE4D, PECAM1, PIM1, PITX3, PLA2G2A, PLAT, PLXNA2, PPIA, PPIC, PRKCD, PRKCZ, MAPK7, NT5E, NRL, MAPK13, MTRR, MFGE8, MGMT, MGP, MIF, MIP, KMT2A, MME, MMP8, CD200, MSI1, MSX1, MTHFD1, MUC4, NRAS, MUC6, MYCN, MYD88, MYO1D, MYO1E, NELL1, NFATC3, NFKBIB, NGF, NHS, NOTCH2, NOTCH3, MAPK9, PRNP, TCF4, SPARC, SLC1A5, SLC1A7, SLC2A4, SLC6A8, SLC11A1, SMN1, SMN2, SMPD1, SMS, SOX9, SP3, SPAM1, SPINT1, SGCA, ST2, STAT1, STAT5A, STAT5B, SUV39H1, SVIL, TACR2, ADAM17, TAF1, MAP3K7, TAZ, SERPINA7, SGSH, SFRP5, KLK6, ROS1, PTCH1, PTGDS, PTPN6, PTPRC, PVT1, RARRES2, REN, RIT1, RNF5, ROBO2, ROM1, RORC, RPGR, SFRP2, RPS3, RRM1, S100A4, S100A5, SATB1, CCL3, CCL24, CXCL11, SDC4, SELL, SELP, SET, H3P40
-
Allergy
Wikipedia
The nature of anaphylaxis is such that the reaction can seem to be subsiding, but may recur throughout a period of time. [27] Skin [ edit ] Substances that come into contact with the skin, such as latex , are also common causes of allergic reactions, known as contact dermatitis or eczema. [28] Skin allergies frequently cause rashes, or swelling and inflammation within the skin, in what is known as a " weal and flare" reaction characteristic of hives and angioedema. [29] With insect stings a large local reaction may occur (an area of skin redness greater than 10 cm in size). [30] It can last one to two days. [30] This reaction may also occur after immunotherapy . [31] Cause [ edit ] Risk factors for allergy can be placed in two general categories, namely host and environmental factors. [32] Host factors include heredity , sex , race , and age, with heredity being by far the most significant. ... American Family Physician . 69 (5): 1123–28. PMID 15023012 . ^ a b Ludman SW, Boyle RJ (2015).CCL2, HLA-B, IL17A, IL4, PPBP, CCL8, CCL7, CCL4, CCL3, MAP2K6, PF4, IL16, MYLK, MTHFR, CXCL9, KNG1, ITGB2, IL18, CCL11, ABCF1, CCL19, CCL20, COMMD1, CLEC4A, CD274, CCR9, IL1R2, TNFRSF1B, TNFRSF1A, TNF, TGFB1, TAC1, SPP1, SELP, CX3CL1, CXCL5, CCL24, CCL17, CCR2, IL13, HLA-DRB4, ALB, CASP1, CD40LG, CCR1, CCR6, CSF2RA, CXCR2, DSG1, CXCR3, CXCL1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRB1, CYP1A1, HLA-DRB5, IL2RB, IL6, IL6ST, IFNG, IL5RA, HP, IL1B, IL1R1, AKR1B1, CHD1, BBS1, ADA, ARID1B, FOXP3, CSTA, CCDC28B, MTOR, TGM5, TRPA1, HAVCR2, IL31, TLR4, CD14, TRPV1, JAK2, TLR2, CRHR1, SLC6A3, SFTPD, F2RL1, NOS1, GZMB, HTR2B, LMAN1
-
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
Wikipedia
Likewise, another growing area of debate is better implementation of rules already in place to protect athletes. [25] Because of the concern that boxing may cause CTE, there is a movement among medical professionals to ban the sport. [7] Medical professionals have called for such a ban as early as the 1950s. [6] Management [ edit ] No cure currently exists for CTE, and because it can't be tested for until an autopsy is performed, people can't know if they have it. [28] Treatment is supportive as with other forms of dementia. [29] Those with CTE-related symptoms may receive medication and non-medication related treatments. [30] Epidemiology [ edit ] Rates of disease have been found to be about 30% among those with a history of multiple head injuries. [1] Population rates, however, are unclear. [2] Professional level athletes are the largest group with CTE, due to frequent concussions and sub-concussive impacts from play in contact sport . [31] These contact-sports include American football , Australian rules football , [32] ice hockey , Rugby football ( Rugby union and Rugby league ), [33] boxing , kickboxing , mixed martial arts , association football , [34] [33] and wrestling . [35] In association football, only prolific headers are known to have developed CTE. [34] Cases of CTE were also recorded in baseball. [36] According to 2017 study on brains of deceased gridiron football players, 99% of tested brains of NFL players, 88% of CFL players, 64% of semi-professional players, 91% of college football players, and 21% of high school football players had various stages of CTE. [37] Other individuals diagnosed with CTE were those involved in military service, had a previous history of chronic seizures , were domestically abused, or were involved in activities resulting in repetitive head collisions. [38] [25] [39] Although a definite cause for Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy is unknown the research has started to point towards the development of many separate mild traumatic brain injuries. ... Brain injury in boxing. Clinics in Sports Medicine, 28(4), 561–78, vi. ^ Concannon, Leah (2014).
-
Occupational Injury
Wikipedia
Older workers are also more likely by be killed in a construction related fall. [6] They are also at higher risk for injury due to age-related hearing loss , [28] visual impairment , [29] and use of multiple prescription medications [30] that has been linked to higher rates of work injuries. [31] In addition to age, other personal risk factors for injury include obesity [32] particularly its associated risk with back injury, and depression . [33] Lack of proper education or training can also predispose an individual to an occupational injury.
-
Substance Abuse
Wikipedia
Cannabis may trigger panic attacks during intoxication and with continued use, it may cause a state similar to dysthymia . [25] Researchers have found that daily cannabis use and the use of high-potency cannabis are independently associated with a higher chance of developing schizophrenia and other psychotic disordera . [26] [27] [28] Severe anxiety and depression are commonly induced by sustained alcohol abuse, which in most cases abates with prolonged abstinence. ... ISBN 978-1-57607-708-5 . ^ University of Miami: Substance Abuse, Substance Abuse and Health Risks ^ "High-strength skunk 'now dominates' UK cannabis market" . nhs.uk . 28 February 2018. ^ Di Forti M, Marconi A, Carra E, Fraietta S, Trotta A, Bonomo M, Bianconi F, Gardner-Sood P, O'Connor J, Russo M, Stilo SA, Marques TR, Mondelli V, Dazzan P, Pariante C, David AS, Gaughran F, Atakan Z, Iyegbe C, Powell J, Morgan C, Lynskey M, Murray RM (2015).OPRM1, DRD2, SLC6A4, FAAH, CYP2D6, NPY, GRM5, CNR1, WDR11, SLC22A3, OPRD1, CSMD1, FHIT, PLA2R1, LIMCH1, THSD4, FAM184A, TTC21B, ZNF385D, PCDH15, CDCP1, SAMD4A, PRPF4, SEMA6D, PRKCE, ETV6, CSRNP3, ZNF606, FHOD3, COLEC12, KLF12, EHHADH, QSOX1, LRMDA, POLR1D, RAD51B, DOCK1, PRKCH, FKBP15, XPO6, PACS1, MSRA, SLC45A2, NME7, CD274, MPC1, CTNNA3, ABLIM1, CHCHD3, FAM184B, APPL2, AFF3, CCDC91, INSR, NRCAM, FRMD4A, XYLT1, TIAM2, PARVA, MYO5C, PBX1, PDE1C, TENM2, RHBDD3, SYNE1, PMAIP1, GBA3, GRM7, GRIK2, GRIA4, DDX1, DNAH8, DSCAM, RTL6, ANO4, CHRM2, BPIFA2, MACROD2, CFTR, MPP7, C10orf82, LDLRAD3, OR51E1, CDH13, C19orf18, SLK, ZNF366, ATP1B1, CERS6, HSPA12A, CHD1L, EIPR1, TMPRSS7, CXCL14, C5orf63, AKAP7, CSRP3, BCAR3, MKNK1, NRXN3, PIWIL1, ADARB2, CHRNA5, MYO6, PATJ, SLC10A2, AGBL4, ABCC4, ZNF804A, CADPS2, SLC2A13, FARP1, FAM126A, CSMD3, XKR4, NR3C1, SLC6A3, MAOA, BDNF, HCRT, GULOP, FKBP5, OPRK1, COMT, WAS, IL6, PDYN, CREB1, CRHR1, GH1, CRP, HTR2A, CRHR2, DRD4, PPP1R1B, CSH2, AGRP, ERCC8, CNR2, TAAR1, SIGMAR1, EPO, ALB, CSH1, NKTR, FOSB, OXTR, HSPA9, POMC, NMU, SLC1A2, KAT2B, RASGRF2, ACTB, BAG3, TXN, BBC3, NTS, TNF, CLOCK, CARTPT, TGFB1, PNOC, TCF21, TLR4, ACKR3, GAL, AMPH, DNASE1L3, CYP2C19, DRD1, DRD3, CYP2B6, FGD1, CRH, GDNF, CECR, GSN, GSTM1, CCND1, ARRB2, MIR143, BCHE, CYP3A4, LOC110806262, IGF1, LOC107987479, NPS, HTR2C, HTR1B, HACD1, SLC35A1, LPAR2, MORN4, PPP1R9B, CAP1, NDRG1, CST12P, LINC02210-CRHR1, IL33, TMX2-CTNND1, GAL3ST1, TOX, MIR29C, ABCG2, ERFE, DDX53, SLC17A8, C20orf181, ACCS, BCAR1, ATG5, BPIFA4P, DPPA3, TPH2, DSTN, EBPL, PSENEN, PART1, ARTN, CHPT1, NMUR2, TWNK, PHGDH, ACSS2, INTS8, PLA2G15, IMPACT, OXR1, CASZ1, SIAE, GPR88, SCLY, SPG21, PRX, SLC7A11, SORBS1, GCC1, CXCR6, CBX1, ASCC1, CALN1, SPACA9, PARP9, DHDDS, VKORC1, BRD4, SARM1, MLST8, PDF, MCCC2, PTBP2, HAMP, COMMD3, A2M, PRL, PKD2L1, FLT4, FGF2, FANCB, ETFA, EPHB2, ENO1, ELK3, ELANE, EDNRB, EDNRA, NQO1, ACE, DBT, DBH, CYP19A1, CYP2C18, FGF14, FMO3, HMGB1, FN1, GTS, GSTT1, GSTP1, GSK3B, GPT, GPR42, GLS, GLP1R, GHSR, GCG, GABRG2, GABRA2, GABRA1, GABPA, MTOR, CYP2C9, CYP2A6, CTNND1, CTAA1, ASL, ARSF, ARRB1, AR, ANPEP, AMY1C, AMY1B, AMY1A, AHR, ADRB2, ADRA2B, ADRA1A, ADH1C, ADH1B, ADCYAP1, BRS3, CAD, CAMK2B, CHRNA4, CSF2, CSE1L, CREM, CREBBP, CPA1, CCR5, CEACAM7, CAPS, CEACAM3, CEL, CEACAM5, CDS1, CDK5, CD40, HBB, HSPB1, NOL3, STX1A, SSTR4, SMS, SLC18A2, SRSF1, CCL3, SAT1, RPS19, RORA, PTBP1, PSMD4, PSG2, PSEN2, MAPK1, PKN1, PRKCB, STAT5A, SULT1A1, HSPB2, TACR1, HSPB3, WASF1, ARHGEF7, LOH19CR1, ST8SIA4, CXCR4, TRPV1, UGT2B17, TTR, TPH1, TP53, TLR2, TJP1, TH, TAL1, POLG, SERPINF2, PLG, PITX2, MAOB, LTBP3, LNPEP, LGALS1, LEP, LAMC2, KRT7, KRAS, IL16, IL10, CXCL8, IFNG, IAPP, HTR3A, HTR2B, CD46, KITLG, MMP2, PNP, SERPINB6, ABCB4, ABCB1, CFP, OPRL1, NTRK2, NOTCH4, MSN, NQO2, NHS, NFKB1, NFE2L2, MUC1, MTHFR, H3P40
-
Plasma Cell Dyscrasias
Wikipedia
These individuals must also; lack detectable IgG, IgA, IgD, IgE, or IgM myeloma proteins in sera; have a free κ/λ or λ/κ light chain ratio outside of 0.26 to 1.65 range but less than 100; and/or have no evidence for the presence of any one of the CRAB criteria, amyloidosis, or end organ damage attributable to the myeloma proteins or plasma cells. [2] [3] [6] In a Mayo clinic study of 101 individuals with light chain SMM, the cumulative probability of progression to active multiple myeloma or light-chain amyloidosis in patients with light-chain SMM was 28%, 45%, and 56% after 5, 10, and 15 years, respectively. ... The syndrome is defined by the presence of; both of two major criteria, peripheral neuropathy and a clonal plasma cell dyscrasia (increased bone marrow plasma cells in ~67% of cases; ≥1 plasmacytoma in ~33% of cases); at least one other major criteria (Castleman's disease, sclerotic bone lesions , elevated serum levels of the cytokine VEGF ); and at least one minor criterion (organomegaly, extravascular volume overload [e.g. ascites , edema , pleural effusion , and/or pericardial effusion ], endocrinopathy [i.e. hypogonadism , defects in the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis ], skin changes, papilledema , and/or hematological manifestations [i.e. thrombocytosis or polycythemia ]). [28] The monoclonal protein in POEMS patients is typically identified as IgA or IgG which in >95% of cases contains a λ chain that is restricted to either of two members of the V lambda 1 subfamily viz., IGLV1-40*01 and IGLV1-44*01 (there are 29 other members in the V lambda family ). ... Patients with >2 plasmacytomas or symptomatic disseminated disease have been treated with chemotherapy often followed by autologous stem-cell transplantation ; these treatments have been found to reduce symptoms of the disease and lead to long-term partial remissions of disease. [28] [29] The overall survival of POEMS patients who have been treated for their disease is relatively good for a disease occurring in patients with an average age of 50 years; one estimate of median overall survival is 14 years.
-
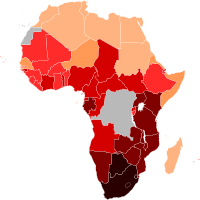
Hiv/aids In Africa
Wikipedia
UNAIDS' combination prevention framework puts structural interventions—including programmes to promote human rights, to remove punitive laws that block the AIDS response, and to combat gender inequality and HIV related stigma and discrimination—at the centre of the HIV prevention agenda. [27] "It is the consensus in the HIV scientific community that abstinence, be faithful, use a condom [(ABC)] principles are vital guides for public health intervention, but are better bundled with biomedical prevention approaches; lone behavioral change approaches are not likely to stop the global pandemic." [28] Uganda has replaced its ABC strategy with a combination prevention programme because of an increase in the annual HIV infection rate.